Detailed explanation of CSS line-height property

(Recommended tutorial: CSS video tutorial)
When I first entered the front-end, I felt that CSS can be used in layout if it only knows display, position, and float. I feel comfortable now. As work problems arise one after another in the future, I gradually understand that CSS is not as simple as a few style attributes. I have recently read some knowledge about row height, so I will summarize it here.
The so-called line height refers to the vertical distance between the baselines of text lines. To understand this sentence, you must first understand a few basic knowledge:
Top line, middle line, baseline, bottom line
nbsp;html>
<title>Test</title>
<style>
span
{
padding:0px;
line-height:1.5;
}
</style>
<div>
<div>
<span>中文English</span>
<span>English中文</span>
</div>
</div>

Four lines from top to bottom They are the top line, the middle line, the baseline, and the bottom line. They are very similar to the four lines and three grids when learning English letters. We know that the vertical-align attribute has top, middle, baseline, and bottom, which are related to these four lines.
Remember especially that the baseline is not the bottom line, the bottom line is the bottom line.
Line height, line spacing and half-line spacing
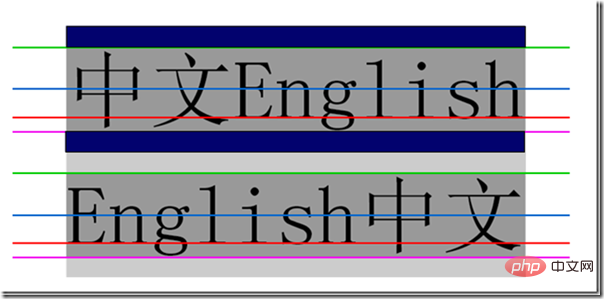
Line height refers to the vertical distance between the baselines of the context line, that is, the vertical distance between the two red lines in the picture.
Line spacing refers to the vertical distance from the bottom line of one row to the top line of the next row, that is, the vertical distance between the pink line of the first row and the green line of the second row.
Half line spacing is half of the line spacing, that is, the vertical distance of area 3/2, the sum of the distances of areas 1, 2, 3, and 4 is the line height, and the sum of the distances of areas 1, 2, and 4 is the font size , so half line spacing can also be calculated like this: (line height-font size)/2
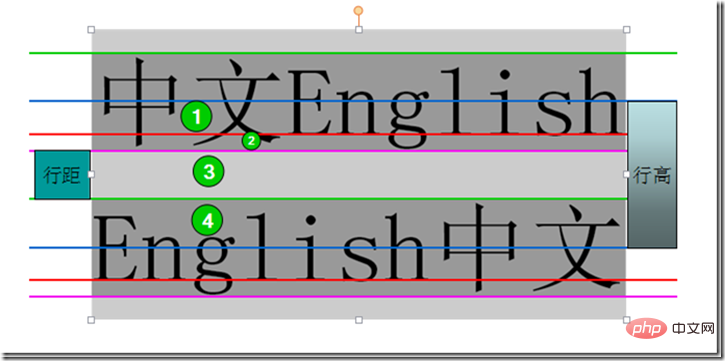
content area, inline box, line box
Content area: The area wrapped by the bottom line and the top line, that is, the dark gray background area in the picture below.
Inline box, each inline element will generate an inline box. The inline box is a concept in the browser rendering model and cannot be displayed. , when there are no other factors (padding, etc.), the inline box is equal to the content area, and when the line height is set, the height of the inline box remains unchanged, and the half line spacing [(line height-font size)/2] increases/decreases to the content respectively. The upper and lower sides of the area (dark blue area)
Line box (line box), The line box refers to a virtual rectangular box of this line, which is a concept in the browser rendering mode , and is not actually displayed. The height of the line box is equal to the largest value of the inline box among all elements in this row (the inline box with the largest row height value is used as the benchmark, and other inline boxes are aligned to the benchmark using their own alignment methods, and the height of the line box is finally calculated). When there are multiple lines content, each line will have its own line box.
<div> <span>中文English</span> <span>中文English</span> <span>English中文</span> <span>English中文</span> </div>

line-height
Once the basic concepts are understood, we can talk about the line-height attribute, the protagonist of this article.
Definition: The line-height attribute sets the distance between lines (line height), and negative values cannot be used. This property affects the layout of the line box. When applied to a block-level element, it defines the minimum distance between baselines in that element rather than the maximum distance. The difference between the calculated values of line-height and font-size (line spacing) is divided into two halves and added to the top and bottom of a line of text content respectively. The smallest box that can contain this content is a line box.
Possible values
| Value | Description |
| normal | Default, set reasonable line spacing. |
| number | Set a number, which will be multiplied by the current font size to set the line spacing. Equivalent to a multiple of |
| length | to set a fixed line spacing. |
| % | Percent line spacing based on the current font size. |
| inherit | Specifies that the value of the line-height attribute should be inherited from the parent element. |
貌似很简单,但感觉没什么用出的样子,那就让我们看看line-height的几个应用
div文字垂直居中
div居中对齐一直是个难题,水平还好解决些,margin:0 auto; 可以解决现代浏览器,IE下text-align:center。但垂直居中就没那么简单了,默认是这样子的。
<div> <span>This is a test.<br> This is a test. </span> </div>

