Introduction to advanced features of redis

Redis (Remote Dictionary Server), the remote dictionary service, is an open source log-type, Key- Value database and provides APIs in multiple languages.
(Learning video sharing: redis video tutorial)
1.redis publish and subscribe mode
In addition to providing message queues like list, Redis mode, also provides a set of commands to implement the publish/subscribe mode. For example, Weibo, public accounts, etc. can all be realized through this.
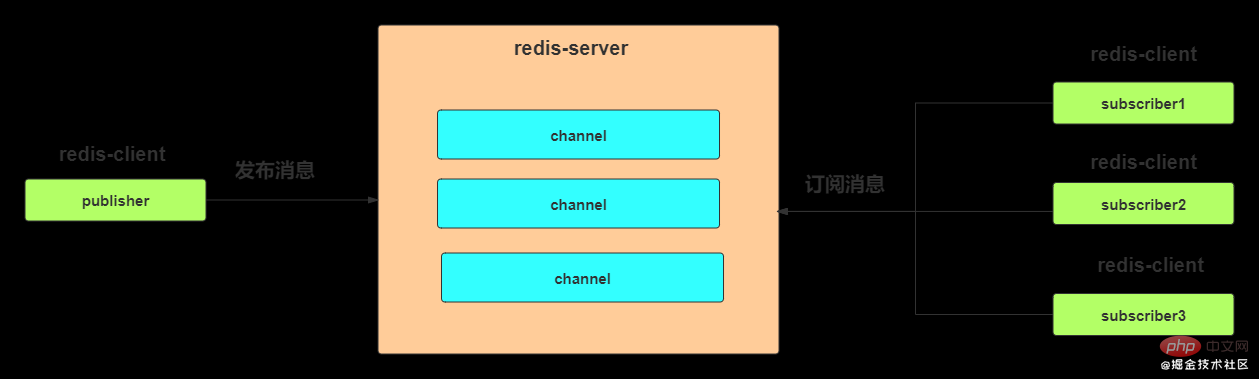
1.2 Subscription to Channel
The publisher needs to send the message to a place where subscribers can subscribe to the message. This place is the channel. Subscribers can subscribe to one or more channels, and all subscribers to this channel will receive this message.
Open two clients for testing
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 |
|
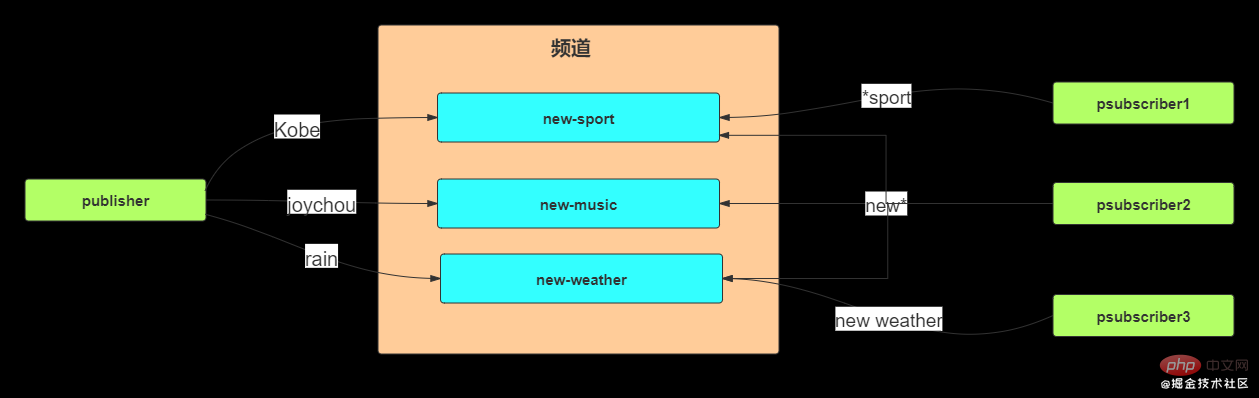
1.2 Subscribe by rules
Supported? and * placeholders. ? represents one character, * represents 0 or more characters.
Start four redis-cli, one as the publisher of the message, and the other three as subscribers.
