What are the computer performance indicators?
Computer performance indicators include: 1. Computer speed; 2. Word length; 3. Storage cycle; 4. Storage capacity. A computer is a modern electronic computing machine used for high-speed calculations. It can perform numerical calculations and logical calculations, and also has a storage and memory function.

The operating environment of this tutorial: Windows 7 system, Dell G3 computer.
The main performance indicators of a computer include computer speed, word length, storage cycle, and storage capacity.
Computer, commonly known as computer, is a modern electronic computing machine used for high-speed calculations. It can perform numerical calculations, logical calculations, and also has storage and memory functions. It is a modern intelligent electronic device that can run according to the program and process massive data automatically and at high speed.
It is composed of a hardware system and a software system. A computer without any software installed is called a bare metal computer. It can be divided into five categories: supercomputer, industrial control computer, network computer, personal computer, and embedded computer. The more advanced computers include biological computers, photon computers, quantum computers, etc.
Computer inventor John von Neumann. The computer is one of the most advanced scientific and technological inventions in the 20th century. It has had an extremely important impact on human production activities and social activities, and is developing rapidly with strong vitality. Its application fields have expanded from its initial application in military scientific research to various fields of society. It has formed a huge computer industry, driven technological progress on a global scale, and triggered profound social changes. Computers have been used in general schools and enterprises. Public institutions have entered the homes of ordinary people and become an indispensable tool in the information society.
Development History
Before 1946
The evolution of computing tools has gone through different stages from simple to complex, from low-level to advanced, such as from The knotted ropes in "Knotting Notes" include abacus chips, abacus slide rules, mechanical computers, etc. They played their respective historical roles in different historical periods, and also inspired the development ideas of modern electronic computers.
In 1889, American scientist Herman Hollery developed an electric tabulating machine based on electricity to store calculation data.
In 1930, American scientist Vannevar Bush built the world's first analog electronic computer.
On February 14, 1946, the world's first electronic computer "Electronic Numerical And Calculator" (ENIAC Electronic Numerical And Calculator) customized by the U.S. military was launched at the University of Pennsylvania. ENIAC (Chinese name: ENIAC) was developed by the Auberdine Weapons Testing Site in the United States to meet the needs of calculating ballistics. This calculator uses 17,840 electron tubes, is 80 feet × 8 feet in size, and weighs 28t ( tons), the power consumption is 170kW, its computing speed is 5,000 addition operations per second, and the cost is approximately US$487,000. The advent of ENIAC has epoch-making significance, indicating the arrival of the electronic computer era. In the next 60 years or so, computer technology has developed at an alarming rate. The performance-price ratio of any technology can increase by 6 orders of magnitude in 30 years.
First generation computer
First generation: tube digital machine (1946-1958)
In terms of hardware, the logic components used vacuum tubes and the main memory used mercury Delay line, cathode ray oscilloscope tube electrostatic memory, magnetic drum, magnetic core; external memory uses magnetic tape. The software uses machine language and assembly language. The application fields are mainly military and scientific computing.
The disadvantages are large size, high power consumption and poor reliability. The speed is slow (generally thousands to tens of thousands of times per second) and expensive, but it lays the foundation for future computer development.
Second Generation Computer
Second Generation: Transistor Digital Machine (1958-1964)
Software operating systems, high-level languages and their compiler application fields and Mainly scientific computing and transaction processing, and began to enter the field of industrial control. It is characterized by reduced size, reduced energy consumption, improved reliability, increased computing speed (generally 100,000 operations per second, and can be as high as 3 million operations), and performance that is greatly improved compared to the first generation computers.
The third generation of computers
The third generation: integrated circuit digital machine (1964-1970)
In terms of hardware, the logic components use medium and small scale integrated circuits (MSI) , SSI), the main memory still uses magnetic cores. In terms of software, time-sharing operating systems and structured and large-scale programming methods have emerged. It is characterized by faster speed (generally millions to tens of millions of times per second), reliability has been significantly improved, prices have further dropped, and products have become generalized, serialized and standardized. Application fields began to enter the fields of word processing and graphics and image processing.
Fourth Generation Computer
The 4th Generation: Large Scale Integrated Circuit Computer (1970 to present)
In terms of hardware, logic components use large-scale and very large-scale integrated circuits ( LSI and VLSI). In terms of software, database management systems, network management systems and object-oriented languages have emerged. In 1971, the world's first microprocessor was born in Silicon Valley, USA, ushering in a new era of microcomputers. The application fields are gradually moving from scientific computing, transaction management, and process control to the home.
Due to the development of integration technology, semiconductor chips have become more integrated. Each chip can accommodate tens of thousands or even millions of transistors, and can integrate arithmetic units and controllers on one chip, thus leading to the emergence of micro-controllers. Processor, and can be assembled into a microcomputer using a microprocessor and large-scale and very large-scale integrated circuits, which is what we often call a microcomputer or PC. Microcomputers are small, cheap, and easy to use, but their functions and computing speed have reached or even exceeded those of large computers in the past. On the other hand, various logic chips manufactured by large-scale and ultra-large-scale integrated circuits have been used to create supercomputers that are not very large in size but can operate at a speed of 100 million or even billions of operations. After our country successfully developed the Galaxy I supercomputer that can perform 100 million operations per second in 1983, it also successfully developed the Galaxy II general-purpose parallel supercomputer that can perform one billion operations per second in 1993. This period also produced a new generation of programming languages, database management systems, and network software.
With the changes in physical components and devices, not only the computer host has undergone upgrading, but its external devices are also constantly changing. For example, external memory has developed from the initial cathode ray display tube to magnetic cores and magnetic drums, and later to general-purpose magnetic disks. Nowadays, smaller, larger, and faster compact discs (CD-ROMs) have appeared. ).
