An article to help you understand the underlying principles of MYSQL
mysql video tutorial column introduces the underlying principles.

MYSQL
A SQL execution process
First look at a query SQL
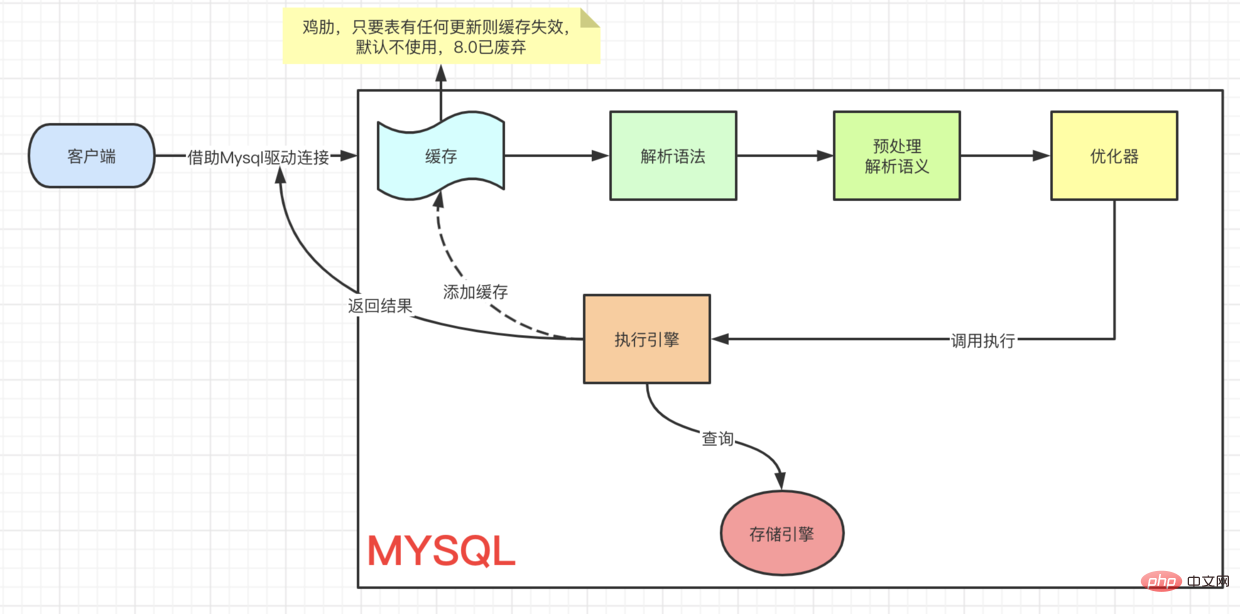
- (Here is the official document description of each storage engine Mysql storage engine)
An update SQL execution
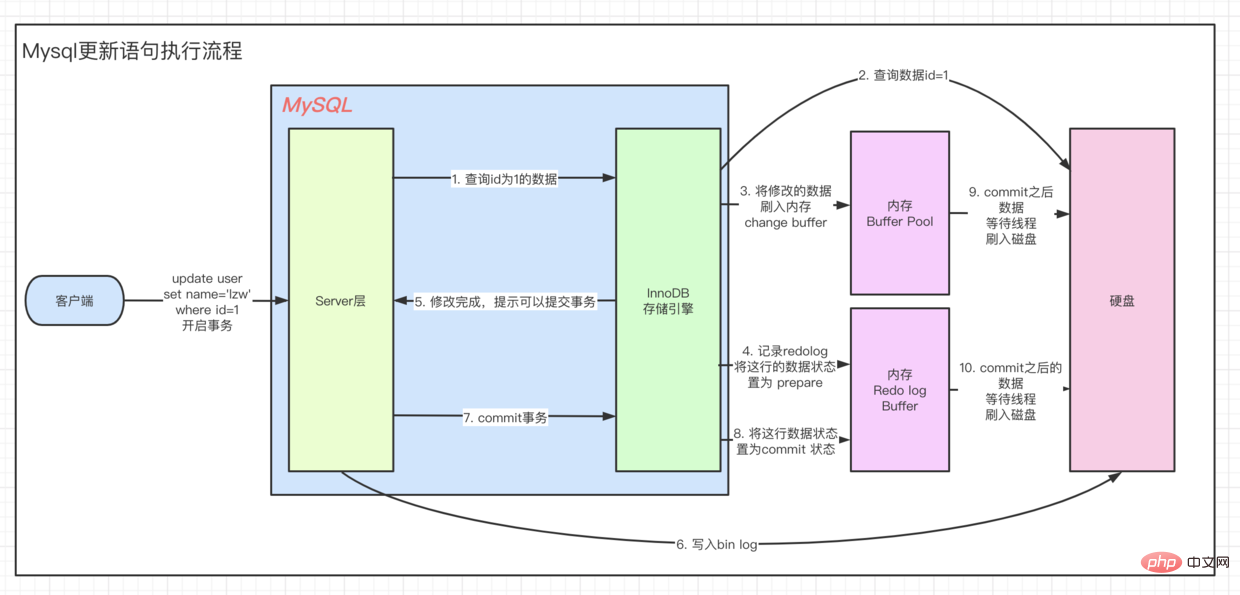
The execution of update starts from Client=> ··· => Execution engine The process is the same. You must first find this data and then update it. To understand the UPDATE process, let’s first take a look at Innodb’s architectural model.
