How to check the process in linux?
How to view processes in Linux: 1. Use the "ps aux" command to view, which can display process information in a simple list; 2. Use the "ps -elf" command to view; 3. Use " top" command to view; 4. Use the "pstree -aup" command to view.

#The operating environment of this tutorial: linux5.9.8 system, thinkpad t480 computer.
How to view the process in Linux
The process is the program code running in the CPU and memory, and each process can create One or more processes (parent and child processes).
**View process method: **
First method:
ps aux
ps command is used to report the process status of the current system. You can use the kill command to interrupt and delete unnecessary programs at any time. The ps command is the most basic and also very powerful process viewing command. Use this command to determine which processes are running and running status, whether the process has ended, whether the process is zombie, which processes occupy too many resources, etc., in short Most of the information can be obtained by executing this command.
a: Display all process information under the current terminal, including processes of other users.
u: Output process information in user-oriented format.
x: Display the processes of the current user in all terminals.
Example:
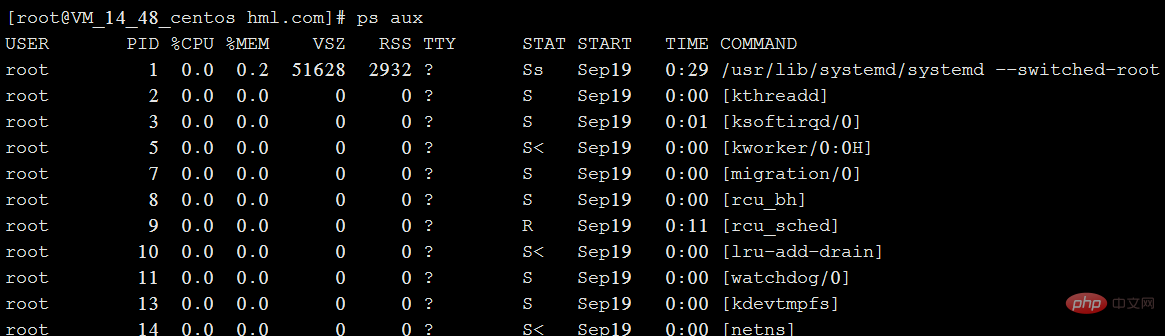
**Explanation of each field in the above figure:**
USER: The name of the user account that started the process
PID: The ID number of the process, which is unique in the current system
%CPU: The percentage occupied by the CPU
%MEM: The percentage occupied by the memory
VSZ: Occupied virtual memory (swap Space)
RSS: The size of resident memory (physical memory) occupied
TTY: On which terminal the process is running. "?" means unknown or no terminal required
STAT: shows the current status of the process, such as S (sleeping), R (running), Z (zombie), < (high priority), N (low priority) ), s (parent process), (foreground process). Processes in a zombie state should be terminated manually.
START: The time to start the process
TIME: The CPU time occupied by the process
COMMAND: The name of the command to start the process
** Summary: ps aux is simple Process information is displayed in list form. **
The second type:
ps -elf
-e: Displays all process information in the system.
-l: Use long (long) format to display process information.
-f: Display process information in full format.
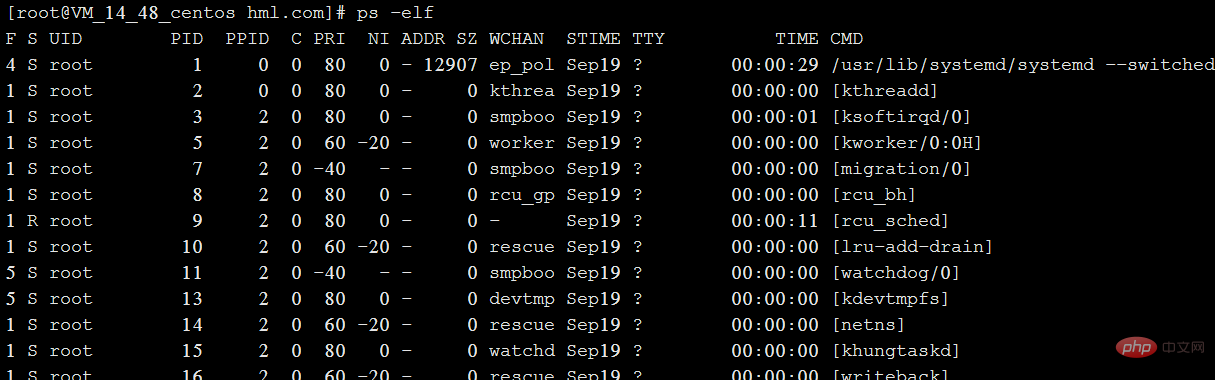
Field explanation in the above figure:
Mostly the same as the first one, PPID is the PID of the parent process.
The third type:
top
Displays process rankings in a full-screen interactive interface, and tracks system resource usage including CPU, memory and other system resources in real time. By default, every three It refreshes once every second and its function is basically similar to the task manager in Windows system.
