Setting up PHP development environment under Linux
How to build a PHP development environment under Linux: first obtain the PHP, Apache and MySQL installation packages; then compile, install and modify the configuration file; then set the environment variables and start automatically at boot; finally test whether PHP is successfully installed. Can.

Recommended: "PHP Video Tutorial"
LAMP is a very popular web development environment at the moment. Many developers will encounter various problems in the process of building LAMP. Thinking of these problems, their heads are about to explode. Today, I specially took the time to record the process of building a PHP development environment for everyone's reference. If you find any problems, I hope you can correct them.
1. Obtain the installation package
- PHP download address: http://cn.php.net/distributions/php-7.1.10.tar.gz
- Apache download address: http://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/apache//httpd/httpd-2.4.28.tar.gz
- MySQL download address: https://dev.mysql .com/get/Downloads/MySQL-5.7/mysql-5.7.19-linux-glibc2.12-x86_64.tar.gz
2. Install Apache
1. Dependencies Package installation
1) Install compiler gcc, gcc-c
yum install -y gcc gcc-c++Copy after login2) Install dependency packages expat-devel, zlib-devel, openssl-devel
yum install -y expat-devel zlib-devel openssl-develCopy after login2) Install dependency package apr
wget http://mirror.bit.edu.cn/apache//apr/apr-1.6.2.tar.gz tar zxvf apr-1.6.2.tar.gz cd apr-1.6.2 ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/apr make && make installCopy after login3) Install dependency package apr-util
wget http://mirror.bit.edu.cn/apache//apr/apr-util-1.6.0.tar.gz tar zxvf apr-util-1.6.0.tar.gz cd apr-util-1.6.0 ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/apr-util --with-apr=/usr/local/apr make && make installCopy after login4) Install dependency package pcre
wget https://ftp.pcre.org/pub/pcre/pcre-8.41.tar.gz tar zxvf pcre-8.41.tar.gz cd pcre-8.41 ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/pcre make && make installCopy after loginNote: Copy the apr and apr-util installation packages to the srclib directory of the Apache installation package
Name them apr, apr-util respectively, without the subsequent version number
2. Installation process
1) Unzip the Apache installation package
tar zxvf httpd-2.4.28.tar.gzCopy after login2) Compile and install
cd httpd-2.4.28 ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/server/apache \ --with-apr=/usr/local/apr \ --with-apr-util=/usr/local/apr-util \ --with-pcre=/usr/local/pcre \ --enable-so \ --enable-ssl \ --enable-deflate \ --enable-rewrite \ --enable-headers \ --enable-expires \ --disable-cgid\ --disable-cgi make && make installCopy after login
3. Modify the configuration file httpd.conf
vim /usr/local/server/apache/conf/httpd.confCopy after loginRemove
# in front of ServerName and change the URL after ServerName to localhost:80
4. Add httpd to the system service and set it to start automatically at boot
1) Add httpd to the system service
cp /usr/local/server/apache/bin/apachectl /etc/init.d/httpdCopy after login2) Modify /etc/init.d/httpd and add the following content to line 3
# chkconfig: 345 85 15 # description: Activates/Deactivates Apache Web ServerCopy after loginNote: The # in the code cannot be removed
3) Set the system service to start automatically at boot
systemctl enable httpdCopy after login4) Start Apache
service httpd startCopy after login
3. Install MySQL
1. Preparation before installation
1) Unzip the installation package
tar zxvf mysql-5.7.19-linux-glibc2.12-x86_64.tar.gz mv mysql-5.7.19-linux-glibc2.12-x86_64 /usr/local/server/mysqlCopy after login2) Create users and user groups and assign corresponding permissions
groupadd mysql useradd -r -g mysql mysql -s /sbin/nologinCopy after login3) Install dependencies
yum -y install numactl.x86_64Copy after login
2. Initialize mysql and make basic configuration
1) Initialize mysql
cd /usr/local/server/mysql bin/mysqld \ --initialize \ --user=mysql \ --basedir=/usr/local/server/mysql \ --datadir=/usr/local/server/mysql/data \Copy after login2) Configure mysql
vim my.cnf # 创建配置文件Copy after loginThis example only ensures that mysql can run normally. For more configuration, please refer to the official documentation
[mysqld] skip-grant-tables basedir = /usr/local/server/mysql datadir = /usr/local/server/mysql/data socket = /usr/local/server/mysql/data/mysql.sock log-error = /usr/local/server/mysql/log/error.log port = 3306 [mysql_safe] pid-file = /var/run/mysql/mysqld.pid log-error = /usr/local/server/mysql/log/error.log [client] port = 3306 socket = /usr/local/server/mysql/data/mysql.sockCopy after loginSoft link the configuration file to the /etc/ directory
