What are the three implementation methods of distributed locks?
Three ways to implement distributed locks: 1. Implement distributed locks based on database; 2. Implement distributed locks based on cache (Redis, etc.); 3. Implement distributed locks based on Zookeeper. From a performance perspective (from high to low): "Cache mode > Zookeeper mode > = Database mode".

The operating environment of this article: Windows system, redis 6.0, thinkpad t480 computer.
Three ways to implement distributed locks:
1. Implement distributed locks based on database;
2. Implement distributed locks based on cache (Redis, etc.) ;
3. Implement distributed locks based on Zookeeper;
1. Implement distributed locks based on database
1. Pessimistic lock
Use select...where...for update exclusive lock
Note: Other additional functions are basically the same as implementation one. What needs to be noted here is "where name=lock", the name field must be indexed, Otherwise the table will be locked. In some cases, such as if the table is not large, the MySQL optimizer will not use this index, causing table lock problems.
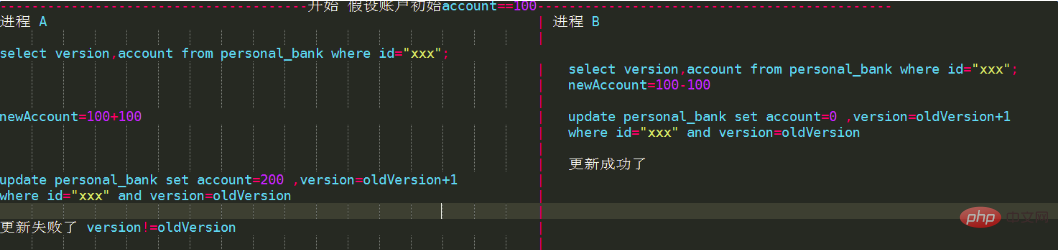
2. Optimistic lock
The biggest difference between the so-called optimistic lock and the previous one is that it is based on the CAS idea. It is not mutually exclusive, does not cause lock waiting and consumes resources, and is considered non-existent during the operation. Concurrency conflicts can only be detected after the update version fails. Our rush sales and flash sales use this implementation to prevent overselling.
Implement optimistic locking by adding an incremental version number field
Second, implement distributed locking based on cache (Redis, etc.)
1. Introduction to using commands:
(1) SETNX
SETNX key val: If and only if the key does not exist, set a string with key val and return 1; if If the key exists, do nothing and return 0.
(2)expire
expire key timeout: Set a timeout for the key, the unit is second. After this time, the lock will be automatically released to avoid deadlock.
(3) delete
delete key: delete key
When using Redis to implement distributed locks, these three commands are mainly used.
2. Implementation idea:
(1) When acquiring a lock, use setnx to lock it, and use the expire command to add a timeout period to the lock. If the time is exceeded, the lock will be automatically released. The value of the lock It is a randomly generated UUID, which is used to judge when releasing the lock.
(2) When acquiring the lock, also set a timeout period for acquisition. If this time is exceeded, acquisition of the lock will be given up.
(3) When releasing a lock, use the UUID to determine whether it is the lock. If it is the lock, execute delete to release the lock.
3. Simple implementation code of distributed lock:
/**
* 分布式锁的简单实现代码 */
public class DistributedLock {
private final JedisPool jedisPool;
public DistributedLock(JedisPool jedisPool) {
this.jedisPool = jedisPool;
}
/**
* 加锁
* @param lockName 锁的key
* @param acquireTimeout 获取超时时间
* @param timeout 锁的超时时间
* @return 锁标识
*/
public String lockWithTimeout(String lockName, long acquireTimeout, long timeout) {
Jedis conn = null;
String retIdentifier = null;
try {
// 获取连接
conn = jedisPool.getResource();
// 随机生成一个value
String identifier = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
// 锁名,即key值
String lockKey = "lock:" + lockName;
// 超时时间,上锁后超过此时间则自动释放锁
int lockExpire = (int) (timeout / );
// 获取锁的超时时间,超过这个时间则放弃获取锁
long end = System.currentTimeMillis() + acquireTimeout;
while (System.currentTimeMillis() results = transaction.exec();
if (results == null) {
continue;
}
retFlag = true;
}
conn.unwatch();
break;
}
} catch (JedisException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (conn != null) {
conn.close();
}
}
return retFlag;
}
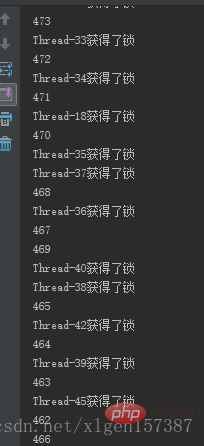
}4. Test the distributed lock just implemented
In the example, 50 threads are used to simulate a flash sale of a product, use -operator to reduce goods, and whether it is locked can be seen from the order of the results.
