
The protocol used to resolve domain names is: Domain Name Resolution Protocol, also known as DNS protocol. DNS is a core service of the Internet. As a distributed database that can map domain names and IP addresses to each other, it allows people to access the Internet more conveniently without having to remember IP strings that can be directly read by machines.

Related recommendations: "Programming Tutorial"
The protocol used to resolve domain names is: domain name resolution protocol, also known as DNS protocol.
DNS is the abbreviation of Domain Name System and is a core service of the Internet. As a distributed database that can map domain names and IP addresses to each other, it can make people more convenient access the Internet without having to remember an IP number string that can be read directly by the machine. This is also the official statement of DNS.
To put it bluntly: communication is carried out through IP addresses on the Internet. However, IP addresses are expressed in numbers, which are difficult to remember (such as 116.213.120.232), so each IP is given a domain name that is easier for humans to remember (such as www.google.com), and DNS is used to resolve the domain name into IP (parse the naming format that is easy for people to understand into a format that the computer can understand, or translate the IP into a domain name)
The role of the DNS service: resolve the domain name into an IP address
The client sends a domain name query request to the DNS server (the DNS server has its own IP address)
The DNS server informs the client of the IP address of the Web server
Communication between client and Web server
DNS is a hierarchical distributed database system that can map domain names and IP addresses to each other. It mainly includes the following three Components:
(1) Domain name space and resource record;
(2) Domain name server (name server);
(3)Resolver.
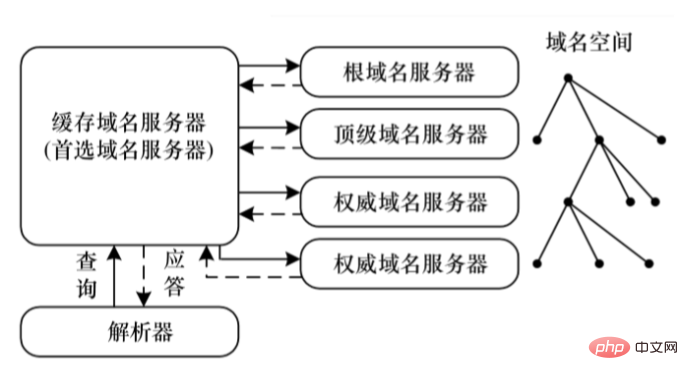
The DNS system uses recursive query requests to respond to user queries. The general process is as follows:
(1) The client first queries the preferred domain name server.
(2) The preferred domain name server checks the local resource record. If it exists, it will give an authoritative answer. If it does not exist, it will check the local cache. If there is a record, it will directly return the result. If neither the local resource record nor the cache record exists, the root domain name server is queried.
(3) The root domain name server returns the address of the authoritative domain name server of the corresponding top-level domain, and the preferred domain name server continues to query the top-level authoritative domain name server.
(4) The top-level authoritative domain name server returns the authoritative domain name server address of the secondary domain. The preferred domain name server iterates the query until it obtains an authoritative answer to the query domain name and saves it in the local cache. And return it to the client to complete the query. At present, most networks will open DNS services, and DNS packets will not be intercepted by network security protection equipment such as firewalls. Therefore, covert channels can be established based on the DNS protocol to smoothly pass through the firewall and covertly between the client and the server. transfer data.
To read more related articles, please visit PHP Chinese website! !
The above is the detailed content of What is the protocol used to resolve domain names?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 linux scheduled shutdown command
linux scheduled shutdown command
 The role of Apple's Do Not Disturb mode
The role of Apple's Do Not Disturb mode
 How to solve the problem of garbled characters when opening a web page
How to solve the problem of garbled characters when opening a web page
 How to connect to access database in vb
How to connect to access database in vb
 Stepper motor control method
Stepper motor control method
 What are the web servers?
What are the web servers?
 What's going on when I can't connect to the network?
What's going on when I can't connect to the network?
 Detailed explanation of onbeforeunload event
Detailed explanation of onbeforeunload event