Innodb architecture
Last MYSQL official InnoDB architecture diagram:
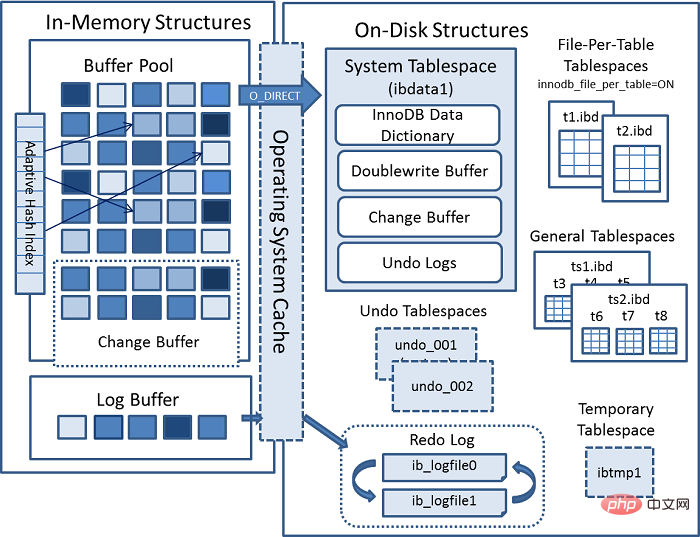
Internal module
Connector (JDBC , ODBC, etc.) =>
[MYSQL Internal
[Connection Pool] (授权、线程复用、连接限制、内存检测等) => [SQL Interface] (DML、DDL、Views等) [Parser] (Query Translation、Object privilege) [Optimizer] (Access Paths、 统计分析) [Caches & Buffers] => [Pluggable Storage Engines]复制代码
]
=> [File]
Memory Structure
There is a key point here. When we query the data, we will first take the page we are currently querying and go to the buffer pool to query whether the current page is in Buffer pool in. If it is, get it directly.
And if it is an update operation , the value in Buffer will be modified directly. At this time, the data in buffer pool is inconsistent with the data actually stored in our disk, and is called dirty page. Every once in a while, the Innodb storage engine will flush dirty page data to the disk. Generally speaking, when updating a piece of data, we need to read the data into the buffer for modification, and then write it back to the disk to complete a disk IO operation.
update, Mysql has been optimized in memory. You can see that there is an area in the buffer pool of the architecture diagram called:change buffer. As the name suggests, is used to create a buffer for the changed data. When updating data without a unique index, the modified data is directly placed in the change buffer. Then the update is completed through the merge operation, thereby reducing the IO operation for that disk drop.
- When the data without a unique index is updated
- , why must
When the data without a unique index is updatedcan it be placed directly How about enteringchange buffer? If it is a field withunique constraints, after we update the data, the updated data may be duplicated with the existing data, so we can onlyread all the data from the disk and compareTo determine uniqueness.So when our data ismore written and less read - , we can adjust
change bufferinby increasinginnodb_change_buffer_max_sizeThe proportion of buffer pool, the default is 25 (ie: 25%) The question comes again, how merge works
There are four situations:
If there is other access, the data of the current page will be merged to the disk- Background thread scheduled merge
- Before the system shuts down normally, merge once
- redo log
- When it is full, merge to the disk
When talking about redo, we must talk about innodb
crash safe, use WAL method (write Ahead Logging, record the log before writing) This way, when the database crashes, directly from
to ensure data correctnessredo log is stored in two files by default
ib_logfile1, both files areFixed size. Why do you need fixed size? This is caused by the
feature of redo log, which must be a continuous storage space 2. Random reading and writing and Sequential reading and writing
Look at a picture
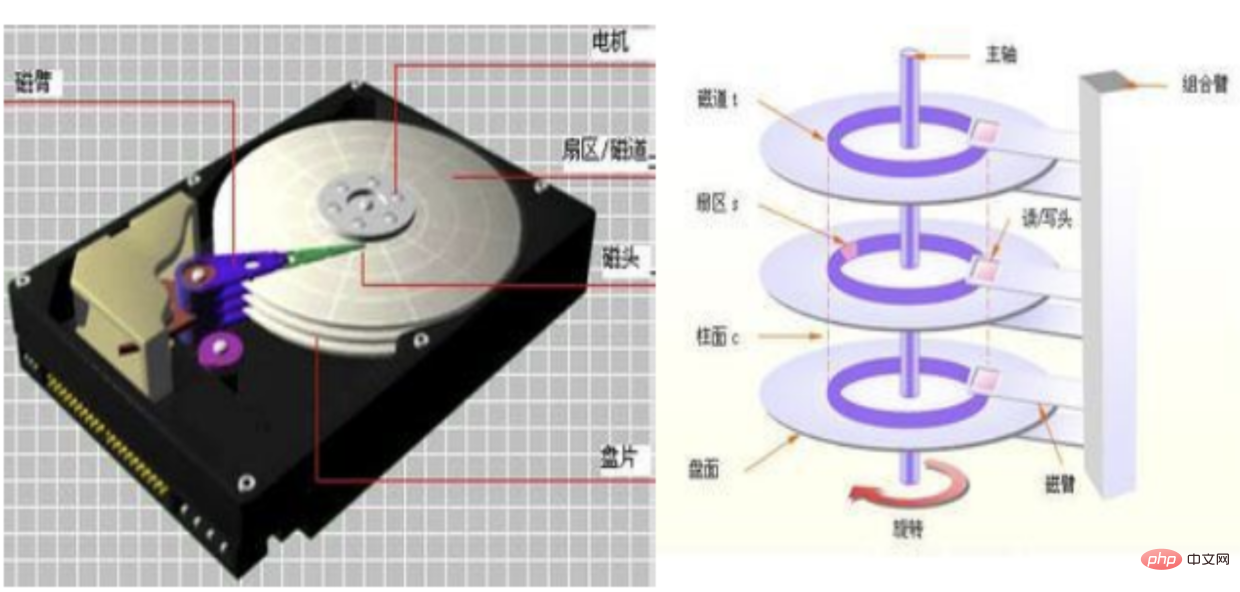 Generally our data is scattered on the disk:
Generally our data is scattered on the disk:
The reading and writing sequence of the mechanical hard disk is:
Locate the track- Wait for rotation to the corresponding sector
- Start reading and writing
- Solid state reading and writing:
- Directly locate the flash memory chip (this is why solid-state is faster than mechanical)
- Start reading and writing
In fact, regardless of mechanical or solid-state, when we go to store, They all deal with the disk through File system, and there are two ways of dealing with them. Random read and write and Sequential read and write
- The data stored in random read and write is distributed in different
blocks(default 1block= 8 sectors = 4K) - As for sequential storage, as the name suggests, the data is distributed in a
series of consecutive blocks, so the reading speed is greatly improved
3. Return to our architecture diagram
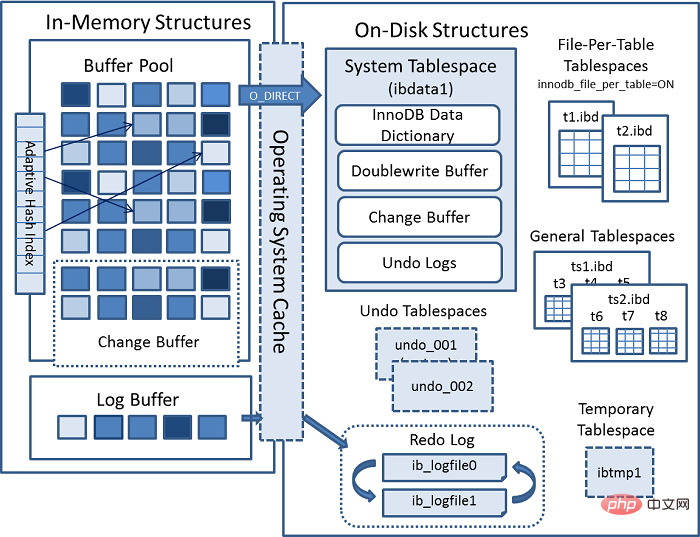
See Log Buffer in buffer pool, which is used to write The buffer that existed before redo log
Here, there are three specific execution strategies for redo log:
- No need to write
Log Buffer, only need to write every second Redo logs disk data once and has high performance, but it will cause data consistency problems within 1 second. Applicable tostrong real-time performance,weak consistency, for example,comments in the comment area - write
Log Buffer, and write at the same time Into the disk, the performance is the worst and the consistency is the highest. Applicable toweak real-time,strong consistency, such aspayment scenario - write
Log Buffer, and write toos buffer(it will callfsyncevery second to flush data to the disk), with good performance and high security. This ismoderate real-timemoderate consistency, such asorder type.
