How many characters is a space?
One space occupies one character, and characters include letters, numbers, arithmetic symbols, punctuation marks and other symbols, as well as some functional symbols; when characters are stored in the computer, the corresponding binary code representing the character should be specified.

#The operating environment of this article: Windows 7 system, Dell G3 computer.
1. A space occupies one character;
2. A Chinese character occupies 2 characters;
3. A letter occupies one character;
4. GB and GBK codes occupy 1 character 2 bytes;
5. UTF8 encoding means that one character occupies 3 bytes;
6. Unicode encoding means that one character occupies 4 bytes;
7. Different encoding intervals are used The bytes represented are also different.
Related introduction:
Characters include letters, numbers, arithmetic symbols, punctuation marks and other symbols, as well as some functional symbols. When characters are stored in the computer, the corresponding binary code representing the character should be specified. The selection of codes should be consistent with the specifications of the relevant peripheral devices. These peripheral devices include keyboard console input and output, printer output, and so on. When characters are input, they are automatically converted into binary codes and stored in the machine; when output, the binary codes in the computer are automatically converted into characters. The conversion between the two is realized by peripheral devices. Character is the smallest data access unit in the data structure. A character is usually represented by 8 binary bits (one byte), but there are also a few computer systems that use 6 binary character representations. The size of the character set in a system is completely determined by the system itself. The number of characters available for computers is generally 128 to 256 (excluding Chinese characters). After each character enters the computer, it will be converted into an 8-bit binary number. Different computer systems and different languages have different character ranges.
In ASCII encoding, one English alphabetic character requires 1 byte to store. In GB 2312 encoding or GBK encoding, one Chinese character storage requires 2 bytes. In UTF-8 encoding, the storage of an English alphabetic character requires 1 byte, and the storage of a Chinese character requires 3 to 4 bytes. In UTF-16 encoding, the storage of an English alphabetic character or a Chinese character requires 2 bytes (some Chinese characters in the Unicode extension area require 4 bytes to store). In UTF-32 encoding, the storage of any character in the world requires 4 bytes.
The above is the detailed content of How many characters is a space?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 What does a space mean in mysql?
Jul 20, 2023 pm 05:17 PM
What does a space mean in mysql?
Jul 20, 2023 pm 05:17 PM
MySQL A space is a special character used to separate keywords, identifiers, values, and other statement elements. Spaces can be used in multiple locations in a SQL statement and usually do not affect the execution of the statement. The purpose of spaces: 1. Used to separate keywords and identifiers; 2. Used to separate operators and values; 3. Used to separate functions, columns and table aliases; 4. Used for indentation and alignment.
 How to type arrows in Word
Apr 16, 2023 pm 11:37 PM
How to type arrows in Word
Apr 16, 2023 pm 11:37 PM
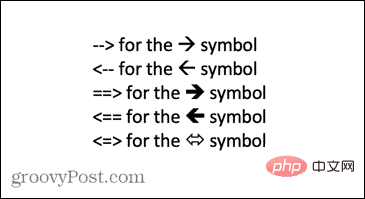
How to use AutoCorrect to type arrows in Word One of the fastest ways to type arrows in Word is to use the predefined AutoCorrect shortcuts. If you type a specific sequence of characters, Word automatically converts those characters into arrow symbols. You can draw many different arrow styles using this method. To type an arrow in Word using AutoCorrect: Move your cursor to the location in the document where you want the arrow to appear. Type one of the following character combinations: If you don't want what you type to be corrected to an arrow symbol, press the backspace key on your keyboard to
 How to apply superscript and subscript formatting options in Microsoft Excel
Apr 14, 2023 pm 12:07 PM
How to apply superscript and subscript formatting options in Microsoft Excel
Apr 14, 2023 pm 12:07 PM
