Install Oracle11g database on centos
oracle databaseThe column introduces the method of installing Oracle11g database

Recommended: oracle database
1. Preparation environment:
Centos 7.5 operating system minimal installation; physical memory 8GB, hard disk 100G; installation directory: /oracle
Installation package: Pay attention to download the corresponding package according to the system (32-bit, 64-bit)
linux.x64_11gR2_database_1of2.zip
linux.x64_11gR2_database_2of2.zip
Add the host name (obtained through hostname) to the loopback IP in the /etc/hosts file and the mapping is as follows :
192.168.31.162 oracle #Local IP host name
Turn off selinux and firewall
[root@oracle ~]# setenforce 0 #临时 [root@oracle ~]# sed -i "/SELINUX=/s/enforcing/disabled/" /etc/selinux/config #永久关闭selinux [root@oracle ~]# getenforce Disabled [root@oracle ~]# systemctl stop firewalld [root@oracle ~]# systemctl disable firewalld
2. Install dependency packages:
[root@oracle ~]# yum -y install gcc make binutils gcc-c++ [root@oracle ~]#yum -y install compat-libstdc++-33 elfutils-libelf-devel elfutils-libelf-devel-static [root@oracle ~]# yum -y install ksh libaio libaio-devel numactl-devel sysstat [root@oracle ~]# yum -y install unixODBC unixODBC-devel pcre-devel
3. Unpack:
[root@oracle ~]# cd /oracle/ [root@oracle oracle]# unzip linux.x64_11gR2_database_1of2.zip [root@oracle oracle]# unzip linux.x64_11gR2_database_2of2.zip 注,解包后在该目录下会有一个database目录
4. Prepare to install users and groups:
[root@oracle oracle]# groupadd oinstall [root@oracle oracle]# groupadd dba [root@oracle oracle]# useradd -g oinstall -G dba -d /home/oracle oracle [root@oracle oracle]# passwd oracle [root@oracle oracle]# id oracle uid=1000(oracle) gid=1000(oinstall) 组=1000(oinstall),1001(dba)
5. Modify kernel parameters:
[root@oracle oracle]# vim /etc/sysctl.conf 添加 fs.aio-max-nr = 1048576 fs.file-max = 6553600 kernel.shmall = 2097152 kernel.shmmax = 2147483648 kernel.shmmni = 4096 kernel.sem = 250 32000 100 128 net.ipv4.ip_local_port_range = 1024 65000 net.core.rmem_default = 262144 net.core.rmem_max = 4194304 net.core.wmem_default = 262144 net.core.wmem_max = 1048586 [root@oracle oracle]# /sbin/sysctl –p 文件生效
6. Modify user restriction files:
[root@oracle oracle]# vim /etc/security/limits.conf 添加 oracle soft nproc 2047 oracle hard nproc 16384 oracle soft nofile 1024 oracle hard nofile 65536 oracle soft stack 10240 [root@oracle oracle]# vim /etc/pam.d/login 添加 session required /lib64/security/pam_limits.so 这里有个注意点,那个64指64位系统,不能省略 session required pam_limits.so [root@oracle oracle]# vim /etc/profile 添加 if [ $USER = "oracle" ]; then if [ $SHELL = "/bin/ksh" ]; then ulimit -p 16384 ulimit -n 65536 else ulimit -u 16384 -n 65536 fi fi
7. Manually create installation documents and set permissions:
[root@oracle oracle]# mkdir /oracle/oracle [root@oracle oracle]# mkdir /oracle/oracle/11.2.0 数据库系统安装目录 [root@oracle oracle]# mkdir /oracle/oradata 数据库数据安装目录 [root@oracle oracle]# mkdir /oracle/oradata_back 数据备份目录 [root@oracle oracle]# mkdir /home/oracle/inventory 清单目录 [root@oracle oracle]# chown -R oracle.oinstall /oracle/oracle [root@oracle oracle]# chown -R oracle.oinstall /oracle/oracle /home/oracle/ [root@oracle oracle]# chmod -R 775 /oracle/oracle
8. Edit silent installation files (non-image interface):
