 Web Front-end
Web Front-end
 JS Tutorial
JS Tutorial
 How to design an algorithm? Introduction to common algorithm paradigms
How to design an algorithm? Introduction to common algorithm paradigms
How to design an algorithm? Introduction to common algorithm paradigms

How to design an algorithm? The following article will analyze common algorithm paradigms for you. It has certain reference value. Friends in need can refer to it. I hope it will be helpful to everyone.
First clarify three concepts:
Algorithm: The process of solving problems step by step.
Paradigm: A mode of thinking about a problem.
Algorithmic Paradigm: A general approach to building efficient solutions to problems.
This article discusses some commonly used algorithm paradigms, such as
- Divide and Conquer Algorithm
- Dynamic Programming
- Greedy Algorithm
- Backtracking Algorithm
Divide and Conquer
Among the sorting algorithms, the common point of the two algorithms, merge and quick sort, is the divide and conquer algorithm.
Divide and conquer is a common algorithm design. The idea is to decompose the problem into smaller sub-problems that are similar to the original problem. Subproblems are usually solved recursively and the solutions to the subproblems are combined to solve the original problem.
The logic of the divide-and-conquer method can be divided into three steps:
- Divide the original problem into smaller sub-problems.
- Solve the sub-problem recursively, and return the solution to the sub-problem after the solution is completed.
- Merge the solutions to the subproblems into the solution to the original problem.
Example of divide-and-conquer method: binary search
The following is a binary search implemented using divide-and-conquer.
function binarySearchRecursive(array, value, low, high) {
if (low <= high) {
const mid = Math.floor((low + high) / 2);
const element = array[mid];
if (element < value) {
return binarySearchRecursive(array, value, mid + 1, high);
} else if (element > value) {
return binarySearchRecursive(array, value, low, mid - 1);
} else {
return mid;
}
}
return null;
}
export function binarySearch(array, value) {
const sortedArray = quickSort(array);
const low = 0;
const high = sortedArray.length - 1;
return binarySearchRecursive(array, value, low, high);
}Please note that the binarySearch function above is for others to call, while binarySearchRecursive is where the divide and conquer method is implemented.
Dynamic Programming
Dynamic Programming is an optimization technique used to solve complex problems by breaking them into smaller sub-problems. It looks a lot like divide and conquer, but instead of decomposing the problem into independent sub-problems and then combining them together, dynamic programming only decomposes the problem into independent sub-problems.
The algorithm logic is divided into three steps:
- Define sub-problems.
- Repeat to solve sub-problems.
- Identify and solve basic problems.
Dynamic Programming Case: Minimum Coin Change Problem
This is a common interview question called the Coin Change Problem. The coin change problem is a way of finding how many specific numbers of coins can be used to make change, given the amount of change. The minimum coin change problem is simply finding the minimum number of coins required to use a given denomination of money. For example, if you need change for 37 cents, you can use 1 2 cent, 1 5 cent, 1 1 dime, and 1 2 cent.
function minCoinChange(coins, amount) {
const cache = [];
const makeChange = (value) => {
if (!value) {
return [];
}
if (cache[value]) {
return cache[value];
}
let min = [];
let newMin;
let newAmount;
for (let i = 0; i < coins.length; i++) {
const coin = coins[i];
newAmount = value - coin;
if (newAmount >= 0) {
newMin = makeChange(newAmount);
}
if (newAmount >= 0 &&
(newMin.length < min.length - 1 || !min.length) && (newMin.length || !newAmount)) {
min = [coin].concat(newMin);
}
}
return (cache[value] = min);
}
return makeChange(amount);
}In the above code, the parameter coins represents the denomination ([1, 2, 5, 10, 20, 50] in RMB). To prevent double counting, a cache is used. The makeChange function is implemented recursively and is an internal function with access to cache.
console.log(minCoinChange([1, 2, 5 10, 20], 37)); // => [2, 5, 10, 20] console.log(minCoinChange([1, 3, 4], 6)) // => [3, 3]
Greedy algorithm
Greedy algorithm is related to the current optimal solution and tries to find a global optimal solution. Unlike dynamic programming, it does not consider the overall situation. Greedy algorithms tend to be simple and intuitive, but may not be the overall optimal solution.