We can set the execution policy through innodb_flush_log_at_trx_commit. The default is 1
Memory structure summary

- ##Buffer Pool is used to speed up reading
- Change Buffer Used to accelerate writing without non-unique indexes
- Log Buffer is used to accelerate redo log writing
- Adaptive Hash index
Mainly used to speed up queriesPage. When querying, Innodb determines whether the current query can go through theHash indexby monitoring the index search mechanism. For example, the LIKE operator and the % wildcard character cannot be used.
ibdata1, which contains:
- InnoDB Data Dictionary stores metadata, such as table structure information, indexes, etc.
- Doublewrite Buffer When
- Buffer Pool
writes the data page, it is not written directly to the file. Instead, it is written to this area first. The advantage of this is that once the operating system, file system or mysql hangs, the data can be obtained directly from thisBuffer.Change Buffer When Mysql shut down, the modifications will be stored on the disk - Undo Logs records transaction modification operations
.ibd to store data and indexes.
- With
- file-per-table tablespace
, the performance ofALTER TABLEandTRUNCATE TABLEcan be greatly improved. For example,ALTER TABLE, compared to a table residing in a shared table space, when modifying the table, atable copy operationwill be performed, which may increase the number of table space occupiedAmount of disk space. Such operations may require as much additional space as the data in the table and the indexes. This space is not released back to the operating system likefile-per-table tablespace.File-per-table tablespace data files can be created on separate storage devices for I/O optimization, space management, or backup. This means that table data and structures are easily migrated between different databases. - When data corruption occurs, backups or binary logs are unavailable, or a MySQL server instance cannot be restarted, storing tables in a single tablespace data file saves time and improves the chance of successful recovery.
- The utilization rate of storage space is low, there will be fragmentation, which will affect the performance when
Drop table(unless you manage the fragmentation yourself) - Because each table is divided into Respective table files, the operating system cannot perform
fsyncone-time flushing of data into the file - mysqld will continue to maintain the
file handleof each table file, to Provides continuous access to files
3. General Tablespaces
- General tablespace is also called
shared tablespace, it can storeData from multiple tables - If you store the same number of tables, the storage consumed is smaller than
Table space per table - in MySQL Support for placing table partitions in regular tablespaces is deprecated in 5.7.24 and will no longer be supported in a future MySQL version.
4. Temporary Tablespaces
are stored in a file called ibtmp1. Under normal circumstances, Mysql will create a temporary table space when it starts, and delete the temporary table space when it stops. And it can automatically expand.
5. Undo Tablespaces
- Provides
atomicityof modification operations, that is, when an exception occurs in the middle of the modification, it can be rolled back through the Undo log. - It stores the original data before the start of the transaction and this modification operation.
- Undo log exists in the rollback segment (rollback segment), and the rollback segment exists in the
system table space `` undo table space `` temporary table space, as shown in the architecture diagram .
Redo Log
As mentioned before
To summarize, what will happen when we execute an update SQL statement
- Query us The piece of data to be modified, we call it
originhere, is returned to the executor - In the executor, modifying the data is called
modification - Flash
modificationinto memory,Change Buffer ofBuffer Pool - Engine layer: record undo log (to achieve transaction atomicity)
- Engine layer: record redo log (used for crash recovery)
- Service layer: record bin log (record DDL)
- Return update success result
- Data waiting Flushed to the disk by the worker thread
Bin log
said Undo, Redo also By the way Bin log.
- This log has little to do with the
innodbengine. The two logs we mentioned earlier are both innodb Engine layer. AndBin logis in theservice layer. So it can be used by various engines. - What is its main function? First of all,
Bin logrecords eachDDL DMLstatement in the form of events. It is a log in a logical sense. - Able to achieve
master-slave replication,Get thebin loglog of themainserver from theserver, and then execute. - Do
data recovery, get the logs of a certain period of time, and execute it again.
