Use Node.js+Vue.js to build file compression applications

Related recommendations: "node js tutorial"
Node.js provides us with a module to assist in file compression. In this article, we will build an application where users can upload a file they want to compress and then download a compressed version of the file using the Node.js Zlib module.
Prerequisites
To continue with this tutorial, you need to have the following qualifications:
-
<li>Familiar with HTML, CSS and Javascript (ES6)
<li>VS Code or any code editor installed on your development machine
<li>Have Postman installed on your development machine
<li>The basics of Vue and Node.js
Setup Project
We will start by building the backend, which is the foundation of our application.
On the desktop, create a folder for the application, name it compressor, and set up a new Node by running npm init -y. js project.
We write the back-end service first, so create another server directory in the project.
Now we need to install the necessary packages for the application:
-
<li>
koa, koa-router: This will help For setting up our server and routing
<li>
nodemon: When we make changes to the application, Nodemon will restart our server
<li>
multer :Middleware for uploading files
<li>
cors:Help adding headers to proxy requests
To install them all, install them in the ## Run the following command in the ##server directory:
npm i --save koa koa-router nodemon multer cors
index.js file in the server directory. This is what we will Where the backend code is written.
.gitignore file and add node_modules to it, this will prevent the node_modules folder from being added to git.
const express = require('express');
const multer = require('multer');
const zlib = require('zlib');
const cors = require('cors');
const fs = require('fs');
const path = require('path');
const app = express();
app.use(cors());
//multer
const storage = multer.memoryStorage();
const upload = multer({
storage: storage,
});
app.listen(3000, () => {
console.log('App is runnuing on port 3000');
});cors as middleware.
zlib, which we will use to do the actual compression. We then use an instance of Express to create a server that will listen on port 3000.
gzip method.
app.post("/compress", upload.single("file"), async (req, res) => {
try {
const destination = `compressed/${req.file.originalname}.gz`;
let fileBuffer = req.file.buffer;
await zlib.gzip(fileBuffer, (err, response) => {
if (err) {
console.log(err);
}
fs.writeFile(path.join(__dirname, destination), response, (err, data) => {
if (err) {
console.log(err);
}
res.download(path.join(__dirname, destination));
});
});
} catch (err) {
console.log(err);
res.json(err);
}
});/compress route, which is a POST request, and then pass the Multer middleware in that route. Our Multer middleware will return the file buffer, which is stored in the fileBuffer variable.
compressed directory and save the compressed files in it.
compressed directory.
const destination = `compressed/${req.file.originalname}.gz`;gzip to compress the file, which takes fileBuffer as the first parameter and then a callback function as the second parameter. The callback function consists of any possible errors and compressed responses.
