 Web Front-end
Web Front-end
 JS Tutorial
JS Tutorial
 JavaScript introduces the life cycle and usage scenarios of Service Worker
JavaScript introduces the life cycle and usage scenarios of Service Worker
JavaScript introduces the life cycle and usage scenarios of Service Worker
This is the eighth article in a series dedicated to exploring JavaScript and the components it is built upon.

## Recommended (free): javascript (video)
As you probably already know, progressive web apps are only growing in popularity because they aim to make the web app user experience smoother, creating an experience that resembles a native app rather than a browser look and feel. . One of the main requirements for building a Progressive Web App is to make it very reliable in terms of network and loading - it should be usable under uncertain or non-existent network conditions. In this article, we’ll take a deep dive intoService Workers: how they work and what you should care about. Finally, we also list some of the unique advantages of Service Workers in which scenarios they are worth using.
Introduction
If you want to know more aboutService Workers, you can read the author's article about Web Workers.
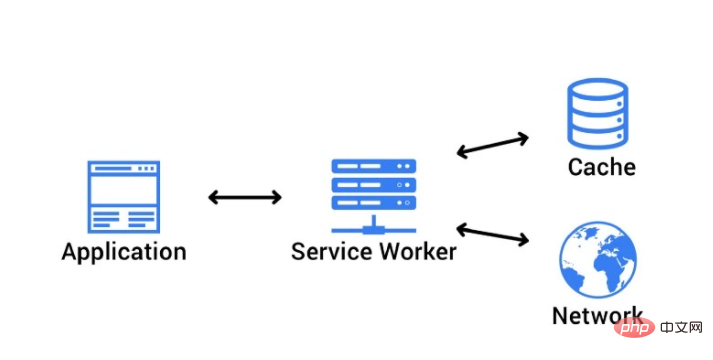
What is Service Worker
Introduction to MDN: Service Worker is a script running behind the browser, independent of the web page, and does not require A page or user interaction feature opens the door. Today, it includes push notifications and background sync functionality. In the future, Service Workers will support functionality including periodic sync or geofencing. Basically, Service Worker is a type of Web Worker, more specifically, it is like Shared Worker:- Service Worker runs in its own global context
- It's not tied to a specific web page
- It doesn't have access to the DOM
Life cycle of Service Worker
The life cycle of Service Worker is completely separated from the web page. It includes the following stages:- Download
- Installation
- Activation
Download
This is when the browser downloads the.js file that contains the Service Worker.
Installation
To install a Service Worker for your web application, you must first register it, which can be done in JavaScript code. After registering the Service Worker, it prompts the browser to start the Service Worker installation step in the background. By registering a Service Worker, you can tell the browser the location of your Service Worker's JavaScript files. Take a look at the following code: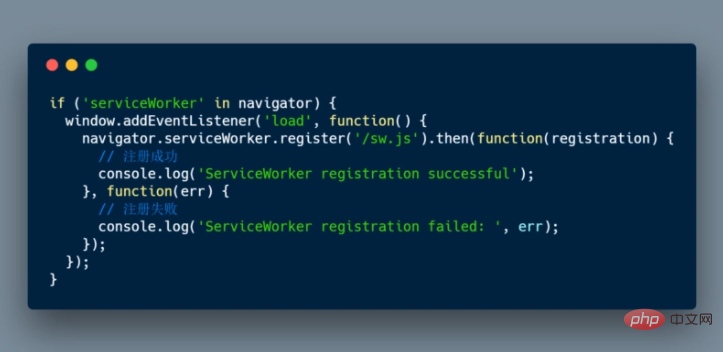
/sw.js this Service Worker will be registered.
register() method can be called every time the page is loaded. The browser will determine whether the Service Worker has been registered, and will give correct processing according to the registration status.
register() An important detail of the method is the location of the Service Worker file. In this example, you can see that the Service Worker file is located at the root of the domain, which means that the Service Worker scope will be under this domain. In other words, this Service Worker will receive fetch events for everything in this domain. If we register the Service Worker file in /example/sw.js, then the Service Worker will only see the fetch events of pages starting with /example/ (for example, /example /page1/, /example/page2/).