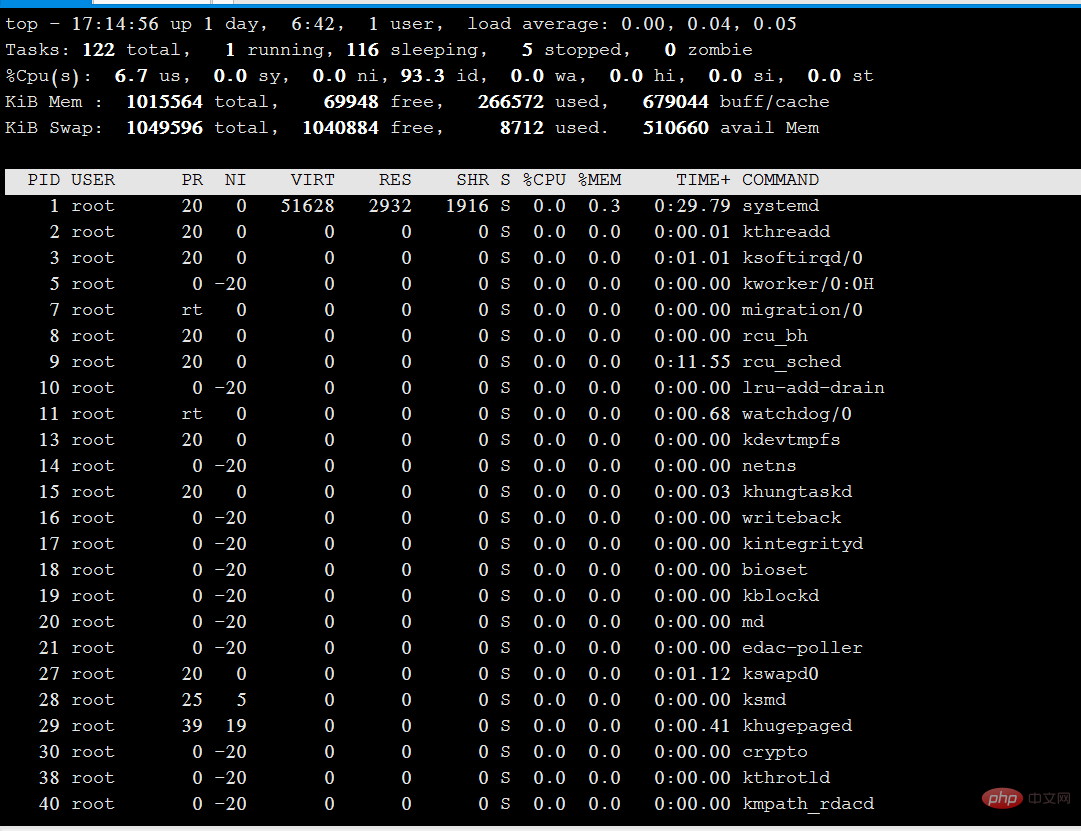
Explanation of the above picture:
Tasks (system tasks) information: total, the total number of processes; running, the number of running processes; sleeping, dormant The number of processes; stopped, the number of terminated processes; zombie, the number of zombie and unresponsive processes.
CPU information: us, occupied by users; sy, occupied by kernel; ni, occupied by priority scheduling; id, occupied by idle CPU; wa, occupied by I/O waiting; hi, occupied by hardware interrupts; si, occupied by software interrupts ; st, virtualization occupation. To understand the idle CPU percentage, mainly look at the %id part.
Mem (memory) information: total, total memory space; used, used memory; free, free memory; buffers, cache area.
Swap (swap space) information: total, total swap space; used, used swap space; free, free swap space; cached, cache space.
Fourth method:
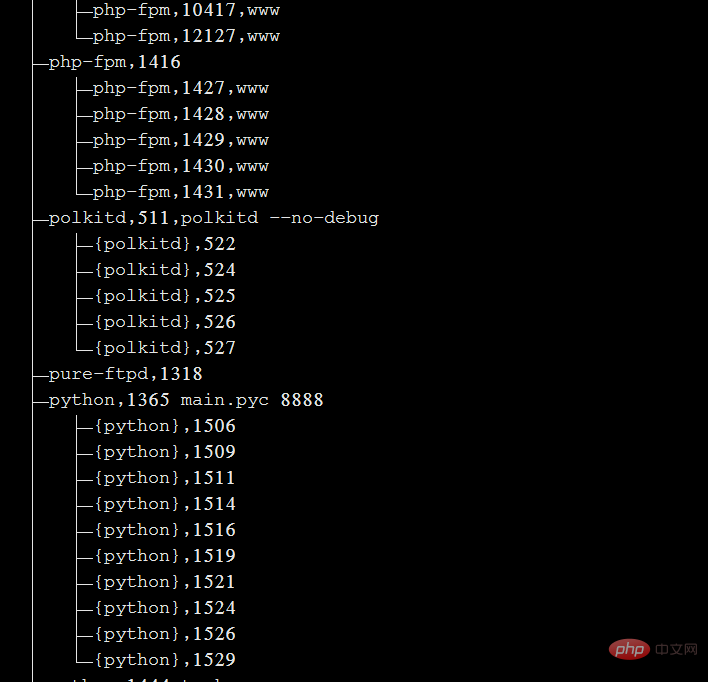
pstree -aup
You can bring |grep to query a specific process. For example, pstree -aup | grep php
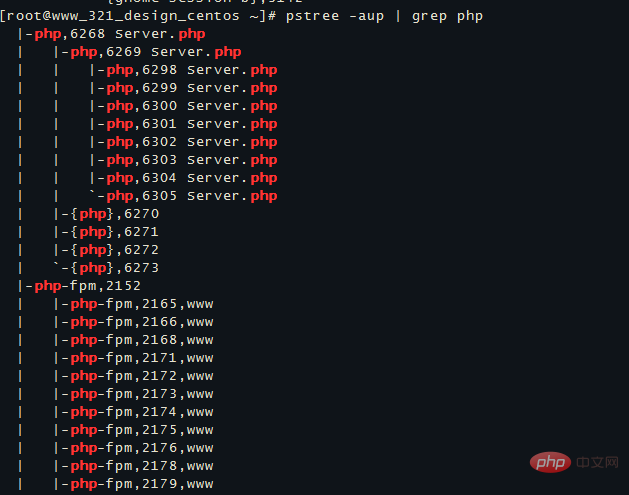
displays the derivation relationship between processes in the form of a tree diagram, and the display effect is relatively intuitive.
