An in-depth analysis of quick sort in JavaScript

Introduction
Sorting refers to arranging the elements of a linear list in a specific order (numeric or alphabetical). Sorting is often used in conjunction with search.
There are many sorting algorithms, and one of the fastest by far is Quicksort(Quicksort).
Quicksort sorts the given list elements using the divide-and-conquer strategy. This means that the algorithm breaks the problem into subproblems until the subproblems become simple enough to be solved directly.
Algorithmically, this can be achieved using recursion or looping. But for this problem, it is more natural to use recursion.
Understand the logic behind quick sort
First look at how quick sort works:
- Select an element in the array, this element is called Benchmark(Pivot). Usually the first or last element in the array is used as the basis.
- Then, rearrange the elements of the array so that all elements to the left of the pivot are smaller than the pivot, and all elements to the right are greater than the pivot. This step is called Partitioning. If an element is equal to the base, it doesn't matter which side it is on.
- Repeat this process for the left and right sides of the benchmark until the array is sorted.
Next, understand these steps through an example. Suppose there is an array containing unsorted elements [7, -2, 4, 1, 6, 5, 0, -4, 2]. Select the last element as the base. The decomposition steps of the array are shown in the figure below:
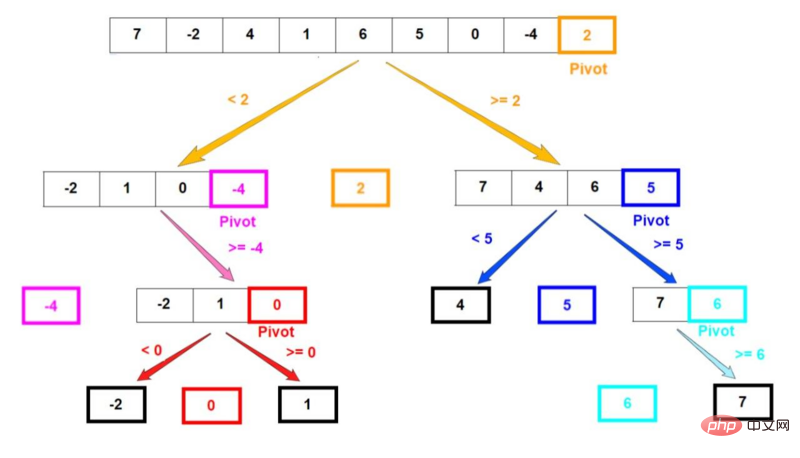
The elements selected as the basis in step 1 of the algorithm are colored. After partitioning, the base element is always at the correct position in the array.
The array with a bold black border represents what it will look like at the end of that particular recursive branch, with the resulting array containing only one element.
Finally you can see the sorting of the results of the algorithm.
Use JavaScript to implement quick sort
The backbone of this algorithm is the "partitioning" step. Whether using recursion or looping, this step is the same.
It is precisely because of this feature that the code for array partitioning is first written partition():
function partition(arr, start, end){
// 以最后一个元素为基准
const pivotValue = arr[end];
let pivotIndex = start;
for (let i = start; i < end; i++) {
if (arr[i] < pivotValue) {
// 交换元素
[arr[i], arr[pivotIndex]] = [arr[pivotIndex], arr[i]];
// 移动到下一个元素
pivotIndex++;
}
}
// 把基准值放在中间
[arr[pivotIndex], arr[end]] = [arr[end], arr[pivotIndex]]
return pivotIndex;
};The code is based on the last element and uses the variable pivotIndex to track the "middle" position where all elements to the left are smaller than pivotValue and elements to the right are larger than pivotValue.
The final step swaps the pivot (last element) with pivotIndex.
Recursive implementation
After implementing the partition() function, we must solve the problem recursively and apply partitioning logic to complete the remaining steps:
function quickSortRecursive(arr, start, end) {
// 终止条件
if (start >= end) {
return;
}
// 返回 pivotIndex
let index = partition(arr, start, end);
// 将相同的逻辑递归地用于左右子数组
quickSort(arr, start, index - 1);
quickSort(arr, index + 1, end);
}In this function, the array is first partitioned, and then the left and right subarrays are partitioned. As long as this function receives an array that is not empty or has more than one element, the process will be repeated.
Empty arrays and arrays containing only one element are considered sorted.
Finally use the following example to test:
array = [7, -2, 4, 1, 6, 5, 0, -4, 2] quickSortRecursive(array, 0, array.length - 1) console.log(array)
Output:
-4,-2,0,1,2,4,5,6,7
Loop implementation
The recursive method of quick sort is more intuitive. But using loops to implement quick sort is a relatively common interview question.
Like most recursive to loop conversion solutions, the first thing that comes to mind is to use a stack to simulate recursive calls. Doing this allows you to reuse some familiar recursive logic and use it in loops.
