Take a look at MySQL's amazing implicit conversions
Mysql tutorial column introduces related implicit conversions

More related free learning Recommended: mysql tutorial(video)
1. Problem description
root@mysqldb 22:12: [xucl]> show create table t1\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
Table: t1
Create Table: CREATE TABLE `t1` (
`id` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
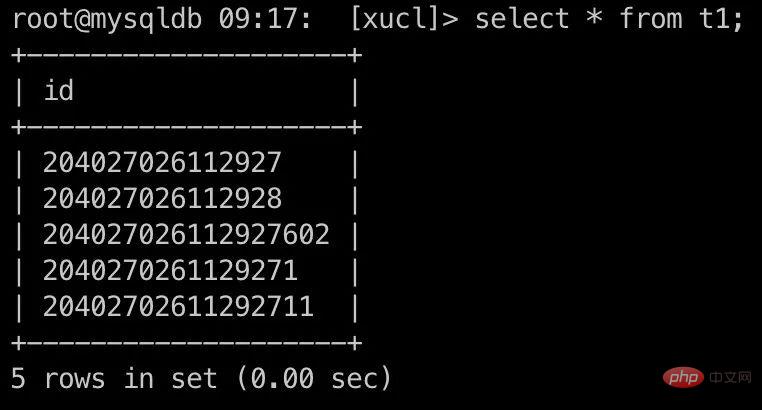
root@mysqldb 22:19: [xucl]> select * from t1;
+--------------------+
| id |
+--------------------+
| 204027026112927605 |
| 204027026112927603 |
| 2040270261129276 |
| 2040270261129275 |
| 100 |
| 101 |
+--------------------+
6 rows in set (0.00 sec)Strange phenomenon:
root@mysqldb 22:19: [xucl]> select * from t1 where id=204027026112927603; +--------------------+ | id | +--------------------+ | 204027026112927605 | | 204027026112927603 | +--------------------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec)

#What the hell, the check is clearly 204027026112927603, why 204027026112927605 also came out
2. Source code explanation
The stack call relationship is as follows:
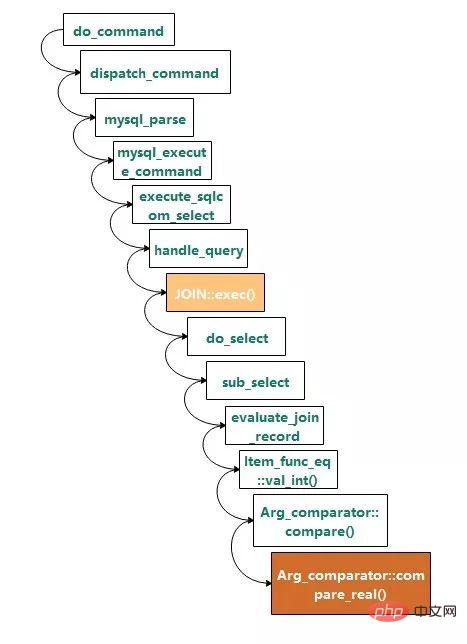
JOIN::exec( ) is the entry point for execution, Arg_comparator::compare_real() is a function for equivalence judgment, and its definition is as follows
int Arg_comparator::compare_real()
{
/*
Fix yet another manifestation of Bug#2338. 'Volatile' will instruct
gcc to flush double values out of 80-bit Intel FPU registers before
performing the comparison.
*/
volatile double val1, val2;
val1= (*a)->val_real();
if (!(*a)->null_value)
{
val2= (*b)->val_real();
if (!(*b)->null_value)
{
if (set_null)
owner->null_value= 0;
if (val1 < val2) return -1;
if (val1 == val2) return 0;
return 1;
}
}
if (set_null)
owner->null_value= 1;
return -1;
}The comparison steps are as shown in the figure below, read line by line The id column of the t1 table is placed in val1, and the constant 204027026112927603 exists in the cache and its type is double (2.0402702611292762E 17), so after passing the value to val2 here, val2=2.0402702611292762E 17.
