What are the features of the system?
System characteristics refer to the properties common to general systems, mainly including: 1. Aggregation, the system is composed of at least two or more elements that can be distinguished from each other; 2. Correlation; 3. Purpose, that is, a certain specific function displayed by the system; 4. Hierarchy; 5. Environmental adaptability; 6. Dynamicity.

# System characteristics refer to properties common to general systems.
The characteristics of the system mainly include:
(1) Aggregation. A system is composed of at least two or more elements (or subsystems) that can be distinguished from each other. A single element cannot constitute a system, and identical elements cannot constitute a system even if they are large in number.
(2) Relevance. Each element (subsystem) in the system is interdependent, restricts and interacts with each other to form an interrelated whole. This specific "relationship" between elements (subsystems) reflects the integrity of the system. The elements are the same but they interact with each other to form an interrelated whole. Different correlation relationships lead to different overall characteristics of the system performance. It is this "relationship" that makes the existence of each element in the system dependent on the existence of other elements. Often when one element changes, other elements will also change accordingly, causing system changes.
(3) Purpose. Both artificial and composite systems have a clear purpose, that is, a specific function that the system performs. This purpose must be the overall purpose of the system, not the partial purpose of the system elements or subsystems. Often, a system may have multiple purposes.
(4) Hierarchy. A complex system consists of many subsystems, which may be divided into many subsystems, and the system itself is a component of a larger system. The system is hierarchical. For example, a living body has several levels: cells, tissues, organs, systems, and organisms; an enterprise has several levels: individuals, teams, workshops, and factories. The structure and function of the system refer to the structure and function at the corresponding level, but cannot represent the structure and function at the high level and low level. Generally speaking, the more layers there are, the more complex the system is.
(5) Environmental adaptability. The system has the ability to self-adjust as the external environment changes to adapt to the new environment. The system and the environment must carry out various forms of exchanges and are subject to environmental constraints and restrictions. Changes in the environment will directly affect the functions and purposes of the system. The system must make corresponding adjustments to its own functions when the environment changes, so as not to affect the purpose of the system. accomplish. A system without environmental adaptability has no vitality.
(6) Dynamic. First of all, the activities of the system are dynamic, and certain functions and purposes of the system are achieved through the exchange of material, energy, and information with the environment. Therefore, the organized movement of matter, energy, and information constitutes a dynamic cycle of system activity. Secondly, the system process is also dynamic. The system itself reflected in the life cycle of the system is also in the changing process of gestation, generation, development, decline and elimination.
The above is the detailed content of What are the features of the system?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1389
1389
 52
52
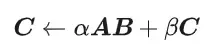 CUDA's universal matrix multiplication: from entry to proficiency!
Mar 25, 2024 pm 12:30 PM
CUDA's universal matrix multiplication: from entry to proficiency!
Mar 25, 2024 pm 12:30 PM
General Matrix Multiplication (GEMM) is a vital part of many applications and algorithms, and is also one of the important indicators for evaluating computer hardware performance. In-depth research and optimization of the implementation of GEMM can help us better understand high-performance computing and the relationship between software and hardware systems. In computer science, effective optimization of GEMM can increase computing speed and save resources, which is crucial to improving the overall performance of a computer system. An in-depth understanding of the working principle and optimization method of GEMM will help us better utilize the potential of modern computing hardware and provide more efficient solutions for various complex computing tasks. By optimizing the performance of GEMM
 Huawei's Qiankun ADS3.0 intelligent driving system will be launched in August and will be launched on Xiangjie S9 for the first time
Jul 30, 2024 pm 02:17 PM
Huawei's Qiankun ADS3.0 intelligent driving system will be launched in August and will be launched on Xiangjie S9 for the first time
Jul 30, 2024 pm 02:17 PM
On July 29, at the roll-off ceremony of AITO Wenjie's 400,000th new car, Yu Chengdong, Huawei's Managing Director, Chairman of Terminal BG, and Chairman of Smart Car Solutions BU, attended and delivered a speech and announced that Wenjie series models will be launched this year In August, Huawei Qiankun ADS 3.0 version was launched, and it is planned to successively push upgrades from August to September. The Xiangjie S9, which will be released on August 6, will debut Huawei’s ADS3.0 intelligent driving system. With the assistance of lidar, Huawei Qiankun ADS3.0 version will greatly improve its intelligent driving capabilities, have end-to-end integrated capabilities, and adopt a new end-to-end architecture of GOD (general obstacle identification)/PDP (predictive decision-making and control) , providing the NCA function of smart driving from parking space to parking space, and upgrading CAS3.0
 Which version of Apple 16 system is the best?
