What are the four types of domain name servers?
Domain name servers can be divided into four types: primary domain name servers, secondary domain name servers, caching domain name servers and forwarding domain name servers. The data of the primary domain name server can be modified, but the data of the secondary domain name server cannot be modified. The information provided by the cache domain name server is indirect information, and the forwarding domain name server is responsible for local queries of all non-local domain names.

#The operating environment of this article: windows10 system, thinkpad t480 computer.
DNS (Domain Name Server) is a server that converts domain name (domain name) and its corresponding IP address (IP address). DNS stores a table of domain names and corresponding IP addresses to resolve the domain names of messages. A domain name is the name of a computer or computer group on the Internet. It is used to identify the electronic location (sometimes also the geographical location) of the computer during data transmission. A domain name is a string of dot-separated names, usually including the name of an organization, and always includes a two- or three-letter suffix to indicate the type of organization or the country in which the domain is located.
Types of domain name servers:
1. Primary domain name server
is responsible for maintaining all domain name information in a region and is the authority for all specific information. Information source, data can be modified.
2. Secondary domain name server
When the primary domain name server fails, shuts down, or is overloaded, the secondary domain name server provides domain name resolution services as a backup to the primary domain name server. The data in the zone file in the secondary domain name server is copied from another primary domain name server and cannot be modified.
3. Caching domain name server
Obtains the query answer of each domain name server from a remote server. Once an answer is obtained, it is placed in the cache, and the same information is queried in the future. Answer with data in the cache. The caching name server is not an authoritative name server because the information it provides is indirect information.
4. Forwarding domain name server
is responsible for local queries of all non-local domain names. After the forwarding domain name server receives the query request, it searches it in its cache. If it cannot find it, it forwards the request to the specified domain name server in turn until the result is found, otherwise it returns a result that cannot be mapped.
The role of the domain name server
After you register the domain name and purchase the hosting service, you need to resolve the domain name to the purchased host in order to see the website content . In most cases, after the DNS domain name server resolves the domain name, you cannot see the website content immediately. Instead, it will take several hours, or even a day or two, to open your website.
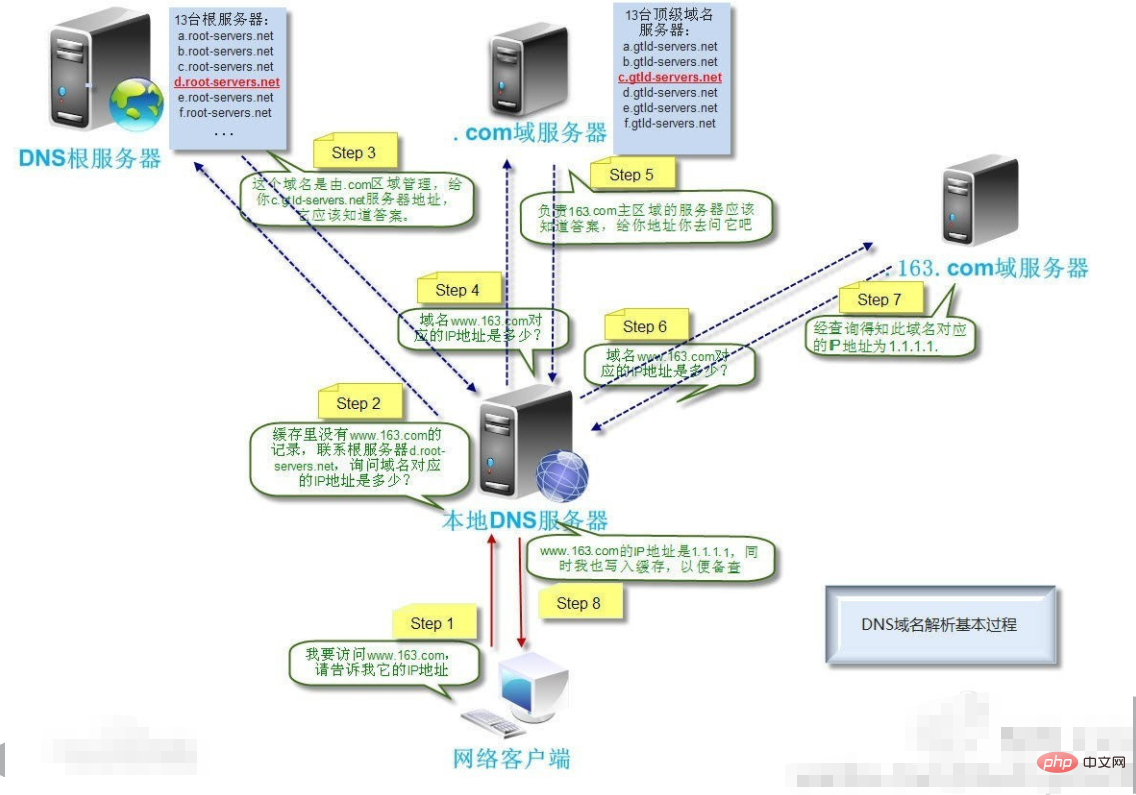
Domain name resolution process
To understand why domain name resolution takes so long, you need to understand the domain name resolution process and the DNS server effect.
Every computer on the Internet is assigned an IP address, and data transmission is actually carried out between different IP addresses. Including the computer we use when surfing the Internet at home, it is also assigned an IP address after connecting to the Internet. This IP address is dynamic in most cases. In other words, if you turn off the modem and turn on the Internet again, your Internet access provider will randomly assign a new IP address.
The website server is essentially a computer connected to the Internet, but the configuration is more suitable as a server and placed in a data center to maintain a low temperature, low dust environment, and at the same time have security. These servers use fixed IP addresses to connect to the Internet.
A domain name is resolved to a certain server, and the web page file is placed on this server. Only then does the user's computer know which server to go to to obtain the web page information of this domain name. This is accomplished through domain name servers.
Domain name server DNS is the abbreviation of English Domain Name Server. Each domain name must have at least two DNS servers, so that if there is a problem with one of the DNS servers, the other one can also return data about the domain name. You can also have more than two DNS servers, but the DNS records on all these DNS servers should be the same.
The DNS records of the domain name are retained in the DNS server, such as A records and MX records. The A record is used to specify the IP address corresponding to the host name (or domain name). MX records are used to resolve domain names to mail servers. In many cases.
When a browser enters a domain name in the browser address box, or clicks on a link from another website to reach this domain name, the browser sends a domain name request to the user's Internet access provider to access the domain name. The DNS server of the merchant needs to query the domain name database to see what the DNS server of this domain name is. Then go to the DNS server to grab the DNS record, that is, get the IP address that the domain name points to. After obtaining this IP information, the access provider's server goes to the server corresponding to this IP address to crawl the web page content, and then transmits it to the browser that made the request.
This process is quite complicated to describe, but in fact it is completed in less than a second or two.
If you want to read more related articles, please visit PHP Chinese website! !
The above is the detailed content of What are the four types of domain name servers?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1392
1392
 52
52