We need a way to keep track of the remaining unsorted subarrays. One approach is to simply keep "pairs" of elements on the stack that represent the start and end of a given unsorted subarray.
JavaScript does not have an explicit stack data structure, but arrays support the push() and pop() functions. However, the peek() function is not supported, so you must use stack [stack.length-1] to manually check the top of the stack.
We will use the same "partitioning" function as the recursive method. Take a look at how to write the Quicksort part:
function quickSortIterative(arr) {
// 用push()和pop()函数创建一个将作为栈使用的数组
stack = [];
// 将整个初始数组做为“未排序的子数组”
stack.push(0);
stack.push(arr.length - 1);
// 没有显式的peek()函数
// 只要存在未排序的子数组,就重复循环
while(stack[stack.length - 1] >= 0){
// 提取顶部未排序的子数组
end = stack.pop();
start = stack.pop();
pivotIndex = partition(arr, start, end);
// 如果基准的左侧有未排序的元素,
// 则将该子数组添加到栈中,以便稍后对其进行排序
if (pivotIndex - 1 > start){
stack.push(start);
stack.push(pivotIndex - 1);
}
// 如果基准的右侧有未排序的元素,
// 则将该子数组添加到栈中,以便稍后对其进行排序
if (pivotIndex + 1 < end){
stack.push(pivotIndex + 1);
stack.push(end);
}
}
}Here is the test code:
ourArray = [7, -2, 4, 1, 6, 5, 0, -4, 2] quickSortIterative(ourArray) console.log(ourArray)
Output:
-4,-2,0,1,2,4,5,6,7
Visual demonstration
When it comes to sorting algorithms, Visualizing them can help us intuitively understand how they work. The following example is taken from Wikipedia:
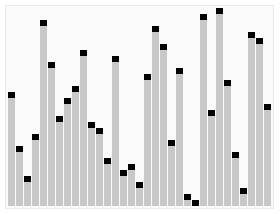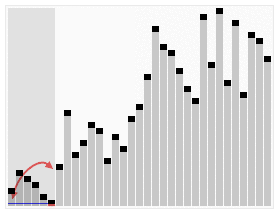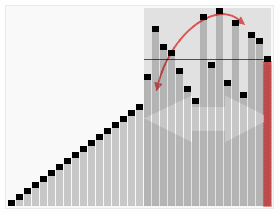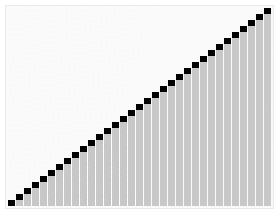
The last element in the figure is also used as a benchmark. Given an array partitioned, recursively traverse the left side until it is completely sorted. Then sort the right side.
Efficiency of quick sort
Now discuss its time and space complexity. The worst-case time complexity of quick sort is $O(n^2)$. The average time complexity is $O(n\log n)$. Typically, worst-case scenarios can be avoided by using a randomized version of quicksort.
The weakness of the quicksort algorithm is the choice of benchmark. Each time you choose a wrong pivot (a pivot larger or smaller than most elements) you will get the worst possible time complexity. When repeatedly selecting a basis, if the element value is smaller or larger than the element's basis, the time complexity is $O(n\log n)$.
It can be observed from experience that no matter which data benchmark selection strategy is adopted, the time complexity of quick sort tends to have $O(n\log n)$.
Quicksort does not take up any additional space (excluding space reserved for recursive calls). This algorithm is called the in-place algorithm and requires no extra space.
For more programming-related knowledge, please visit: Introduction to Programming! !
The above is the detailed content of An in-depth analysis of quick sort in JavaScript. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 CLIP-BEVFormer: Explicitly supervise the BEVFormer structure to improve long-tail detection performance
Mar 26, 2024 pm 12:41 PM
CLIP-BEVFormer: Explicitly supervise the BEVFormer structure to improve long-tail detection performance
Mar 26, 2024 pm 12:41 PM
Written above & the author’s personal understanding: At present, in the entire autonomous driving system, the perception module plays a vital role. The autonomous vehicle driving on the road can only obtain accurate perception results through the perception module. The downstream regulation and control module in the autonomous driving system makes timely and correct judgments and behavioral decisions. Currently, cars with autonomous driving functions are usually equipped with a variety of data information sensors including surround-view camera sensors, lidar sensors, and millimeter-wave radar sensors to collect information in different modalities to achieve accurate perception tasks. The BEV perception algorithm based on pure vision is favored by the industry because of its low hardware cost and easy deployment, and its output results can be easily applied to various downstream tasks.
 Implementing Machine Learning Algorithms in C++: Common Challenges and Solutions
Jun 03, 2024 pm 01:25 PM
Implementing Machine Learning Algorithms in C++: Common Challenges and Solutions
Jun 03, 2024 pm 01:25 PM
Common challenges faced by machine learning algorithms in C++ include memory management, multi-threading, performance optimization, and maintainability. Solutions include using smart pointers, modern threading libraries, SIMD instructions and third-party libraries, as well as following coding style guidelines and using automation tools. Practical cases show how to use the Eigen library to implement linear regression algorithms, effectively manage memory and use high-performance matrix operations.