After following a SQL statement to complete the global preview, let's look back and make the SQL richer. Let's add an indexTry
Gorgeous dividing line
Index article
If you want to completely understand what the index in InnoDB is, you must understand its File storage levels
Innodb divides file storage into four levels
Pages, Extents, Segments, and Tablespaces
Their relationship is:
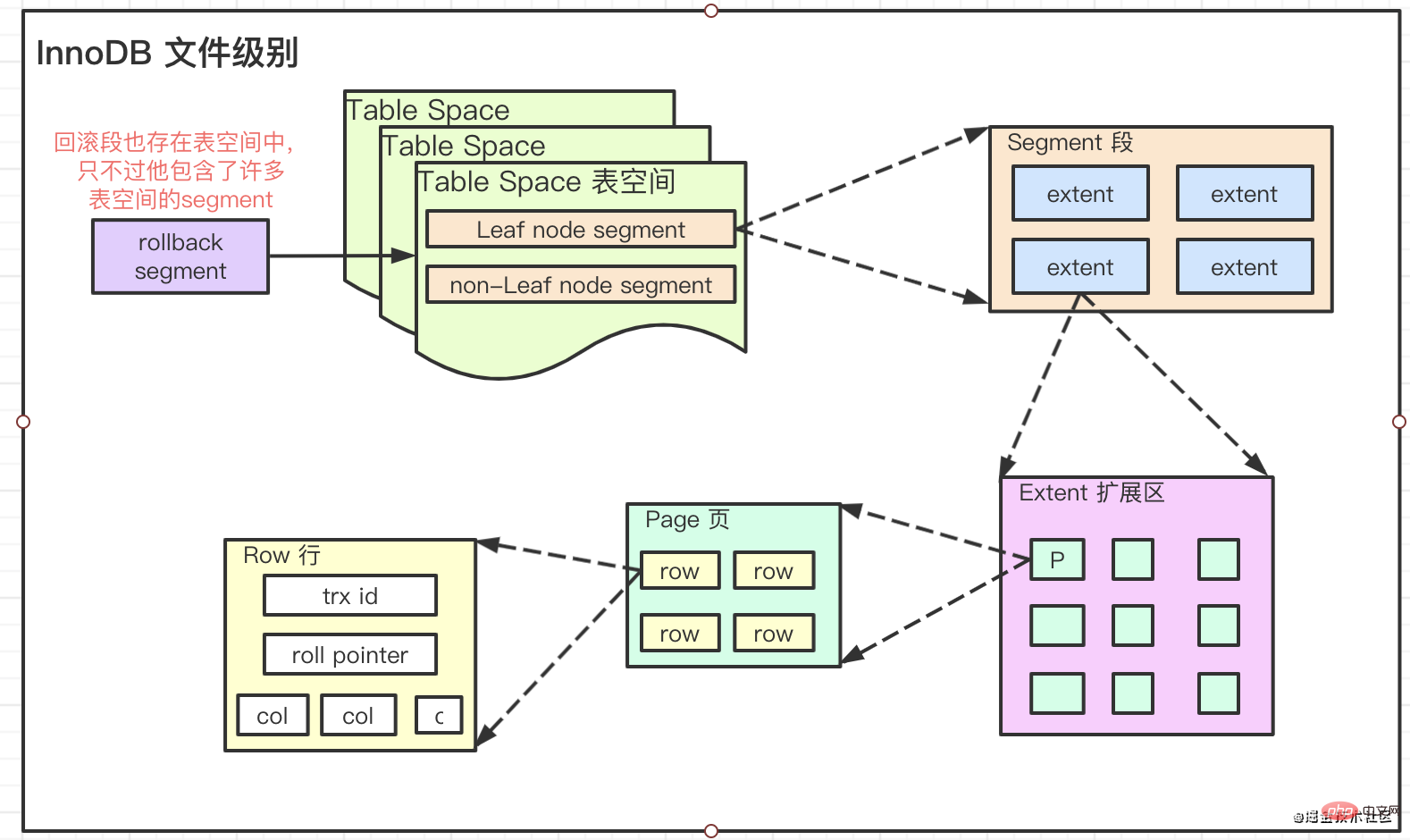
- The default
extentsize is1M, which is6416KBPage. The page size usually referred to by our file system is4KB, containing8sectors of512Byte.
Storage structure B tree variant B tree
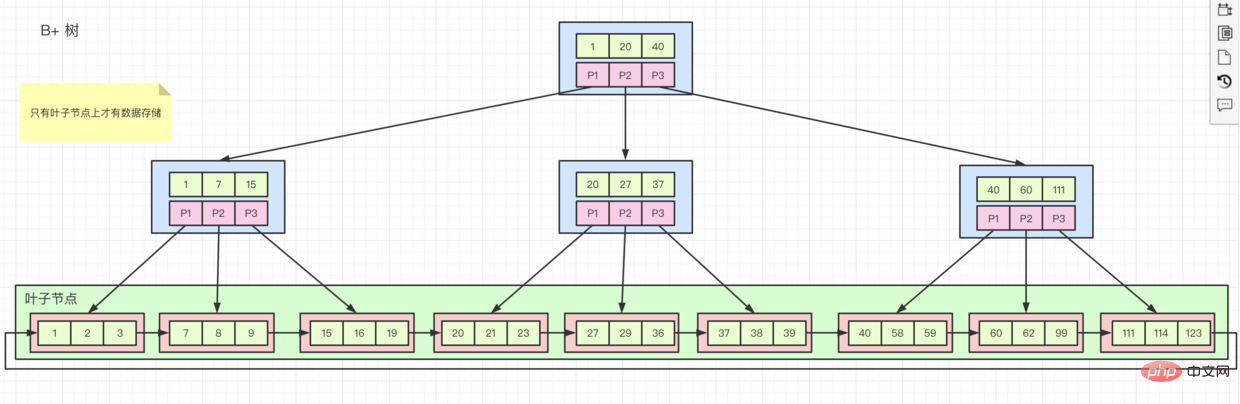
So sometimes, we are asked why the primary key must be ordered. The reason is that if we On an ordered field, create an index and then insert data.
When storing, innodb will store it on page one by one in order. When one page is full, it will apply for a new page, and then continue to save.
But if our fields are unordered, the storage locations will be on different pages. When our data is stored on a page that has been full, it will cause page splits, thus forming fragments.
