What does vue.js componentization mean?
vue.js componentization is used to divide the UI page into several components for combination and nesting; componentization is an efficient way to deal with complex application systems and better clarify the role of functional modules; the purpose is In order to decouple, complex systems are split into multiple components, and component boundaries and responsibilities are separated to facilitate independent upgrades and maintenance.

The operating environment of this tutorial: Windows 7 system, Vue version 2.9.6, Dell G3 computer.
Recommended: "vue Tutorial"
Vue is a progressive framework for building user interfaces. It has the following characteristics:
Progressive framework, using bottom-up incremental development design
Template two-way binding mechanism
Use directives to encapsulate DOM
Component design idea
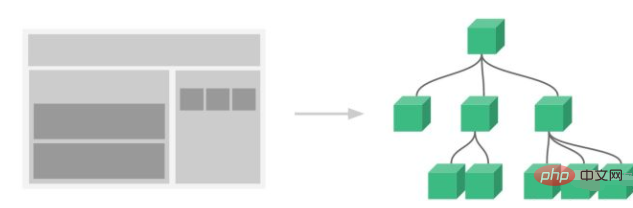
Vue's componentization divides the UI page into several components for combination and nesting.
Vue componentization
Componentization is an efficient way to handle complex application systems and better clarify the role of functional modules. The purpose is: to decouple, split complex systems into multiple components, separate component boundaries and responsibilities, and facilitate independent upgrades and maintenance.
We all know the benefits of componentization without going into details. Components are one of the most powerful functions of Vue.js. Let us use independent and reusable small components to build large-scale applications and improve development efficiency. Faster and more agile.
For better reuse, here we take creating a pop-up component as an example to talk about how to build a component library for a project.
Vue component standardization
Without rules, it is difficult to achieve success.
To build a good component library, you should set some general rules at the beginning.
1. Naming
The naming of components should have nothing to do with the business, but should be named according to the functions implemented by the components. At the same time, it should also be distinguished from business file naming, and some unique prefixes can be added. For example, here, "UI" is added to the prefix of all components, and the pop-up component is named "UIDialog".
2. Implementation
Reusable components should implement common functions, and what they implement should be:
UI display
with users Interaction (event)
Animation effect
Reusable components should minimize dependence on external conditions. It is best not to split an independent functional component into several small components to implement.
3. Understand component properties and events
In Vue components, states are called props, events are called events, and fragments are called slots.
props allows the external environment to pass data to components.
Declare your own properties through props. It can be understood through the dialog/index.vue code above. Its type is: String, Number, Boolean, Array, Object, Date, Function, Symbol.
events allows components to trigger side effects from the external environment.
You can use v-on to listen to Dom events. Syntax: v-on: event type = "event processing function name". The abbreviation is: @event type = "event processing function name".
An intuitive example is:
<ulid="app">
<liv-on:click="clickMe">单击事件</li>
</ul>
<script>
var app = new Vue({
el : '#app',
data : {
},
methods : {
clickMe : function(){
console.log('单击事件发生');
}
}
})
</script>slot allows the external environment to combine additional content in the component.
slot is equivalent to setting a place in the subcomponent. When it is called and something is placed between its opening and closing tags, it will put these things in the slot. Through slot, when we call the component, we can change the actual content of the component as needed.
For example, child component template:
<div> <h2 id="我是子组件的标题">我是子组件的标题</h2> <slot> 只有在没有要分发的内容时才会显示。 </slot> </div>
Parent component template:
<div> <h1 id="我是父组件的标题">我是父组件的标题</h1> <my-component> <p>这是一些初始内容</p> </my-component> </div>
Rendering result:
<div> <h1 id="我是父组件的标题">我是父组件的标题</h1> <div> <h2 id="我是子组件的标题">我是子组件的标题</h2> <p>这是一些初始内容</p> </div> </div>
The above is the detailed content of What does vue.js componentization mean?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to use echarts in vue
May 09, 2024 pm 04:24 PM
How to use echarts in vue
May 09, 2024 pm 04:24 PM
Using ECharts in Vue makes it easy to add data visualization capabilities to your application. Specific steps include: installing ECharts and Vue ECharts packages, introducing ECharts, creating chart components, configuring options, using chart components, making charts responsive to Vue data, adding interactive features, and using advanced usage.
 The role of export default in vue
May 09, 2024 pm 06:48 PM
The role of export default in vue
May 09, 2024 pm 06:48 PM
Question: What is the role of export default in Vue? Detailed description: export default defines the default export of the component. When importing, components are automatically imported. Simplify the import process, improve clarity and prevent conflicts. Commonly used for exporting individual components, using both named and default exports, and registering global components.
 How to use map function in vue
May 09, 2024 pm 06:54 PM
How to use map function in vue
May 09, 2024 pm 06:54 PM
The Vue.js map function is a built-in higher-order function that creates a new array where each element is the transformed result of each element in the original array. The syntax is map(callbackFn), where callbackFn receives each element in the array as the first argument, optionally the index as the second argument, and returns a value. The map function does not change the original array.
 The role of onmounted in vue
May 09, 2024 pm 02:51 PM
The role of onmounted in vue
May 09, 2024 pm 02:51 PM
onMounted is a component mounting life cycle hook in Vue. Its function is to perform initialization operations after the component is mounted to the DOM, such as obtaining references to DOM elements, setting data, sending HTTP requests, registering event listeners, etc. It is only called once when the component is mounted. If you need to perform operations after the component is updated or before it is destroyed, you can use other lifecycle hooks.
 What are hooks in vue
May 09, 2024 pm 06:33 PM
What are hooks in vue
May 09, 2024 pm 06:33 PM
Vue hooks are callback functions that perform actions on specific events or lifecycle stages. They include life cycle hooks (such as beforeCreate, mounted, beforeDestroy), event handling hooks (such as click, input, keydown) and custom hooks. Hooks enhance component control, respond to component life cycles, handle user interactions and improve component reusability. To use hooks, just define the hook function, execute the logic and return an optional value.
 Promise usage in vue
May 09, 2024 pm 03:27 PM
Promise usage in vue
May 09, 2024 pm 03:27 PM
Promise can be used to handle asynchronous operations in Vue.js. The steps include: creating a Promise object, performing an asynchronous operation and calling resolve or reject based on the result, and processing the Promise result (use .then() to handle success, .catch() to handle errors) . Advantages of Promises include readability, ease of debugging, and composability.
 validator method in vue
May 09, 2024 pm 04:09 PM
validator method in vue
May 09, 2024 pm 04:09 PM
The Validator method is the built-in validation method of Vue.js and is used to write custom form validation rules. The usage steps include: importing the Validator library; creating validation rules; instantiating Validator; adding validation rules; validating input; and obtaining validation results.
 How to disable the change event in vue
May 09, 2024 pm 07:21 PM
How to disable the change event in vue
May 09, 2024 pm 07:21 PM
In Vue, the change event can be disabled in the following five ways: use the .disabled modifier to set the disabled element attribute using the v-on directive and preventDefault using the methods attribute and disableChange using the v-bind directive and :disabled






