 Java
Java
 Javagetting Started
Javagetting Started
 Java implements addition, deletion, query and modification of sequence table
Java implements addition, deletion, query and modification of sequence table
Java implements addition, deletion, query and modification of sequence table

What is a sequence table? What kind of structure is it?
The sequence table is a linear structure that is stored sequentially in a segment of storage units with continuous physical addresses. Generally, array storage is used. Complete the addition, deletion, checking and modification of data on the array.
(Learning video sharing: java video tutorial)
The sequence table is divided into:
Static sequence table: Use fixed-length array storage
Dynamic sequence table: Use dynamically opened array storage
The static sequence table is suitable for scenarios where you know how much data needs to be stored.
The fixed-length array of the static sequence table causes N to be fixedly large. If the space is opened too much, it is a waste, and if it is opened too little, it will not be enough.
Sequential table implementation
First of all, you must give the length of a sequence table. If you want to insert elements into the list, we must first insert the first number into position 0. If position 0 Without counting, we cannot directly insert it at position 1 or further back. If there is data at positions 0, 1, and 2, and we want to insert it into position 0 or 1, we have to traverse the sequence table backwards to move the previous data one step back.
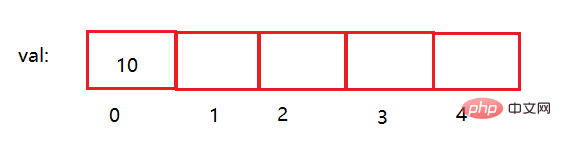
Added:
public class SepList {
public int[] val;//定义数据
public int size;//存放一个数据则让size++;
//构造方法 顺序表大小
public SepList(){
this.val = new int[5];
}
//也可以往进传大小
public SepList(int ret){
this.val = new int[ret];
}
//增加数据 得传要插入的位置与对应位置的数据 就比如0号位置插10
public void addVal(int pos,int val){
//首先判断顺序表是否满
if(this.val.length == this.size) return;
//其次得看看给的位置是否合法 pos不能小于0 也不能比如0号位置有数据 1号位置没有数据 然后插在2号或者更后边的位置
if(pos < 0 || pos > this.size) return;
//如果0 1 2 3位置都有数据,要往1号位置插,得让后边的位置往后移一步
for(int i = this.size; i >= pos; i--){
this.val[i + 1] = this.val[i];
}
//此时在给定位置插数据
this.val[pos] = val;
this.size++;
}
//打印链表
public void disPlay(){
for(int i = 0; i < this.size; i++){
System.out.print(this.val[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();//打印完后空行
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SepList myList = new SepList();//默认用5个元素
// SepList myList = new SepList(10);//这时候顺序表的大小是10
myList.addVal(0,10);//在0位置插入第一个数据
myList.disPlay();//打印
}
}
//执行结果
10If you want to insert multiple data, just call the method
For example:
myList.addVal(0,10);//第一次插入
myList.addVal(1,20);
myList.addVal(2,30);
myList.addVal(3,40);
myList.addVal(4,50);
myList.disPlay();//打印
//执行结果
10 20 30 40 50The order at this time What if the table is full and I insert more?
myList.addVal(0,10);//第一次插入
myList.addVal(1,20);
myList.addVal(2,30);
myList.addVal(3,40);
myList.addVal(4,50);
myList.addVal(5,60);
myList.addVal(6,70);
myList.disPlay();//打印
//执行结果
10 20 30 40 50Why is it still the same and no error is reported? This is because when entering the add function, it determines that the sequence table is full. If it is full, it jumps directly to the print function. No error will be reported. At this point the increment function is written.