Simulate the flash sale service, configure the jedis thread pool in it, and pass it to the distributed lock during initialization for its use.
public class Service {
private static JedisPool pool = null;
private DistributedLock lock = new DistributedLock(pool);
int n = 500;
static {
JedisPoolConfig config = new JedisPoolConfig();
// 设置最大连接数
config.setMaxTotal(200);
// 设置最大空闲数
config.setMaxIdle(8);
// 设置最大等待时间
config.setMaxWaitMillis(1000 * 100);
// 在borrow一个jedis实例时,是否需要验证,若为true,则所有jedis实例均是可用的
config.setTestOnBorrow(true);
pool = new JedisPool(config, "127.0.0.1", 6379, 3000);
}
public void seckill() {
// 返回锁的value值,供释放锁时候进行判断
String identifier = lock.lockWithTimeout("resource", 5000, 1000);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "获得了锁");
System.out.println(--n);
lock.releaseLock("resource", identifier);
}
}Simulate threads for flash kill service;
public class ThreadA extends Thread {
private Service service;
public ThreadA(Service service) {
this.service = service;
}
@Override
public void run() {
service.seckill();
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Service service = new Service();
for (int i = 0; i <p>The results are as follows, the results are in order:</p><p><img src="/static/imghw/default1.png" data-src="https://img.php.cn/upload/article/000/000/024/0c1cb2ceea4c8cbfa184228a02822f99-1.png" class="lazy" alt="What are the three implementation methods of distributed locks?"></p>##If you comment out the use of locks Part: <p></p><pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">public void seckill() {
// 返回锁的value值,供释放锁时候进行判断
//String indentifier = lock.lockWithTimeout("resource", 5000, 1000);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "获得了锁");
System.out.println(--n);
//lock.releaseLock("resource", indentifier);
}
Three, distributed based on Zookeeper Lock
ZooKeeper is an open source component that provides consistent services for distributed applications. Internally it is a hierarchical file system directory tree structure, which stipulates that there can only be one in the same directory. Unique file name. The steps to implement distributed locks based on ZooKeeper are as follows: (1) Create a directory mylock; (2) Thread A creates a temporary sequence node in the mylock directory if it wants to acquire the lock;
(3 ) Get all the child nodes in the mylock directory, and then get the sibling nodes smaller than itself. If it does not exist, it means that the current thread sequence number is the smallest and the lock is obtained;
(4) Thread B gets all the nodes and determines that it is not the smallest Node, set to monitor the node smaller than itself;
(5) After thread A finishes processing, delete its own node, thread B listens to the change event, determines whether it is the smallest node, and if so, obtains the lock.
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.apache.commons.lang.StringUtils;
import org.apache.curator.framework.CuratorFramework;
import org.apache.curator.framework.CuratorFrameworkFactory;
import org.apache.curator.retry.RetryNTimes;
import org.apache.zookeeper.CreateMode;
import org.apache.zookeeper.data.Stat;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* 分布式锁Zookeeper实现
*
*/
@Slf4j
@Component
public class ZkLock implements DistributionLock {
private String zkAddress = "zk_adress";
private static final String root = "package root";
private CuratorFramework zkClient;
private final String LOCK_PREFIX = "/lock_";
@Bean
public DistributionLock initZkLock() {
if (StringUtils.isBlank(root)) {
throw new RuntimeException("zookeeper 'root' can't be null");
}
zkClient = CuratorFrameworkFactory
.builder()
.connectString(zkAddress)
.retryPolicy(new RetryNTimes(2000, 20000))
.namespace(root)
.build();
zkClient.start();
return this;
}
public boolean tryLock(String lockName) {
lockName = LOCK_PREFIX+lockName;
boolean locked = true;
try {
Stat stat = zkClient.checkExists().forPath(lockName);
if (stat == null) {
log.info("tryLock:{}", lockName);
stat = zkClient.checkExists().forPath(lockName);
if (stat == null) {
zkClient
.create()
.creatingParentsIfNeeded()
.withMode(CreateMode.EPHEMERAL)
.forPath(lockName, "1".getBytes());
} else {
log.warn("double-check stat.version:{}", stat.getAversion());
locked = false;
}
} else {
log.warn("check stat.version:{}", stat.getAversion());
locked = false;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
locked = false;
}
return locked;
}
public boolean tryLock(String key, long timeout) {
return false;
}
public void release(String lockName) {
lockName = LOCK_PREFIX+lockName;
try {
zkClient
.delete()
.guaranteed()
.deletingChildrenIfNeeded()
.forPath(lockName);
log.info("release:{}", lockName);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("删除", e);
}
}
public void setZkAddress(String zkAddress) {
this.zkAddress = zkAddress;
}
}Four, comparison
Database distributed lock implementationDisadvantages:
1. The db operation performance is poor, and there is a risk of table locking
2. After the non-blocking operation fails, polling is required, occupying CPU resources;
3. No commit for a long time or polling for a long time , may occupy more connection resources
Redis (cache) distributed lock implementation
Disadvantages:
1. The expiration time of lock deletion failure is difficult to control
2. Non-blocking, after the operation fails, polling is required and CPU resources are occupied;
ZK distributed lock implementation
Disadvantages: The performance is not as good as redis implementation, the main reason is that writing All operations (lock acquisition and lock release) need to be performed on the leader and then synchronized to the follower.
In short: ZooKeeper has good performance and reliability.