The bottom line is that if you install a Service Worker on your page, you run the risk of lazy loading and rendering - instead of making the page available to your users as quickly as possible.
Note that this situation only occurs when you visit the page for the first time. Subsequent page visits will not be affected by the Service Worker installation. Once the Service Worker is activated on the first visit to a page, it can handle load/cache events for subsequent visits to the web application. This all makes sense because it needs to be prepared to handle limited network connections.
Activate
After installing the Service Worker, the next step will be to activate it, which is a good opportunity to take care of old cache management.
After the activation step, the Service Worker will control all pages that fall within its scope, although the page for which the Service Worker was first registered will not be controlled until loaded again.
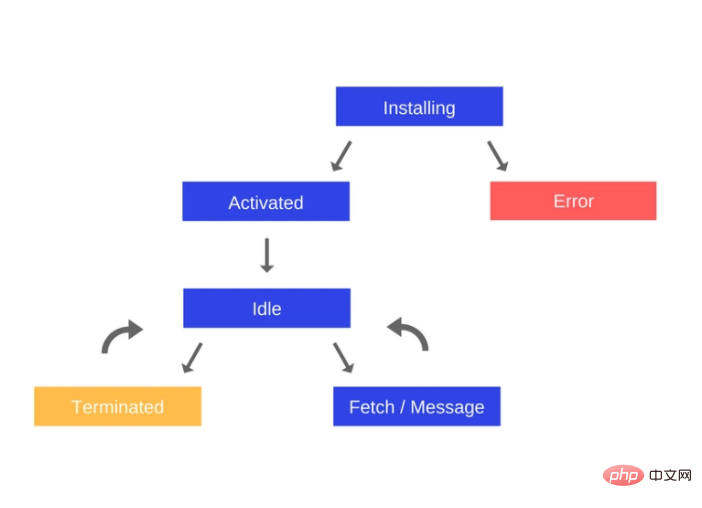
Once a Service Worker takes control, it will be in one of two states:
- Handle fetch and message events that occur when a network request or message is made from a web page
- Service Worker will be terminated to save memory
Service Worker life cycle is as follows:
Internal mechanism of Service Worker installation
After the page starts the registration process, take a look at what happens in the Service Worker script. It handles the install event by adding an event listener to the Service Worker instance:
Here are the steps you need to take when handling an installation event:
- Turn on a cache
- Cache our files
- Confirm that all required resources are cached
For the most basic example, you need to define callbacks for installation events and decide which files to cache.
1 |
|
The following is a simple internal installation process of Service Worker:
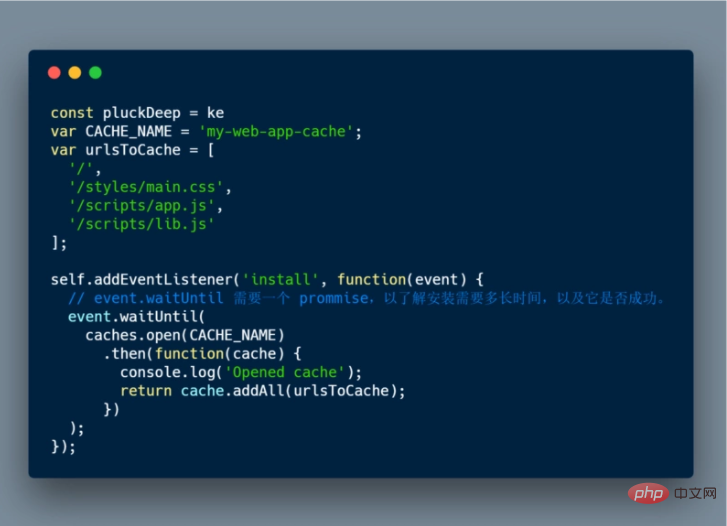
From the above example code, we can get:
calledcaches.open() and the cache name we want, then call cache.addAll() and pass in the file array. This is a chain of promises ( caches.open() and cache.addAll() ). event.waitUntil() The method accepts a promise and uses it to know how long the installation will take and whether it was successful.