Check
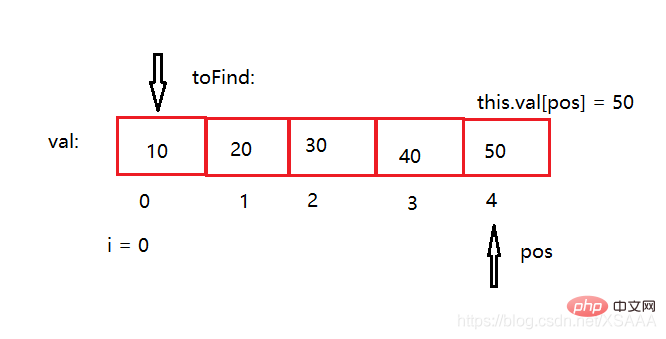
//判定链表是否包含某个元素
public boolean contains(int toFind){
for(int i = 0; i < this.size; i++){
if(toFind == this.val[i]){
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
//查找某个元素对应的位置
public int search(int toFind){
for(int i = 0; i < this.size; i++){
if(toFind == this.val[i]){
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
//获取pos位置的数据
public int getPos(int pos){
//首先判断pos是否合法
if(pos < 0 || pos > this.size) return -1;
for(int i = 0; i < this.size; i++){
if(this.val[i] == this.val[pos]){
return this.val[pos];
}
}
return -1;
}
//调用方法 在这没有粘贴主函数 你们一定要加上
boolean flag1 = myList.contains(10);//判定元素
boolean flag2 = myList.contains(60);
System.out.println(flag1);
System.out.println(flag2);
int ret = myList.search(10);//查找
int ret1 = myList.search(50);
System.out.println(ret);
System.out.println(ret1);
int ret2 = myList.getPos(0);//获取pos位置数据
int ret3 = myList.getPos(4);
System.out.println(ret2);
System.out.println(ret3);
//执行结果
true
false
0
4
10
50Change
Directly find the data corresponding to the pos position and assign the new data to it Just fine
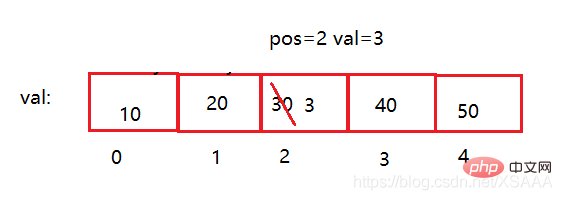
//修改pos位置的值
public void remove(int pos,int val){
if(pos < 0 || pos > this.size){
return;
} else {
this.val[pos] = val;
}
}
myList.remove(2,3);//2号位置改为3
myList.remove(3,4);//3号位置改为4
myList.disPlay();//打印
//执行结果
10 20 3 4 50Delete
After deleting the specified data, just overwrite the subsequent data forward
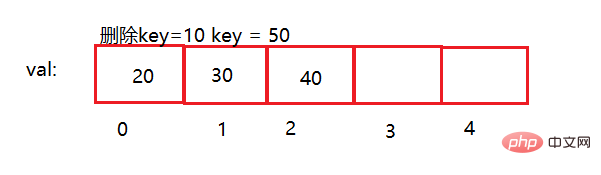
//删除元素
public void delVal(int key){
int i,j = 0;
//找到该位置
for(i = 0; i < this.size; i++){
if(this.val[i] == key){
j = i;
break;
}
}
//删除该位置数据,后边数据往前覆盖
for(i = j; i < this.size - 1; i++){
this.val[i] = this.val[i + 1];
}
this.size--;
}
myList.delVal(10);
myList.delVal(50);
myList.disPlay();//打印
//执行结果
20 30 40Related recommendations: java introductory tutorial
The above is the detailed content of Java implements addition, deletion, query and modification of sequence table. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Perfect Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check Perfect number in Java?, examples with code implementation.
 Random Number Generator in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:27 PM
Random Number Generator in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:27 PM
Guide to Random Number Generator in Java. Here we discuss Functions in Java with examples and two different Generators with ther examples.
 Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Weka in Java. Here we discuss the Introduction, how to use weka java, the type of platform, and advantages with examples.
 Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Smith Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check smith number in Java? example with code implementation.
 Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
In this article, we have kept the most asked Java Spring Interview Questions with their detailed answers. So that you can crack the interview.
 Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8 introduces the Stream API, providing a powerful and expressive way to process data collections. However, a common question when using Stream is: How to break or return from a forEach operation? Traditional loops allow for early interruption or return, but Stream's forEach method does not directly support this method. This article will explain the reasons and explore alternative methods for implementing premature termination in Stream processing systems. Further reading: Java Stream API improvements Understand Stream forEach The forEach method is a terminal operation that performs one operation on each element in the Stream. Its design intention is
 TimeStamp to Date in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
TimeStamp to Date in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to TimeStamp to Date in Java. Here we also discuss the introduction and how to convert timestamp to date in java along with examples.
 Java Program to Find the Volume of Capsule
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Java Program to Find the Volume of Capsule
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Capsules are three-dimensional geometric figures, composed of a cylinder and a hemisphere at both ends. The volume of the capsule can be calculated by adding the volume of the cylinder and the volume of the hemisphere at both ends. This tutorial will discuss how to calculate the volume of a given capsule in Java using different methods. Capsule volume formula The formula for capsule volume is as follows: Capsule volume = Cylindrical volume Volume Two hemisphere volume in, r: The radius of the hemisphere. h: The height of the cylinder (excluding the hemisphere). Example 1 enter Radius = 5 units Height = 10 units Output Volume = 1570.8 cubic units explain Calculate volume using formula: Volume = π × r2 × h (4