Mar 08, 2024 pm 05:16 PM
Which version of Apple 16 system is the best?
Mar 08, 2024 pm 05:16 PM
The best version of the Apple 16 system is iOS16.1.4. The best version of the iOS16 system may vary from person to person. The additions and improvements in daily use experience have also been praised by many users. Which version of the Apple 16 system is the best? Answer: iOS16.1.4 The best version of the iOS 16 system may vary from person to person. According to public information, iOS16, launched in 2022, is considered a very stable and performant version, and users are quite satisfied with its overall experience. In addition, the addition of new features and improvements in daily use experience in iOS16 have also been well received by many users. Especially in terms of updated battery life, signal performance and heating control, user feedback has been relatively positive. However, considering iPhone14
 Always new! Huawei Mate60 series upgrades to HarmonyOS 4.2: AI cloud enhancement, Xiaoyi Dialect is so easy to use
Jun 02, 2024 pm 02:58 PM
Always new! Huawei Mate60 series upgrades to HarmonyOS 4.2: AI cloud enhancement, Xiaoyi Dialect is so easy to use
Jun 02, 2024 pm 02:58 PM
On April 11, Huawei officially announced the HarmonyOS 4.2 100-machine upgrade plan for the first time. This time, more than 180 devices will participate in the upgrade, covering mobile phones, tablets, watches, headphones, smart screens and other devices. In the past month, with the steady progress of the HarmonyOS4.2 100-machine upgrade plan, many popular models including Huawei Pocket2, Huawei MateX5 series, nova12 series, Huawei Pura series, etc. have also started to upgrade and adapt, which means that there will be More Huawei model users can enjoy the common and often new experience brought by HarmonyOS. Judging from user feedback, the experience of Huawei Mate60 series models has improved in all aspects after upgrading HarmonyOS4.2. Especially Huawei M
 What are the computer operating systems?
Jan 12, 2024 pm 03:12 PM
What are the computer operating systems?
Jan 12, 2024 pm 03:12 PM
A computer operating system is a system used to manage computer hardware and software programs. It is also an operating system program developed based on all software systems. Different operating systems have different users. So what are the computer systems? Below, the editor will share with you what computer operating systems are. The so-called operating system is to manage computer hardware and software programs. All software is developed based on operating system programs. In fact, there are many types of operating systems, including those for industrial use, commercial use, and personal use, covering a wide range of applications. Below, the editor will explain to you what computer operating systems are. What computer operating systems are Windows systems? The Windows system is an operating system developed by Microsoft Corporation of the United States. than the most
 Detailed explanation of how to modify system date in Oracle database
Mar 09, 2024 am 10:21 AM
Detailed explanation of how to modify system date in Oracle database
Mar 09, 2024 am 10:21 AM
Detailed explanation of the method of modifying the system date in the Oracle database. In the Oracle database, the method of modifying the system date mainly involves modifying the NLS_DATE_FORMAT parameter and using the SYSDATE function. This article will introduce these two methods and their specific code examples in detail to help readers better understand and master the operation of modifying the system date in the Oracle database. 1. Modify NLS_DATE_FORMAT parameter method NLS_DATE_FORMAT is Oracle data
 Differences and similarities of cmd commands in Linux and Windows systems
Mar 15, 2024 am 08:12 AM
Differences and similarities of cmd commands in Linux and Windows systems
Mar 15, 2024 am 08:12 AM
Linux and Windows are two common operating systems, representing the open source Linux system and the commercial Windows system respectively. In both operating systems, there is a command line interface for users to interact with the operating system. In Linux systems, users use the Shell command line, while in Windows systems, users use the cmd command line. The Shell command line in Linux system is a very powerful tool that can complete almost all system management tasks.
 How to solve the 0xc0000428 error in win10 system
Dec 27, 2023 pm 04:41 PM
How to solve the 0xc0000428 error in win10 system
Dec 27, 2023 pm 04:41 PM
After installing the win10 operating system on our computers, some friends may experience a system blue screen and prompt error code 0xc0000428 when using the computer. Don't worry about this kind of problem. The editor thinks that we can troubleshoot the problem on the system first to see if it is caused by hardware or software, and then solve the problem in a targeted manner. Let’s take a look at what the editor did for the specific details~ How to solve the problem of 0xc0000428 in win10 system 1. Restart continuously and then force shutdown three times to let the win10 system automatically enter the advanced startup options. 2. In the win10 system advanced startup options interface, open in sequence: Troubleshooting-Advanced Options-Startup Settings, in Startup Settings