[root@oracle oracle]# su - oracle [oracle@oracle ~]$ cp -R /oracle/database/response/ /home/oracle/ [oracle@oracle ~]$ cd /home/oracle/response/ [oracle@oracle response]$ mv db_install.rsp db_install_swonly.rsp 因为下面的安装是只安装软件不安装启动数据库实例,所以改个名字以提示自己 [oracle@oracle response]$vim db_install_swonly.rsp 29 oracle.install.option=INSTALL_DB_SWONLY ##3选1 37 ORACLE_HOSTNAME=oracle 42 UNIX_GROUP_NAME=oinstall 47 INVENTORY_LOCATION=/home/oracle/inventory 99 oracle.install.db.InstallEdition=EE oracle.install.db.customComponents=oracle.server:11.2.0.1.0, //保持系统默认值 oracle.sysman.ccr:10.2.7.0.0,oracle.xdk:11.2.0.1.0,oracle.rdbms.oci:11.2.0.1.0, oracle.network:11.2.0.1.0,oracle.network.listener:11.2.0.1.0,oracle.rdbms:11.2.0.1.0, oracle.options:11.2.0.1.0,oracle.rdbms.partitioning:11.2.0.1.0, oracle.oraolap:11.2.0.1.0,oracle.rdbms.dm:11.2.0.1.0, oracle.rdbms.dv:11.2.0.1.0,orcle.rdbms.lbac:11.2.0.1.0, oracle.rdbms.rat:11.2.0.1.0 142 oracle.install.db.DBA_GROUP=dba 147 oracle.install.db.OPER_GROUP=dba 385 DECLINE_SECURITY_UPDATES=true
9. Install oracle based on response files:
[oracle@oracle oracle]$ cd /oracle/database/ [oracle@oracle database]$ ./runInstaller -silent -ignorePrereq -responseFile /home/oracle/response/db_install_swonly.rsp
If Report: ./runInstaller: /data/oracle/database/install/.oui: /lib/ld-linux.so.2: bad ELF interpreter: No such file or directory
Solution: yum install -y ld- linux.so.2
Note: During the installation process, if it prompts [warning], ignore it, the program is still being installed. If it prompts [fatal], the installation will stop. Open another terminal to check the log and check (you can also check the installation progress) the error message: tail –f /home/oracle/inventory/logs/installActions2018-11-04_11-16-12PM.log
When it appears: Successfully Setup Software. Indicates successful installation
Exit and execute the following two scripts to initialize as root:
[root@oracle database]# cd /home/oracle/inventory/ [root@oracle inventory]# ./orainstRoot.sh #注:重装oracle前,删除/etc/oraInst.loc文件,否则没有./orainstRoot.sh [root@oracle inventory]# cd /oracle/oracle/11.2.0/ [root@oracle 11.2.0]# ./root.sh
10. Edit the silent library creation response file (library creation):
[oracle@oracle ~]$ cd /home/oracle/response/ [oracle@oracle response]$ mv dbca.rsp dbca_hello.rsp 实例名 [oracle@oracle ~]$ vim .bash_profile 设置用户变量,否测没有命令 export ORACLE_BASE=/oracle/oracle export ORACLE_HOME=/oracle/oracle/11.2.0 export ORACLE_SID=hello PATH=$PATH:$HOME/.local/bin:$HOME/bin:/oracle/oracle/11.2.0/bin/ [oracle@oracle ~]$ vim /home/oracle/response/dbca_hello.rsp 建库建实例 78 GDBNAME = "orcl11g" 数据库名字 ###192.168.1.201 yfpw 149 SID = "hello" 实例名 ###192.168.1.201 orcl 190 SYSPASSWORD = "password" 管理员密码 200 SYSTEMPASSWORD = "password" 管理员密码 357 DATAFILEDESTINATION = /oracle/oracle 数据文件存放目录 367 RECOVERYAREADESTINATION= /oracle/oradata_back 数据备份目录 415 CHARACTERSET = "ZHS16GBK" 字符集,重要!!! 建库后一般不能更改,所以建库前要确定清楚。 ###我司线上为:AMERICAN_AMERICA.AL32UTF8 540 TOTALMEMORY = "5120" 设置内存5120M
11. Configure silent monitoring :
[oracle@oracle ~]$ netca /silent /responsefile /home/oracle/response/netca.rsp 正在对命令行参数进行语法分析: 参数"silent" = true 参数"responsefile" = /home/oracle/response/netca.rsp 完成对命令行参数进行语法分析。 Oracle Net Services 配置: 完成概要文件配置。 Oracle Net 监听程序启动: 正在运行监听程序控制: /oracle/oracle/11.2.0/bin/lsnrctl start LISTENER 监听程序控制完成。 监听程序已成功启动。 监听程序配置完成。 成功完成 Oracle Net Services 配置。退出代码是0 成功运行后(退出代码是0),在/oracle/oracle/11.2.0/network/admin目录下生成sqlnet.ora和listener.ora两个文件,通过命令netstat –ntlp 可以看到服务端口1521,说明监听器已经在1521端口上开始工作了。
Twelve starting library examples:
[oracle@oracle admin]$ dbca -silent -responseFile /home/oracle/response/dbca_hello.rsp 复制数据库文件 1% 已完成 3% 已完成 11% 已完成 18% 已完成 26% 已完成 37% 已完成 正在创建并启动 Oracle 实例 40% 已完成 45% 已完成 50% 已完成 55% 已完成 56% 已完成 60% 已完成 62% 已完成 正在进行数据库创建 66% 已完成 70% 已完成 73% 已完成 85% 已完成 96% 已完成 100% 已完成
For more information, see the log file "/oracle/oracle/cfgtoollogs/dbca/orcl11g/orcl11g.log".
