Detailed explanation of file viewing and editing in CentOS
The following column of centos Basic Tutorial will introduce you to the file viewing and editing of CentOS. I hope you can learn more about it if you need it. Friends help!

First of all, let’s introduce cat. The original meaning of cat command is concatenate, which is used to connect the contents of multiple files and output them to the standard output stream (the standard output stream defaults to for the screen). In actual application, we often use it to display file contents.
cat file1.php displays the contents of the file1.php file;
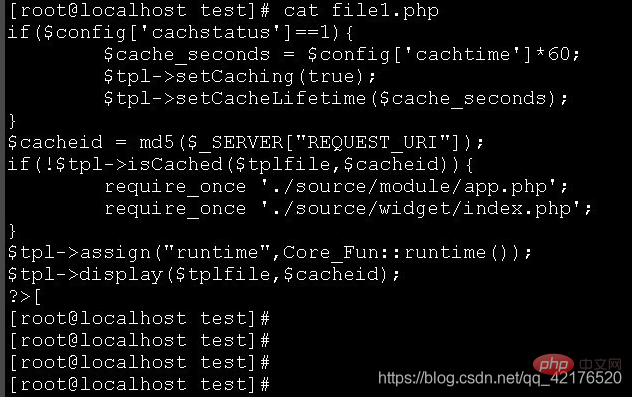
cat -n file2.py displays the contents of the file2.py file and displays the line number ;
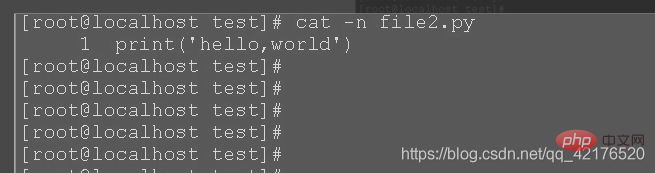
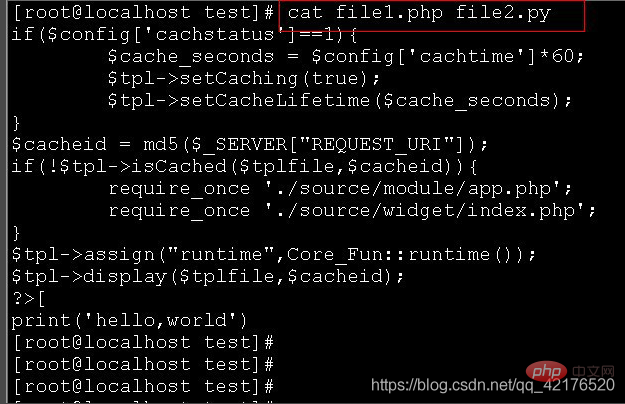
cat file1.php file2.py displays the contents of file1.php and file2.py files;
vi is the abbreviation of "Visual Interface", and the vi editor is the most basic text editor on Linux and Unix. It can perform many text operations such as output, delete, find, replace, block operations, etc., and users can customize it according to their own needs, which is not available in other editing programs. vi is not a typesetting program. It cannot edit fonts, formats, paragraphs and other attributes like Word or WPS. It is just a text editing program. vi has no menus, only commands, and there are many commands. Due to space limitations, this article only introduces commonly used commands. vi has three basic working modes: command line mode, text input mode and last line mode.
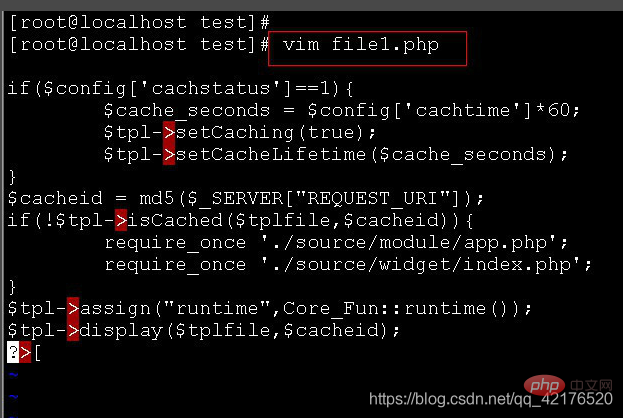
To enter and exit vi, enter the file name to be edited in shell mode, such as: vim file1.php to edit the file.
