
查询mysql语句的方法:查询一张表中的记录时,代码为【select * from 表名 where name='long' and age ='18'】,from后面加表名,where后面是条件,select后面是筛选出的字段。

本教程操作环境:windows7系统、mysql8.0.22版,该方法适用于所有品牌电脑。
相关免费学习推荐:mysql视频教程
查询mysql语句的方法:
在mysql中 查询一张表中的记录的时候
书写顺序是: select * from 表名 where name='long' and age ='18';
但是mysql中的执行顺序是
from 后面加表名 确定你是那张表
where后面是条件 通过条件 来筛选这表的内容
select后面是 你where筛选出的数据中的 某些字段 * 是所有字段
# 查询语句执行的结果也是一张表,可以看成虚拟表
我们创建一张 emp的员工表
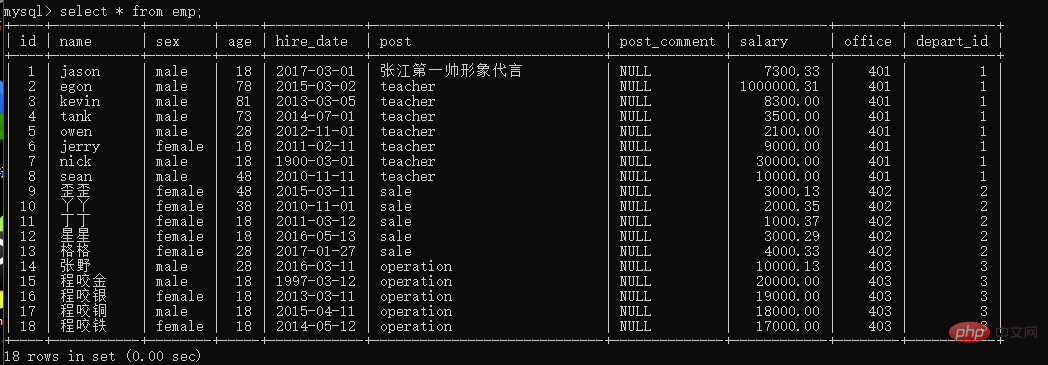
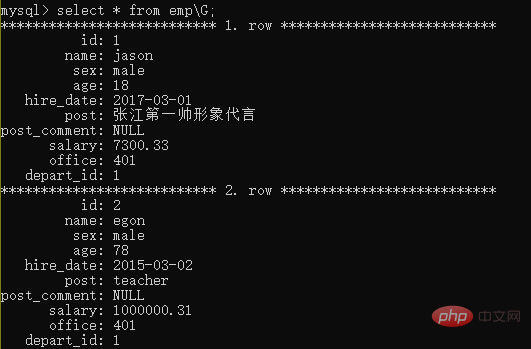
当我们的字段特别多的时候 结果的排版可能会出现凌乱现象 我们可以在查询语句末尾 加上\G来规范查询结果
select * from 表名\G;

1.查询id大于等于3小于等于6的数据
给你展示下实际操作 1.先确定 来自哪一张表 from emp 2. 筛选条件 where id >= 3 and id <=6; 3.select *
select * from emp where id >= 3 and id <= 6;
select * from emp where id between 3 and 6; between 等价于id >= 3 and id <= 62.查询薪资是20000或者18000或者17000的数据
select id,name from emp where salary = 20000 or salary = 18000 or salary = 17000;
select id,name from emp where salary in (20000,18000,17000);3.查询员工姓名中包含o字母的员工姓名和薪资
模糊匹配 % 匹配多个任意字符 _ 匹配 一个任意字符
select name,salary from emp where name like '%o%';
4.查询员工姓名是由四个字符组成的员工姓名与其薪资
select name, salary from emp where length(name) =4; select name ,salary from emp where name like "____"
5.查询id小于3或者大于6的数据
select * from emp where id<3 or id >6; select * from emp where id not between 3 and 6;
6.查询薪资不在20000,18000,17000范围的数据
select * from emp where salary not in (20000,17000,18000);
7.查询岗位描述为空的员工名与岗位名 针对null判断的时候只能用is 不能用=
select name ,post from emp where post_comment is null;
MySQL对大小写不敏感 平时写的时候大小写都可以
select * from emp group by post; # 按照部门分组

分组后 应该做到 最小单位是 组 ,而不应该是 展示 组内的单个数据信息
向上面那样 他会直接给你 打印出来而没有给你报错 说明你的严格模没有设置
show variables '%mode%'; # 找到严格模式所在的地方set session # 临时有效 set global # 永久有效set global sql_mode= 'strict_trans_tables' # 设置字符类型的自动截取set global sql_mode="strict_trans_tables,pad_char_to_full_length" #char 取出时 取消自动去空格set global sql_mode='strict_trans_tables,only_full_group_by' # 设置分组后 最小单位是组


此时你如果还使用 select name from emp group by post; 就会报错 #ERROR 1055 (42000): 'day37.emp.name' isn't in GROUP BYselest 后应该接的是 你分组的字段名
mysql中 分组之后 只能拿到分组的字段信息 无法直接 获取其他字段的信息 但是 你可以通过其他方法来间接的获取(聚合函数)
获取每个部门的最高工资
需求是 每一个部门 说明有分组 所以 先分组 在使用聚合函数来取值
select post ,max(salary) from emp group by post;
每个部门的最低工资
select post,min(salary) emp group by post; select post,min(salary) as '最小' from emp group by post;
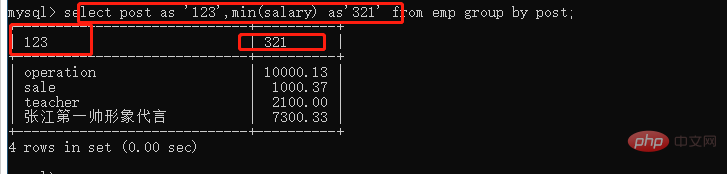
每个部门的平均工资
select post,avg(salary) from emp group by post;
每个部门的工资总和
select post,sum(salary) from emp group by post;
每个部门的人数
select post,count(age) from emp group by post;
select post,count(salary) from emp group by post;
select post,count(id) from emp group by post;
select post,count(post_comment) from emp group by post;在统计分组内个数的时候 填写任意非空字段都可以完成计数,推荐使用能够唯一标识数据的字段 比如id字段
聚合函数会自动将每一个分组内的单个数据做想要的计算,无需你考虑
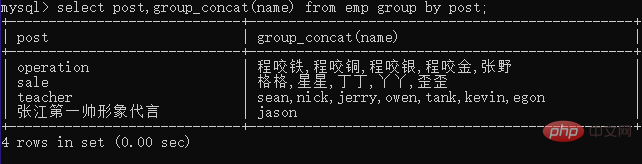
查询分组之后的部门名称和每个部门下所有的学生姓
select post, group_concat(name) from emp group by post;
select post,group_concat('hahha',name) from emp group by post;
还可以拼接
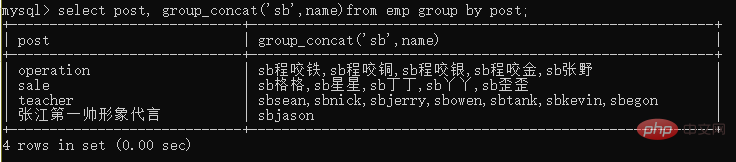
group_concat()能够拿到分组后每一个数据指定字段(可以是多个)对应的值
group_concat(分组之后用)
concat(不分组时用)
查询每个员工的年薪
select name,salary*12 from emp;
相关免费学习推荐:php编程(视频)
The above is the detailed content of How to query mysql statement. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