Subscriber 1: Subscribe to sports related
1 |
|
Subscriber 2: Subscribe to news related
1 |
|
Subscriber 3: Subscribe to weather related
1 |
|
Publisher:
1 2 3 |
|
At this time, subscriber 1 will receive Kobe, subscriber 2 will receive all information, and subscriber 3 will receive rain.
2.redis transaction
2.1 Why use transaction
We all know that a single command of redis is atomic, but If you need to use multiple commands as an inseparable sequence of operations, you need to use transactions.
For example, using setnx to implement distributed locks, we usually set it first, and then set expire on the key to prevent the lock from being released when an exception occurs in del. After the business is processed, we want these three operations to be used as a set of commands in del. implement.
Redis transactions have two characteristics:
Execution in the order of entering the queue
will not be affected by other client requests
Redis' transaction design has four commands: multi (start transaction), exec (execute transaction), dicard (cancel transaction), watch (monitor)
2.2 Usage of transaction
Transfer scenario A and B each have 100 yuan, A transfers 10 yuan to B, A subtracts 10 yuan, and B adds 10 yuan
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 |
|
Open the transaction through the multi command. Transactions cannot be nested. Multiple multi commands have the same effect
After using multi to start a transaction, the client sends multiple commands to the server. These commands will not be executed immediately, but will be placed in a queue. After the exec command is called, the commands in the queue will be executed.
We can use discard to clear the transaction queue.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 |
|
When a problem occurs when we execute a transaction, will it be rolled back?
An error occurred before exec (such as command syntax error)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |
|
An error occurred after exec (using commands of different data types for the same key)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |
|
Through the above operations, We can know that when an error occurs in a transaction before exec, all operations will be rolled back; if an error occurs after exec, only the wrong command will not be executed.
Why does redis not roll back when there is an error in a transaction?
We can see from the above operation that redis only rolls back when the instruction syntax is wrong, and instruction operation errors are bugs caused by developers. For example: you perform 1 on an int type, and then accidentally 2, Or perform 1 on a string type, rollback is not applicable
2.3 watch instruction
It can provide CAS optimistic locking operation for Redis transactions, that is, multiple threads update a certain variable At this time, the old value will be compared with the memory address. If they are equal, it will be updated to the new value.
We can use watch to monitor one or more keys. If after starting a transaction, at least one of the monitored keys is modified before exec is executed, the entire transaction will be cancelled.
First, client 1 executes watch to monitor the key money, and starts a transaction to increase money by 100
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
|
Before the transaction ends, client 2 decreases money by 100
1 2 |
|
At this time, client 1 ends the transaction, and the value of money has not been increased, but decreased, indicating that the modification of the transaction has failed
1 2 3 4 |
|
3. Lua script
Lua script is a lightweight script Language, written in C language, is somewhat similar to stored procedures. Why use lua script?
Send multiple commands at one time to reduce network overhead. Redis will execute the script as a whole to ensure atomicity (transactions can be replaced in this way) and script reuse, making it easier for multiple clients to complete the same logic.
3.1 Using
we can use the following command to call the lua script
1 |
|
eval executes the lua script
script represents the content of the lua script
numkeys key number
[key1 key2 key3 ....] 键名参数,表示在脚本中所用到的那些 Redis 键(key),这些键名参数可以在 Lua 中通过全局变量 KEYS 数组,用 1 为基址的形式访问( KEYS[1] , KEYS[2] ,以此类推)。
[arg1 arg2 arg3 ....] 全局变量,可以在 Lua 中通过全局变量 ARGV 数组访问,访问的形式和 KEYS 变量类似( ARGV[1] 、 ARGV[2] ,诸如此类)
来个简单的例子
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 |
|
在lua脚本如何调用redis命令呢?