 Explore the underlying principles and algorithm selection of the C++sort function
Apr 02, 2024 pm 05:36 PM
Explore the underlying principles and algorithm selection of the C++sort function
Apr 02, 2024 pm 05:36 PM
The bottom layer of the C++sort function uses merge sort, its complexity is O(nlogn), and provides different sorting algorithm choices, including quick sort, heap sort and stable sort.
 Can artificial intelligence predict crime? Explore CrimeGPT's capabilities
Mar 22, 2024 pm 10:10 PM
Can artificial intelligence predict crime? Explore CrimeGPT's capabilities
Mar 22, 2024 pm 10:10 PM
The convergence of artificial intelligence (AI) and law enforcement opens up new possibilities for crime prevention and detection. The predictive capabilities of artificial intelligence are widely used in systems such as CrimeGPT (Crime Prediction Technology) to predict criminal activities. This article explores the potential of artificial intelligence in crime prediction, its current applications, the challenges it faces, and the possible ethical implications of the technology. Artificial Intelligence and Crime Prediction: The Basics CrimeGPT uses machine learning algorithms to analyze large data sets, identifying patterns that can predict where and when crimes are likely to occur. These data sets include historical crime statistics, demographic information, economic indicators, weather patterns, and more. By identifying trends that human analysts might miss, artificial intelligence can empower law enforcement agencies
 PHP and Vue: a perfect pairing of front-end development tools
Mar 16, 2024 pm 12:09 PM
PHP and Vue: a perfect pairing of front-end development tools
Mar 16, 2024 pm 12:09 PM
PHP and Vue: a perfect pairing of front-end development tools. In today's era of rapid development of the Internet, front-end development has become increasingly important. As users have higher and higher requirements for the experience of websites and applications, front-end developers need to use more efficient and flexible tools to create responsive and interactive interfaces. As two important technologies in the field of front-end development, PHP and Vue.js can be regarded as perfect tools when paired together. This article will explore the combination of PHP and Vue, as well as detailed code examples to help readers better understand and apply these two
 Improved detection algorithm: for target detection in high-resolution optical remote sensing images
Jun 06, 2024 pm 12:33 PM
Improved detection algorithm: for target detection in high-resolution optical remote sensing images
Jun 06, 2024 pm 12:33 PM
01 Outlook Summary Currently, it is difficult to achieve an appropriate balance between detection efficiency and detection results. We have developed an enhanced YOLOv5 algorithm for target detection in high-resolution optical remote sensing images, using multi-layer feature pyramids, multi-detection head strategies and hybrid attention modules to improve the effect of the target detection network in optical remote sensing images. According to the SIMD data set, the mAP of the new algorithm is 2.2% better than YOLOv5 and 8.48% better than YOLOX, achieving a better balance between detection results and speed. 02 Background & Motivation With the rapid development of remote sensing technology, high-resolution optical remote sensing images have been used to describe many objects on the earth’s surface, including aircraft, cars, buildings, etc. Object detection in the interpretation of remote sensing images
 Questions frequently asked by front-end interviewers
Mar 19, 2024 pm 02:24 PM
Questions frequently asked by front-end interviewers
Mar 19, 2024 pm 02:24 PM
In front-end development interviews, common questions cover a wide range of topics, including HTML/CSS basics, JavaScript basics, frameworks and libraries, project experience, algorithms and data structures, performance optimization, cross-domain requests, front-end engineering, design patterns, and new technologies and trends. . Interviewer questions are designed to assess the candidate's technical skills, project experience, and understanding of industry trends. Therefore, candidates should be fully prepared in these areas to demonstrate their abilities and expertise.
 Application of algorithms in the construction of 58 portrait platform
May 09, 2024 am 09:01 AM
Application of algorithms in the construction of 58 portrait platform
May 09, 2024 am 09:01 AM
1. Background of the Construction of 58 Portraits Platform First of all, I would like to share with you the background of the construction of the 58 Portrait Platform. 1. The traditional thinking of the traditional profiling platform is no longer enough. Building a user profiling platform relies on data warehouse modeling capabilities to integrate data from multiple business lines to build accurate user portraits; it also requires data mining to understand user behavior, interests and needs, and provide algorithms. side capabilities; finally, it also needs to have data platform capabilities to efficiently store, query and share user profile data and provide profile services. The main difference between a self-built business profiling platform and a middle-office profiling platform is that the self-built profiling platform serves a single business line and can be customized on demand; the mid-office platform serves multiple business lines, has complex modeling, and provides more general capabilities. 2.58 User portraits of the background of Zhongtai portrait construction