If all files are successfully cached, the Service Worker will be installed. If one of the files fails to download, the installation step will fail. This means that you need to be careful when deciding on the list of files to cache during the installation step. Defining a long list of files will increase the chance that a file may not be cached, causing your service worker to not be installed.
Handling the install event is completely optional, you can avoid it, in which case you don't need to perform any steps here.
Runtime Cache Request
After the Service Worker is installed, the user navigates to another page or refreshes the current page, the Service Worker will receive fetch event. Here is an example that demonstrates how to return a cached resource or perform a new request and then cache the result:
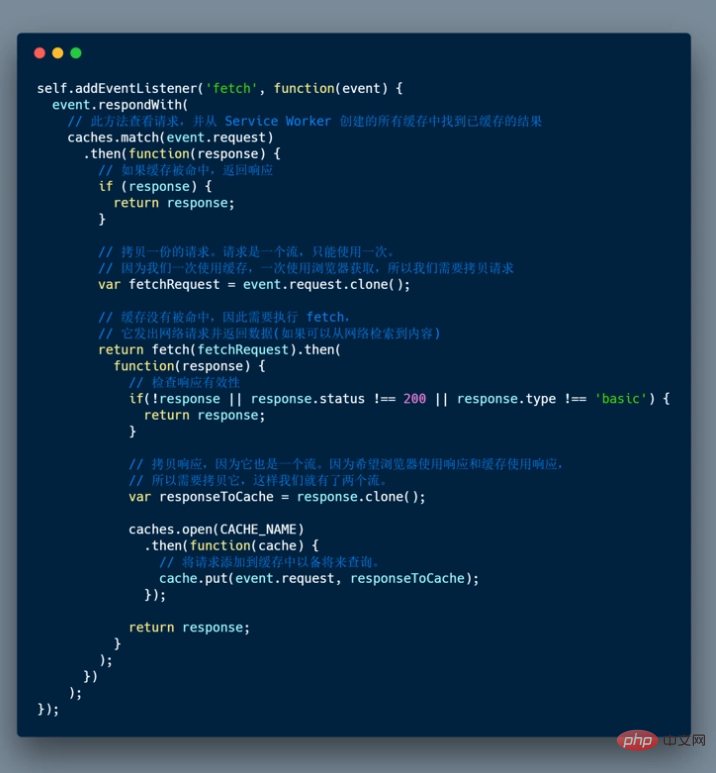
The above process:
- In Here we define the
fetchevent, and inevent.respondWith()we pass apromise## fromcaches.match() #. This method looks at the request and looks for any cached results from any caches created by the service worker. If it is in the cache, the response content is restored. - Otherwise, fetch will be executed.
- Check whether the status code is 200 and check whether the response type is basic, indicating that the response comes from our original request. In this case, requests for third-party resources are not cached.
- The response is cached
Update Service Worker
When a user accesses your web application, the browser attempts to re-download the.js file containing the Service Worker code , which is done in the background.
waiting state.
Once the currently open page of your web application is closed, the old Service Worker will be killed by the browser, the new Service Worker takes over control, and its activation event will be fired
Why is it needed These? In order to avoid the problem of two versions of the web application running on different tabs at the same time - this is very common on the web and can produce very serious bugs (for example, using different methods when storing data locally in the browser) mode).