Several different index organization forms
- Clustered index, as shown in the
B treediagram above,rows of dataare stored on the child nodes, And if thearrangement order of the indexis consistent with theindex key value order, it isclustered index. The primary key index is a clustered index. Except for the primary key index, all others areauxiliary indexes - auxiliary indexes. If we create a
auxiliary index, its leaf nodes Only's own valueandthe value of the primary key indexare stored. This means that if we query all data through the auxiliary index, we will first find theprimary key valuein theauxiliary index, and then go to theprimary key indexInside, relevantdatawas found. This process is calledBack to the table -
rowidWhat should I do if there is noprimary key index?- There is no primary key, but there is a Unique key and it is not null, then a
clustered indexwill be created based on this key. - If you don’t have either of the above, don’t worry, innodb maintains something called
rowid, and creates aclustered index based on this id
- There is no primary key, but there is a Unique key and it is not null, then a
How index works
After figuring out what an index is and what its structure is. Let’s take a look at when we need to use indexes. Understanding these can better help us create correct and efficient indexes
If the dispersion is low, no index will be built, that is, the data If there is not much difference between them, there is no need to create an index. (Because of the index creation, most of the data in innodb are the same when querying. If there is no difference between the index and the whole table, I will directly
full table query). For example, the gender field. This wastes a lot of storage space.-
Joint field index, such as
idx(name, class_name)- When executing
select * from stu where class_name = When querying xx and name = lzw, you can also use the indexidx, because the optimizer optimizes SQL toname = lzw and class_name = xx - When you need to
select ··· where name = lzw, you do not need to create a separatenameindex, you will go directly toidxthis index -
Covering Index. Ifall the datawe query this time are included in the index, there is no need toreturn to the tableto query. For example:select class_name from stu where name =lzw
- When executing
-
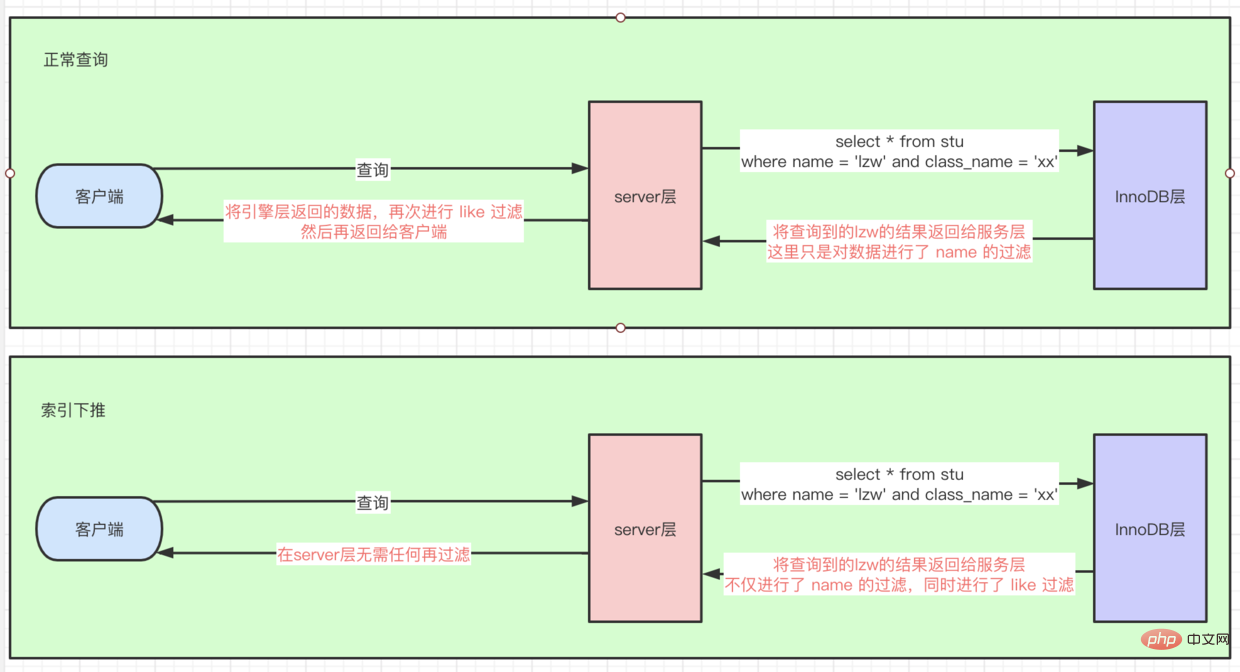
Index condition pushdown (index_condition_pushdown)
- There is such an article SQL,
select * from stu where name = lzw and class_name like '%xx' - If there is no
index condition, push down, because it is followed bylike ' %xx'query conditions, so here we first go to theidx joint indexbased onname. After querying several pieces of data, we willreturn to the tablequeryFull row data, and then perform like filtering on theserver layerto find the data - If there is, then directly filter the like on the
engine layer, which is equivalent to pushing the filtering operationof theserver layerdown to the engine layer. As shown in the figure:
- There is such an article SQL,
Notes on index creation
- On where, order, join When used frequently, index
- fields with high discreteness can be added to create an index.
- Joint index puts high discreteness first (because it is first matched based on the first field, which can quickly Locate the data location.)
- Frequently updated fields cannot be indexed (causing
page splits, the index is stored in order, if the storage page is full, inserting again will cause page splits) - The index will not be used when using
functions such as replace, sum, count, etc., so there is no need to build additional ones. - When implicit conversion occurs, such as string conversion to int , and you don’t need to index
- particularly long fields, you can intercept the first few bits to create an index (you can use
select count(distinct left(name, 10))/count(*)to Look at the degree of dispersion and decide to extract the top few)
- tips: When executing a SQL, you can’t exactly say whether it can use the index. After all, it’s all an optimizer. decided
. For example, if you use theCost Base Optimizercost-based optimizer, use whichever optimization has the lowest cost.
Lock chapter
Four major features Let’s first review some basic concepts that we are familiar with:
- Atomicity (implemented by Undo log)
- Consistency
- Isolation
- Persistence (crash recovery, Redo log double write)
The read consistency problem should be solved by the transaction isolation level of the database (SQL92 standard)
Prerequisite, in a transaction:
- Dirty read (read The data has not yet been committed by others, and then others roll it back)
- Non-repeatable reading (the data is read for the first time, and then someone else modifies the commit, and then reads it again and reads the data that others have committed) Data)
- Phantom reading (read newly added data by others during range query)
SQL92 standard regulations: (Concurrency decreases from left to right)

- #tips: In Innodb, the phantom read of Repeatable Read cannot exist because it solves it by itself
How to solve the problem of phantom reads in Repeatable Read (RR) in Innodb
Lock Model
- LBCC (Lock Based Concurrency Control) Add a lock before reading, but this may cause performance problems => Locking during reading will prevent other transactions from reading and writing, resulting in low performance
- MVCC (Multi Version Concurrency Control) Record the current time when reading Snapshot, others can just read the snapshot => Performance consumption, storage consumption
These two solutions are used together in Innodb. Here is a brief explanation of the MVCC implementation of RR. The initial value of the rollback id in the figure should not be 0 but NULL. For convenience, it is written as 0

-
RC's MVCC implementation creates a version for multiple reads of the same transaction, whileRR creates a version for any one of the same transaction
Through the combination of MVCC and LBCC, InnoDB can solve the problem of phantom reading under no locking conditions. Instead of being like Serializable, the transaction must be seriallyed without any concurrency.
