What are the ways to enter the docker container?

There are many ways to enter a Docker container. Here we focus on several commonly used methods of entering a Docker container.
(Learning video sharing: php video tutorial)
Some of the more common ways to enter a Docker container are as follows:
Use docker attach
Use SSH
Use nsenter
Use exec
1. Use docker attach to enter the Docker container
Docker provides the attach command to enter the Docker container.
Next we create a daemon Docker container, and then use the docker attach command to enter the container.
$ sudo docker run -itd ubuntu:14.04 /bin/bash
Then we use docker ps to view the container information, and then use docker attach to enter the container
$ sudo docker attach 44fc0f0582d9
We can see that we have entered the container.
But there is a problem with using this command. When multiple windows use this command to enter the container at the same time, all windows will be displayed simultaneously. If one window is blocked, other windows will no longer be able to operate.
For this reason, the docker attach command is not suitable for production environments. You can use this command when developing your own applications.
2. Use SSH to enter the Docker container
After excluding using the docker attach command to enter the container in the production environment, I believe the first thing that everyone thinks of is ssh. Install SSH Server in the image (or container), so that multiple people can enter the container without interfering with each other. I believe everyone does this in the current production environment (without using Docker). However, it is not recommended to use ssh to enter the Docker container after using it.
3. Use nsenter to enter the Docker container
If the above two methods are not suitable, there is a more convenient method, which is to use nsenter to enter the Docker container.
After understanding what nsenter is, the system will install the nsenter we need into the host by default.
If it is not installed, just follow the steps below to install it (note that it is the host and not the container or Mirror)
The specific installation command is as follows:
$ wget https://www.kernel.org/pub/linux/utils/util-linux/v2.24/util-linux-2.24.tar.gz $ tar -xzvf util-linux-2.24.tar.gz $ cd util-linux-2.24/ $ ./configure --without-ncurses $ make nsenter $ sudo cp nsenter /usr/local/bin
After installing nsenter, you can check the use of this command.
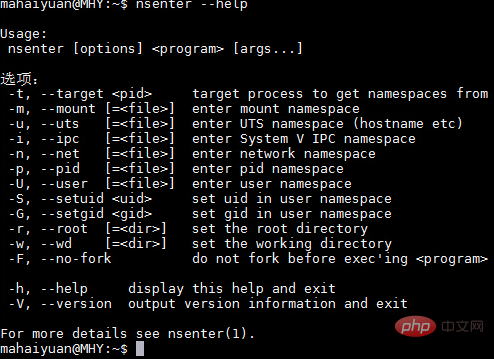
#nsenter can access the namespace of another process. So in order to connect to a container we also need to get the PID of the first process of the container. You can use the docker inspect command to get the PID.
The docker inspect command is used as follows:
$ sudo docker inspect --help
The inspect command can display information about an image or container hierarchically. For example, we currently have a running container.
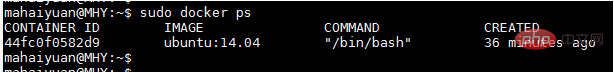
You can use docker inspect to view the details of the container.
$ sudo docker inspect 44fc0f0582d9
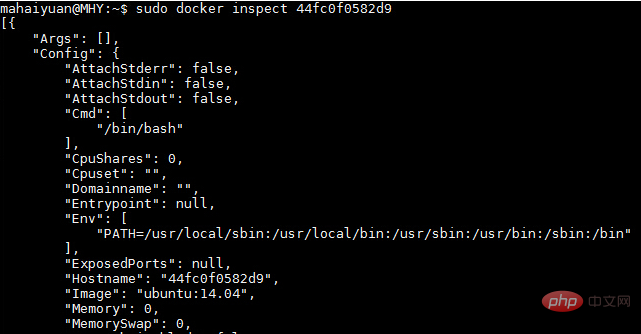
Since there is a lot of information, only part of it is captured here for display. If you want to display the first PID of the container, you can use the following method
$ sudo docker inspect -f {{.State.Pid}} 44fc0f0582d9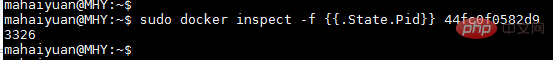
After getting the PID of the process, we can use the nsenter command to access the container.
$ sudo nsenter --target 3326 --mount --uts --ipc --net --pid $ sudo nsenter --target 3326 --mount --uts --ipc --net --pid
The 3326 is the PID of the process just obtained.
4. Use docker exec to enter the Docker container
In addition to the above methods, docker also provides a new command exec after version 1.3.X for entering the container. This The method is relatively simpler. Let’s take a look at the use of this command:
$ sudo docker exec --help
Next we use this command to enter an already running container
$ sudo docker ps $ sudo docker exec -it 775c7c9ee1e1 /bin/bash
Related recommendations: docker tutorial
The above is the detailed content of What are the ways to enter the docker container?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 How to update the image of docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:03 PM
How to update the image of docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:03 PM
The steps to update a Docker image are as follows: Pull the latest image tag New image Delete the old image for a specific tag (optional) Restart the container (if needed)
 How to create a mirror in docker
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:27 AM
How to create a mirror in docker
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:27 AM
Steps to create a Docker image: Write a Dockerfile that contains the build instructions. Build the image in the terminal, using the docker build command. Tag the image and assign names and tags using the docker tag command.
 How to use docker desktop
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:45 AM
How to use docker desktop
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:45 AM
How to use Docker Desktop? Docker Desktop is a tool for running Docker containers on local machines. The steps to use include: 1. Install Docker Desktop; 2. Start Docker Desktop; 3. Create Docker image (using Dockerfile); 4. Build Docker image (using docker build); 5. Run Docker container (using docker run).
 How to save docker image
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:54 AM
How to save docker image
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:54 AM
To save the image in Docker, you can use the docker commit command to create a new image, containing the current state of the specified container, syntax: docker commit [Options] Container ID Image name. To save the image to the repository, you can use the docker push command, syntax: docker push image name [: tag]. To import saved images, you can use the docker pull command, syntax: docker pull image name [: tag].
 What to do if the docker image fails
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:21 AM
What to do if the docker image fails
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:21 AM
Troubleshooting steps for failed Docker image build: Check Dockerfile syntax and dependency version. Check if the build context contains the required source code and dependencies. View the build log for error details. Use the --target option to build a hierarchical phase to identify failure points. Make sure to use the latest version of Docker engine. Build the image with --t [image-name]:debug mode to debug the problem. Check disk space and make sure it is sufficient. Disable SELinux to prevent interference with the build process. Ask community platforms for help, provide Dockerfiles and build log descriptions for more specific suggestions.
 How to copy files in docker to outside
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:12 PM
How to copy files in docker to outside
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:12 PM
Methods for copying files to external hosts in Docker: Use the docker cp command: Execute docker cp [Options] <Container Path> <Host Path>. Using data volumes: Create a directory on the host, and use the -v parameter to mount the directory into the container when creating the container to achieve bidirectional file synchronization.
 How to exit the container by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:15 PM
How to exit the container by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:15 PM
Four ways to exit Docker container: Use Ctrl D in the container terminal Enter exit command in the container terminal Use docker stop <container_name> Command Use docker kill <container_name> command in the host terminal (force exit)
 How to check the name of the docker container
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
How to check the name of the docker container
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
You can query the Docker container name by following the steps: List all containers (docker ps). Filter the container list (using the grep command). Gets the container name (located in the "NAMES" column).




