What is mvc design pattern
The mvc design pattern is a software design pattern that divides the application into the above three core modules: business layer, view layer, and control layer. The business layer is responsible for implementing the business logic of the application and encapsulating various data processing methods; the view layer is responsible for displaying the application to the user. It obtains input data from the user and passes it to the business layer for processing through the control layer. The layer obtains the results returned by the business layer and displays them to the user. The control layer is responsible for controlling the flow of the application. It receives data from the view layer and then selects a business in the business layer to process.

The operating environment of this tutorial: Windows 7 system, Dell G3 computer.
What is the MVC design pattern
MVC is Model-View-Controller (Model-View-Controller) is a software design pattern that first appeared in the Smalltalk language , and was later recommended by Sun as a design pattern for the Java EE platform.
MVC divides the application into the above three core modules. These three modules can also be called business layer-view layer-control layer. As the names suggest, the main roles of the three of them in the application are as follows:
Business layer: Responsible for implementing the business logic of the application and encapsulating various data processing methods. It doesn't care how it will be displayed by the view layer or called by the controller, it only accepts the data, processes it, and returns a result.
View layer: Responsible for the display of the application to the user. It obtains input data from the user and passes it to the business layer for processing through the control layer, and then obtains the data returned by the business layer through the control layer. The results are displayed to the user.
Control layer: Responsible for controlling the process of the application. It receives the data passed from the view layer, then selects a business in the business layer to process, and receives the results returned by the business layer. and select a view in the view layer to display the results.
The following figure can be used to represent the relationship between the three in the MVC pattern:
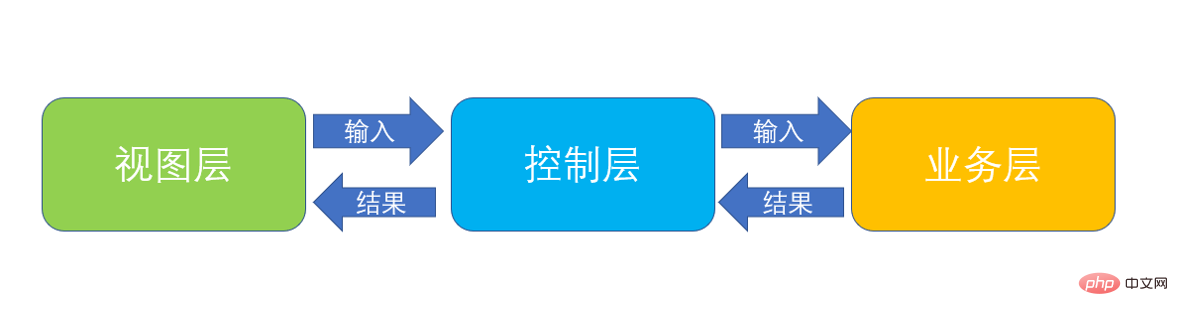
MVC is a design idea, and it does not have a unified standard , one of the typical implementations of MVC ideas is JavaBean (mode) jsp (view) servlet (controller), and I like to list the business logic in JavaBean separately to form service (mode) JavaBean (data set) jsp ( View) servlet (controller) structure, let's implement it below.