Let’s take an in-depth look at how InnoDB lock is implemented RR Transaction isolation level
Lock in-depth implementation of MVCC in Innodb
1. Innodb’s locks
- Shared and Exclusive Locks Shared and Exclusive Locks=> (S, X)
- Intention Locks Intention Locks=> What this refers to There are two locks, which are actually shared and exclusive locks at
table level=> (IS, IX)
The above four locks are The most basic types of locks
- Record Locks Record Locks
- Gap Locks Gap Locks
- Next-key Locks
These three locks are understood as the three algorithm methods implemented for the above four locks. We will temporarily call them here: High-order locks
- Insert Intention Locks Insert locks
- AUTO-INC Locks Auto-increment key locks
- Predicate Locks for Spatial Indexes Specially used for Spatial Indexes
The above three are additional extended locks
2. In-depth explanation of read-write locks
- To use shared locks, add
lock in share modeafter the statement . Exclusive locks will be used byInsert, Update, and Deleteby default. Display usingfor updateafter the statement. - Intention locks are maintained by the database itself. (The main function is to mark the table
to record whether the table is locked) => If there is no such lock, when other transactions want to lock the table, they must go to the entire table Scanning for locks is too inefficient. That's why intention locks exist.
- You have created a Primary key, which is a clustered index (which stores
- Complete data
)There is no primary key, but there is a Unique key and it is not null, then a - clustered index will be created based on this key
- rowid
, and creates aclustered index based on this id
locking query on a table for which you have not explicitly created an index, the database actually does not know what data to check. Tables may be used. So simply lock the entire table.
- If you are adding a write lock to the
auxiliary index, for example,select * from where name = 'xxx' for updateFinally,return to the tablecheck Information on the primary key, so at this time in addition to lockingauxiliary index, we also need to lockprimary key index
x, (-∞,1), (1,3), (3,6), (6,9), (9, ∞)
When locking, what is locked is (-∞,1], (1,3], (3,6], (6,9], (9, ∞]. The left-open and right-closed intervals
exclusive locks, and temporary key lock = record lock gap lock
- when
- select * from xxx where id = 3 for update
Whenselect * from xxx where id = 5 for update , a gap lock is generated => (3,6) is locked. Pay special attention here. : There is no conflict between gap locks. -
Whenselect * from xxx where id = 5 for update , a temporary key lock is generated => locked (3,6] , mysql uses temporary key locks by default. If conditions 1 and 2 are not met, all row locks are temporary key locks
- prevents other transactions from modifying or deleting,
- Gap Lock gap lock
prevents other transactions from being added,Gap Lock and Record Lockare combined to formNext- Key lockjointly solvesRR levelthe phantom read problem when writing data.When it comes to locks, there is no way to escape but let’s talk about deadlock
-
Innodb_row_lock_current_waits How many locks are currently waiting for- Innodb_row_lock_time in total How long to wait
- Innodb_row_lock_time_avg Average waiting time
- Innodb_row_lock_time_max Maximum waiting time
- Innodb_row_lock_waits How many waits have occurred in total
You can view the currently running and locked transactions -
show full processlist = - select * from information_schema.processlist
Can we query which useris on which machine host and which portWhich database is connectedWhat instructions are executed#Status and timeDeadlock preventionEnsure the order of accessing data
Avoid using an index when using where (this will lock the table , not only deadlocks are more likely to occur, but also performance is lower)
- Split a very large transaction into multiple small transactions
- Try to use equivalent queries (even if you use range queries) Limit a range, instead of just opening or closing it. For example, if id > 1, lock all the following)
- Optimization Chapter
- Sub-database and sub-table
#If you want to get better query performance, you can start from this
Query execution process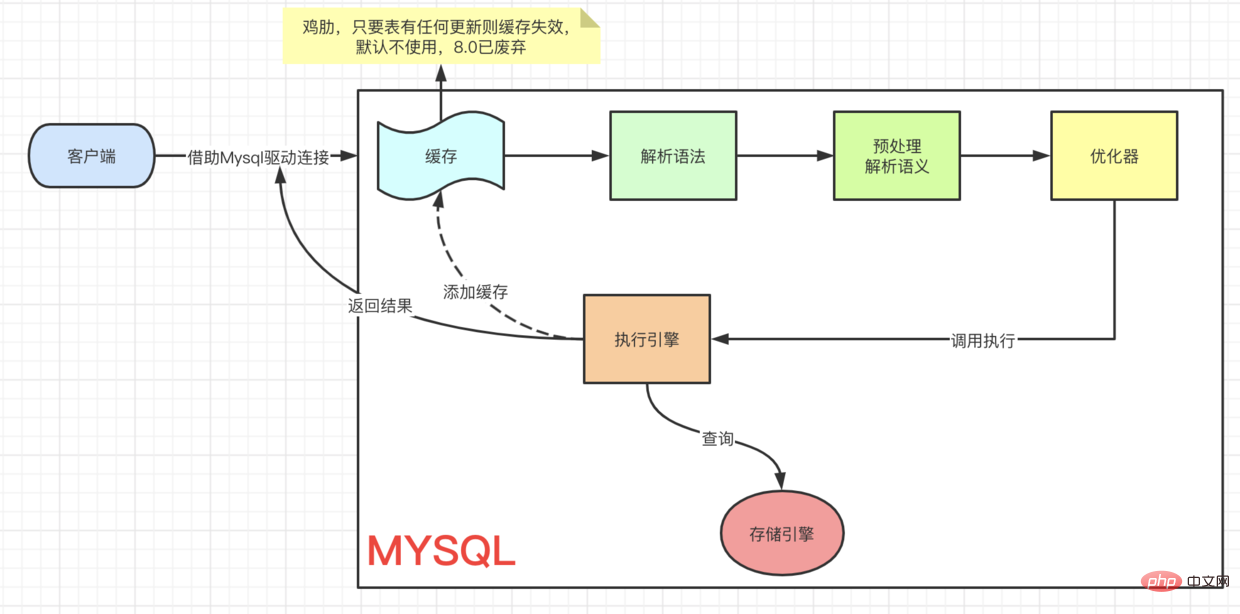
Add a connection pool to avoid creating and destroying connections every time
- Our concurrent execution of SQL will not become faster as the number of connections increases. why? If I have 10,000 connections executing concurrently, wouldn't it be much faster than your 10 connections? The answer is no, not only is it not fast but it is getting slower and slower.