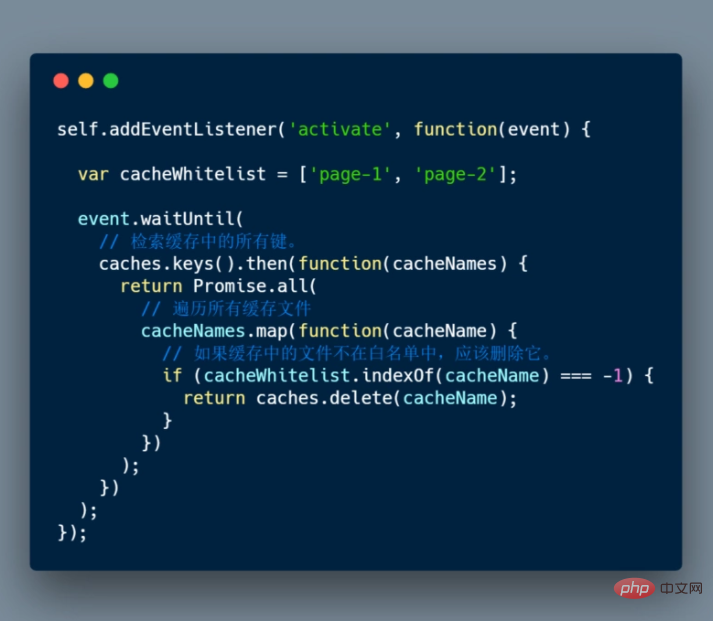
Delete data from cache
A common task that occurs in activation callbacks is cache management. The reason you want to do this in the activation callback is that if you were to clear all old caches during the installation step, any old Service Worker that is retaining all current pages will suddenly stop serving files from that cache.
Here is an example of how to delete some files that are not in the whitelist from the cache (in this example, there are two entities page-1 and page-2):
Reason for requiring HTTPS
When building a web application, use Service Workers over localhost, but once you deploy it to a production environment, you need to prepare Good HTTPS (This is the last reason to use HTTPS).
Using Service Worker, it is easy to hijack the connection and forge responses. Without using HTTPs, human web applications are vulnerable to hackers.
For greater security, you need to register the Service Worker on pages served over HTTPS to know that the Service Worker received by the browser has not been modified while being transmitted over the network.
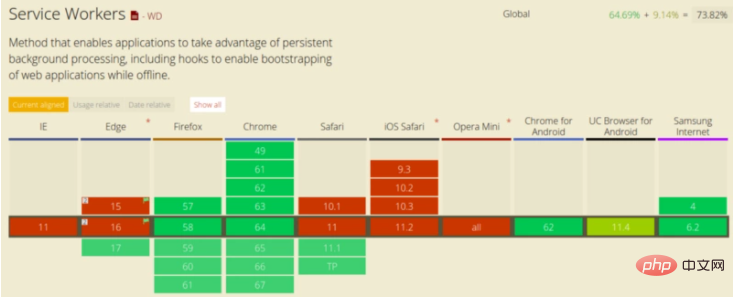
Browser support
Browser support for Service Worker is getting better and better:
Service Workers features will become more and more complete and powerful
Some unique features provided by Service Workers include:
- Push Notification — Allow users to choose timely updates from web applications.
- Background Sync — Allows operations to be delayed until the user has a stable connection. In this way, you can ensure that whatever the user wants to send can actually be sent.
- Periodic synchronization (open later) — Provides an API to manage the regular background synchronization function.
- Geofencing (Open to follow) — You can define parameters, also known as geofences, around areas of interest. When a device passes through the geofence, the web application receives a notification that allows for a better experience based on the user's geolocation.
The above is the detailed content of JavaScript introduces the life cycle and usage scenarios of Service Worker. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1389
1389
 52
52
 Which AI programmer is the best? Explore the potential of Devin, Tongyi Lingma and SWE-agent
Apr 07, 2024 am 09:10 AM
Which AI programmer is the best? Explore the potential of Devin, Tongyi Lingma and SWE-agent
Apr 07, 2024 am 09:10 AM
On March 3, 2022, less than a month after the birth of the world's first AI programmer Devin, the NLP team of Princeton University developed an open source AI programmer SWE-agent. It leverages the GPT-4 model to automatically resolve issues in GitHub repositories. SWE-agent's performance on the SWE-bench test set is similar to Devin, taking an average of 93 seconds and solving 12.29% of the problems. By interacting with a dedicated terminal, SWE-agent can open and search file contents, use automatic syntax checking, edit specific lines, and write and execute tests. (Note: The above content is a slight adjustment of the original content, but the key information in the original text is retained and does not exceed the specified word limit.) SWE-A
 PHP and Vue: a perfect pairing of front-end development tools
Mar 16, 2024 pm 12:09 PM
PHP and Vue: a perfect pairing of front-end development tools
Mar 16, 2024 pm 12:09 PM
PHP and Vue: a perfect pairing of front-end development tools. In today's era of rapid development of the Internet, front-end development has become increasingly important. As users have higher and higher requirements for the experience of websites and applications, front-end developers need to use more efficient and flexible tools to create responsive and interactive interfaces. As two important technologies in the field of front-end development, PHP and Vue.js can be regarded as perfect tools when paired together. This article will explore the combination of PHP and Vue, as well as detailed code examples to help readers better understand and apply these two
 Revealing the appeal of C language: Uncovering the potential of programmers
Feb 24, 2024 pm 11:21 PM
Revealing the appeal of C language: Uncovering the potential of programmers
Feb 24, 2024 pm 11:21 PM
