In-depth analysis of css z-index (with examples)

Students who have done page layout should be very familiar with the z-index attribute. Z-index is a special attribute for web page display. Because the pattern displayed by the monitor is a two-dimensional plane, it has an x-axis and a y-axis to represent the position attribute. In order to represent the three-dimensional concept such as the superposition order of the upper and lower layers of display elements, the z-index attribute is introduced to represent the difference in the z-axis. Indicates the upper and lower three-dimensional relationship of an element in the superposition order.
Elements with a larger z-index value will be superimposed on elements with a smaller z-index value. For positioned objects that do not specify this property, objects with positive z-index values are above them and objects with negative z-index values are below them. (Recommended tutorial: CSS video tutorial)
Simple demonstration
<div style="width:200px;height:200px;background-color:#0e0;"></div>
<div style="position:relative; top:-50px; width:100px;height:100px;background-color:#00e;"><div>Two p, the second one moves up 50px, the normal situation should be Like this
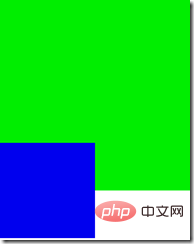
The second p covers the first p, and adding the z-index attribute to the second one
<div style="width:200px;height:200px;background-color:#0e0;"></div>
<div style="position:relative; top:-50px; width:100px;height:100px;background-color:#00e;z-index:-5;"><div>The result will become Like this, the simplest application of z-index is like this

Only valid for positioned elements
The z-index attribute is applicable to Positioned elements (objects whose position attribute value is relative or absolute or fixed) are used to determine the stacking order of positioned elements in the direction perpendicular to the display screen (called the Z axis). That is to say, if the element is not positioned, it The set z-index will be invalid.
<div style="width:200px;height:200px;background-color:#0e0;z-index:30"></div> <div style="position:relative; top:-50px; width:100px;height:100px;background-color:#00e;z-index:10;"><div>
Although the z-index of the first p is larger than that of the second p, because the first p is not positioned and its z-index attribute does not work, it will still be covered by the second p. .
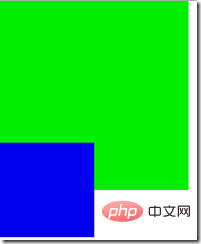
Who goes up and who goes down for the same z-index
There are actually two situations for the same z-index
1. If neither element is positioned and the position overlaps, or both elements are positioned and the z-index is the same, the position of the element overlaps, then according to the document flow order, the later one will overwrite the previous one.
<div style="position:relative;width:200px;height:200px;background-color:#0e0;"></div> <div style="position:relative; top:-50px; width:100px;height:100px;background-color:#00e;"><div>

#2. If neither element has z-index set, the default value is used, one is positioned and the other is not positioned, then the positioned element covers the unpositioned element
<div style="position:relative;top:50px;width:200px;height:200px;background-color:#0e0;"></div> <div style=" width:100px;height:100px;background-color:#00e;"><div>

Father-child relationship processing
If the z-index of the parent element is valid, then the child element will be consistent with the parent element regardless of whether the z-index is set. Will be above the parent element
<div style="position:relative;width:200px;height:200px;background-color:#0e0;z-index:10;">
<div style="position:relative;width:100px;height:100px;background-color:#00e;z-index:-5;"><div>
</div>Although the child element sets the z-index smaller than the parent element, the child element still appears above the parent element
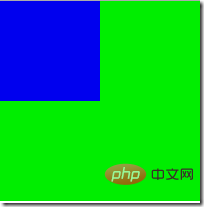
If the parent The z-index of the element is invalid (not positioned or using the default value), then the z-index setting of the positioned child element takes effect
<div style="position:relative;width:200px;height:200px;background-color:#0e0;">
<div style="position:relative;width:100px;height:100px;background-color:#00e;z-index:-5;"><div>
</div>The z-index=-5 of the child element takes effect and is overwritten by the parent element

Child elements between brothers
If the z-index of the sibling element is effective, then the coverage relationship of its child elements is determined by the parent element
<div style="position:relative;width:100px;height:100px;background-color:#0e0;z-index:5;">
<div style="position:relative;width:50px;height:250px;background-color:#00e;z-index:50;"></div>
</div>
<div style="position:relative;width:100px;height:100px;background-color:#0e0;z-index:10;margin-top:4px;">
<div style="position:relative;width:30px;height:150px;background-color:#e0e;z-index:-10;"></div>
</div>Although the z-index of the child element of the first p is relatively high, because its parent element has a lower z-index than the second p, the child element of the first p will be replaced by the second p and its child elements. Overwriting