- In computers, we all know that only
CPUcan actually executethreads. Because the operating system usestime slicingtechnology, it makes us think that oneCPU coreexecutesmultiple threads. - But in fact, the previous
CPUcan only execute onethreadduring a certainperiod of time, so no matter how we increase concurrency,CPUcan still only process so much data in this time period.Then even if - CPU
cannot process so much data, how can it become slower? Because oftime slicing, when multiple threads appear to be"executing simultaneously", in factcontext switchingbetween them is very time-consumingSo, once the number of threads exceeds the number of CPU cores, increasing the number of threads will only make the system slower, not faster.
Of course, this is only the core reason. The disk will also have an impact on the speed, and it will also have an impact on our connection number configuration. - In computers, we all know that only
- For example, with the mechanical hard disk we use, we need to rotate it, address it to a certain location, and then perform
- I/O
operations. At this time,CPUcan Slice time to otherthreadsto improve processing efficiency and speedSo, if you are using a mechanical hard drive, we can usually add more connections to maintain high concurrency - But if you are using SSD, because the
- I/O
waiting time is very short, we cannot add too many connections
Generally speaking, you need to follow this formula: - I/O
- Number of threads = ((Number of cores * 2) Number of effective disks)
. For example, ai7 4core 1hard diskmachine is 4 * 2 1 = 9 I wonder if you are familiar with this formula. This is not only applicable to database connections, but also For any - many CPU computing and I/O scenarios
For example: setting the maximum number of threads, etc.
Redis
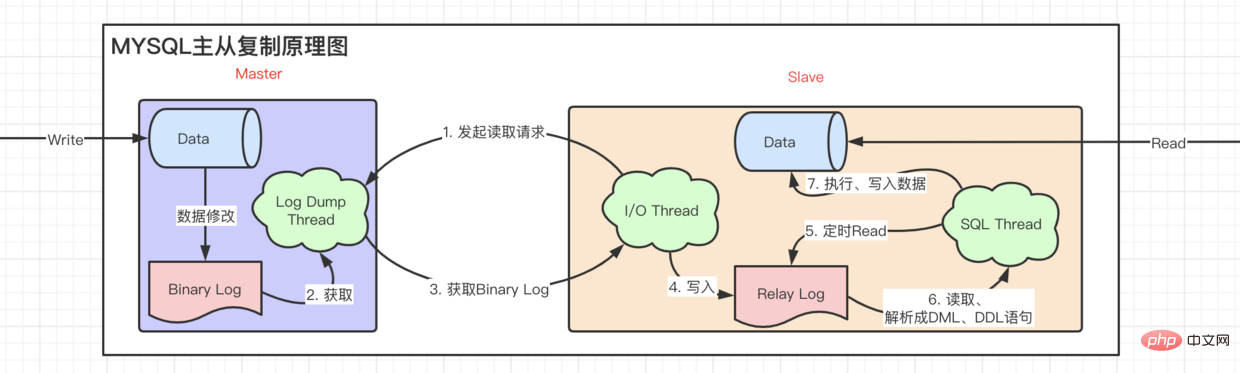
read-write separation asynchronous replication characteristic.
- tips: After writing
- Binary Log
torelay log,slavewill read the latestBinary Log Positionis recorded tomaster info, and will be fetched directly from this position next time.
asynchronous master-slave replication is that the update is not timely. When a piece of data is written and immediately read by a user, the data read is still the previous data, which means there is a delay.
To solve the delay problem, it is necessary to introduce transactions
- fully synchronous replication, which is executed in transaction mode. The master node writes first, and then all slaves are allowed to write. All slaves must The node completes writing the data before returning the write success. This will greatly affect the writing performance.
- Semi-synchronous replication, as long as there is one salve writing data, it is considered successful. (If semi-synchronous replication is required, both the master and slave nodes need to install the semisync_mater.so and semisync_slave.so plug-ins)
- GTID (global transaction identities) replication, when the master library replicates in parallel, the slave library also replicates in parallel, solved The master-slave synchronous replication delay realizes the automatic
- failover
action, that is, if the master node hangs up and the slave node is elected, data loss can be quickly and automatically avoided.
- Master-Slave HAPrxoy keeplive
- NDB
- Glaera Cluster for MySQL
- MHA (Master-Mater replication manager for MySQL), MMM (MySQL Master High Available)
- MGR (MySQL Group Replication) => MySQL Cluster
Lock operationsAffected performance
Table structure
- Design reasonable field types
- Design reasonable field length
3. Optimizer and execution engine
Slow log
turns onshow_query_log, and SQL statements whose execution time exceeds the variable long_query_time will be recorded.
You can use mysqldumpslow /var/lib/mysql/mysql-slow.log. There are many plug-ins that can provide more elegant analysis than this, so I won’t go into details here.
explain analysis SQL
After writing any SQL, you should explain
1. Driver table - For example, abuse of left/right join leads to low performance
- Using
left/right joinwill directly specify the driver table. In MYSQL,Nest loop joinis used by default for table association (that is, the result set of thedriven tableis used as the basic data of the loop, and then the next associated table is filtered through each piece of data in this set data, and finally merge the results to get what we often calltemporary table). - If the data in the
driven tableismillions and millionslevel, you can imagine how slow the query of this joint table will be. But on the other hand, ifsmall tableis used asdriven table, the query can become very fast with the help ofindexof tens of millions of tables.If you are not sure who should be used as the - driven table
, then please let the optimizer decide, for example:select xxx from table1, table2, table3 where ·· ·, the optimizer will use the table with a small number of query record rows as the driving table.If you just want to specify the - driver table
by yourself, then please grab theExplainweapon. Among the results ofExplain, the first one isBasic driver table Sort. Similarly, there is a big performance difference in sorting different - tables
. We try to sort thedriver tableinstead of thetemporary table, which is the merged result. Setto sort. That is,using temporaryappears in the execution plan, and optimization needs to be performed.