Greedy Algorithm Case: Minimum Coin Change Problem
The coin problem solved by dynamic programming above can also be solved by greedy algorithm. Whether this solution is optimal or not depends on the denomination used.
function minCoinChange(coins, amount) {
const change = [];
let total = 0;
for (let i = coins.length; i>= 0; i--) {
const coin = coins[i];
while (total + coin <= amount) {
change.push(coin);
total += coin;
}
}
return change;
}As you can see, the greedy algorithm is much simpler than the dynamic programming solution. Let’s take a look at the same solution case to understand the difference between the two:
console.log(minCoinChange([1, 2, 5 10, 20], 37)); // => [2, 5, 10, 20] console.log(minCoinChange([1, 3, 4], 6)) // => [4, 1, 1]
The greedy algorithm gives the optimal solution to the first problem, but the second one is not the optimal solution ( It should be [3,3]).
The greedy algorithm is simpler and faster than the dynamic programming algorithm, but the solution obtained may not be the optimal solution.
Backtracking Algorithm
Backtracking Algorithm is great for finding and building solutions step by step.
- Try to solve the problem one way.
- If it doesn’t work, backtrack and repeat step 1 until you find a suitable solution.
For the backtracking algorithm, I will write another article to introduce more complex algorithms. I haven't figured out what to write yet. Maybe it's to write a program for solving Sudoku. If you are interested in this, please follow my official account!
Algorithms are never-ending. I hope this article can help you understand some common algorithm paradigms.
Related free learning recommendations: js video tutorial
The above is the detailed content of How to design an algorithm? Introduction to common algorithm paradigms. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
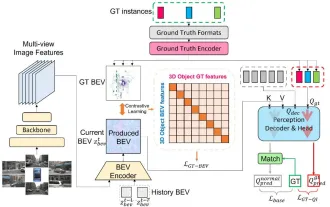 CLIP-BEVFormer: Explicitly supervise the BEVFormer structure to improve long-tail detection performance
Mar 26, 2024 pm 12:41 PM
CLIP-BEVFormer: Explicitly supervise the BEVFormer structure to improve long-tail detection performance
Mar 26, 2024 pm 12:41 PM
Written above & the author’s personal understanding: At present, in the entire autonomous driving system, the perception module plays a vital role. The autonomous vehicle driving on the road can only obtain accurate perception results through the perception module. The downstream regulation and control module in the autonomous driving system makes timely and correct judgments and behavioral decisions. Currently, cars with autonomous driving functions are usually equipped with a variety of data information sensors including surround-view camera sensors, lidar sensors, and millimeter-wave radar sensors to collect information in different modalities to achieve accurate perception tasks. The BEV perception algorithm based on pure vision is favored by the industry because of its low hardware cost and easy deployment, and its output results can be easily applied to various downstream tasks.
 Implementing Machine Learning Algorithms in C++: Common Challenges and Solutions
Jun 03, 2024 pm 01:25 PM
Implementing Machine Learning Algorithms in C++: Common Challenges and Solutions
Jun 03, 2024 pm 01:25 PM
Common challenges faced by machine learning algorithms in C++ include memory management, multi-threading, performance optimization, and maintainability. Solutions include using smart pointers, modern threading libraries, SIMD instructions and third-party libraries, as well as following coding style guidelines and using automation tools. Practical cases show how to use the Eigen library to implement linear regression algorithms, effectively manage memory and use high-performance matrix operations.
 Explore the underlying principles and algorithm selection of the C++sort function
Apr 02, 2024 pm 05:36 PM
Explore the underlying principles and algorithm selection of the C++sort function
Apr 02, 2024 pm 05:36 PM
The bottom layer of the C++sort function uses merge sort, its complexity is O(nlogn), and provides different sorting algorithm choices, including quick sort, heap sort and stable sort.