compressed directory, the file will have the .gz file extension because it is used Identifies Zlib compression.
package.lock.json file, its size is 48kb.
client directory inside the compressor root directory. In the client directory, create two files: index.html and main.js.
main.js file at the end of the body tag.
nbsp;html> <meta> <meta> <title>Vue Compressor</title> <link> <script></script> <script></script> <p> </p><h1 id="压缩">压缩</h1> <script></script>
对于此应用程序,用户将通过拖放添加其文件。让我们为我们的应用程序定义一个简单的用户界面。
修改模板为:
nbsp;html>
<meta>
<meta>
<title>Vue Compressor</title>
<link>
<script></script>
<script></script>
<style>
body {
background: #ccc !important;
}
.wrapper {
width: 350px;
height: 350px;
border: 2px dotted gray
}
.wrapper h4 {
text-align: center;
font-family: sans-serif;
}
</style>
<p>
</p><p>
</p><p>
</p><p>
</p><p>
</p><h4 id="在这里拖放">在这里拖放</h4>
-
<li>FileName -> File Size
你可以使用任何实时服务器运行你的应用程序,这里我使用 live-server 。
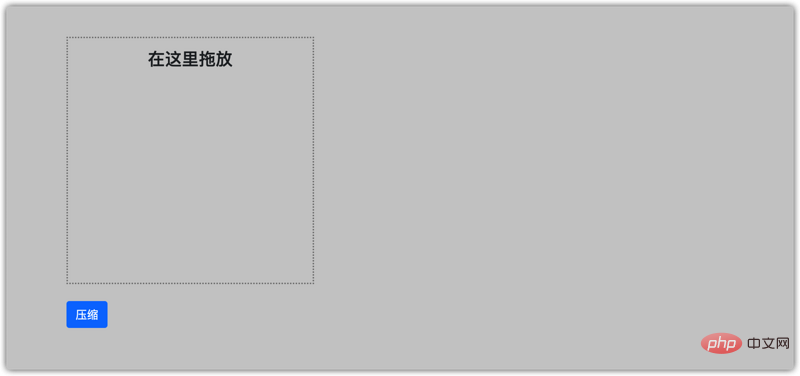
拖放功能
我们先在 main.js 文件中定义我们的Vue.js实例。然后,我们将创建一个state来保存我们的文件。
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
files: [],
loading:false
},
methods: {
addFile(e) {
},
removeFile(file) {
},
compressFile() {
}
}
})在Vue中实现拖放,我们需要添加一个 @drop 事件来选择我们的文件,还有一个 v-cloak 属性,这个属性用于在应用加载之前隐藏 {{tags}}。
<p> </p><h4 id="在这里拖放">在这里拖放</h4>
@drop 事件监听 addFile 方法,我们必须定义:
addFile(e) {
let files = e.dataTransfer.files;
[...files].forEach(file => {
this.files.push(file);
console.log(this.files)
});
}使用这种方法,放置在框中的所有文件都将记录在我们的控制台上。
但是,我们想在框内显示文件,因此我们必须将 <li> 元素修改为:
这样,每当我们将文件放入框中时,都会显示文件名和大小。
我们可以通过向 X 按钮添加点击事件来添加额外的功能,以从框中删除文件:@click = ‘removeFile(file)’。
然后,我们定义 removeFile 方法:
removeFile(file) {
this.files = this.files.filter(f => {
return f != file;
});
},让我们定义压缩函数,该函数将压缩所选文件,这就是Axios的作用所在。我们将向我们在后端定义的 /compress 路由发出请求:
compressFile() {
this.loading = true;
let formdata = new FormData();
formdata.append('file', this.files[0])
axios.post('http://localhost:3000/compress', formdata, {
responseType: 'blob'
}).then(response => {
let fileURL = window.URL.createObjectURL(new Blob([(response.data)]))
let fileLink = document.createElement('a');
fileLink.href = fileURL;
fileLink.setAttribute('download', `${this.files[0].name}.gz`);
document.body.appendChild(fileLink);
fileLink.click();
this.loading = false;
}).catch(err => {
this.loading = false;
console.log(err)
})
}我们使用 FormData 上传文件。上载文件后,后端会压缩文件并将压缩后的文件返回给我们。
我们使用 URL.createObjectURL 创建一个 DOMstring,其中包含表示给定对象的URL。然后,我们从后端下载给定的数据。
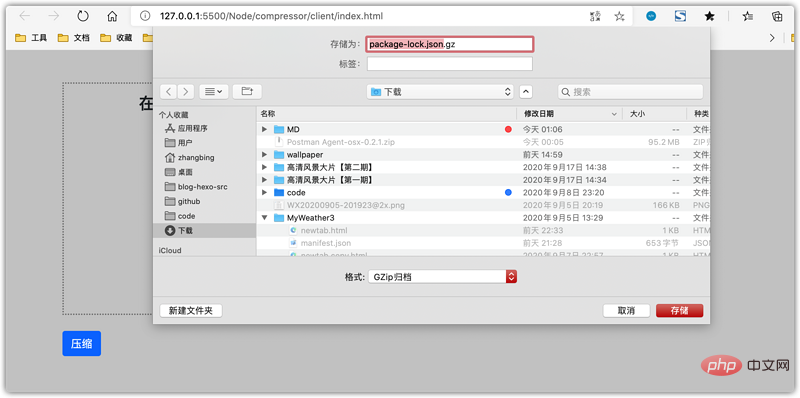
现在,我们需要在compress按钮中添加一个click事件,以侦听我们创建的方法:
<button> <span></span> 压缩 </button>
单击我们的压缩按钮将触发文件下载:
就是这样!
我们只是建立了一个简单的压缩应用程序。最后我们很想添加一个简单的方法,通过创建一个Vue.js过滤器,将我们的文件大小以千字节为单位进行格式化。
filters: {
kb(val) {
return Math.floor(val / 1024);
}
},在模板中使用
{{ file.size | kb }} kb这会将文件的大小格式化为更易读的格式。
源码
Node.js使文件压缩变得容易。它可以进一步用于压缩HTTP请求和响应,以提高应用程序性能。要获得更多Zlib功能,可以查看Zlib上的Node.js文档。
源代码:https://github.com/dunizb/CodeTest/tree/master/Node/compressor
原文地址:https://blog.logrocket.com/build-a-file-compression-application-in-node-js-and-vue-js/
相关推荐:
更多编程相关知识,请访问:编程入门!!