When exiting vi, you need to enter the exit command "q" in the last line mode. If you are in text input mode, first press the "ESC" key to enter the command mode, and then enter ":" to enter the last line mode. In the last line mode, you can use the following exit command.
When exiting: 1. :q is to exit directly; 2. wq is to exit after saving; 3. :q! - does not save the content, force exit
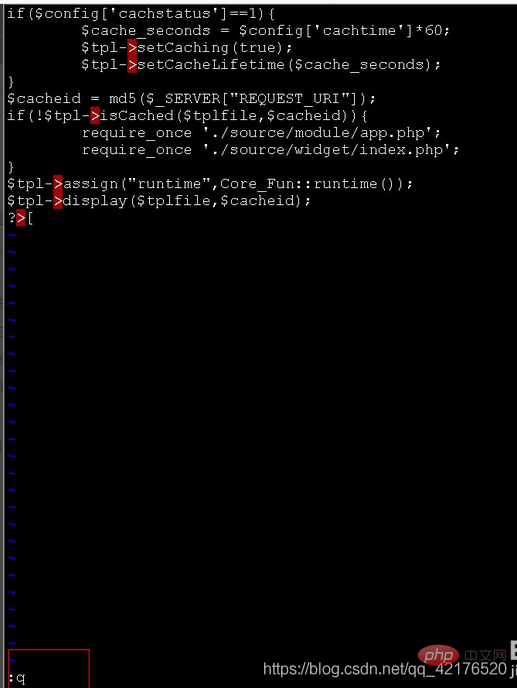
In the last line mode, enter set number to display the line number
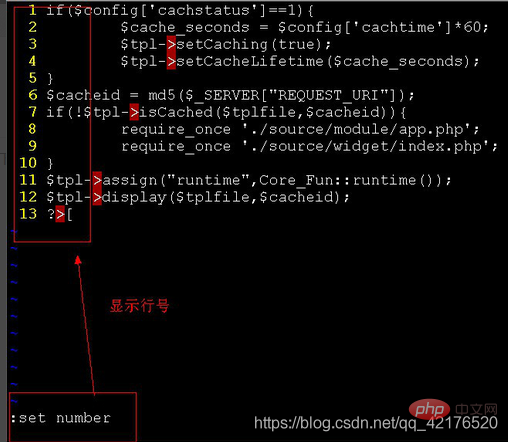
In the last line mode, you can use the following "nu" command (abbreviation for number) to display the line number of the line where the cursor is located and the content of the line.
vi provides two insert commands: i and I.
1. The i command inserts text starting from before the cursor position, and you can use the key to delete incorrect input during the insertion process. At this time, vi is in the insert state, and the word "-INSERT-" is displayed on the bottom line of the screen.
2. I command This command moves the cursor to the beginning of the current line and then inserts text before it.
#vi also provides many deletion commands. These commands x (lowercase) 0 delete the character at the cursor. X (uppercase) deletes the character before the cursor dd deletes the entire line where the cursor is. The D or d$ commands have the same function, they both delete the content from the cursor position to the end of the line. d0 deletes the content starting from the character before the cursor to the beginning of the line. dw deletes a word.
vi also has a text copy command yy to copy the entire line where the cursor is located. Once the line of text has been copied, it can be pasted anywhere by using the "p" command introduced above.
Related recommendations: "linux course"
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of file viewing and editing in CentOS. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1385
1385
 52
52
 CentOS Containerization with Docker: Deploying and Managing Applications
Apr 03, 2025 am 12:08 AM
CentOS Containerization with Docker: Deploying and Managing Applications
Apr 03, 2025 am 12:08 AM
Using Docker to containerize, deploy and manage applications on CentOS can be achieved through the following steps: 1. Install Docker, use the yum command to install and start the Docker service. 2. Manage Docker images and containers, obtain images through DockerHub and customize images using Dockerfile. 3. Use DockerCompose to manage multi-container applications and define services through YAML files. 4. Deploy the application, use the dockerpull and dockerrun commands to pull and run the container from DockerHub. 5. Carry out advanced management and deploy complex applications using Docker networks and volumes. Through these steps, you can make full use of D
 CentOS Backup and Recovery: Ensuring Data Integrity and Availability
Apr 04, 2025 am 12:02 AM
CentOS Backup and Recovery: Ensuring Data Integrity and Availability
Apr 04, 2025 am 12:02 AM
The steps for backup and recovery in CentOS include: 1. Use the tar command to perform basic backup and recovery, such as tar-czvf/backup/home_backup.tar.gz/home backup/home directory; 2. Use rsync for incremental backup and recovery, such as rsync-avz/home//backup/home_backup/ for the first backup. These methods ensure data integrity and availability and are suitable for the needs of different scenarios.