The Charm of Learning C Language: Unlocking the Potential of Programmers With the continuous development of technology, computer programming has become a field that has attracted much attention. Among many programming languages, C language has always been loved by programmers. Its simplicity, efficiency and wide application make learning C language the first step for many people to enter the field of programming. This article will discuss the charm of learning C language and how to unlock the potential of programmers by learning C language. First of all, the charm of learning C language lies in its simplicity. Compared with other programming languages, C language
 Simple JavaScript Tutorial: How to Get HTTP Status Code
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
Simple JavaScript Tutorial: How to Get HTTP Status Code
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
JavaScript tutorial: How to get HTTP status code, specific code examples are required. Preface: In web development, data interaction with the server is often involved. When communicating with the server, we often need to obtain the returned HTTP status code to determine whether the operation is successful, and perform corresponding processing based on different status codes. This article will teach you how to use JavaScript to obtain HTTP status codes and provide some practical code examples. Using XMLHttpRequest
 Questions frequently asked by front-end interviewers
Mar 19, 2024 pm 02:24 PM
Questions frequently asked by front-end interviewers
Mar 19, 2024 pm 02:24 PM
In front-end development interviews, common questions cover a wide range of topics, including HTML/CSS basics, JavaScript basics, frameworks and libraries, project experience, algorithms and data structures, performance optimization, cross-domain requests, front-end engineering, design patterns, and new technologies and trends. . Interviewer questions are designed to assess the candidate's technical skills, project experience, and understanding of industry trends. Therefore, candidates should be fully prepared in these areas to demonstrate their abilities and expertise.
 Is Django front-end or back-end? check it out!
Jan 19, 2024 am 08:37 AM
Is Django front-end or back-end? check it out!
Jan 19, 2024 am 08:37 AM
Django is a web application framework written in Python that emphasizes rapid development and clean methods. Although Django is a web framework, to answer the question whether Django is a front-end or a back-end, you need to have a deep understanding of the concepts of front-end and back-end. The front end refers to the interface that users directly interact with, and the back end refers to server-side programs. They interact with data through the HTTP protocol. When the front-end and back-end are separated, the front-end and back-end programs can be developed independently to implement business logic and interactive effects respectively, and data exchange.
 Exploring Go language front-end technology: a new vision for front-end development
Mar 28, 2024 pm 01:06 PM
Exploring Go language front-end technology: a new vision for front-end development
Mar 28, 2024 pm 01:06 PM
As a fast and efficient programming language, Go language is widely popular in the field of back-end development. However, few people associate Go language with front-end development. In fact, using Go language for front-end development can not only improve efficiency, but also bring new horizons to developers. This article will explore the possibility of using the Go language for front-end development and provide specific code examples to help readers better understand this area. In traditional front-end development, JavaScript, HTML, and CSS are often used to build user interfaces
 Django: A magical framework that can handle both front-end and back-end development!
Jan 19, 2024 am 08:52 AM
Django: A magical framework that can handle both front-end and back-end development!
Jan 19, 2024 am 08:52 AM
Django: A magical framework that can handle both front-end and back-end development! Django is an efficient and scalable web application framework. It is able to support multiple web development models, including MVC and MTV, and can easily develop high-quality web applications. Django not only supports back-end development, but can also quickly build front-end interfaces and achieve flexible view display through template language. Django combines front-end development and back-end development into a seamless integration, so developers don’t have to specialize in learning