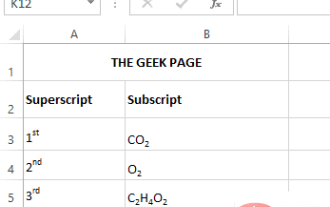
A superscript is a character or characters, either letters or numbers, that you need to set slightly above the normal line of text. For example, if you need to write 1st, the letter st needs to be slightly higher than the character 1. Likewise, a subscript is a group of characters or a single character and needs to be set slightly lower than normal text level. For example, when you write a chemical formula, you need to place the numbers below the normal line of characters. The following screenshots show some examples of superscript and subscript formatting. Although it may seem like a daunting task, applying superscript and subscript formatting to your text is actually quite simple. In this article, we will explain in some simple steps how to easily format text using superscript or subscript. Hope you enjoyed reading this article. How to apply superscript in Excel
 The difference between full-width spaces and half-width spaces
Mar 25, 2024 pm 12:45 PM
The difference between full-width spaces and half-width spaces
Mar 25, 2024 pm 12:45 PM
The difference between full-width spaces and half-width spaces. When we use word processing software or edit text content, we sometimes encounter the concept of spaces. Space is a very basic element in typesetting and formatting text, but many people may not know the difference between full-width spaces and half-width spaces. In daily use, we may feel that full-width spaces and half-width spaces have different effects in different situations, but we may not be aware of the subtle differences. First of all, the difference between full-width spaces and half-width spaces is the width they occupy.
 How do you enter extended characters, such as the degree symbol, on iPhone and Mac?
Apr 22, 2023 pm 02:01 PM
How do you enter extended characters, such as the degree symbol, on iPhone and Mac?
Apr 22, 2023 pm 02:01 PM
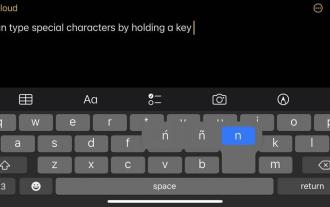
Your physical or numeric keyboard provides a limited number of character options on the surface. However, there are several ways to access accented letters, special characters, and more on iPhone, iPad, and Mac. The standard iOS keyboard gives you quick access to uppercase and lowercase letters, standard numbers, punctuation, and characters. Of course, there are many other characters. You can choose from letters with diacritics to upside-down question marks. You may have stumbled upon a hidden special character. If not, here's how to access them on iPhone, iPad, and Mac. How to Access Extended Characters on iPhone and iPad Getting extended characters on your iPhone or iPad is very simple. In "Information", "
 Use java's Character.isDigit() function to determine whether a character is a number
Jul 27, 2023 am 09:32 AM
Use java's Character.isDigit() function to determine whether a character is a number
Jul 27, 2023 am 09:32 AM
Use Java's Character.isDigit() function to determine whether a character is a numeric character. Characters are represented in the form of ASCII codes internally in the computer. Each character has a corresponding ASCII code. Among them, the ASCII code values corresponding to the numeric characters 0 to 9 are 48 to 57 respectively. To determine whether a character is a number, you can use the isDigit() method provided by the Character class in Java. The isDigit() method is of the Character class
 Correct way to display Chinese characters in matplotlib
Jan 13, 2024 am 11:03 AM
Correct way to display Chinese characters in matplotlib
Jan 13, 2024 am 11:03 AM
Correctly displaying Chinese characters in matplotlib is a problem often encountered by many Chinese users. By default, matplotlib uses English fonts and cannot display Chinese characters correctly. To solve this problem, we need to set the correct Chinese font and apply it to matplotlib. Below are some specific code examples to help you display Chinese characters correctly in matplotlib. First, we need to import the required libraries: importmatplot
 How to replace spaces in vue
Dec 22, 2022 am 09:40 AM
How to replace spaces in vue
Dec 22, 2022 am 09:40 AM
How to replace spaces in Vue: 1. Create a Vue sample file; 2. Replace all spaces through the regular expression "string = string.replace(/\s/g," ");"; 3. Through "console. log(string);" just output the replaced string.





