Learn more about constructors in JavaScript

Having a good understanding of constructors is the key to mastering the JavaScript language. We all know that JavaScript is not like other languages. It does not have the class keyword, but it has a constructor that is very similar to function. In this article, let’s learn in detail how JavaScript constructors construct objects.
Constructors are very similar to ordinary functions, but we use them through the new keyword. There are two main types of constructors, native constructors (Array, Object), which can be automatically generated in the execution environment, and custom constructors, where you can define your own methods and properties.
Using constructors is very effective when you want to create many similar objects (with the same properties and methods). Most programmers follow the convention of using a capital letter to distinguish constructors from ordinary functions. Take a look at the code below.
function Book() {
// unfinished code
}
var myBook = new Book();The last line of code creates a Book object and assigns it to a variable; after this is completed, myBook is also a Book instance even if the Book constructor does not do anything. As you can see, apart from capitalizing the first letter and using the new keyword, there is no difference between constructors and ordinary functions.
Determine the type of instance
To determine whether an object is an instance of some kind, we can use the instanceof operator:
myBook instanceof Book // => true myBook instanceof String // => false
Note: If the right side is not an instance of a function, an error will be reported:
myBook instanceof {}; // => TypeError: invalid 'instanceof' operand ({})Another method is to use the constructor attribute. All object instances have a constructor attribute. This attribute Points to the constructor that created it.
myBook.constructor == Book; // => true
Just like the constructor of myBook points to Book. All objects inherit the constructor attribute from their prototype:
var s = new String("text");
s.constructor === String; // => true
"text".constructor === String; // => true
var o = new Object();
o.constructor === Object; // => true
var o = {};
o.constructor === Object; // => true
var a = new Array();
a.constructor === Array; // => true
[].constructor === Array; // => trueAlthough using constructor can be used to detect instance types, it is recommended to use the instanceof method. Because the constructor attribute can be overridden... it is not very reliable to use.
Custom Constructor
Constructors are like cookie stampers. Made from the same impression, they are all the same model (the same is true for men who don’t have a good thing).
function Book(name, year) {
this.name = name;
this.year = '(' + year + ')';
}The Book constructor requires two parameters. When using the new keyword to construct an object, the two formal parameters will be passed to the name and year of the Book object.
var firstBook = new Book("Pro AngularJS", 2014);
var secondBook = new Book("Secrets Of The JavaScript Ninja", 2013);
var thirdBook = new Book("JavaScript Patterns", 2010);
console.log(firstBook.name, firstBook.year);
console.log(secondBook.name, secondBook.year);
console.log(thirdBook.name, thirdBook.year);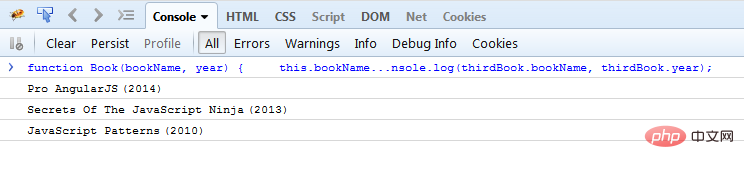
As you can see, we can quickly create another book by passing different parameters. The same is true for JavaScript's Array() and Date().
Object.defineProperty method
The Object.defineProperty method can be used in the constructor to configure properties.
function Book(name) {
Object.defineProperty(this, "name", {
get: function() {
return "Book: " + name;
},
set: function(newName) {
name = newName;
},
configurable: false
});
}
var myBook = new Book("Single Page Web Applications");
console.log(myBook.name); // => Book: Single Page Web Applications
// we cannot delete the name property because "configurable" is set to false
delete myBook.name;
console.log(myBook.name); // => Book: Single Page Web Applications
// but we can change the value of the name property
myBook.name = "Testable JavaScript";
console.log(myBook.name); // => Book: Testable JavaScriptThe above code calls the ancestor method. It provides getter and setter interfaces. The getter method is responsible for returning the encapsulated value, and the setter method accepts parameters and assigns the value to the property. When we operate access on a property, these two methods are called. By configuring configurable, we can set whether the value can be deleted.
Object literal representation is the preferred constructor
The JavaScript language has nine built-in constructors: Object(), Array(), String(), Number(), Boolean(), Date(), Function(), Error() and RegExp(). When we need to create these values, we are free to use literals or constructors. But under the same circumstances, literal objects are not only easier to read, but also faster because they can be optimized during parsing. So use literals when you need to use simple objects.
// a number object
// numbers have a toFixed() method
var obj = new Object(5);
obj.toFixed(2); // => 5.00
// we can achieve the same result using literals
var num = 5;
num.toFixed(2); // => 5.00
// a string object
// strings have a slice() method
var obj = new String("text");
obj.slice(0,2); // => "te"
// same as above
var string = "text";
string.slice(0,2); // => "te"Using the new keyword is essential
Remember to use the new keyword when using the constructor. If you accidentally forget, then the constructor This in points to the global object (default is window in the browser).
function Book(name, year) {
console.log(this);
this.name = name;
this.year = year;
}
var myBook = Book("js book", 2014);
console.log(myBook instanceof Book);
console.log(window.name, window.year);
var myBook = new Book("js book", 2014);
console.log(myBook instanceof Book);
console.log(myBook.name, myBook.year);The result of running the above code is as follows:
If it is in strict mode, the above code will throw an error because of strict mode We are not allowed to call the constructor without using the new keyword.