MVC implementation
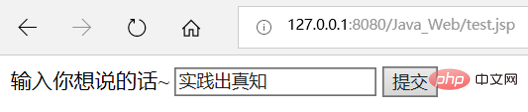
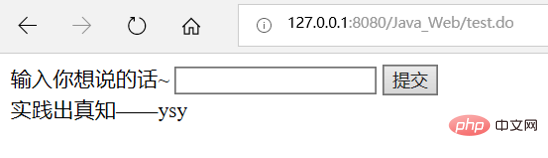
Here, I will apply the MVC design pattern to realize that the user enters a piece of text in the foreground, and the background obtains and splices the string "——ysy ” and then returns a simple application to be displayed in the foreground. The specific effect is as shown in the figure:
1. View layer
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=utf-8"
pageEncoding="utf-8"%>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>test</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="./test.do" method="post">
输入你想说的话~
<input type="text" name="input"/>
<input type="submit" value="提交" />
<br/>
<%
String s = (String)request.getAttribute("outPut"); <!--从request域中获取结果-->
if(s != null){ <!--如果有结果,显示结果-->
%>
<%=s %>
<%
}
%>
</form>
</body>
</html>2. Control layer
servlet writing:
package servlet;
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import bean.TestBean;
import service.TestService;
@WebServlet("/test.do") //通过注释配置servlet
public class TestServlet extends HttpServlet {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
public TestServlet() {
super();
}
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
doPost(request, response);
}
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
request.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8"); //设置字符集,防止中文乱码
TestBean testBean = new TestBean(); //获取数据集对象
TestService testService = new TestService(); //获取业务层对象
String s =request.getParameter("input"); //获取视图层提交的数据
testBean.setInput(s); //将数据存入数据集中
s = testService.change(testBean); //调用业务层,传入数据,接收返回结果
request.setAttribute("outPut", s); //将结果存入request域中
request.getRequestDispatcher("test.jsp").forward(request, response); //跳转到视图层
}
}If you don’t want to use comments to configure the servlet, you can also It can be configured through web.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee" xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd" id="WebApp_ID" version="4.0"> <display-name>Java_Web</display-name> <welcome-file-list> <welcome-file>index.html</welcome-file> <welcome-file>index.htm</welcome-file> <welcome-file>index.jsp</welcome-file> <welcome-file>default.html</welcome-file> <welcome-file>default.htm</welcome-file> <welcome-file>default.jsp</welcome-file> </welcome-file-list> <servlet> //通过配置文件配置servlet <servlet-name>test</servlet-name> <servlet-class>servlet.TestServlet</servlet-class> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>test</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/test.do</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> </web-app>
3, data set
package bean;
public class TestBean {
private String input;
public String getInput() {
return input;
}
public void setInput(String input) {
this.input = input;
}
}4, business layer
package service;
import bean.TestBean;
public class TestService {
public String change(TestBean testBean) {
String s = testBean.getInput(); //从数据集中获取数据
if(s != null && s != "") { //如果有数据,则拼接字符串
s += "——ysy";
}
return s;
}
}3. Advantages of MVC framework pattern
1. Conducive to code reuse
2. Conducive to developers Division of labor
3. It is helpful to reduce the coupling between program modules and facilitate program maintenance and expansion.
For more related knowledge, please visit the FAQ column!
The above is the detailed content of What is mvc design pattern. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 PHP MVC Architecture: Building Web Applications for the Future
Mar 03, 2024 am 09:01 AM
PHP MVC Architecture: Building Web Applications for the Future
Mar 03, 2024 am 09:01 AM
Introduction In today's rapidly evolving digital world, it is crucial to build robust, flexible and maintainable WEB applications. The PHPmvc architecture provides an ideal solution to achieve this goal. MVC (Model-View-Controller) is a widely used design pattern that separates various aspects of an application into independent components. The foundation of MVC architecture The core principle of MVC architecture is separation of concerns: Model: encapsulates the data and business logic of the application. View: Responsible for presenting data and handling user interaction. Controller: Coordinates the interaction between models and views, manages user requests and business logic. PHPMVC Architecture The phpMVC architecture follows the traditional MVC pattern, but also introduces language-specific features. The following is PHPMVC
 An advanced guide to PHP MVC architecture: unlocking advanced features
Mar 03, 2024 am 09:23 AM
An advanced guide to PHP MVC architecture: unlocking advanced features
Mar 03, 2024 am 09:23 AM