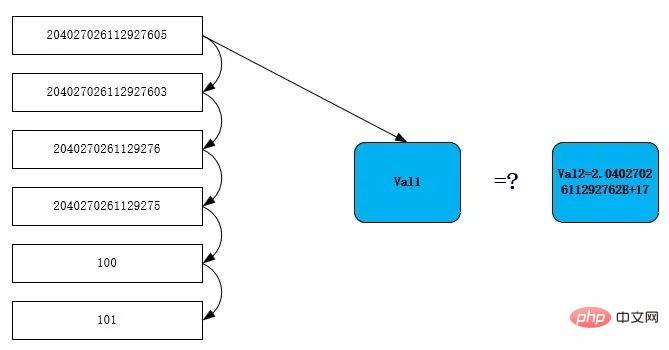
When the first row is scanned, the value of 204027026112927605 converted into doule is 2.0402702611292762e17. The equation is established and the row is determined to meet the conditions. Continue to scan down. Reason 204027026112927603 is also consistent with
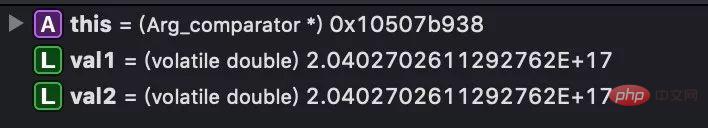
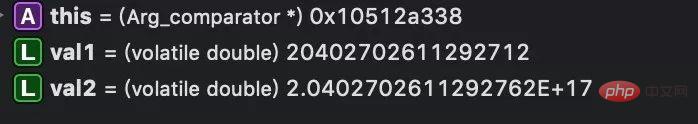
How to detect whether the string type number converted to doule type overflows?After testing here, when the number exceeds 16 digits, it is converted into The double type is already inaccurate, for example, 20402702611292711 will be expressed as 20402702611292712 (val1 in the picture)
{
char buf[DTOA_BUFF_SIZE];
double res;
DBUG_ASSERT(end != NULL && ((str != NULL && *end != NULL) ||
(str == NULL && *end == NULL)) &&
error != NULL);
res= my_strtod_int(str, end, error, buf, sizeof(buf));
return (*error == 0) ? res : (res < 0 ? -DBL_MAX : DBL_MAX);
}Copy after login
The real conversion function {
char buf[DTOA_BUFF_SIZE];
double res;
DBUG_ASSERT(end != NULL && ((str != NULL && *end != NULL) ||
(str == NULL && *end == NULL)) &&
error != NULL);
res= my_strtod_int(str, end, error, buf, sizeof(buf));
return (*error == 0) ? res : (res < 0 ? -DBL_MAX : DBL_MAX);
}my_strtod_int is located in dtoa.c (it’s too complicated, just post a comment)
/*
strtod for IEEE--arithmetic machines.
This strtod returns a nearest machine number to the input decimal
string (or sets errno to EOVERFLOW). Ties are broken by the IEEE round-even
rule.
Inspired loosely by William D. Clinger's paper "How to Read Floating
Point Numbers Accurately" [Proc. ACM SIGPLAN '90, pp. 92-101].
Modifications:
1. We only require IEEE (not IEEE double-extended).
2. We get by with floating-point arithmetic in a case that
Clinger missed -- when we're computing d * 10^n
for a small integer d and the integer n is not too
much larger than 22 (the maximum integer k for which
we can represent 10^k exactly), we may be able to
compute (d*10^k) * 10^(e-k) with just one roundoff.
3. Rather than a bit-at-a-time adjustment of the binary
result in the hard case, we use floating-point
arithmetic to determine the adjustment to within
one bit; only in really hard cases do we need to
compute a second residual.
4. Because of 3., we don't need a large table of powers of 10
for ten-to-e (just some small tables, e.g. of 10^k
for 0 <= k <= 22).
*/root@mysqldb 23:30: [xucl]> select * from t1 where id=2040270261129276; +------------------+ | id | +------------------+ | 2040270261129276 | +------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) root@mysqldb 23:30: [xucl]> select * from t1 where id=101; +------+ | id | +------+ | 101 | +------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
root@mysqldb 22:19: [xucl]> select * from t1 where id='204027026112927603'; +--------------------+ | id | +--------------------+ | 204027026112927603 | +--------------------+ 1 row in set (0.01 sec)
3. Conclusion
Avoid implicit type conversion. The types of implicit conversion mainly include inconsistent field types, in parameters containing multiple types, inconsistent character set types or collation rules, etc.
Implicit type conversion may lead to the inability to use the index, inaccurate query results, etc., so you must carefully screen when using it
It is recommended that the numeric type be defined as int or bigint when defining the field. When the table is associated, the associated fields must maintain the same type, character set, and collation rules
Finally, please post the instructions on implicit type conversion from the official website
1、If one or both arguments are NULL, the result of the comparison is NULL, except for the NULL-safe <=> equality comparison operator. For NULL <=> NULL, the result is true. No conversion is needed. 2、If both arguments in a comparison operation are strings, they are compared as strings. 3、If both arguments are integers, they are compared as integers. 4、Hexadecimal values are treated as binary strings if not compared to a number. 5、If one of the arguments is a TIMESTAMP or DATETIME column and the other argument is a constant, the constant is converted to a timestamp before the comparison is performed. This is done to be more ODBC-friendly. This is not done for the arguments to IN(). To be safe, always use complete datetime, date, or time strings when doing comparisons. For example, to achieve best results when using BETWEEN with date or time values, use CAST() to explicitly convert the values to the desired data type. A single-row subquery from a table or tables is not considered a constant. For example, if a subquery returns an integer to be compared to a DATETIME value, the comparison is done as two integers. The integer is not converted to a temporal value. To compare the operands as DATETIME values, use CAST() to explicitly convert the subquery value to DATETIME. 6、If one of the arguments is a decimal value, comparison depends on the other argument. The arguments are compared as decimal values if the other argument is a decimal or integer value, or as floating-point values if the other argument is a floating-point value. 7、In all other cases, the arguments are compared as floating-point (real) numbers.