13. Configure monitoring TNS listening string (convenient for third-party software management such as plsql):
[oracle@oracle ~]$ cd /oracle/oracle/11.2.0/network/admin/ [oracle@oracle admin]$ vim listener.ora 添加监听串 SID_LIST_LISTENER = (SID_LIST = (SID_DESC = (SID_NAME = hello) sid实例名 (ORACLE_HOME = /oracle/oracle/11.2.0) 家目录 ) ) [oracle@oracle admin]$ lsnrctl status Listening Endpoints Summary... (DESCRIPTION=(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=ipc)(KEY=EXTPROC1521))) (DESCRIPTION=(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=tcp)(HOST=localhost)(PORT=1521))) Services Summary... Service "helloXDB" has 1 instance(s). Instance "hello", status READY, has 1 handler(s) for this service... Service "orcl11g" has 1 instance(s). Instance "hello", status READY, has 1 handler(s) for this service... The command completed successfully 即监听成功 [<u>https://www.cnblogs.com/softidea/p/3912369.html</u>](https://www.cnblogs.com/softidea/p/3912369.html)
14. Enter the database, no password is required by default:
[oracle@oracle admin]$ sqlplus / as sysdba SQL*Plus: Release 11.2.0.1.0 Production on Mon Nov 5 00:42:01 2018 Copyright (c) 1982, 2009, Oracle. All rights reserved. Connected to: Oracle Database 11g Enterprise Edition Release 11.2.0.1.0 - 64bit Production With the Partitioning, OLAP, Data Mining and Real Application Testing options SQL> SQL> shutdown immediate; 关闭实例 SQL> startup 开启实例 SQL> exit 退出
Attached is the oracle structure Picture one:
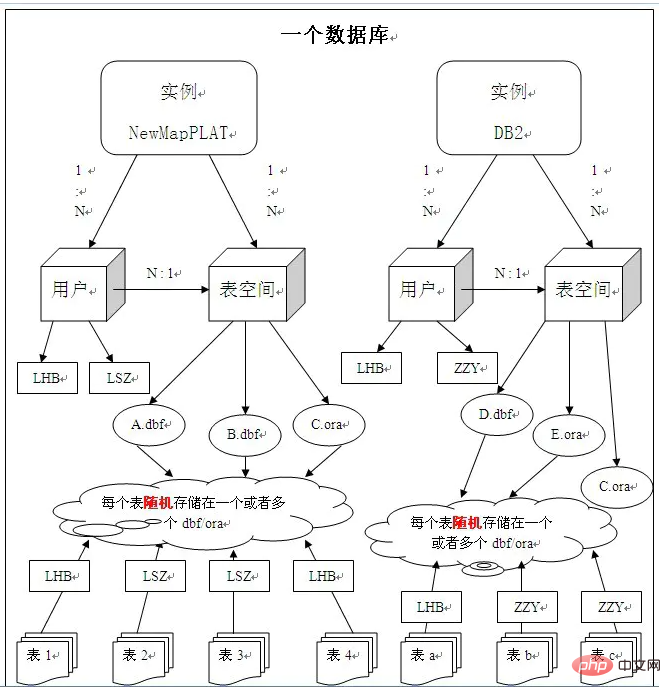
Supplement
su - oracle sqlplus /nolog; (sqlplus 用户名/密码;) select table_name from user_tables; //当前用户的表 1、su – oracle 不是必需,适合于没有DBA密码时使用,可以不用密码来进入sqlplus界面。 2、sqlplus /nolog 或sqlplus system/manager 或./sqlplus ; 3、SQL>connect / as sysdba ;(as sysoper)或 connect internal/oracle AS SYSDBA ;(scott/tiger) conn sys/change_on_install as sysdba; 4、SQL>startup; 启动数据库实例 5、 查看当前的所有数据库: select * from v$database;
The above is the detailed content of Install Oracle11g database on centos. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 How to optimize CentOS HDFS configuration
Apr 14, 2025 pm 07:15 PM
How to optimize CentOS HDFS configuration
Apr 14, 2025 pm 07:15 PM
Improve HDFS performance on CentOS: A comprehensive optimization guide to optimize HDFS (Hadoop distributed file system) on CentOS requires comprehensive consideration of hardware, system configuration and network settings. This article provides a series of optimization strategies to help you improve HDFS performance. 1. Hardware upgrade and selection resource expansion: Increase the CPU, memory and storage capacity of the server as much as possible. High-performance hardware: adopts high-performance network cards and switches to improve network throughput. 2. System configuration fine-tuning kernel parameter adjustment: Modify /etc/sysctl.conf file to optimize kernel parameters such as TCP connection number, file handle number and memory management. For example, adjust TCP connection status and buffer size
 Centos stops maintenance 2024
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
Centos stops maintenance 2024
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
CentOS will be shut down in 2024 because its upstream distribution, RHEL 8, has been shut down. This shutdown will affect the CentOS 8 system, preventing it from continuing to receive updates. Users should plan for migration, and recommended options include CentOS Stream, AlmaLinux, and Rocky Linux to keep the system safe and stable.