The MVC architecture (Model-View-Controller) is one of the most popular patterns in PHP development because it provides a clear structure for organizing code and simplifying the development of WEB applications. While basic MVC principles are sufficient for most web applications, it has some limitations for applications that need to handle complex data or implement advanced functionality. Separating the model layer Separating the model layer is a common technique in advanced MVC architecture. It involves breaking down a model class into smaller subclasses, each focusing on a specific functionality. For example, for an e-commerce application, you might break down the main model class into an order model, a product model, and a customer model. This separation helps improve code maintainability and reusability. Use dependency injection
 Uncovering the success of the SpringMVC framework: why it is so popular
Jan 24, 2024 am 08:39 AM
Uncovering the success of the SpringMVC framework: why it is so popular
Jan 24, 2024 am 08:39 AM
SpringMVC framework decrypted: Why is it so popular, specific code examples are needed Introduction: In today's software development field, the SpringMVC framework has become a very popular choice among developers. It is a Web framework based on the MVC architecture pattern, providing a flexible, lightweight, and efficient development method. This article will delve into the charm of the SpringMVC framework and demonstrate its power through specific code examples. 1. Advantages of SpringMVC framework Flexible configuration method Spr
 How to implement the MVC pattern using PHP
Jun 07, 2023 pm 03:40 PM
How to implement the MVC pattern using PHP
Jun 07, 2023 pm 03:40 PM
The MVC (Model-View-Controller) pattern is a commonly used software design pattern that can help developers better organize and manage code. The MVC pattern divides the application into three parts: Model, View and Controller, each part has its own role and responsibilities. In this article, we will discuss how to implement the MVC pattern using PHP. Model A model represents an application's data and data processing. usually,
 How to use MVC architecture to design projects in PHP
Jun 27, 2023 pm 12:18 PM
How to use MVC architecture to design projects in PHP
Jun 27, 2023 pm 12:18 PM
In Web development, MVC (Model-View-Controller) is a commonly used architectural pattern for processing and managing an application's data, user interface, and control logic. As a popular web development language, PHP can also use the MVC architecture to design and build web applications. This article will introduce how to use MVC architecture to design projects in PHP, and explain its advantages and precautions. What is MVCMVC is a software architecture pattern commonly used in web applications. MV
 Developing MVC with PHP8 framework: Important concepts and techniques that beginners need to know
Sep 11, 2023 am 09:43 AM
Developing MVC with PHP8 framework: Important concepts and techniques that beginners need to know
Sep 11, 2023 am 09:43 AM
Developing MVC with PHP8 framework: Important concepts and techniques that beginners need to know Introduction: With the rapid development of the Internet, Web development plays an important role in today's software development industry. PHP is widely used for web development, and there are many mature frameworks that help developers build applications more efficiently. Among them, the MVC (Model-View-Controller) architecture is one of the most common and widely used patterns. This article will introduce how beginners can use the PHP8 framework to develop MVC applications.
 Revealing the secrets of PHP MVC architecture: Make your website fly
Mar 03, 2024 am 09:25 AM
Revealing the secrets of PHP MVC architecture: Make your website fly
Mar 03, 2024 am 09:25 AM
Model-view-controller (mvc) architecture is a powerful design pattern for building maintainable and scalable WEB applications. The PHPMVC architecture decomposes application logic into three distinct components: Model: represents the data and business logic in the application. View: Responsible for presenting data to users. Controller: Acts as a bridge between the model and the view, handling user requests and coordinating other components. Advantages of MVC architecture: Code separation: MVC separates application logic from the presentation layer, improving maintainability and scalability. Reusability: View and model components can be reused across different applications, reducing code duplication. Performance Optimization: MVC architecture allows caching of view and model results, thus increasing website speed. Test Friendly: Detachment
 Developing MVC with PHP8 Framework: A Step-by-Step Guide
Sep 11, 2023 am 10:05 AM
Developing MVC with PHP8 Framework: A Step-by-Step Guide
Sep 11, 2023 am 10:05 AM
Developing MVC with PHP8 Framework: A Step-by-Step Guide Introduction: MVC (Model-View-Controller) is a commonly used software architecture pattern that is used to separate the logic, data and user interface of an application. It provides a structure that separates the application into three distinct components for better management and maintenance of the code. In this article, we will explore how to use the PHP8 framework to develop an application that conforms to the MVC pattern. Step One: Understand the MVC Pattern Before starting to develop an MVC application, I