From the perspective of ease of understanding (from low to high) Database > Cache > Zookeeper
From the perspective of implementation complexity (from low to high) Zookeeper >= Cache > ; Database
From a performance perspective (from high to low) Cache> Zookeeper >= Database
From a reliability perspective (from high to low) Zookeeper > Cache> Database
Related recommendations: "Programming Teaching"
The above is the detailed content of What are the three implementation methods of distributed locks?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 Distributed lock: 5 cases, from entry to burial
Aug 24, 2023 pm 02:48 PM
Distributed lock: 5 cases, from entry to burial
Aug 24, 2023 pm 02:48 PM
What I want to share with you today is distributed locks. This article uses five cases, diagrams, source code analysis, etc. to analyze. Common locks such as synchronized and Lock are all implemented based on a single JVM. What should we do in a distributed scenario? At this time, distributed locks appeared.
 Using ZooKeeper for distributed lock processing in Java API development
Jun 17, 2023 pm 10:36 PM
Using ZooKeeper for distributed lock processing in Java API development
Jun 17, 2023 pm 10:36 PM
As modern applications continue to evolve and the need for high availability and concurrency grows, distributed system architectures are becoming more common. In a distributed system, multiple processes or nodes run at the same time and complete tasks together, and synchronization between processes becomes particularly important. Since many nodes in a distributed environment can access shared resources at the same time, how to deal with concurrency and synchronization issues has become an important task in a distributed system. In this regard, ZooKeeper has become a very popular solution. ZooKee
 Comparison of Etcd in Redis implementation of distributed locks
Jun 20, 2023 pm 05:51 PM
Comparison of Etcd in Redis implementation of distributed locks
Jun 20, 2023 pm 05:51 PM
With the gradual popularization of distributed systems, distributed locks have become an important means to ensure system stability and data consistency. As a high-performance distributed memory database, Redis has naturally become one of the important implementations of distributed locks. However, in recent years, Etcd has received more and more attention as an emerging distributed consistency solution. This article will discuss the similarities and differences between Redis' implementation of distributed locks and Etcd from aspects such as implementation principles and comparative analysis. The principle of Redis implementing distributed locks The implementation of Redis distributed locks
 The king solution among distributed locks - Redisson
Aug 24, 2023 pm 03:31 PM
The king solution among distributed locks - Redisson
Aug 24, 2023 pm 03:31 PM
If you have been using Redis before, you will get twice the result with half the effort by using Redisson. Redisson provides the simplest and most convenient way to use Redis. The purpose of Redisson is to promote users' separation of concerns (Separation of Concern) from Redis, so that users can focus more on processing business logic.
 Using Redis to implement distributed locks in PHP
May 15, 2023 pm 03:51 PM
Using Redis to implement distributed locks in PHP
May 15, 2023 pm 03:51 PM
With the rapid development of the Internet and the sharp increase in website visits, the importance of distributed systems has gradually become prominent. In distributed systems, issues of concurrency synchronization and data consistency are inevitably involved. Distributed locks, as a means of solving concurrency synchronization problems, have gradually been widely used in distributed systems. In PHP, Redis can be used to implement distributed locks, which this article will introduce. What is a distributed lock? In a distributed system, when multiple machines process the same task together, in order to avoid the occurrence of multiple machines
 How to use distributed locks to control concurrent access in MySQL?
Jul 30, 2023 pm 10:04 PM
How to use distributed locks to control concurrent access in MySQL?
Jul 30, 2023 pm 10:04 PM
How to use distributed locks to control concurrent access in MySQL? In database systems, high concurrent access is a common problem, and distributed locks are one of the common solutions. This article will introduce how to use distributed locks in MySQL to control concurrent access and provide corresponding code examples. 1. Principle Distributed locks can be used to protect shared resources to ensure that only one thread can access the resource at the same time. In MySQL, distributed locks can be implemented in the following way: Create a file named lock_tabl
 Detailed explanation of distributed lock implementation in Redis
Jun 21, 2023 am 11:02 AM
Detailed explanation of distributed lock implementation in Redis
Jun 21, 2023 am 11:02 AM
With the rapid development of mobile Internet and the explosive growth of data volume, distributed systems are becoming more and more popular. In distributed systems, the problem of concurrent operations has become more and more prominent. When multiple threads request shared resources at the same time, these resources need to be locked to ensure data consistency. Distributed locks are one of the effective solutions for implementing concurrent operations in distributed systems. This article will introduce in detail how to use Redis to implement distributed locks. Redis Basics Redis is a memory-based key-value storage system that is distributed
 Consul comparison of Redis implementation of distributed locks
Jun 20, 2023 pm 02:38 PM
Consul comparison of Redis implementation of distributed locks
Jun 20, 2023 pm 02:38 PM
Comparison of Consul implementing distributed locks in Redis In distributed systems, locks are an essential synchronization mechanism. As a commonly used NoSQL database, the distributed lock function provided by Redis has received widespread attention and application. However, Redis has certain problems when implementing distributed locks, such as lock reacquisition and timeout processing, so some new tools have been developed to solve these problems, including Consul. This article will implement distributed locks in Redis and implement Consul