-a: Display the complete instructions of each program, including path, parameters or identification of resident services;
-c: Do not use simplified notation;
-G: Use the column of VT100 terminal Drawing characters;
-h: When listing the tree diagram, specifically indicate the currently executing program;
-H
-l: Display the tree diagram in long column format;
-n: Sort by program identification code. The default is to sort by program name;
-p: display program identification code;
-u: display user name;
If you want to read more related articles, please visit PHP Chinese website! !
The above is the detailed content of How to check the process in linux?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 How to start nginx in Linux
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:51 PM
How to start nginx in Linux
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:51 PM
Steps to start Nginx in Linux: Check whether Nginx is installed. Use systemctl start nginx to start the Nginx service. Use systemctl enable nginx to enable automatic startup of Nginx at system startup. Use systemctl status nginx to verify that the startup is successful. Visit http://localhost in a web browser to view the default welcome page.
 How to check whether nginx is started
Apr 14, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
How to check whether nginx is started
Apr 14, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
How to confirm whether Nginx is started: 1. Use the command line: systemctl status nginx (Linux/Unix), netstat -ano | findstr 80 (Windows); 2. Check whether port 80 is open; 3. Check the Nginx startup message in the system log; 4. Use third-party tools, such as Nagios, Zabbix, and Icinga.
 How to start nginx server
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:27 PM
How to start nginx server
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:27 PM
Starting an Nginx server requires different steps according to different operating systems: Linux/Unix system: Install the Nginx package (for example, using apt-get or yum). Use systemctl to start an Nginx service (for example, sudo systemctl start nginx). Windows system: Download and install Windows binary files. Start Nginx using the nginx.exe executable (for example, nginx.exe -c conf\nginx.conf). No matter which operating system you use, you can access the server IP
 How to solve nginx403
Apr 14, 2025 am 10:33 AM
How to solve nginx403
Apr 14, 2025 am 10:33 AM
How to fix Nginx 403 Forbidden error? Check file or directory permissions; 2. Check .htaccess file; 3. Check Nginx configuration file; 4. Restart Nginx. Other possible causes include firewall rules, SELinux settings, or application issues.
 How to solve nginx304 error
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:45 PM
How to solve nginx304 error
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:45 PM
Answer to the question: 304 Not Modified error indicates that the browser has cached the latest resource version of the client request. Solution: 1. Clear the browser cache; 2. Disable the browser cache; 3. Configure Nginx to allow client cache; 4. Check file permissions; 5. Check file hash; 6. Disable CDN or reverse proxy cache; 7. Restart Nginx.
 How to check whether nginx is started?
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:48 PM
How to check whether nginx is started?
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:48 PM
In Linux, use the following command to check whether Nginx is started: systemctl status nginx judges based on the command output: If "Active: active (running)" is displayed, Nginx is started. If "Active: inactive (dead)" is displayed, Nginx is stopped.
 How to solve nginx403 error
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:54 PM
How to solve nginx403 error
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:54 PM
The server does not have permission to access the requested resource, resulting in a nginx 403 error. Solutions include: Check file permissions. Check the .htaccess configuration. Check nginx configuration. Configure SELinux permissions. Check the firewall rules. Troubleshoot other causes such as browser problems, server failures, or other possible errors.
 How to clean nginx error log
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
How to clean nginx error log
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
The error log is located in /var/log/nginx (Linux) or /usr/local/var/log/nginx (macOS). Use the command line to clean up the steps: 1. Back up the original log; 2. Create an empty file as a new log; 3. Restart the Nginx service. Automatic cleaning can also be used with third-party tools such as logrotate or configured.