 How to optimize CentOS HDFS configuration
Apr 14, 2025 pm 07:15 PM
How to optimize CentOS HDFS configuration
Apr 14, 2025 pm 07:15 PM
Improve HDFS performance on CentOS: A comprehensive optimization guide to optimize HDFS (Hadoop distributed file system) on CentOS requires comprehensive consideration of hardware, system configuration and network settings. This article provides a series of optimization strategies to help you improve HDFS performance. 1. Hardware upgrade and selection resource expansion: Increase the CPU, memory and storage capacity of the server as much as possible. High-performance hardware: adopts high-performance network cards and switches to improve network throughput. 2. System configuration fine-tuning kernel parameter adjustment: Modify /etc/sysctl.conf file to optimize kernel parameters such as TCP connection number, file handle number and memory management. For example, adjust TCP connection status and buffer size
 CentOS Interview Questions: Ace Your Linux System Administrator Interview
Apr 09, 2025 am 12:17 AM
CentOS Interview Questions: Ace Your Linux System Administrator Interview
Apr 09, 2025 am 12:17 AM
Frequently asked questions and answers to CentOS interview include: 1. Use the yum or dnf command to install software packages, such as sudoyumininstallnginx. 2. Manage users and groups through useradd and groupadd commands, such as sudouseradd-m-s/bin/bashnewuser. 3. Use firewalld to configure the firewall, such as sudofirewall-cmd--permanent-add-service=http. 4. Set automatic updates to use yum-cron, such as sudoyumininstallyum-cron and configure apply_updates=yes.
 Centos stops maintenance 2024
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
Centos stops maintenance 2024
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
CentOS will be shut down in 2024 because its upstream distribution, RHEL 8, has been shut down. This shutdown will affect the CentOS 8 system, preventing it from continuing to receive updates. Users should plan for migration, and recommended options include CentOS Stream, AlmaLinux, and Rocky Linux to keep the system safe and stable.
 What are the methods of tuning performance of Zookeeper on CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 03:18 PM
What are the methods of tuning performance of Zookeeper on CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 03:18 PM
Zookeeper performance tuning on CentOS can start from multiple aspects, including hardware configuration, operating system optimization, configuration parameter adjustment, monitoring and maintenance, etc. Here are some specific tuning methods: SSD is recommended for hardware configuration: Since Zookeeper's data is written to disk, it is highly recommended to use SSD to improve I/O performance. Enough memory: Allocate enough memory resources to Zookeeper to avoid frequent disk read and write. Multi-core CPU: Use multi-core CPU to ensure that Zookeeper can process it in parallel.
 How to check CentOS HDFS configuration
Apr 14, 2025 pm 07:21 PM
How to check CentOS HDFS configuration
Apr 14, 2025 pm 07:21 PM
Complete Guide to Checking HDFS Configuration in CentOS Systems This article will guide you how to effectively check the configuration and running status of HDFS on CentOS systems. The following steps will help you fully understand the setup and operation of HDFS. Verify Hadoop environment variable: First, make sure the Hadoop environment variable is set correctly. In the terminal, execute the following command to verify that Hadoop is installed and configured correctly: hadoopversion Check HDFS configuration file: The core configuration file of HDFS is located in the /etc/hadoop/conf/ directory, where core-site.xml and hdfs-site.xml are crucial. use
 Centos shutdown command line
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:12 PM
Centos shutdown command line
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:12 PM
The CentOS shutdown command is shutdown, and the syntax is shutdown [Options] Time [Information]. Options include: -h Stop the system immediately; -P Turn off the power after shutdown; -r restart; -t Waiting time. Times can be specified as immediate (now), minutes ( minutes), or a specific time (hh:mm). Added information can be displayed in system messages.