ln -s /usr/local/server/mysql/my.cnf /etc/my.cnfCopy after loginNote: If you are prompted that the file exists when creating a soft link, you can delete /etc/my.cnf and then create a soft link
3) Create a database to store information Required Directories and Files
mkdir /usr/local/server/mysql/data mkdir /usr/local/server/mysql/log mkdir /var/run/mysql touch /usr/local/server/mysql/log/error.logCopy after login4) Set directory owner
chown -R mysql:mysql /usr/local/server/mysql/ chown -R mysql:mysql /var/run/mysql/Copy after login
3. Set environment variables and auto-start at boot
1) Set environment variables
Edit profile file
vim /etc/profileCopy after loginAdd the following information to the end of profile
export PATH=$PATH:/usr/local/server/mysql/binCopy after loginMake environment variables take effect immediately
source /etc/profileCopy after login2) Set up auto-start at boot
cp support-files/mysql.server /etc/init.d/mysqld chkconfig --add mysqld chkconfig mysqld onCopy after login
4. Firewall settings
CentOS has the firewall enabled by default. Below we use firewall to open the 3306l port
1) Before we enable it First check whether port 3306 is open
firewall-cmd --query-port=3306/tcpCopy after login2) If it is not turned on, turn on the firewall firewall
systemctl start firewalld.serviceCopy after login3) We can choose to temporarily open or permanently open port 3306
firewall-cmd --add-port=3306/tcp # 临时开启3306端口 firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-port=3306/tcp # 永久开启3306端口Copy after login4) Restart firewall
firewall-cmd --reloadCopy after login
5. Start mysql and set the root user password
1) Start mysql
/usr/local/server/mysql/support-files/mysql.server start # 启动MySQL /usr/local/server/mysql/bin/mysql -uroot -p # 这里直接回车,无须输入密码Copy after login2) Set root user password
use mysql; update user set authentication_string=password('root') where user='root'; exit;Copy after loginNote 1: After successfully changing the password, log out of skip-grant-tables in the configuration file
Restart mysql and log in again using the root user, and then execute the following code
set password=password('root');Copy after loginNote 2: It is a system requirement to reset the password for the second time, otherwise the database cannot be operated
6. Remote access
1) Give access to any host mysql permissions
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO 'root'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'your password' WITH GRANT OPTION;Copy after login2) Make permission modification take effect
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;Copy after login
4. Install PHP
1. Installation steps
1) Install the dependency package libxml-devel
yum -y install libxml2-develCopy after login2) Unzip the PHP installation package
tar zxvf php-7.1.10.tar.gzCopy after login3) Compile and install
cd php-7.1.10 ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/server/php \ --with-apxs2=/usr/local/server/apache/bin/apxs \ --with-config-file-path=/usr/local/server/php \ --with-pdo-mysql make && make installCopy after login
2. Configure php.ini
1) Copy the configuration file to the PHP installation directory
cp php.ini-* /usr/local/server/php/Copy after login2) Generate php.ini
cp php.ini-development /usr/local/server/php/php.iniCopy after login
3. Modify httpd.conf
载入PHP模块,如httpd.conf中有下列代码则直接去掉前面#即可,没有则加入
LoadModule php7_module modules/libphp7.soCopy after login在底部加入以下代码使得Apache可以解析php文件
<IfModule mod_php7.c> AddType application/x-httpd-php .php </IfModule>Copy after login找到如下代码,在index.html后面加入index.php
<IfModule dir_module> DirectoryIndex index.html </IfModule>Copy after login重启Apache
service httpd restartCopy after login
4. 测试PHP是否成功安装
创建/usr/local/server/apache/htdocs/index.php
vim /usr/local/server/apache/htdocs/index.phpCopy after login在index.php中编写以下代码
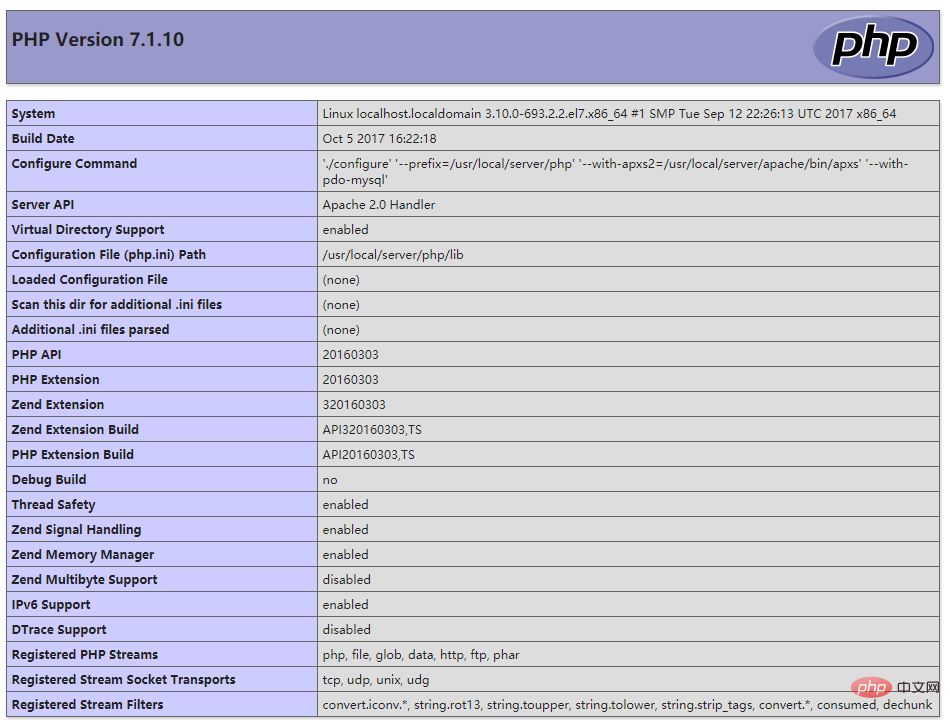
<?php phpinfo(); ?>Copy after login如果出现以下页面则安装成功
The above is the detailed content of Setting up PHP development environment under Linux. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1377
1377
 52
52
 PHP: A Key Language for Web Development
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:08 AM
PHP: A Key Language for Web Development
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:08 AM
PHP is a scripting language widely used on the server side, especially suitable for web development. 1.PHP can embed HTML, process HTTP requests and responses, and supports a variety of databases. 2.PHP is used to generate dynamic web content, process form data, access databases, etc., with strong community support and open source resources. 3. PHP is an interpreted language, and the execution process includes lexical analysis, grammatical analysis, compilation and execution. 4.PHP can be combined with MySQL for advanced applications such as user registration systems. 5. When debugging PHP, you can use functions such as error_reporting() and var_dump(). 6. Optimize PHP code to use caching mechanisms, optimize database queries and use built-in functions. 7