The above is the detailed content of Use Node.js+Vue.js to build file compression applications. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 PHP and Vue: a perfect pairing of front-end development tools
Mar 16, 2024 pm 12:09 PM
PHP and Vue: a perfect pairing of front-end development tools
Mar 16, 2024 pm 12:09 PM
PHP and Vue: a perfect pairing of front-end development tools. In today's era of rapid development of the Internet, front-end development has become increasingly important. As users have higher and higher requirements for the experience of websites and applications, front-end developers need to use more efficient and flexible tools to create responsive and interactive interfaces. As two important technologies in the field of front-end development, PHP and Vue.js can be regarded as perfect tools when paired together. This article will explore the combination of PHP and Vue, as well as detailed code examples to help readers better understand and apply these two
 Questions frequently asked by front-end interviewers
Mar 19, 2024 pm 02:24 PM
Questions frequently asked by front-end interviewers
Mar 19, 2024 pm 02:24 PM
In front-end development interviews, common questions cover a wide range of topics, including HTML/CSS basics, JavaScript basics, frameworks and libraries, project experience, algorithms and data structures, performance optimization, cross-domain requests, front-end engineering, design patterns, and new technologies and trends. . Interviewer questions are designed to assess the candidate's technical skills, project experience, and understanding of industry trends. Therefore, candidates should be fully prepared in these areas to demonstrate their abilities and expertise.
 Is Django front-end or back-end? check it out!
Jan 19, 2024 am 08:37 AM
Is Django front-end or back-end? check it out!
Jan 19, 2024 am 08:37 AM
Django is a web application framework written in Python that emphasizes rapid development and clean methods. Although Django is a web framework, to answer the question whether Django is a front-end or a back-end, you need to have a deep understanding of the concepts of front-end and back-end. The front end refers to the interface that users directly interact with, and the back end refers to server-side programs. They interact with data through the HTTP protocol. When the front-end and back-end are separated, the front-end and back-end programs can be developed independently to implement business logic and interactive effects respectively, and data exchange.
 C# development experience sharing: front-end and back-end collaborative development skills
Nov 23, 2023 am 10:13 AM
C# development experience sharing: front-end and back-end collaborative development skills
Nov 23, 2023 am 10:13 AM
As a C# developer, our development work usually includes front-end and back-end development. As technology develops and the complexity of projects increases, the collaborative development of front-end and back-end has become more and more important and complex. This article will share some front-end and back-end collaborative development techniques to help C# developers complete development work more efficiently. After determining the interface specifications, collaborative development of the front-end and back-end is inseparable from the interaction of API interfaces. To ensure the smooth progress of front-end and back-end collaborative development, the most important thing is to define good interface specifications. Interface specification involves the name of the interface
 Comparative analysis of Express and Laravel: Choose the framework that suits you better
Mar 10, 2024 pm 10:15 PM
Comparative analysis of Express and Laravel: Choose the framework that suits you better
Mar 10, 2024 pm 10:15 PM
Express and Laravel are two very popular web frameworks, representing the excellent frameworks of the two major development languages of JavaScript and PHP respectively. This article will conduct a comparative analysis of these two frameworks to help developers choose a framework that is more suitable for their project needs. 1. Framework Introduction Express is a web application framework based on the Node.js platform. It provides a series of powerful functions and tools that enable developers to quickly build high-performance web applications. Express
 In-depth comparison of Express and Laravel: How to choose the best framework?
Mar 09, 2024 pm 01:33 PM
In-depth comparison of Express and Laravel: How to choose the best framework?
Mar 09, 2024 pm 01:33 PM
In-depth comparison of Express and Laravel: How to choose the best framework? When choosing a back-end framework suitable for your project, Express and Laravel are undoubtedly two popular choices among developers. Express is a lightweight framework based on Node.js, while Laravel is a popular framework based on PHP. This article will provide an in-depth comparison of the advantages and disadvantages of these two frameworks and provide specific code examples to help developers choose the framework that best suits their needs. Performance and scalabilityExpr
 What is a front-end modular ESM?
Feb 25, 2024 am 11:48 AM
What is a front-end modular ESM?
Feb 25, 2024 am 11:48 AM
What is front-end ESM? Specific code examples are required. In front-end development, ESM refers to ECMAScriptModules, a modular development method based on the ECMAScript specification. ESM brings many benefits, such as better code organization, isolation between modules, and reusability. This article will introduce the basic concepts and usage of ESM and provide some specific code examples. The basic concept of ESM In ESM, we can divide the code into multiple modules, and each module exposes some interfaces for other modules to
 Exploring Go language front-end technology: a new vision for front-end development
Mar 28, 2024 pm 01:06 PM
Exploring Go language front-end technology: a new vision for front-end development
Mar 28, 2024 pm 01:06 PM
As a fast and efficient programming language, Go language is widely popular in the field of back-end development. However, few people associate Go language with front-end development. In fact, using Go language for front-end development can not only improve efficiency, but also bring new horizons to developers. This article will explore the possibility of using the Go language for front-end development and provide specific code examples to help readers better understand this area. In traditional front-end development, JavaScript, HTML, and CSS are often used to build user interfaces






