What is the difference between tcp and udp
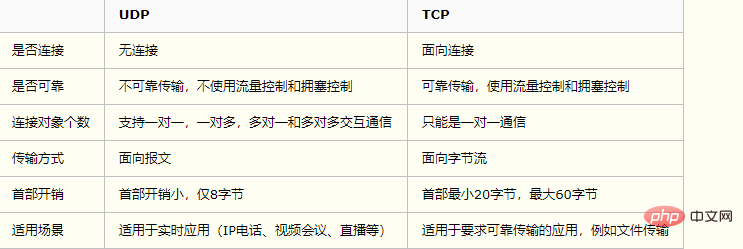
The differences between tcp and udp are: 1. udp is connectionless, tcp is connection-oriented; 2. udp is unreliable transmission, tcp is reliable transmission; 3. udp is message transmission-oriented, tcp It is oriented to byte stream transmission.

Comparison:
(Learning video recommendation: java video tutorial)
UDP
The full name of UDP protocol is User Datagram Protocol. It is used to process data packets like TCP protocol in the network. It is a connectionless protocol. In the OSI model, the fourth layer - the transport layer, is the upper layer of the IP protocol. UDP has the disadvantage of not providing data packet grouping, assembly, and inability to sort data packets. That is to say, after a message is sent, it is impossible to know whether it has arrived safely and completely.
It has the following characteristics:
1. Connectionless oriented
First of all, UDP does not need to perform a three-way handshake to establish a connection before sending data like TCP. Send data to start sending. And it is only a porter of data packets and will not perform any splitting or splicing operations on data packets.
Specifically:
At the sending end, the application layer passes the data to the UDP protocol of the transport layer. UDP will only add a UDP header to the data. Under the UDP protocol, then Passed to the network layer. At the receiving end, the network layer passes the data to the transport layer. UDP only removes the IP header and passes it to the application layer without any splicing operation.
2. There are unicast and multicast , broadcast function
UDP not only supports one-to-one transmission, but also supports one-to-many, many-to-many, and many-to-one. In other words, UDP provides unicast, multicast, and broadcast. Function.
3. UDP is message-oriented
The sender's UDP delivers the message to the application program. After adding the header, it is delivered down to the IP layer. UDP neither merges nor splits the packets handed over by the application layer, but retains the boundaries of these packets. Therefore, the application must choose a message of appropriate size
4. Unreliability
First of all, unreliability is reflected in the lack of connection. There is no need to establish a connection for communication. You can send whenever you want. Such a situation is certainly unreliable.
And any data received will be transferred, and the data will not be backed up. When sending data, it will not care whether the other party has received the data correctly.
Furthermore, the network environment is good and bad, but UDP will always send data at a constant speed because there is no congestion control. Even if the network conditions are not good, the sending rate will not be adjusted. The disadvantage of this implementation is that it may cause packet loss when the network conditions are not good, but the advantages are also obvious. In some scenarios with high real-time requirements (such as conference calls), UDP needs to be used instead of TCP.
5. The header overhead is small and it is very efficient when transmitting data messages.
TCP
When one computer wants to communicate with another computer, the communication between the two computers needs to be smooth and reliable so that data can be sent and received correctly. For example, when you want to view a web page or check your email, you want to see the web page completely and in order without losing any content. When you download a file, you hope to get the complete file, not just a part of the file, because if the data is lost or out of order, it is not the result you want, so TCP is used.
The full name of TCP protocol is Transmission Control Protocol. It is a connection-oriented, reliable, byte stream-based transport layer communication protocol, defined by RFC 793 of IETF. TCP is a connection-oriented, reliable streaming protocol. A stream refers to an uninterrupted data structure. You can think of it like water flowing in a drainpipe.
1. TCP connection process
First handshake
The client sends a connection request segment to the server. This message segment contains its own data communication initial sequence number. After the request is sent, the client enters the SYN-SENT state.
Second handshake
After the server receives the connection request segment, if it agrees to the connection, it will send a response, which will also include its own initial sequence number for data communication. After the transmission is completed, it enters the SYN-RECEIVED state.