The above is the detailed content of Take a look at MySQL's amazing implicit conversions. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to use MySQL backup and restore in PHP?
Jun 03, 2024 pm 12:19 PM
How to use MySQL backup and restore in PHP?
Jun 03, 2024 pm 12:19 PM
Backing up and restoring a MySQL database in PHP can be achieved by following these steps: Back up the database: Use the mysqldump command to dump the database into a SQL file. Restore database: Use the mysql command to restore the database from SQL files.
 How to optimize MySQL query performance in PHP?
Jun 03, 2024 pm 08:11 PM
How to optimize MySQL query performance in PHP?
Jun 03, 2024 pm 08:11 PM
MySQL query performance can be optimized by building indexes that reduce lookup time from linear complexity to logarithmic complexity. Use PreparedStatements to prevent SQL injection and improve query performance. Limit query results and reduce the amount of data processed by the server. Optimize join queries, including using appropriate join types, creating indexes, and considering using subqueries. Analyze queries to identify bottlenecks; use caching to reduce database load; optimize PHP code to minimize overhead.
 How to insert data into a MySQL table using PHP?
Jun 02, 2024 pm 02:26 PM
How to insert data into a MySQL table using PHP?
Jun 02, 2024 pm 02:26 PM
How to insert data into MySQL table? Connect to the database: Use mysqli to establish a connection to the database. Prepare the SQL query: Write an INSERT statement to specify the columns and values to be inserted. Execute query: Use the query() method to execute the insertion query. If successful, a confirmation message will be output.
 How to create a MySQL table using PHP?
Jun 04, 2024 pm 01:57 PM
How to create a MySQL table using PHP?
Jun 04, 2024 pm 01:57 PM
Creating a MySQL table using PHP requires the following steps: Connect to the database. Create the database if it does not exist. Select a database. Create table. Execute the query. Close the connection.
 How to use MySQL stored procedures in PHP?
Jun 02, 2024 pm 02:13 PM
How to use MySQL stored procedures in PHP?
Jun 02, 2024 pm 02:13 PM
To use MySQL stored procedures in PHP: Use PDO or the MySQLi extension to connect to a MySQL database. Prepare the statement to call the stored procedure. Execute the stored procedure. Process the result set (if the stored procedure returns results). Close the database connection.
 How to fix mysql_native_password not loaded errors on MySQL 8.4
Dec 09, 2024 am 11:42 AM
How to fix mysql_native_password not loaded errors on MySQL 8.4
Dec 09, 2024 am 11:42 AM
One of the major changes introduced in MySQL 8.4 (the latest LTS release as of 2024) is that the "MySQL Native Password" plugin is no longer enabled by default. Further, MySQL 9.0 removes this plugin completely. This change affects PHP and other app
 The difference between oracle database and mysql
May 10, 2024 am 01:54 AM
The difference between oracle database and mysql
May 10, 2024 am 01:54 AM
Oracle database and MySQL are both databases based on the relational model, but Oracle is superior in terms of compatibility, scalability, data types and security; while MySQL focuses on speed and flexibility and is more suitable for small to medium-sized data sets. . ① Oracle provides a wide range of data types, ② provides advanced security features, ③ is suitable for enterprise-level applications; ① MySQL supports NoSQL data types, ② has fewer security measures, and ③ is suitable for small to medium-sized applications.
 How to use bool in c language
May 09, 2024 pm 01:00 PM
How to use bool in c language
May 09, 2024 pm 01:00 PM
The bool type in C language represents true/false, and the value is 1 (true) or 0 (false). You can use bool is_true = true; to declare and initialize Boolean variables, or you can use the true/false keyword. Bool variables can use logical NOT, AND, OR, and XOR operations. Bool expressions are used in conditional statements and loops. The bool type can be implicitly converted to the int type (1: true, 0: false); the int type can also be implicitly converted to the bool type (non-zero: true, 0: false).






