Every time the CPU executes something, it completes a basic operation
Every time the cpu executes an "instruction", it completes a basic operation or judgment. In the CPU, the execution of an instruction includes three steps: instruction fetching, analysis and execution. Therefore, executing an instruction will complete a basic operation or judgment.

#The operating environment of this tutorial: Windows 7 system, Dell G3 computer.
Cpu completes basic operations by executing "instructions". Every time the computer's CPU executes an "instruction", it completes a basic operation or judgment. In the CPU, the execution of an instruction includes three steps: fetching, analysis and execution. Therefore, executing an instruction will complete one basic operation or judgment.
Central processing unit (CPU) is one of the main devices of electronic computers and the core component of computers. Its function is mainly to interpret computer instructions and process data in computer software. The CPU is the core component of the computer that reads instructions, decodes them, and executes them. The central processing unit mainly consists of two parts, namely the controller and the arithmetic unit, which also include cache memory and the data and control bus that realize the connection between them. The three core components of an electronic computer are the CPU, internal memory, and input/output devices. The main functions of the central processing unit are to process instructions, perform operations, control time, and process data.
In the computer architecture, the CPU is the core hardware unit that controls and allocates all hardware resources of the computer (such as memory, input and output units) and performs general operations. The CPU is the computing and control core of the computer. The operations of all software layers in the computer system will eventually be mapped to CPU operations through the instruction set.
How the CPU works
The Von Neumann architecture is the foundation of modern computers. Under this architecture, programs and data are stored uniformly. Instructions and data need to be accessed from the same storage space and transmitted through the same bus, and cannot be executed overlappingly. According to the von Neumann system, the work of the CPU is divided into the following five stages: instruction fetch stage, instruction decoding stage, instruction execution stage, memory access and result write back.
Instruction fetch (IF, instruction fetch) is the process of fetching an instruction from the main memory to the instruction register. The value in the program counter indicates the location of the current instruction in main memory. When an instruction is fetched, the value in the PC will be automatically incremented according to the length of the instruction word.
Instruction decoding stage (ID, instruction decode), after fetching the instruction, the instruction decoder splits and interprets the fetched instruction according to the predetermined instruction format, and identifies and distinguishes different instruction categories. Various methods of obtaining operands.
Execution instruction phase (EX, execute), specifically implements the function of the instruction. Different parts of the CPU are connected to perform the required operations.
Access and access phase (MEM, memory), according to the instruction needs to access the main memory and read the operand, the CPU gets the address of the operand in the main memory, and reads the operand from the main memory Used for operations. Some instructions do not require access to main memory, so this stage can be skipped.
Result write back stage (WB, write back), as the last stage, the result write back stage "writes back" the running result data of the execution instruction stage to some storage form. The result data is generally written to the internal register of the CPU so that it can be quickly accessed by subsequent instructions; many instructions also change the status of the flag bits in the program status word register. These flag bits identify different operation results and can be Used to affect program actions.
After the instruction is executed and the result data is written back, if no unexpected events (such as result overflow, etc.) occur, the computer will obtain the next instruction address from the program counter and start a new cycle. The instruction cycle will fetch the next instruction sequentially.
If you want to read more related articles, please visit PHP Chinese website! !
The above is the detailed content of Every time the CPU executes something, it completes a basic operation. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
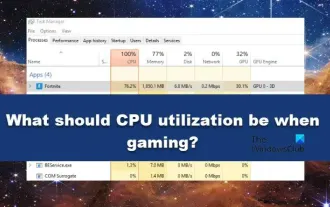 What should the CPU utilization be when gaming?
Feb 19, 2024 am 11:21 AM
What should the CPU utilization be when gaming?
Feb 19, 2024 am 11:21 AM
It's common for games to slow down your computer because they consume a lot of resources. It's crucial to understand your CPU usage when gaming so you can avoid overloading it. Therefore, keeping track of appropriate CPU usage is key to keeping your gaming experience smooth. In this article, we'll look at the appropriate CPU usage you should achieve while your game is running. CPU utilization during gaming CPU utilization is an important indicator of processor workload and depends on the performance specifications of the CPU. More powerful CPUs generally have higher usage. A CPU with more cores and threads can improve the overall performance of your system. Multi-threading support helps unleash the full potential of your CPU. In games, CPU usage depends on processor utilization, which can affect the game
 How to get items using commands in Terraria? -How to collect items in Terraria?
Mar 19, 2024 am 08:13 AM
How to get items using commands in Terraria? -How to collect items in Terraria?
Mar 19, 2024 am 08:13 AM
How to get items using commands in Terraria? 1. What is the command to give items in Terraria? In the Terraria game, giving command to items is a very practical function. Through this command, players can directly obtain the items they need without having to fight monsters or teleport to a certain location. This can greatly save time, improve the efficiency of the game, and allow players to focus more on exploring and building the world. Overall, this feature makes the gaming experience smoother and more enjoyable. 2. How to use Terraria to give item commands 1. Open the game and enter the game interface. 2. Press the "Enter" key on the keyboard to open the chat window. 3. Enter the command format in the chat window: "/give[player name][item ID][item quantity]".
