What is the difference between vps and cloud server
The difference between vps and cloud servers is: 1. vps has a fixed performance level, and cloud servers have unlimited scalability; 2. vps runs in an independent environment, and cloud servers are completely independent from other servers 3. The scalability of vps is limited, and the scalability of cloud hosts is much higher.

#The operating environment of this article: Windows 7 system, Dell G3 computer.
The difference between vps and cloud servers:
The vps host is part of an independent server. Using a VPS means that you only own a certain part of the server's space and a set of resources assigned to you. Users can customize these resources in a way that suits them.
(Learning video sharing: Programming video)
Cloud hosts can contain an almost unlimited number of computers. All of these physical servers are in different locations, but they work together to form the "cloud," essentially giving users access to the entire infrastructure of connected servers and data storage.
Performance Difference
VPS has a fixed performance level. Because a server is shared with other users and is only allocated a certain amount of data and bandwidth, there are no additional resources at your disposal or use. Additionally, if the server itself fails, all VPS on that computer will also be down.
Cloud servers have unlimited scalability. With countless different computers forming part of a network, it is almost impossible to encounter a situation where resources are limited. Likewise, if any one server (or even an entire group of servers) fails, a computer at another location will take over the workload until the problem is resolved.
Security is different
VPS is much more secure than a shared hosting environment. Each VPS runs in an independent environment, completely separated from all other VPS sharing the machine. This means that even if one VPS is infected with a virus, it will not affect other VPS. However, if an entire computer becomes infected, the entire fleet is affected.
Cloud servers work completely independently from all other servers. Even if one of the nodes fails, it can automatically switch to other normal server nodes.
Scalability
The scalability of a VPS host is limited, which is determined by its physical host, and the physical computer will limit such additions. If a website requires more resources than the service allocates, the website owner will need to upgrade to a new account or switch to a different type of server, both of which involve some downtime.
Cloud hosting is much more scalable. Because each cloud is made up of hundreds or thousands of different physical computers, it can scale based on user needs. You only pay for the data used in any given period, which also makes costs more flexible.
As with any hosting decision, choosing a vps or cloud server really comes down to the individual business and its specific needs. Websites that are growing rapidly and need to handle large amounts of traffic should choose cloud servers even if they only consider scalability.
The above is the detailed content of What is the difference between vps and cloud server. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1377
1377
 52
52
 How to deploy SpringBoot project to cloud server
May 13, 2023 pm 12:49 PM
How to deploy SpringBoot project to cloud server
May 13, 2023 pm 12:49 PM
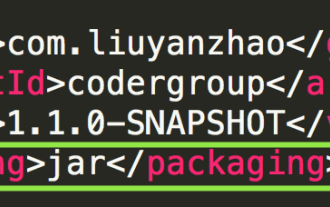
1. Set the Maven packaging type here to jar. According to my experience, packaging into a war is a pitfall, and you need to follow Tomcat, and you will encounter many problems when deploying for the first time. By packaging it into a jar, you don’t need to install Tomcat. You can start the project with just one command: java-jarcodergroup-1.0.0-SNAPSHOT.jar. 2. Packaging the SpringBoot project. I use IntelliJIDEA here. Directly in the Maven plug-in, click package. Then you can see in the target of the project that the jar file is uploaded to the server. 3. Install MySQL and JDK for convenience
 How to manually configure DNS for Linux cloud server
May 16, 2023 pm 03:22 PM
How to manually configure DNS for Linux cloud server
May 16, 2023 pm 03:22 PM
Configuring the DNS service of the cloud server is indispensable for the cloud server to access the public domain name. DNS is the record of the domain name pointing to the IP. Only by setting up the DNS server can the public network resolution record of the domain name be obtained. The local DNS server configuration information is stored in the file /etc/resolv.conf. Write the following DNS configuration nameserver8.8.8.8nameserver114.114.114.114 in the configuration information. This will successfully set up two default dns servers, which will take effect immediately after saving. If you need to specify the resolution record of a certain domain name, you need to use the /etc/hosts file and write the ip address, space, and domain name in the configuration information to manually specify it.