 How to check CentOS HDFS configuration
Apr 14, 2025 pm 07:21 PM
How to check CentOS HDFS configuration
Apr 14, 2025 pm 07:21 PM
Complete Guide to Checking HDFS Configuration in CentOS Systems This article will guide you how to effectively check the configuration and running status of HDFS on CentOS systems. The following steps will help you fully understand the setup and operation of HDFS. Verify Hadoop environment variable: First, make sure the Hadoop environment variable is set correctly. In the terminal, execute the following command to verify that Hadoop is installed and configured correctly: hadoopversion Check HDFS configuration file: The core configuration file of HDFS is located in the /etc/hadoop/conf/ directory, where core-site.xml and hdfs-site.xml are crucial. use
 Centos shutdown command line
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:12 PM
Centos shutdown command line
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:12 PM
The CentOS shutdown command is shutdown, and the syntax is shutdown [Options] Time [Information]. Options include: -h Stop the system immediately; -P Turn off the power after shutdown; -r restart; -t Waiting time. Times can be specified as immediate (now), minutes ( minutes), or a specific time (hh:mm). Added information can be displayed in system messages.
 Difference between centos and ubuntu
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:09 PM
Difference between centos and ubuntu
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:09 PM
The key differences between CentOS and Ubuntu are: origin (CentOS originates from Red Hat, for enterprises; Ubuntu originates from Debian, for individuals), package management (CentOS uses yum, focusing on stability; Ubuntu uses apt, for high update frequency), support cycle (CentOS provides 10 years of support, Ubuntu provides 5 years of LTS support), community support (CentOS focuses on stability, Ubuntu provides a wide range of tutorials and documents), uses (CentOS is biased towards servers, Ubuntu is suitable for servers and desktops), other differences include installation simplicity (CentOS is thin)
 What are the backup methods for GitLab on CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 05:33 PM
What are the backup methods for GitLab on CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 05:33 PM
Backup and Recovery Policy of GitLab under CentOS System In order to ensure data security and recoverability, GitLab on CentOS provides a variety of backup methods. This article will introduce several common backup methods, configuration parameters and recovery processes in detail to help you establish a complete GitLab backup and recovery strategy. 1. Manual backup Use the gitlab-rakegitlab:backup:create command to execute manual backup. This command backs up key information such as GitLab repository, database, users, user groups, keys, and permissions. The default backup file is stored in the /var/opt/gitlab/backups directory. You can modify /etc/gitlab
 What files do you need to modify in HDFS configuration CentOS?
Apr 14, 2025 pm 07:27 PM
What files do you need to modify in HDFS configuration CentOS?
Apr 14, 2025 pm 07:27 PM
When configuring Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) on CentOS, the following key configuration files need to be modified: core-site.xml: fs.defaultFS: Specifies the default file system address of HDFS, such as hdfs://localhost:9000. hadoop.tmp.dir: Specifies the storage directory for Hadoop temporary files. hadoop.proxyuser.root.hosts and hadoop.proxyuser.ro
 Centos configuration IP address
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:06 PM
Centos configuration IP address
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:06 PM
Steps to configure IP address in CentOS: View the current network configuration: ip addr Edit the network configuration file: sudo vi /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0 Change IP address: Edit IPADDR= Line changes the subnet mask and gateway (optional): Edit NETMASK= and GATEWAY= Lines Restart the network service: sudo systemctl restart network verification IP address: ip addr




