
mysql video tutorial Column introduces MySQL system architecture

Recommended (free): mysql video tutorial
MySQL architecture
MySQL architecture is mainly divided into two parts: Client and server
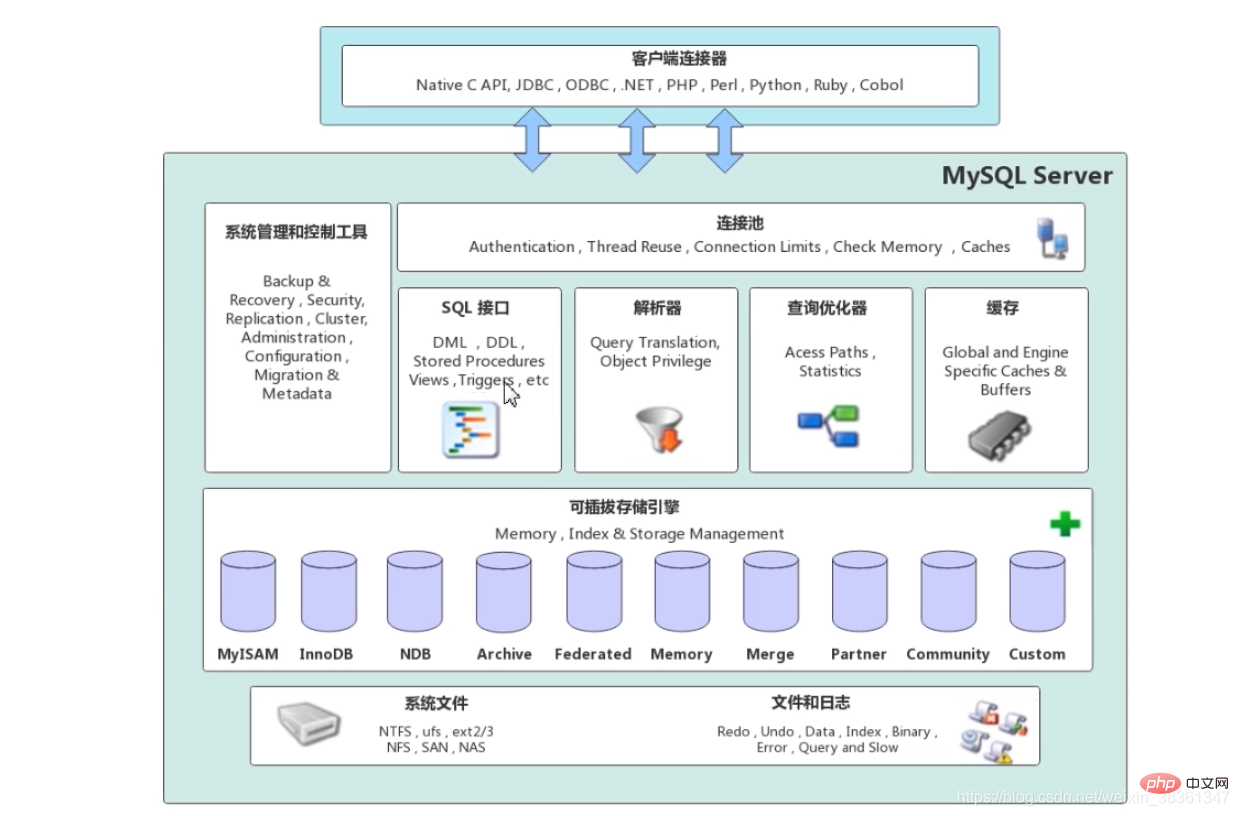
Client
The client connector is mainly responsible for the connection of some clients, targeting different programming languages The driver provides connection services.
Server
The service layer includes: system management and control tools, connection pool, SQL interface, parser, query optimizer, cache.
Connection pool
Responsible for managing the connection between the client and the service layer data processing, and verifying the user's permission to perform operations.
System management and control tools
Responsible for backup security, security management, cluster management services and tools, etc.
SQL interface
Receives client sql commands and returns the results required by the user. Such as: dml, ddl, stored procedures, views, triggers and other commands.
Parser
Word (keyword) analysis, syntax analysis, receiving sql, parsing it, generating a parse tree, and syntax verification check.
Query optimizer: After generating the parse tree and passing the parser grammar, the optimizer selects an appropriate index, then generates an execution plan, and then interacts with the execution engine.
Caching
The caching mechanism is composed of a series of caches.
Such as: table cache, record cache (sql query results are cached, and the same sql query will be returned from the cache next time),
permission cache, engine cache, etc. If the cache hits, the data will be fetched directly from the cache.
Storage engine layer
Responsible for reading and accessing Mysql data, such as InnoDB, MyISAM, etc. Pluggable, different storage engines can be replaced.