 Which cloud server is cheaper?
Mar 21, 2024 am 09:54 AM
Which cloud server is cheaper?
Mar 21, 2024 am 09:54 AM
Cost-effective cloud server service providers include Alibaba Cloud, Tencent Cloud, Amazon AWS and Huawei Cloud. These service providers provide rich product lines, affordable prices, complete ecosystems and technical support. When choosing, in addition to price, you should also consider stability, performance, security, customer service, etc., and choose the service provider that best suits your needs after a comprehensive evaluation.
 What is the difference between lightweight application server and cloud server?
Jul 27, 2023 am 10:12 AM
What is the difference between lightweight application server and cloud server?
Jul 27, 2023 am 10:12 AM
The differences between lightweight application servers and cloud servers are: 1. Lightweight application servers have smaller hardware configurations and resource consumption, while cloud servers have larger hardware configurations and resources; 2. Cloud servers provide more functions and services , while lightweight application servers do not; 3. Lightweight application servers are usually simpler and easier to use, while cloud servers require more technical knowledge and management experience; 4. Lightweight application servers are relatively cheap, while cloud servers cost more Higher.
 Teach you how to deploy NGINX and PM2 on a VPS server
Sep 27, 2023 pm 01:25 PM
Teach you how to deploy NGINX and PM2 on a VPS server
Sep 27, 2023 pm 01:25 PM
Teach you how to deploy NGINX and PM2 on a VPS server. Preface: The deployment of a VPS server is one of the key steps for a website or application. Here, I will introduce to you how to deploy NGINX and PM2 on a VPS server. These two tools can greatly improve the performance and stability of the website. This article will introduce the installation and configuration process in detail and provide specific code examples. Install NGINX: First, we need to install NGINX as our web server. 1.1 Update apt-get package management
 How to deploy Java projects to cloud servers
May 11, 2023 am 10:58 AM
How to deploy Java projects to cloud servers
May 11, 2023 am 10:58 AM
1. When purchasing a cloud server and installing the system, you usually choose which operating system to install. I usually use CentOS, either 6.x or 7.x. 2. Installing the Pagoda Panel is the same on any server, but different operating systems may have different commands. 1. The account and password for ssh connection to the server are usually set when purchasing the server, and can be modified later. If ssh cannot connect, make sure port 22 is allowed. 2. Type the installation command Centos installation script yuminstall-ywget&&wget-Oinstall.shhttp://download.bt.cn/install/install_6
 How to install MariaDB database on Debian 12
Feb 20, 2024 pm 02:24 PM
How to install MariaDB database on Debian 12
Feb 20, 2024 pm 02:24 PM
MariaDB is an open source multi-threaded relational database management system and a replacement for MySQL. MariaDB is the default replacement for MySQL in Debian. This tutorial explains how to install MariaDB on Debian12. Preparation conditions 1. A VPS virtual machine with Debian12 installed (it is recommended that you purchase an Alibaba Cloud VPS or Tencent Cloud VPS virtual host. If you prefer foreign servers, it is recommended that you try VPS on Vultr, and you will receive a $50 trial experience when you register) , very cost-effective), of course you can also use it on your own computer or virtual machine. 2. If you use VPS, for security reasons, it is recommended to use a non-root account, which can be done in Debian12
 NGINX PM2 VPS: Building a resilient application service infrastructure
Sep 27, 2023 pm 03:49 PM
NGINX PM2 VPS: Building a resilient application service infrastructure
Sep 27, 2023 pm 03:49 PM
NGINXPM2VPS: Building a flexible application service infrastructure requires specific code examples. With the development of the Internet and the increase in application requirements, building a flexible application service infrastructure has become an important technical challenge. NGINX, PM2 and VPS (VirtualPrivateServer), as three important technical components, can help us achieve high availability and high performance application deployment and management. This article describes how to use these three components to build a resilient application service infrastructure and



