A brief analysis of Buffer in NodeJS

Related recommendations: "node js tutorial"
I read Pu Ling's Nine Lights and One Deep NodeJS to get started with Node. , Park Dada’s book talks very little about practice and devotes more space to explaining principles. After listening to so many principles, he later started to use NodeJS in the field of front-end engineering but was hampered everywhere. Summarizing the reasons, he found that the difficult part in NodeJS is nothing more than files and files. Networking, file operations and networking all rely on a very important object - Stream, which is exactly what Park did not mention in his book.
Buffer Park Dada mentioned it in the book, but because the stream is actually processing the Buffer, it still needs to be briefly summarized.
What is Buffer
As introduced in the official API, before ES6 introduced TypedArray, JavaScript had no mechanism to read or operate binary data streams. The Buffer class was introduced as part of the NodeJS API to be able to interact with network streams such as TCP and file streams.
Now that TypedArray has been added to ES6, the Buffer class implements the Unit8Array API in a way that is more optimized and suitable for NodeJS operations.
In short, the Buffer class is used to process binary data. Because it is so commonly used, it is placed directly in a global variable, and there is no need to require when using it.
Instances of the Buffer class are similar to integer arrays, but the size of the buffer is determined when it is created and cannot be adjusted. The difference with the Buffer object is that it does not go through V8's memory allocation mechanism. Buffer is a module that combines JavaScript and C. The memory is applied for by C and allocated by JavaScript.
We will not discuss the related knowledge of Buffer memory allocation. Interested students can read Park Laoshi's book.
Instancing Buffer
Before NodeJS v6, Buffer was instantiated by calling the constructor, returning different results according to the parameters. For security reasons, this method has been abolished in versions after v6, and
- Buffer.from()
- Buffer.alloc() ## is provided #Buffer.allocUnsafe()
- Buffer.from(array): Returns a Buffer containing a copy of the provided byte. Each item in the array is a number representing an octet, so the value must be between 0 ~ between 255, otherwise it will be modulo
- Buffer.from(arrayBuffer): Returns a new Buffer that shares memory with the given ArrayBuffer
- Buffer.from(buffer): Returns the given Buffer A copy of Buffer
- Buffer.from(string [, encoding]): Returns a Buffer containing the given string
- Buffer.alloc(size [, fill [, encoding]]) : Returns a Buffer of the specified size and "filled"
- Buffer.allocUnsafe(size): Returns a Buffer of the specified size, the content must be filled with methods such as buf.fill(0)
// 0x 表示 16 进制
Buffer.from([1, 2, 3]) // [0x1, 0x2, 0x3]
Buffer.from('test', 'utf-8') // [0x74, 0x65, 0x73, 0x74]
Buffer.alloc(5, 1) // [0x1, 0x1, 0x1, 0x1, 0x1]
Buffer.allocUnsafe(5); // 值不确定,后面详谈Buffer.allocUnsafe() will execute faster than Buffer.alloc() It is unsafe to look at the name, and it is indeed unsafe.
Buffer.allocUnsafe() is called, the allocated memory segment has not been initialized (not returned to zero), so the memory allocation speed is very slow, but the allocated memory segment may contain old data. If you do not overwrite these old data when using it, it may cause memory leaks. Although it is fast, try to avoid using it.
Encoding
Buffer supports the following encoding formats- ascii
- utf8
- utf16le
- base64
- binary
- hex
Buffer and String conversion
String to Buffer is relatively simpleBuffer.from(string [, encoding])
buf.toString([encoding[, start[, end]]])
Buffer splicing
Use the concat method to speak multiple Buffer instances are spliced into one Buffer instanceBuffer.concat(list[, totalLength])
StringDecoder
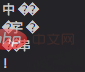
In NodeJS, a Chinese character is represented by three bytes. If we use something other than 3 when processing Chinese characters Multiples of the number of bytes will cause garbled character splicing problems.const buf = Buffer.from('中文字符串!');
for(let i = 0; i < buf.length; i+=5){
var b = Buffer.allocUnsafe(5);
buf.copy(b, 0, i);
console.log(b.toString());
}
const StringDecoder = require('string_decoder').StringDecoder;
const decoder = new StringDecoder('utf8');
const buf = Buffer.from('中文字符串!');
for(let i = 0; i < buf.length; i+=5){
var b = Buffer.allocUnsafe(5);
buf.copy(b, 0, i);
console.log(decoder.write(b));
}Buffer Other commonly used APIs
There are also some Buffer commonly used APIs- Buffer.isBuffer: Determine whether the object is a Buffer
- Buffer.isEncoding: Determine the encoding of the Buffer object
- buf.length: Return the bytes of memory requested for this Buffer instance The number is not the number of bytes of the Buffer instance content
- buf.indexOf: Similar to the indexOf of the array, returns the position of a certain string, acsii code or buf in the modified buf
- buf. copy: Copy (part of) the contents of one buf to another buf
For more programming-related knowledge, please visit:Programming Video! !