System file layer
Such as logs, data files, etc.
A SQL execution process
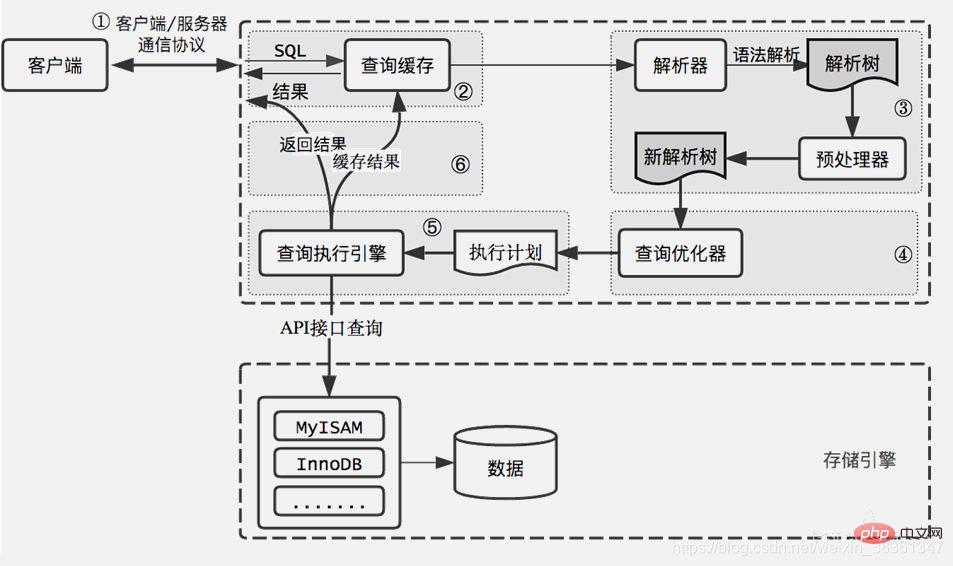
Storage engine layer
The storage engine is The subsystem in MySQL that specifically deals with files is a system abstracted based on the file system for dealing with mysql and disk files;
Commonly used storage engines, MyISAM, InnoDB that supports transactions;
Function comparison
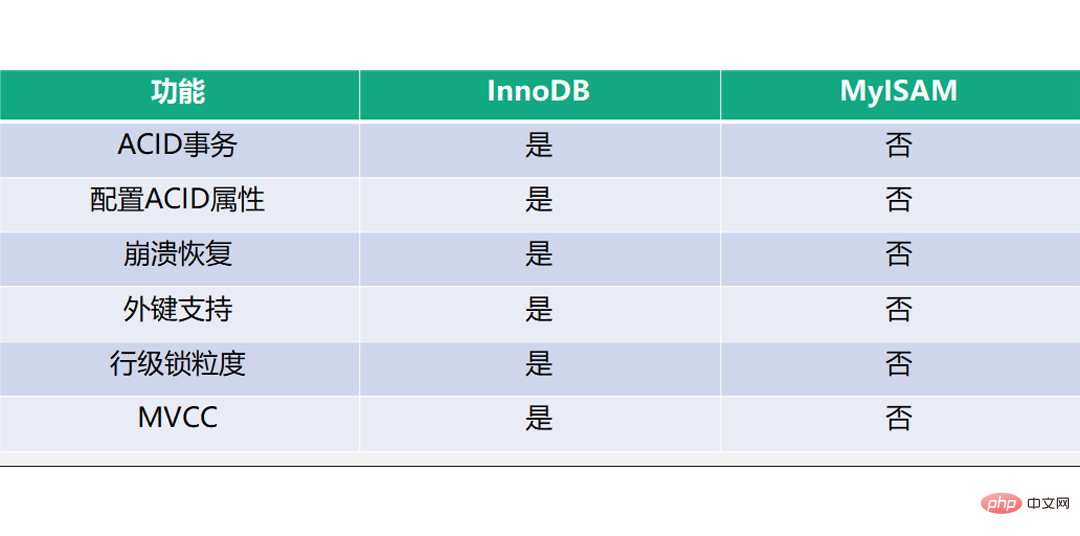
InnoDB supports 4 transaction characteristics of ACID, but MyISAM does not support it;
InnoDB supports 4 transaction isolation levels, the default is repeatable Read Repeatable Read, MyISAM does not support it;
InnoDB supports crash safe recovery, MyISAM does not support it;
InnoDB supports foreign keys, MyISAM does not Support;
InnoDB supports row-level lock granularity, MyISAM does not support it, and only supports table-level lock granularity;
InnoDB supports MVCC, MyISAM is not supported;
The above is the detailed content of Understand MySQL architecture. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!