Application
There is often such a mistake. In the last row of the table, put a td and a p, and click to pop up the subtitles. The menu does some operations such as deletion and modification, but every time the pop-up menu is covered by p in the following lines, like the picture below, the pop-up menu is not at the top of the page.
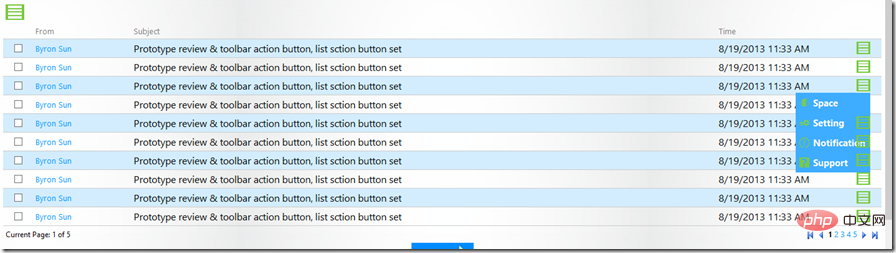
写个简单的例子看看
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Test</title>
<style type="text/css" >
html,body
{
height:100%;
width:100%;
padding:0;
margin:0;
}
.menu
{
background-color:#0e0;
position:relative;
z-index:10;
}
.options
{
display:none;
position:absolute;
top:
z-index:30;
}
.options div
{
background-color:#00e;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<table border="1" cellpadding="4px" cellspacing="0">
<tr>
<th>Name</th>
<th>Age</th>
<th>Options</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Byron</td>
<td>24</td>
<td>
<div class="menu" >
<div>Options</div>
<div class="options" style="display:block;position:absolute;top:20px;">
<div>Opion1</div>
<div>Opion2</div>
<div>Opion3</div>
<div>Opion4</div>
</div>
</div>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Byron</td>
<td>24</td>
<td>
<div class="menu">
<div>Options</div>
<div class="options" >
<div>Opion1</div>
<div>Opion2</div>
<div>Opion3</div>
<div>Opion4</div>
</div>
</div>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Byron</td>
<td>24</td>
<td>
<div class="menu">
<div>Options</div>
<div class="options" >
<div>Opion1</div>
<div>Opion2</div>
<div>Opion3</div>
<div>Opion4</div>
</div>
</div>
</td>
</tr>
</table>
</body>
<html>| 期望样式 | 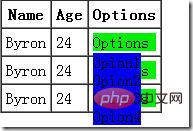 |
实际样式 | 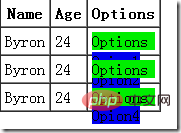 |
这时候习惯于增大options 的z-index却发现于事无补,为什么呢?因为每个menu的z-index相同,它们的层叠顺序按文档流顺序,无论子元素z-index调到多大,上面menu的options还是会被下面menu遮盖。这时候我的做法一般是把options放到外面,所有的menu用一个,使menu与options没有父子关系,或者干脆在点击menu的时候把它的z-index调大,这样其子元素就不会被遮盖住了。
最后
本文的例子都是以符合W3C的Chrome浏览器做验证,但在IE6,7 z-index的默认值并不是auto而是0,这样会导致很多奇怪现象,这时候就需要考虑这点了。
更多编程相关知识,请访问:编程入门!!
The above is the detailed content of In-depth analysis of css z-index (with examples). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1392
1392
 52
52
 36
36
 110
110
 How to use bootstrap in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:33 PM
How to use bootstrap in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:33 PM
Using Bootstrap in Vue.js is divided into five steps: Install Bootstrap. Import Bootstrap in main.js. Use the Bootstrap component directly in the template. Optional: Custom style. Optional: Use plug-ins.
 The Roles of HTML, CSS, and JavaScript: Core Responsibilities
Apr 08, 2025 pm 07:05 PM
The Roles of HTML, CSS, and JavaScript: Core Responsibilities
Apr 08, 2025 pm 07:05 PM
HTML defines the web structure, CSS is responsible for style and layout, and JavaScript gives dynamic interaction. The three perform their duties in web development and jointly build a colorful website.
 How to write split lines on bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:12 PM
How to write split lines on bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:12 PM
There are two ways to create a Bootstrap split line: using the tag, which creates a horizontal split line. Use the CSS border property to create custom style split lines.
 Understanding HTML, CSS, and JavaScript: A Beginner's Guide
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:02 AM
Understanding HTML, CSS, and JavaScript: A Beginner's Guide
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:02 AM
WebdevelopmentreliesonHTML,CSS,andJavaScript:1)HTMLstructurescontent,2)CSSstylesit,and3)JavaScriptaddsinteractivity,formingthebasisofmodernwebexperiences.
 How to use bootstrap button
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:09 PM
How to use bootstrap button
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:09 PM
How to use the Bootstrap button? Introduce Bootstrap CSS to create button elements and add Bootstrap button class to add button text
 How to resize bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:18 PM
How to resize bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:18 PM
To adjust the size of elements in Bootstrap, you can use the dimension class, which includes: adjusting width: .col-, .w-, .mw-adjust height: .h-, .min-h-, .max-h-
 How to set up the framework for bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:27 PM
How to set up the framework for bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:27 PM
To set up the Bootstrap framework, you need to follow these steps: 1. Reference the Bootstrap file via CDN; 2. Download and host the file on your own server; 3. Include the Bootstrap file in HTML; 4. Compile Sass/Less as needed; 5. Import a custom file (optional). Once setup is complete, you can use Bootstrap's grid systems, components, and styles to create responsive websites and applications.
 How to insert pictures on bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:30 PM
How to insert pictures on bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:30 PM
There are several ways to insert images in Bootstrap: insert images directly, using the HTML img tag. With the Bootstrap image component, you can provide responsive images and more styles. Set the image size, use the img-fluid class to make the image adaptable. Set the border, using the img-bordered class. Set the rounded corners and use the img-rounded class. Set the shadow, use the shadow class. Resize and position the image, using CSS style. Using the background image, use the background-image CSS property.