Related recommendations: windows
The above is the detailed content of What are the computer performance indicators?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
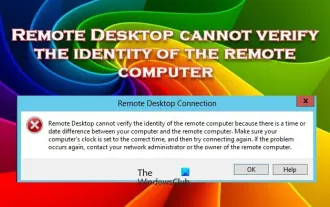 Remote Desktop cannot authenticate the remote computer's identity
Feb 29, 2024 pm 12:30 PM
Remote Desktop cannot authenticate the remote computer's identity
Feb 29, 2024 pm 12:30 PM
Windows Remote Desktop Service allows users to access computers remotely, which is very convenient for people who need to work remotely. However, problems can be encountered when users cannot connect to the remote computer or when Remote Desktop cannot authenticate the computer's identity. This may be caused by network connection issues or certificate verification failure. In this case, the user may need to check the network connection, ensure that the remote computer is online, and try to reconnect. Also, ensuring that the remote computer's authentication options are configured correctly is key to resolving the issue. Such problems with Windows Remote Desktop Services can usually be resolved by carefully checking and adjusting settings. Remote Desktop cannot verify the identity of the remote computer due to a time or date difference. Please make sure your calculations
 2024 CSRankings National Computer Science Rankings Released! CMU dominates the list, MIT falls out of the top 5
Mar 25, 2024 pm 06:01 PM
2024 CSRankings National Computer Science Rankings Released! CMU dominates the list, MIT falls out of the top 5
Mar 25, 2024 pm 06:01 PM
The 2024CSRankings National Computer Science Major Rankings have just been released! This year, in the ranking of the best CS universities in the United States, Carnegie Mellon University (CMU) ranks among the best in the country and in the field of CS, while the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign (UIUC) has been ranked second for six consecutive years. Georgia Tech ranked third. Then, Stanford University, University of California at San Diego, University of Michigan, and University of Washington tied for fourth place in the world. It is worth noting that MIT's ranking fell and fell out of the top five. CSRankings is a global university ranking project in the field of computer science initiated by Professor Emery Berger of the School of Computer and Information Sciences at the University of Massachusetts Amherst. The ranking is based on objective
 What is e in computer
Aug 31, 2023 am 09:36 AM
What is e in computer
Aug 31, 2023 am 09:36 AM
The "e" of computer is the scientific notation symbol. The letter "e" is used as the exponent separator in scientific notation, which means "multiplied to the power of 10". In scientific notation, a number is usually written as M × 10^E, where M is a number between 1 and 10 and E represents the exponent.
 Fix: Microsoft Teams error code 80090016 Your computer's Trusted Platform module has failed
Apr 19, 2023 pm 09:28 PM
Fix: Microsoft Teams error code 80090016 Your computer's Trusted Platform module has failed
Apr 19, 2023 pm 09:28 PM
<p>MSTeams is the trusted platform to communicate, chat or call with teammates and colleagues. Error code 80090016 on MSTeams and the message <strong>Your computer's Trusted Platform Module has failed</strong> may cause difficulty logging in. The app will not allow you to log in until the error code is resolved. If you encounter such messages while opening MS Teams or any other Microsoft application, then this article can guide you to resolve the issue. </p><h2&
 What does computer cu mean?
Aug 15, 2023 am 09:58 AM
What does computer cu mean?
Aug 15, 2023 am 09:58 AM
The meaning of cu in a computer depends on the context: 1. Control Unit, in the central processor of a computer, CU is the component responsible for coordinating and controlling the entire computing process; 2. Compute Unit, in a graphics processor or other accelerated processor, CU is the basic unit for processing parallel computing tasks.
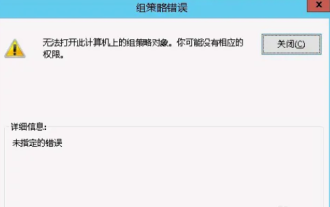 Unable to open the Group Policy object on this computer
Feb 07, 2024 pm 02:00 PM
Unable to open the Group Policy object on this computer
Feb 07, 2024 pm 02:00 PM
Occasionally, the operating system may malfunction when using a computer. The problem I encountered today was that when accessing gpedit.msc, the system prompted that the Group Policy object could not be opened because the correct permissions may be lacking. The Group Policy object on this computer could not be opened. Solution: 1. When accessing gpedit.msc, the system prompts that the Group Policy object on this computer cannot be opened because of lack of permissions. Details: The system cannot locate the path specified. 2. After the user clicks the close button, the following error window pops up. 3. Check the log records immediately and combine the recorded information to find that the problem lies in the C:\Windows\System32\GroupPolicy\Machine\registry.pol file
 What should I do if steam cannot connect to the remote computer?
Mar 01, 2023 pm 02:20 PM
What should I do if steam cannot connect to the remote computer?
Mar 01, 2023 pm 02:20 PM
Solution to the problem that steam cannot connect to the remote computer: 1. In the game platform, click the "steam" option in the upper left corner; 2. Open the menu and select the "Settings" option; 3. Select the "Remote Play" option; 4. Check Activate the "Remote Play" function and click the "OK" button.
 Python script to log out of computer
Sep 05, 2023 am 08:37 AM
Python script to log out of computer
Sep 05, 2023 am 08:37 AM
In today's digital age, automation plays a vital role in streamlining and simplifying various tasks. One of these tasks is to log off the computer, which is usually done manually by selecting the logout option from the operating system's user interface. But what if we could automate this process using a Python script? In this blog post, we'll explore how to create a Python script that can log off your computer with just a few lines of code. In this article, we'll walk through the step-by-step process of creating a Python script for logging out of your computer. We'll cover the necessary prerequisites, discuss different ways to log out programmatically, and provide a step-by-step guide to writing the script. Additionally, we will address platform-specific considerations and highlight best practices



