

WebStorage is one of the local storage solutions in HTML5. Before the introduction of the WebStorage concept of HTML5, IE User Data, Flash Cookies, Google Gears, etc. were removed and the names were unreliable solutions. scheme, the browser-compatible local storage scheme only uses cookies. Some students may ask, since we have cookie local storage, why do we need to introduce the concept of WebStorage?
The flaws of cookie are very obvious
1. Data size: As a storage container, the size of cookie is limited to about 4KB, which is very cheating. , especially for today’s complex business logic requirements, the 4KB capacity not only stores some configuration fields but also simple single-value information. For most developers, they really don’t know what to expect.
2. Security issues: Since the cookie in the HTTP request is passed in clear text (HTTPS is not), the security issues are still huge.
3. Network burden: We know that cookies will be attached to each HTTP request and will be transmitted in the headers of HttpRequest and HttpResponse, so some unnecessary traffic losses will be added.
WebStorage is one of the new local storage solutions for HTML, but it is not a standard developed to replace cookies. Cookies are used as part of the HTTP protocol to handle clients and servers. Communication is indispensable, and session relies on the implementation of client state retention. The purpose of WebStorage is to solve the problem of local storage that should not be done with cookies, but has to use cookies.
WebStorage provides two types of APIs: localStorage and sessionStorage. The difference between the two can be roughly understood by looking at the names. LocalStorage stores data locally permanently unless it is explicitly deleted or cleared. The data stored in sessionStorage It is only valid during the session and is automatically deleted when the browser is closed. Both objects have a common API
interface Storage {
readonly attribute unsigned long length;
DOMString? key(unsigned long index);
getter DOMString getItem(DOMString key);
setter creator void setItem(DOMString key, DOMString value);
deleter void removeItem(DOMString key); void clear();
};In a browser that implements WebStorage, the page has Two global objects localStorage and sessionStorage

Taking localStorage as an example, look at a simple operation code
var ls=localStorage;
console.log(ls.length);//0
ls.setItem('name','Byron');
ls.setItem('age','24');
console.log(ls.length);//2
//遍历localStorage
for(var i=0;i<ls.length><h3>Event</h3>
<p>At the same time HTML5 A storage event is specified, which is triggered when WebStorage changes. You can use this to monitor storage modifications on different pages. </p>
<pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">interface StorageEvent : Event {
readonly attribute DOMString key;
readonly attribute DOMString? oldValue;
readonly attribute DOMString? newValue;
readonly attribute DOMString url;
readonly attribute Storage? storageArea;
};Definition in index.php
<a>Test</a>
window.addEventListener('storage',function(e){
console.log(e.key+' is changed form '+e.oldValue+' to '+e.newValue+' by '+e.url );
console.log(e.storageArea ==localStorage);
},false);
localStorage.setItem('userName','Byron');test.php
localStorage.setItem('userName','Casper');You can see the index when you click the link on the index.php page to access test.php .php console output log:
userName is changed form Byron to Casper by http://localhost/test.php
true
1. In terms of capacity, WebStorage generally provides 5M of storage space in browsers, which is not enough to store videos and pictures, but it is enough for most operations.
2. In terms of security WebStorage is not sent as an HTTP header by the browser, so it is relatively safe
3. In terms of traffic, because WebStorage is not transmitted to the server, unnecessary traffic can be saved, so that for high-frequency visits or targeted The web pages for mobile devices are still very good.
This does not mean that WebStorage can replace cookies, but that with WebStorage, cookies can only do what they should do - serve as a channel for client-server interaction and maintain client state. So WebStorage is superior to cookies just as a local storage solution.
1. Browser compatibility, this is almost the easiest to implement among all new HTML5 features, because it is supported by IE8 browsers and can be used in IE7 and IE6 IE User Data implementation.

2. Since localStorage and sessionStorage are both objects, we can also obtain and modify key-value pairs through ".key" or "[key]". , but this is not recommended
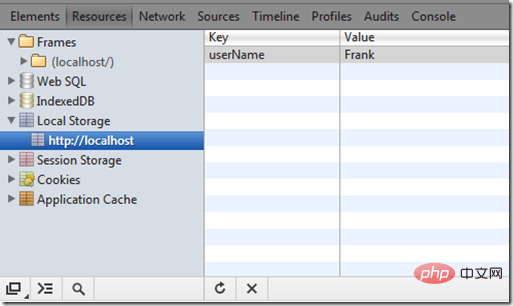
localStorage.userName='Frank'; console.log(localStorage['userName']);
3. Although localStorage is stored locally, different browsers store data independently, so localStorage stored on Chrome cannot be obtained on FireFox.
4. localStorage and sessionStorage can only store string types. For complex objects, you can use the stringify and parse of the JSON object provided by ECMAScript to handle them. For lower versions of IE, you can use json2.js
5. In addition to the console, Chrome also provides a very intuitive display method for local storage, which is very convenient when debugging.
For more programming-related knowledge, please visit : Programming learning website! !
The above is the detailed content of Introduction to WebStorage for HTML5 local storage. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 What are the production methods of html5 animation production?
What are the production methods of html5 animation production?
 The difference between HTML and HTML5
The difference between HTML and HTML5
 How to turn off automatic updates in win10
How to turn off automatic updates in win10
 php development tools
php development tools
 How to close the window opened by window.open
How to close the window opened by window.open
 What does mobile phone hd mean?
What does mobile phone hd mean?
 Apple pay cannot add card
Apple pay cannot add card
 Top ten digital currency exchanges
Top ten digital currency exchanges