What are the commonly used instructions in Vue?
Vue common instructions include: v-once instruction, v-show instruction, v-if instruction, v-else instruction, v-else-if instruction, v-for instruction, v-html instruction, v- text instruction, v-bind instruction, v-on instruction, v-model instruction, etc.

vue.js officially defines itself as a data template engine and provides a set of instructions for rendering data.
Vue.js directives start with v-. They act on HTML elements. The directives provide some special features. When binding the directive to an element, the directive will add For some special behaviors, we can think of instructions as special HTML attributes. The purpose of the
directive is to apply certain behaviors to the DOM accordingly when the value of the expression changes.
Summary of vue common instructions
1.v-once
can be executed once Interpolation, when the data changes, the content at the interpolation will not be updated. But please note that this will affect other data bindings on the node:
<div id="app">
<p v-once>原始值: {{msg}}</p>
<p>后面的: {{msg}}</p>
<input type="text" v-model="msg">
</div>
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
msg: '今天的天气很好!'
}
});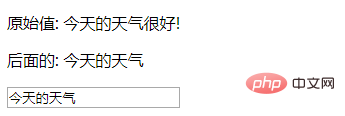
It will not change after adding the v-once command
2.v-show
The same as v-if. The difference is that if is commented out, v-show is given a display:none attribute so that it is not displayed. ! For usage, refer to the next v-if directive.
The difference between v-show and v-if:
v-if is a true conditional rendering, because it will ensure Conditional blocks properly destroy and rebuild event listeners and subcomponents within the conditional block during switching; v-show simply switches based on CSS.
v-if has a higher switching cost and v-show has a higher initial rendering cost. Therefore, if frequent switching is required, it is better to use v-show , and if conditions are unlikely to change during runtime, it is better to use v-if.
3.v-if
What is followed by v-if is an expression or an expression that returns true or false. And the value is true and fasle If it is false, it will be commented v-show is to give a display:none attribute so that it will not be displayed! true will display normally.
<div id="app">
<p v-if="show">要显示出来!</p>
<p v-if="hide">不要显示出来!</p>
<p v-if="height > 1.55">小明的身高: {{height}}m</p>
<p v-if="height1 > 1.55">小明的身高: {{height1}}m</p>
<p v-if="3>2">打死你: {{height1}}m</p>
</div>
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
show: true,
hide: false,
height: 1.68,
height1: 1.50
}
});
</script>4.v-else
Must be used together with v-if It cannot be used alone and must be in the middle below v-if Other tags will also report errors
<div id="app">
<p v-if="height > 1.7">小明的身高是: {{height}}m</p>
<p v-else>小明的身高不足1.70m</p>
</div>
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
height: 1.88
}
});
</script>5.v-else-if
This is relatively simple and you can just look at the code hahaha. Enter the score and the corresponding display will be displayed. Level
<div id="app">
<p>输入的成绩对应的等级是:</p>
<p v-if="score >= 90">优秀</p>
<p v-else-if="score >= 75">良好</p>
<p v-else-if="score >= 60">及格</p>
<p v-else>不及格</p>
<input type="text" v-model="score">
</div>
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
score: 90 // 优秀 良好 及格 不及格
}
});
</script>6.v-for
Renders a list based on data, similar to traversal in JS. Its data type can be Array | Object | number | string