 PHP and Vue: a perfect pairing of front-end development tools
Mar 16, 2024 pm 12:09 PM
PHP and Vue: a perfect pairing of front-end development tools
Mar 16, 2024 pm 12:09 PM
PHP and Vue: a perfect pairing of front-end development tools. In today's era of rapid development of the Internet, front-end development has become increasingly important. As users have higher and higher requirements for the experience of websites and applications, front-end developers need to use more efficient and flexible tools to create responsive and interactive interfaces. As two important technologies in the field of front-end development, PHP and Vue.js can be regarded as perfect tools when paired together. This article will explore the combination of PHP and Vue, as well as detailed code examples to help readers better understand and apply these two
 Can artificial intelligence predict crime? Explore CrimeGPT's capabilities
Mar 22, 2024 pm 10:10 PM
Can artificial intelligence predict crime? Explore CrimeGPT's capabilities
Mar 22, 2024 pm 10:10 PM
The convergence of artificial intelligence (AI) and law enforcement opens up new possibilities for crime prevention and detection. The predictive capabilities of artificial intelligence are widely used in systems such as CrimeGPT (Crime Prediction Technology) to predict criminal activities. This article explores the potential of artificial intelligence in crime prediction, its current applications, the challenges it faces, and the possible ethical implications of the technology. Artificial Intelligence and Crime Prediction: The Basics CrimeGPT uses machine learning algorithms to analyze large data sets, identifying patterns that can predict where and when crimes are likely to occur. These data sets include historical crime statistics, demographic information, economic indicators, weather patterns, and more. By identifying trends that human analysts might miss, artificial intelligence can empower law enforcement agencies
 Improved detection algorithm: for target detection in high-resolution optical remote sensing images
Jun 06, 2024 pm 12:33 PM
Improved detection algorithm: for target detection in high-resolution optical remote sensing images
Jun 06, 2024 pm 12:33 PM
01 Outlook Summary Currently, it is difficult to achieve an appropriate balance between detection efficiency and detection results. We have developed an enhanced YOLOv5 algorithm for target detection in high-resolution optical remote sensing images, using multi-layer feature pyramids, multi-detection head strategies and hybrid attention modules to improve the effect of the target detection network in optical remote sensing images. According to the SIMD data set, the mAP of the new algorithm is 2.2% better than YOLOv5 and 8.48% better than YOLOX, achieving a better balance between detection results and speed. 02 Background & Motivation With the rapid development of remote sensing technology, high-resolution optical remote sensing images have been used to describe many objects on the earth’s surface, including aircraft, cars, buildings, etc. Object detection in the interpretation of remote sensing images
 Questions frequently asked by front-end interviewers
Mar 19, 2024 pm 02:24 PM
Questions frequently asked by front-end interviewers
Mar 19, 2024 pm 02:24 PM
In front-end development interviews, common questions cover a wide range of topics, including HTML/CSS basics, JavaScript basics, frameworks and libraries, project experience, algorithms and data structures, performance optimization, cross-domain requests, front-end engineering, design patterns, and new technologies and trends. . Interviewer questions are designed to assess the candidate's technical skills, project experience, and understanding of industry trends. Therefore, candidates should be fully prepared in these areas to demonstrate their abilities and expertise.
 Application of algorithms in the construction of 58 portrait platform
May 09, 2024 am 09:01 AM
Application of algorithms in the construction of 58 portrait platform
May 09, 2024 am 09:01 AM
1. Background of the Construction of 58 Portraits Platform First of all, I would like to share with you the background of the construction of the 58 Portrait Platform. 1. The traditional thinking of the traditional profiling platform is no longer enough. Building a user profiling platform relies on data warehouse modeling capabilities to integrate data from multiple business lines to build accurate user portraits; it also requires data mining to understand user behavior, interests and needs, and provide algorithms. side capabilities; finally, it also needs to have data platform capabilities to efficiently store, query and share user profile data and provide profile services. The main difference between a self-built business profiling platform and a middle-office profiling platform is that the self-built profiling platform serves a single business line and can be customized on demand; the mid-office platform serves multiple business lines, has complex modeling, and provides more general capabilities. 2.58 User portraits of the background of Zhongtai portrait construction