- select_type (type of query):
- Normal query
andComplex query( Union query, subquery, etc.)- SIMPLE
, if the query does not contain a subquery or UNION - PRIMARY
, if the query containscomplex querysubstructure, then you need to use the primary key query - SUBQUERY
, and include thesubstructure inselectorwhereQuery - DERIVED
, contains subqueryUNION RESULT, in - from
, fromunionTable query subquery
table The table name used - SIMPLE
- type (access type), how to find the required rows, query from top to bottom Speed
- Getting faster
- const or system
Constant level scan, the fastest way to query the table, system is a special case of const (in the table Only one piece of data) - eq_ref
Unique index scan - ref
Non-unique index scan - range
Index range scan, such as between, and other range queries - index
(index full) scans all index trees - ALL
Scan the entire table - NULL
, no need to access the table or index
listed here do not necessarily use the - const or system
-
key: which index is actually used - . If not, it is NULL
key_len: the number of bytes occupied by the index used - ref: which field or constant is used together with the index (key)
-
rows: How many rows were scanned in total - filtered (percentage): How much data is filtered at the server layer
- Extra: Additional information
-
- only index
- The information only needs to be retrieved from the index. Covering indexes may be used, and the query is very fast.
- If the query does not use the index, it will be in
serverlayer filtering and then usewhereto filter the result set impossible where - Nothing was found
- , as long as there is no sorting by index, but other sorting methods are used, filesort
- (the result set needs to be temporarily stored through a temporary table, and then Calculation.) Generally speaking, in this case,
DISTINCT, sorting, and groupingusing index condition - are pushed down. As mentioned above, the index is pushed down.
server layerThis filtering operationis pushed down to the engine layer
- The information only needs to be retrieved from the index. Covering indexes may be used, and the query is very fast.
When there are only
inserts and queries- , you can use
- MyISAM
Storage EngineWhen you only use temporary data, you can usememory -
Wheninsert, update, query etc. are concurrent, you can use - InnoDB
Summary
SQL and index
- Storage engine and table structure
- Database architecture
- MySQL configuration
- Hardware and operating system
- In addition, if data query is slow, we should not just blindly "optimize" the database, but should analyze it from the business application level. For example, caching data, limiting requests, etc.
Related free learning recommendations: mysql video tutorial
The above is the detailed content of An article to help you understand the underlying principles of MYSQL. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1390
1390
 52
52
 How to open phpmyadmin
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:51 PM
How to open phpmyadmin
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:51 PM
You can open phpMyAdmin through the following steps: 1. Log in to the website control panel; 2. Find and click the phpMyAdmin icon; 3. Enter MySQL credentials; 4. Click "Login".
 MySQL: An Introduction to the World's Most Popular Database
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:18 AM
MySQL: An Introduction to the World's Most Popular Database
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:18 AM
MySQL is an open source relational database management system, mainly used to store and retrieve data quickly and reliably. Its working principle includes client requests, query resolution, execution of queries and return results. Examples of usage include creating tables, inserting and querying data, and advanced features such as JOIN operations. Common errors involve SQL syntax, data types, and permissions, and optimization suggestions include the use of indexes, optimized queries, and partitioning of tables.
 How to use single threaded redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:12 PM
How to use single threaded redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:12 PM
Redis uses a single threaded architecture to provide high performance, simplicity, and consistency. It utilizes I/O multiplexing, event loops, non-blocking I/O, and shared memory to improve concurrency, but with limitations of concurrency limitations, single point of failure, and unsuitable for write-intensive workloads.
 MySQL's Place: Databases and Programming
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:18 AM
MySQL's Place: Databases and Programming
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:18 AM
MySQL's position in databases and programming is very important. It is an open source relational database management system that is widely used in various application scenarios. 1) MySQL provides efficient data storage, organization and retrieval functions, supporting Web, mobile and enterprise-level systems. 2) It uses a client-server architecture, supports multiple storage engines and index optimization. 3) Basic usages include creating tables and inserting data, and advanced usages involve multi-table JOINs and complex queries. 4) Frequently asked questions such as SQL syntax errors and performance issues can be debugged through the EXPLAIN command and slow query log. 5) Performance optimization methods include rational use of indexes, optimized query and use of caches. Best practices include using transactions and PreparedStatemen
 Why Use MySQL? Benefits and Advantages
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:17 AM
Why Use MySQL? Benefits and Advantages
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:17 AM
MySQL is chosen for its performance, reliability, ease of use, and community support. 1.MySQL provides efficient data storage and retrieval functions, supporting multiple data types and advanced query operations. 2. Adopt client-server architecture and multiple storage engines to support transaction and query optimization. 3. Easy to use, supports a variety of operating systems and programming languages. 4. Have strong community support and provide rich resources and solutions.
 How to connect to the database of apache
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
How to connect to the database of apache
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
Apache connects to a database requires the following steps: Install the database driver. Configure the web.xml file to create a connection pool. Create a JDBC data source and specify the connection settings. Use the JDBC API to access the database from Java code, including getting connections, creating statements, binding parameters, executing queries or updates, and processing results.
 Monitor Redis Droplet with Redis Exporter Service
Apr 10, 2025 pm 01:36 PM
Monitor Redis Droplet with Redis Exporter Service
Apr 10, 2025 pm 01:36 PM
Effective monitoring of Redis databases is critical to maintaining optimal performance, identifying potential bottlenecks, and ensuring overall system reliability. Redis Exporter Service is a powerful utility designed to monitor Redis databases using Prometheus. This tutorial will guide you through the complete setup and configuration of Redis Exporter Service, ensuring you seamlessly build monitoring solutions. By studying this tutorial, you will achieve fully operational monitoring settings
 How to view sql database error
Apr 10, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
How to view sql database error
Apr 10, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
The methods for viewing SQL database errors are: 1. View error messages directly; 2. Use SHOW ERRORS and SHOW WARNINGS commands; 3. Access the error log; 4. Use error codes to find the cause of the error; 5. Check the database connection and query syntax; 6. Use debugging tools.