Third handshake
When the client receives the connection approval response, it also sends a confirmation message to the server. After the client sends this message segment, it enters the ESTABLISHED state. After the server receives this response, it also enters the ESTABLISHED state. At this time, the connection is successfully established.
You may have a question here: Why does TCP require three handshakes to establish a connection, instead of two? This is because this is to prevent invalid connection request segments from being received by the server, resulting in errors.
2. TCP disconnection
TCP is full-duplex, and both ends need to send FIN and ACK when disconnecting.
First handshake
If client A thinks that the data transmission is completed, it needs to send a connection release request to server B.
Second handshake
B After receiving the connection release request, it will tell the application layer to release the TCP link. Then an ACK packet will be sent and the CLOSE_WAIT state will be entered. This indicates that the connection from A to B has been released and the data sent by A will no longer be received. But because the TCP connection is bidirectional, B can still send data to A.
The third handshake
If there is still unfinished data at this time, B will continue to send. After completion, it will send a connection release request to A, and then B will enter the LAST-ACK state.
The fourth handshake
After A receives the release request, it sends a confirmation response to B. At this time, A enters the TIME-WAIT state. This state will last for 2MSL (maximum segment lifetime, which refers to the time the message segment survives in the network, and will be discarded after timeout). If there is no resend request from B within this time period, it will enter the CLOSED state. When B receives the confirmation response, it also enters the CLOSED state.
3. Characteristics of TCP protocol
Connection-oriented
Connection-oriented means that a connection must be established at both ends before sending data. The method of establishing a connection is the "three-way handshake", which can establish a reliable connection. Establishing a connection lays the foundation for reliable transmission of data.
Only supports unicast transmission
Each TCP transmission connection can only have two endpoints, can only perform point-to-point data transmission, and does not support multicast and broadcast transmission methods.
Oriented to byte streams
TCP does not transmit messages independently like UDP, but transmits them in a byte stream without retaining message boundaries.
Reliable transmission
For reliable transmission, determining packet loss and error depends on the TCP segment number and confirmation number. In order to ensure the reliability of message transmission, TCP gives each packet a sequence number. At the same time, the sequence number also ensures that the packets transmitted to the receiving end entity are received in order. The receiving entity then sends back a corresponding acknowledgment (ACK) for the successfully received bytes; if the sending entity does not receive the acknowledgment within a reasonable round trip delay (RTT), then the corresponding data (assumed to be lost) will be retransmitted.
Provide congestion control
When the network is congested, TCP can reduce the rate and quantity of data injected into the network and alleviate congestion
TCP provides full-duplex communication
TCP allows applications on both sides of the communication to send data at any time, because both ends of the TCP connection have caches to temporarily store data for two-way communication. Of course, TCP can send a data segment immediately, or it can cache it for a period of time to send more data segments at once (the maximum data segment size depends on the MSS)
Related recommendations: php training
The above is the detailed content of What is the difference between tcp and udp. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to implement asynchronous communication using PHP and UDP protocols
Jul 30, 2023 pm 07:31 PM
How to implement asynchronous communication using PHP and UDP protocols
Jul 30, 2023 pm 07:31 PM
How to use PHP and UDP protocols to implement asynchronous communication In modern Internet applications, asynchronous communication has become a very important method. By using asynchronous communication, user requests can be processed concurrently without blocking the main thread, improving system performance and response speed. As a popular back-end programming language, PHP how to use UDP protocol to achieve asynchronous communication? This article will introduce how to use the UDP protocol in PHP to implement simple asynchronous communication, and attach specific code examples. 1. Introduction to UDP protocolU
 How to reset tcp/ip protocol in win10? How to reset the tcp/ip protocol stack in windows 10
Mar 16, 2024 am 11:07 AM
How to reset tcp/ip protocol in win10? How to reset the tcp/ip protocol stack in windows 10
Mar 16, 2024 am 11:07 AM
How to reset tcp/ip protocol in win10? In fact, the method is very simple. Users can directly enter the command prompt, and then press the ctrl shift enter key combination to perform the operation, or directly execute the reset command to set it up. Let this site do the following. Let us carefully introduce to users how to reset the TCP/IP protocol stack in Windows 10. Method 1 to reset the tcp/ip protocol stack in Windows 10. Administrator permissions 1. We use the shortcut key win R to directly open the run window, then enter cmd and hold down the ctrl shift enter key combination. 2. Or we can directly search for command prompt in the start menu and right-click
 What are the UDP port numbers?