我们可以利用line-block这样做
<div> <span>This is a test.<br> This is a test. </span> </div>

单行就比较简单了,把line-height设置为box的大小可以实现单行文字的垂直居中
<div> This is a test. </div>

元素对行高影响
行框高度是行内最高的行内框高度,通过line-height调整,内容区行高与字体尺寸有关,padding不对行高造成影响。
<div> <span>This is a test</span> </div> <div> <span>This is a test</span> </div>

第二个span虽然因为padding原因内容区变大,当行高并未改变
行高的继承
行高是可继承的,但并不是简单的copy父元素行高,继承的是计算得来的值。
<div> <p> 1232<br> 123 </p> </div>
按一般理解既然line-height可以继承,那么p元素的行高也是150%了,可是事实是这样的

非但没有变成150%,反而连100%都没有,重叠了!这就是继承计算的结果,如果父元素的line-height有单位(px、%),那么继承的值则是换算后的一个具体的px级别的值;上例p得到的是10px*150%=15px的行高,而P的字体大小为30px,所以发生了重叠。
而如果属性值没有单位,则浏览器会直接继承这个“因子(数值)”,而非计算后的具体值,此时它的line-height会根据本身的font-size值重新计算得到新的line-height 值。
<div> <p> 1232<br> 123 </p> </div>

所以在使用line-height时,除非你刻意否则尽量使用倍数设值
更多编程相关知识,请访问:编程教学!!
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of CSS line-height property. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 How to use bootstrap in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:33 PM
How to use bootstrap in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:33 PM
Using Bootstrap in Vue.js is divided into five steps: Install Bootstrap. Import Bootstrap in main.js. Use the Bootstrap component directly in the template. Optional: Custom style. Optional: Use plug-ins.
 The Roles of HTML, CSS, and JavaScript: Core Responsibilities
Apr 08, 2025 pm 07:05 PM
The Roles of HTML, CSS, and JavaScript: Core Responsibilities
Apr 08, 2025 pm 07:05 PM
HTML defines the web structure, CSS is responsible for style and layout, and JavaScript gives dynamic interaction. The three perform their duties in web development and jointly build a colorful website.
 How to write split lines on bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:12 PM
How to write split lines on bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:12 PM
There are two ways to create a Bootstrap split line: using the tag, which creates a horizontal split line. Use the CSS border property to create custom style split lines.
 Understanding HTML, CSS, and JavaScript: A Beginner's Guide
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:02 AM
Understanding HTML, CSS, and JavaScript: A Beginner's Guide
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:02 AM
WebdevelopmentreliesonHTML,CSS,andJavaScript:1)HTMLstructurescontent,2)CSSstylesit,and3)JavaScriptaddsinteractivity,formingthebasisofmodernwebexperiences.
 How to set up the framework for bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:27 PM
How to set up the framework for bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:27 PM
To set up the Bootstrap framework, you need to follow these steps: 1. Reference the Bootstrap file via CDN; 2. Download and host the file on your own server; 3. Include the Bootstrap file in HTML; 4. Compile Sass/Less as needed; 5. Import a custom file (optional). Once setup is complete, you can use Bootstrap's grid systems, components, and styles to create responsive websites and applications.
 How to resize bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:18 PM
How to resize bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:18 PM
To adjust the size of elements in Bootstrap, you can use the dimension class, which includes: adjusting width: .col-, .w-, .mw-adjust height: .h-, .min-h-, .max-h-
 How to use bootstrap button
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:09 PM
How to use bootstrap button
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:09 PM
How to use the Bootstrap button? Introduce Bootstrap CSS to create button elements and add Bootstrap button class to add button text
 How to insert pictures on bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:30 PM
How to insert pictures on bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:30 PM
There are several ways to insert images in Bootstrap: insert images directly, using the HTML img tag. With the Bootstrap image component, you can provide responsive images and more styles. Set the image size, use the img-fluid class to make the image adaptable. Set the border, using the img-bordered class. Set the rounded corners and use the img-rounded class. Set the shadow, use the shadow class. Resize and position the image, using CSS style. Using the background image, use the background-image CSS property.