 How to set CPU performance to full in Win11
Feb 19, 2024 pm 07:42 PM
How to set CPU performance to full in Win11
Feb 19, 2024 pm 07:42 PM
Many users find that the computer is not running smoothly enough when using the Win11 system. They want to improve CPU performance, but they don't know how to do it. The following will introduce in detail how to set the CPU performance to the highest level in Win11 system to make your computer more efficient. Setting method: 1. Right-click "This PC" on the desktop and select "Properties" in the option list. 2. After entering the new interface, click "Advanced System Settings" in "Related Links". 3. In the window that opens, click the "Advanced" tab at the top, then click the & at the bottom of "Performance"
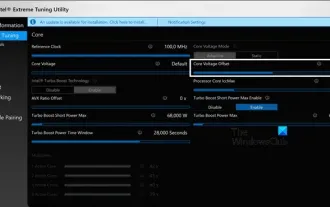 How to undervolt and overclock your CPU using Intel XTU
Feb 19, 2024 am 11:06 AM
How to undervolt and overclock your CPU using Intel XTU
Feb 19, 2024 am 11:06 AM
Intel XTU is a powerful application that allows you to easily manage your computer's performance. You can fix overheating issues by adjusting the CPU voltage, or boost performance by overclocking. In this article, we'll look at how you can take advantage of Intel XTU to optimize your computer's performance, whether that's adjusting voltage or overclocking. What effect do undervolting and overclocking have on the CPU? Before we move on to learning how to undervolt and overclock a CPU, we first have to understand what they are. Undervolting refers to gradually reducing the voltage required by the CPU. This process helps reduce heat emissions, as high voltage results in higher temperatures. By reducing the voltage supply to the CPU, the temperature can be effectively reduced. If your laptop starts to slow down after getting hot, you should solve the problem promptly.
 The difference between boxed and bulk cpu
Jan 23, 2024 am 09:46 AM
The difference between boxed and bulk cpu
Jan 23, 2024 am 09:46 AM
The differences between boxed and bulk CPUs: 1. Quality; 2. Warranty period; 3. Fan; 4. Price; 5. Packaging; 6. Sales channels. Detailed introduction: 1. Quality, whether it is boxed or bulk, there is no difference in the quality of the CPU itself. They are all manufactured by the same manufacturer and undergo the same quality testing and quality control process; 2. Warranty period, boxed CPU A longer warranty period is usually provided, usually three years, while bulk CPUs usually only have a one-year warranty, this is because boxed CPUs are usually sold by official or authorized dealers, etc.
 How to increase the clock frequency of your computer's CPU
Feb 20, 2024 am 09:54 AM
How to increase the clock frequency of your computer's CPU
Feb 20, 2024 am 09:54 AM
How to Overclock Computer CPUs With the continuous advancement of technology, people's demand for computer performance is also getting higher and higher. An effective way to improve computer performance is to increase the CPU's operating frequency through overclocking. Overclocking allows the CPU to process data faster, providing higher computing power. So, how to overclock a computer CPU? The following will introduce you to the basic principles and specific operation methods of overclocking. First, let's understand how overclocking works. The operating frequency of the CPU is determined by the crystal oscillator on the motherboard
 The operation process of WIN10 service host occupying too much CPU
Mar 27, 2024 pm 02:41 PM
The operation process of WIN10 service host occupying too much CPU
Mar 27, 2024 pm 02:41 PM
1. First, we right-click the blank space of the taskbar and select the [Task Manager] option, or right-click the start logo, and then select the [Task Manager] option. 2. In the opened Task Manager interface, we click the [Services] tab on the far right. 3. In the opened [Service] tab, click the [Open Service] option below. 4. In the [Services] window that opens, right-click the [InternetConnectionSharing(ICS)] service, and then select the [Properties] option. 5. In the properties window that opens, change [Open with] to [Disabled], click [Apply] and then click [OK]. 6. Click the start logo, then click the shutdown button, select [Restart], and complete the computer restart.
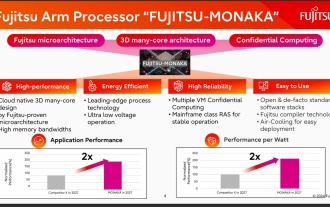 144-core, 3D-stacked SRAM: Fujitsu details next-generation data center processor MONAKA
Jul 29, 2024 am 11:40 AM
144-core, 3D-stacked SRAM: Fujitsu details next-generation data center processor MONAKA
Jul 29, 2024 am 11:40 AM
According to news from this website on July 28, foreign media TechRader reported that Fujitsu introduced in detail the FUJITSU-MONAKA (hereinafter referred to as MONAKA) processor planned to be shipped in 2027. MONAKACPU is based on the "cloud native 3D many-core" architecture and adopts the Arm instruction set. It is oriented to the data center, edge and telecommunications fields. It is suitable for AI computing and can realize mainframe-level RAS1. Fujitsu said that MONAKA will achieve a leap in energy efficiency and performance: thanks to technologies such as ultra-low voltage (ULV) technology, the CPU can achieve 2 times the energy efficiency of competing products in 2027, and cooling does not require water cooling; in addition, the application performance of the processor It can also reach twice as much as your opponent. In terms of instructions, MONAKA is equipped with vector