Feb 23, 2023 pm 02:00 PM
What are the UDP port numbers?
Feb 23, 2023 pm 02:00 PM
Common UDP port numbers are 53, 69, 161, 2049, 68, and 520. UDP uses port numbers to reserve their own data transmission channels for different applications: 1. Network File System (NFS), the port number is 2049; 2. Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP), the port number is 161; 3. Domain Name System (DNS) , the port number is 53; 4. Simple File Transfer System (TFTP), the port number is 69; 5. Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP), the port number is 68; 6. Routing Information Protocol, the port number is 520, etc.
 How to use TCP to implement conversation between client and server in python
May 17, 2023 pm 03:40 PM
How to use TCP to implement conversation between client and server in python
May 17, 2023 pm 03:40 PM
TCP client A client sample code that uses the TCP protocol to achieve continuous dialogue: importsocket#Client configuration HOST='localhost'PORT=12345#Create a TCP socket and connect to the server client_socket=socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket .SOCK_STREAM)client_socket.connect((HOST,PORT))whileTrue:#Get user input message=input("Please enter the message to be sent:&
 See you soon! TCP waves twice, have you seen it? What about the four handshakes?
Jul 24, 2023 pm 05:18 PM
See you soon! TCP waves twice, have you seen it? What about the four handshakes?
Jul 24, 2023 pm 05:18 PM
The "connection-oriented" mentioned here means that you need to establish a connection, use the connection, and release the connection. Establishing a connection refers to the well-known TCP three-way handshake. When using a connection, data is transmitted in the form of one send and one confirmation. There is also the release of the connection, which is our common TCP four wave waves.
 Using Netty4 for TCP communication in Java API development
Jun 17, 2023 pm 11:18 PM
Using Netty4 for TCP communication in Java API development
Jun 17, 2023 pm 11:18 PM
TCP is a type of computer network communication protocol and a connection-oriented transmission protocol. In Java application development, TCP communication is widely used in various scenarios, such as data transmission between client and server, real-time transmission of audio and video, etc. Netty4 is a high-performance, highly scalable, and high-performance network programming framework that can optimize the data exchange process between the server and the client to make it more efficient and reliable. The specific implementation steps of using Netty4 for TCP communication are as follows: Introduction
 How does Java network programming use UDP for connectionless communication?
Apr 15, 2024 pm 12:51 PM
How does Java network programming use UDP for connectionless communication?
Apr 15, 2024 pm 12:51 PM
UDP (User Datagram Protocol) is a lightweight connectionless network protocol commonly used in time-sensitive applications. It allows applications to send and receive data without establishing a TCP connection. Sample Java code can be used to create a UDP server and client, with the server listening for incoming datagrams and responding, and the client sending messages and receiving responses. This code can be used to build real-world use cases such as chat applications or data collection systems.
 How to send multiple files using a single TCP connection in Java?
Apr 27, 2023 am 08:49 AM
How to send multiple files using a single TCP connection in Java?
Apr 27, 2023 am 08:49 AM
Why is there this blog about using one TCP connection to send multiple files? I have been reading some related things recently. There is no problem in simply using Socket for programming, but this only establishes some basic concepts. Still nothing can be done about the real problem. When I need to transfer files, I find that I seem to have just sent the data (binary data), but some information about the file is lost (the file extension). And each time I can only use one Socket to send one file, there is no way to send files continuously (because I rely on closing the stream to complete sending files, which means that I actually don’t know the length of the file, so I can only send files as one Socket connection represents a file).