The above is the detailed content of A brief analysis of Buffer in NodeJS. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 The difference between nodejs and tomcat
Apr 21, 2024 am 04:16 AM
The difference between nodejs and tomcat
Apr 21, 2024 am 04:16 AM
The main differences between Node.js and Tomcat are: Runtime: Node.js is based on JavaScript runtime, while Tomcat is a Java Servlet container. I/O model: Node.js uses an asynchronous non-blocking model, while Tomcat is synchronous blocking. Concurrency handling: Node.js handles concurrency through an event loop, while Tomcat uses a thread pool. Application scenarios: Node.js is suitable for real-time, data-intensive and high-concurrency applications, and Tomcat is suitable for traditional Java web applications.
 The difference between nodejs and vuejs
Apr 21, 2024 am 04:17 AM
The difference between nodejs and vuejs
Apr 21, 2024 am 04:17 AM
Node.js is a server-side JavaScript runtime, while Vue.js is a client-side JavaScript framework for creating interactive user interfaces. Node.js is used for server-side development, such as back-end service API development and data processing, while Vue.js is used for client-side development, such as single-page applications and responsive user interfaces.
 Is nodejs a backend framework?
Apr 21, 2024 am 05:09 AM
Is nodejs a backend framework?
Apr 21, 2024 am 05:09 AM
Node.js can be used as a backend framework as it offers features such as high performance, scalability, cross-platform support, rich ecosystem, and ease of development.
 What is the difference between npm and npm.cmd files in the nodejs installation directory?
Apr 21, 2024 am 05:18 AM
What is the difference between npm and npm.cmd files in the nodejs installation directory?
Apr 21, 2024 am 05:18 AM
There are two npm-related files in the Node.js installation directory: npm and npm.cmd. The differences are as follows: different extensions: npm is an executable file, and npm.cmd is a command window shortcut. Windows users: npm.cmd can be used from the command prompt, npm can only be run from the command line. Compatibility: npm.cmd is specific to Windows systems, npm is available cross-platform. Usage recommendations: Windows users use npm.cmd, other operating systems use npm.
 Is nodejs a back-end development language?
Apr 21, 2024 am 05:09 AM
Is nodejs a back-end development language?
Apr 21, 2024 am 05:09 AM
Yes, Node.js is a backend development language. It is used for back-end development, including handling server-side business logic, managing database connections, and providing APIs.
 How to connect nodejs to mysql database
Apr 21, 2024 am 06:13 AM
How to connect nodejs to mysql database
Apr 21, 2024 am 06:13 AM
To connect to a MySQL database, you need to follow these steps: Install the mysql2 driver. Use mysql2.createConnection() to create a connection object that contains the host address, port, username, password, and database name. Use connection.query() to perform queries. Finally use connection.end() to end the connection.
 What are the global variables in nodejs
Apr 21, 2024 am 04:54 AM
What are the global variables in nodejs
Apr 21, 2024 am 04:54 AM
The following global variables exist in Node.js: Global object: global Core module: process, console, require Runtime environment variables: __dirname, __filename, __line, __column Constants: undefined, null, NaN, Infinity, -Infinity
 Which one to choose between nodejs and java?
Apr 21, 2024 am 04:40 AM
Which one to choose between nodejs and java?
Apr 21, 2024 am 04:40 AM
Node.js and Java each have their pros and cons in web development, and the choice depends on project requirements. Node.js excels in real-time applications, rapid development, and microservices architecture, while Java excels in enterprise-grade support, performance, and security.