我们可以使用 redis.call(command, key [param1, param2…])进行操作
commond redis的命令,如set,get等key 被操作的键[param1, param2…]表示给key的参数
1 2 3 4 5 |
|
以上命令等价于 mset name lisi age 18, key的数量为2,2 后面两个值为key,在之后就是args
直接在redis-cli中写lua脚本不够方便,通常我们会把脚本放在文件中,然后执行这个文件
我们在一个目录下新建一个test.lua的脚本,填写以下内容后执行。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 |
|
值得注意的是key和arg之间需要加上空格逗号空格(myname , Armin)
3.2 缓存lua脚本
之所以需要缓存lua脚本,这是因为每次调用的时候都将整个脚本传给redis服务端,会产生较大的网络开销。为了解决这个问题,Redis提供了evalsha命令,让开发人员通过脚本内容的SHA1摘要执行脚本。
那么怎么将生成这个SHA1并将脚本内容加载到缓存呢,这就用到script load命令去计算脚本的SHA1摘要并记录脚本到缓存中,执行evalsha时,redis会根据提供的摘要去脚本缓存找到对应脚本内容,如果找到则执行,否则返回错误提示: “NOSCRIPT No matching script. Please use EVAL”
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
|
Redis还给lua脚本的执行提供了超时时间,默认的超时时间为5s,超过5s之后redis会接受其他命令但是会返回一个"BUSY"的错误
可在redis.conf中修改指定参数
1 |
|
Redis提供了个script kill的命令来终止正在运行的脚本
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
|
如果数据进行了修改操作,将无法使用script kill终止脚本,因为违反了原子性。此时只能通过shutdown nosave来强行终止redis。
shutdown nosave 和 shutdown 的区别在于 shutdown nosave 不会进行持久化
操作,意味着发生在上一次快照后的数据库修改都会丢失。
相关推荐:redis数据库教程
The above is the detailed content of Introduction to advanced features of redis. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
Redis cluster mode deploys Redis instances to multiple servers through sharding, improving scalability and availability. The construction steps are as follows: Create odd Redis instances with different ports; Create 3 sentinel instances, monitor Redis instances and failover; configure sentinel configuration files, add monitoring Redis instance information and failover settings; configure Redis instance configuration files, enable cluster mode and specify the cluster information file path; create nodes.conf file, containing information of each Redis instance; start the cluster, execute the create command to create a cluster and specify the number of replicas; log in to the cluster to execute the CLUSTER INFO command to verify the cluster status; make
 How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear Redis data: Use the FLUSHALL command to clear all key values. Use the FLUSHDB command to clear the key value of the currently selected database. Use SELECT to switch databases, and then use FLUSHDB to clear multiple databases. Use the DEL command to delete a specific key. Use the redis-cli tool to clear the data.
 How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
To read a queue from Redis, you need to get the queue name, read the elements using the LPOP command, and process the empty queue. The specific steps are as follows: Get the queue name: name it with the prefix of "queue:" such as "queue:my-queue". Use the LPOP command: Eject the element from the head of the queue and return its value, such as LPOP queue:my-queue. Processing empty queues: If the queue is empty, LPOP returns nil, and you can check whether the queue exists before reading the element.
 How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
Using the Redis directive requires the following steps: Open the Redis client. Enter the command (verb key value). Provides the required parameters (varies from instruction to instruction). Press Enter to execute the command. Redis returns a response indicating the result of the operation (usually OK or -ERR).
 How to use redis lock
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
How to use redis lock
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
Using Redis to lock operations requires obtaining the lock through the SETNX command, and then using the EXPIRE command to set the expiration time. The specific steps are: (1) Use the SETNX command to try to set a key-value pair; (2) Use the EXPIRE command to set the expiration time for the lock; (3) Use the DEL command to delete the lock when the lock is no longer needed.
 How to read the source code of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
How to read the source code of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
The best way to understand Redis source code is to go step by step: get familiar with the basics of Redis. Select a specific module or function as the starting point. Start with the entry point of the module or function and view the code line by line. View the code through the function call chain. Be familiar with the underlying data structures used by Redis. Identify the algorithm used by Redis.
 How to solve data loss with redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:24 PM
How to solve data loss with redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:24 PM
Redis data loss causes include memory failures, power outages, human errors, and hardware failures. The solutions are: 1. Store data to disk with RDB or AOF persistence; 2. Copy to multiple servers for high availability; 3. HA with Redis Sentinel or Redis Cluster; 4. Create snapshots to back up data; 5. Implement best practices such as persistence, replication, snapshots, monitoring, and security measures.
 How to use the redis command line
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
How to use the redis command line
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
Use the Redis command line tool (redis-cli) to manage and operate Redis through the following steps: Connect to the server, specify the address and port. Send commands to the server using the command name and parameters. Use the HELP command to view help information for a specific command. Use the QUIT command to exit the command line tool.