Constructor with a higher scope of application
In order to solve the risk of forgetting to use the new keyword, we can create a constructor with a higher scope of application by judging the value of this Constructor.
function Book(name) {
if (!(this instanceof Book)) {
// the constructor was called without "new".
return new Book(name);
}
}After adding this code, we can use the constructor 'unscrupulously'.
function Book(name, year) {
if (!(this instanceof Book)) {
return new Book(name, year);
}
this.name = name;
this.year = year;
}
var person1 = new Book("js book", 2014);
var person2 = Book("js book", 2014);
console.log(person1 instanceof Book); // => true
console.log(person2 instanceof Book); // => trueMany built-in constructors do this. By judging whether this is the current type. If the programmer forgets to add the new keyword, then we will return an object passed through new.
Conclusion
JavaScript does not have such a term (but it can be object-oriented), so it is confusing for programmers who are accustomed to using classes. Of course, JavaScript's constructor is no different from an ordinary function, it is just generated through the new keyword. It is very useful if we need to "print cookies".
Recommended tutorial: "JavaScript Video Tutorial"
The above is the detailed content of Learn more about constructors in JavaScript. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1387
1387
 52
52
 How to implement an online speech recognition system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 pm 02:54 PM
How to implement an online speech recognition system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 pm 02:54 PM
How to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online speech recognition system Introduction: With the continuous development of technology, speech recognition technology has become an important part of the field of artificial intelligence. The online speech recognition system based on WebSocket and JavaScript has the characteristics of low latency, real-time and cross-platform, and has become a widely used solution. This article will introduce how to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online speech recognition system.
 WebSocket and JavaScript: key technologies for implementing real-time monitoring systems
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:30 PM
WebSocket and JavaScript: key technologies for implementing real-time monitoring systems
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:30 PM
WebSocket and JavaScript: Key technologies for realizing real-time monitoring systems Introduction: With the rapid development of Internet technology, real-time monitoring systems have been widely used in various fields. One of the key technologies to achieve real-time monitoring is the combination of WebSocket and JavaScript. This article will introduce the application of WebSocket and JavaScript in real-time monitoring systems, give code examples, and explain their implementation principles in detail. 1. WebSocket technology
 How to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 12:09 PM
How to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 12:09 PM
Introduction to how to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system: With the popularity of the Internet and the advancement of technology, more and more restaurants have begun to provide online ordering services. In order to implement a real-time online ordering system, we can use JavaScript and WebSocket technology. WebSocket is a full-duplex communication protocol based on the TCP protocol, which can realize real-time two-way communication between the client and the server. In the real-time online ordering system, when the user selects dishes and places an order
 How to implement an online reservation system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 am 09:39 AM
How to implement an online reservation system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 am 09:39 AM
How to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online reservation system. In today's digital era, more and more businesses and services need to provide online reservation functions. It is crucial to implement an efficient and real-time online reservation system. This article will introduce how to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online reservation system, and provide specific code examples. 1. What is WebSocket? WebSocket is a full-duplex method on a single TCP connection.
 JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecasting system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecasting system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecast system Introduction: Today, the accuracy of weather forecasts is of great significance to daily life and decision-making. As technology develops, we can provide more accurate and reliable weather forecasts by obtaining weather data in real time. In this article, we will learn how to use JavaScript and WebSocket technology to build an efficient real-time weather forecast system. This article will demonstrate the implementation process through specific code examples. We
 Simple JavaScript Tutorial: How to Get HTTP Status Code
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
Simple JavaScript Tutorial: How to Get HTTP Status Code
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
JavaScript tutorial: How to get HTTP status code, specific code examples are required. Preface: In web development, data interaction with the server is often involved. When communicating with the server, we often need to obtain the returned HTTP status code to determine whether the operation is successful, and perform corresponding processing based on different status codes. This article will teach you how to use JavaScript to obtain HTTP status codes and provide some practical code examples. Using XMLHttpRequest
 How to use insertBefore in javascript
Nov 24, 2023 am 11:56 AM
How to use insertBefore in javascript
Nov 24, 2023 am 11:56 AM
Usage: In JavaScript, the insertBefore() method is used to insert a new node in the DOM tree. This method requires two parameters: the new node to be inserted and the reference node (that is, the node where the new node will be inserted).
 JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time image processing system
Dec 17, 2023 am 08:41 AM
JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time image processing system
Dec 17, 2023 am 08:41 AM
JavaScript is a programming language widely used in web development, while WebSocket is a network protocol used for real-time communication. Combining the powerful functions of the two, we can create an efficient real-time image processing system. This article will introduce how to implement this system using JavaScript and WebSocket, and provide specific code examples. First, we need to clarify the requirements and goals of the real-time image processing system. Suppose we have a camera device that can collect real-time image data