The value of this command, Specific syntax (item, index) in items must be used, index is the index and can be omitted. item provides an alias for the currently traversed element (you can name it whatever you want). v-for has a higher priority than other instructions such as v-if
<body>
<div id="app">
<!-- 遍历数组 -->
<p v-for="(d,index) in msg">
{{index +':'+d}}
</p>
<!-- 遍历对象 -->
<div v-for="(dd,index) in obj">
{{index+':'+dd}}
</div>
<!-- 遍历对象 也可以不要index索引 -->
<div v-for="dd2 in obj">
{{dd2}}
</div>
<!-- 遍历num和string -->
<p v-for="gg in num2">{{gg}}</p>
<p v-for="gg2 in string2">{{gg2}}</p>
</div>
</body>
<script src="vue/vue.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript">
new Vue({
el:'#app',
data:{
msg:[123,98,25,63],
obj:{name:'敏敏',age:'21',height:'160'},
num2:'1335454', //注意这里不要写成了num2:1335154
string2:'xvzhiming'
}
})
</script> 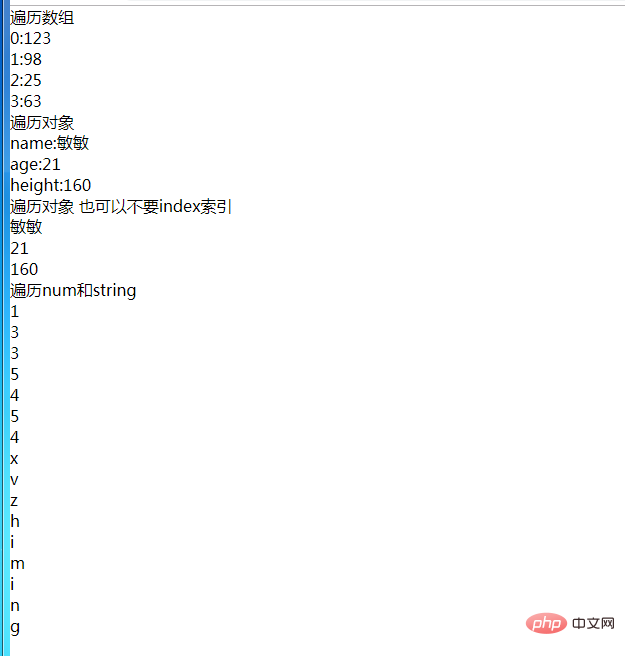
7.v-html
Double curly braces will interpret the data as normal text instead of HTML code. In order to output real HTML, you need to use v-html and adding v-html to a tag will overwrite the tags contained in it.
Note that v-html should be used with caution because security issues may arise. The official website explains: Any HTML dynamically rendered on your site may be very dangerous because it can easily lead to XSS attacks. Only use HTML interpolation for trusted content and never for user-supplied content.
<div id="app" v-html="html">
<p v-text="msg">哈哈哈</p>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
new Vue({
el:'#app',
data:{
msg:'我爱敏敏!!',
html:'<p>大海森林我都不爱!</p>'
}
})
</script> 8.v-text
Adding v-text to a note will overwrite the original content inside the tag, such as the example below, hahaha, it will not be displayed
<div id="app">
<p v-text="msg">哈哈哈</p>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
new Vue({
el:'#app',
data:{
msg:'我爱敏敏'
}
})
</script>9.v-bind
Usage
##
<!-- 完整语法 --> <a v-bind:href="url">...</a> <!-- 缩写 --> <a :href="url">...</a>
<div id="app">
改变src alt等属性
<img v-bind:src="imgSrc" :alt="alt">
<img :src="imgSrc1" :alt="alt">
</div>
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
imgSrc: 'img/img_01.jpg',
imgSrc1: 'img/img_02.jpg',
alt: '我是美女'
}
});
</script><div id="app">
//v-for是一个遍历 给他一个calss 如果index===cative class名是active,如果不等就为空
//index 是v-for的索引
<p v-for="(college, index) in colleges" :class="index === activeIndex ? 'active': ''">
{{college}}
</p>
<p :style="{color: fontColor}">今天的天气很好!</p>
</div>
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
colleges: [
'iOS学院',
'Java学院',
'HTML5学院',
'UI学院',
'VR学院'
],
activeIndex: 0,
fontColor: 'green'
}
});
</script>Note that v-blnd is used in the input. The writing method is not wrapped in {{}};
<body>
<div id="app"> <br> //加粗的内容刚刚学时 很容易出错 注意不要加{{}};
原始值<input type="" name="" id="" <strong>:value=name</strong> />
模板<input type="" name="" id="" <strong>:value=name.split('').reverse().join()</strong> />
methods<input type="" name="" id="" <strong>:value=fz()</strong> />
conputed<input type="" name="" id="" <strong>:value=fz2</strong> />
</div>
</body>
<script type="text/javascript">
new Vue({
el:'#app',
data:{
name:'chenglianjie'
},
methods:{
fz(){
return this.name.split('').reverse().join('');
}
},<br> //这是vue的计算属性 在我的博客vue分类里面有介绍
computed:{
fz2(){
return this.name.split('').reverse().join('');
}
}
})
</script>10.v-on
There are also some usages of binding events that will be mentioned in later blogs
<!-- 完整语法 --> <a v-on:click="doSomething">...</a> <!-- 缩写 --> <a @click="doSomething">...</a>
11.v-model
v-model is a directive, limited to,