 PHP's Current Status: A Look at Web Development Trends
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:20 AM
PHP's Current Status: A Look at Web Development Trends
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:20 AM
PHP remains important in modern web development, especially in content management and e-commerce platforms. 1) PHP has a rich ecosystem and strong framework support, such as Laravel and Symfony. 2) Performance optimization can be achieved through OPcache and Nginx. 3) PHP8.0 introduces JIT compiler to improve performance. 4) Cloud-native applications are deployed through Docker and Kubernetes to improve flexibility and scalability.
 PHP vs. Python: Core Features and Functionality
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:16 AM
PHP vs. Python: Core Features and Functionality
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:16 AM
PHP and Python each have their own advantages and are suitable for different scenarios. 1.PHP is suitable for web development and provides built-in web servers and rich function libraries. 2. Python is suitable for data science and machine learning, with concise syntax and a powerful standard library. When choosing, it should be decided based on project requirements.
 PHP vs. Other Languages: A Comparison
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:19 AM
PHP vs. Other Languages: A Comparison
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:19 AM
PHP is suitable for web development, especially in rapid development and processing dynamic content, but is not good at data science and enterprise-level applications. Compared with Python, PHP has more advantages in web development, but is not as good as Python in the field of data science; compared with Java, PHP performs worse in enterprise-level applications, but is more flexible in web development; compared with JavaScript, PHP is more concise in back-end development, but is not as good as JavaScript in front-end development.
 PHP: The Foundation of Many Websites
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:07 AM
PHP: The Foundation of Many Websites
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:07 AM
The reasons why PHP is the preferred technology stack for many websites include its ease of use, strong community support, and widespread use. 1) Easy to learn and use, suitable for beginners. 2) Have a huge developer community and rich resources. 3) Widely used in WordPress, Drupal and other platforms. 4) Integrate tightly with web servers to simplify development deployment.
 What to do if the apache80 port is occupied
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:24 PM
What to do if the apache80 port is occupied
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:24 PM
When the Apache 80 port is occupied, the solution is as follows: find out the process that occupies the port and close it. Check the firewall settings to make sure Apache is not blocked. If the above method does not work, please reconfigure Apache to use a different port. Restart the Apache service.
 How to start apache
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:06 PM
How to start apache
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:06 PM
The steps to start Apache are as follows: Install Apache (command: sudo apt-get install apache2 or download it from the official website) Start Apache (Linux: sudo systemctl start apache2; Windows: Right-click the "Apache2.4" service and select "Start") Check whether it has been started (Linux: sudo systemctl status apache2; Windows: Check the status of the "Apache2.4" service in the service manager) Enable boot automatically (optional, Linux: sudo systemctl
 How to monitor Nginx SSL performance on Debian
Apr 12, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
How to monitor Nginx SSL performance on Debian
Apr 12, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
This article describes how to effectively monitor the SSL performance of Nginx servers on Debian systems. We will use NginxExporter to export Nginx status data to Prometheus and then visually display it through Grafana. Step 1: Configuring Nginx First, we need to enable the stub_status module in the Nginx configuration file to obtain the status information of Nginx. Add the following snippet in your Nginx configuration file (usually located in /etc/nginx/nginx.conf or its include file): location/nginx_status{stub_status