How to install redis database under centos system

The specific installation steps are as follows:
1. Install redis
The first step: Download the redis installation package
[root@iZwz991stxdwj560bfmadtZ local]# wget http://download.redis.io/releases/redis-4.0.6.tar.gz --2017-12-13 12:35:12-- http://download.redis.io/releases/redis-4.0.6.tar.gz Resolving download.redis.io (download.redis.io)... 109.74.203.151 Connecting to download.redis.io (download.redis.io)|109.74.203.151|:80... connected. HTTP request sent, awaiting response... 200 OK Length: 1723533 (1.6M) [application/x-gzip] Saving to: ‘redis-4.0.6.tar.gz’ 100%[==========================================================================================================>] 1,723,533 608KB/s in 2.8s 2017-12-13 12:35:15 (608 KB/s) - ‘redis-4.0.6.tar.gz’ saved [1723533/1723533]
Second Step: Unzip the compressed package
tar -zxvf redis-4.0.6.tar.gz [root@iZwz991stxdwj560bfmadtZ local]# tar -zxvf redis-4.0.6.tar.gz
Step three: yum installs gcc dependencies
yum install gcc [root@iZwz991stxdwj560bfmadtZ local]# yum install gcc
When you encounter a choice, enter y
Step four: Jump to redis to decompress Directory
cd redis-4.0.6 [root@iZwz991stxdwj560bfmadtZ local]# cd redis-4.0.6
Step 5: Compile and install
make MALLOC=libc [root@iZwz991stxdwj560bfmadtZ redis-4.0.6]# make MALLOC=libc
Add the files in the /usr/local/redis-4.0.6/src directory to the /usr/local/bin directory
cd src && make install
[root@iZwz991stxdwj560bfmadtZ redis-4.0.6]# cd src && make install
CC Makefile.dep
Hint: It's a good idea to run 'make test' ;)
INSTALL install
INSTALL install
INSTALL install
INSTALL install
INSTALL install2. Three ways to start redis
First switch to the redis src directory
[root@iZwz991stxdwj560bfmadtZ redis-4.0.6]# cd src
1. Start redis directly
./redis-server
[root@iZwz991stxdwj560bfmadtZ src]# ./redis-server
18685:C 13 Dec 12:56:12.507 # oO0OoO0OoO0Oo Redis is starting oO0OoO0OoO0Oo
18685:C 13 Dec 12:56:12.507 # Redis version=4.0.6, bits=64, commit=00000000, modified=0, pid=18685, just started
18685:C 13 Dec 12:56:12.507 # Warning: no config file specified, using the default config. In order to specify a config file use ./redis-server /path/to/redis.conf
_._
_.-``__ ''-._
_.-`` `. `_. ''-._ Redis 4.0.6 (00000000/0) 64 bit
.-`` .-```. ```\/ _.,_ ''-._
( ' , .-` | `, ) Running in standalone mode
|`-._`-...-` __...-.``-._|'` _.-'| Port: 6379
| `-._ `._ / _.-' | PID: 18685
`-._ `-._ `-./ _.-' _.-'
|`-._`-._ `-.__.-' _.-'_.-'|
| `-._`-._ _.-'_.-' | http://redis.io
`-._ `-._`-.__.-'_.-' _.-'
|`-._`-._ `-.__.-' _.-'_.-'|
| `-._`-._ _.-'_.-' |
`-._ `-._`-.__.-'_.-' _.-'
`-._ `-.__.-' _.-'
`-._ _.-'
`-.__.-'
18685:M 13 Dec 12:56:12.508 # WARNING: The TCP backlog setting of 511 cannot be enforced because /proc/sys/net/core/somaxconn is set to the lower value of 128.
18685:M 13 Dec 12:56:12.508 # Server initialized
18685:M 13 Dec 12:56:12.508 # WARNING overcommit_memory is set to 0! Background save may fail under low memory condition. To fix this issue add 'vm.overcommit_memory = 1' to /etc/sysctl.conf and then reboot or run the command 'sysctl vm.overcommit_memory=1' for this to take effect.
18685:M 13 Dec 12:56:12.508 # WARNING you have Transparent Huge Pages (THP) support enabled in your kernel. This will create latency and memory usage issues with Redis. To fix this issue run the command 'echo never > /sys/kernel/mm/transparent_hugepage/enabled' as root, and add it to your /etc/rc.local in order to retain the setting after a reboot. Redis must be restarted after THP is disabled.
18685:M 13 Dec 12:56:12.508 * Ready to accept connectionsAs shown above: redis starts successfully, but this startup method requires the window to be opened all the time, and other operations cannot be performed, which is not convenient.
Press ctrl c to close the window.
2. Start redis as a background process
The first step: modify the redis.conf file
will
daemonize no
Modify to
daemonize yes
Step 2: Specify the redis.conf file to start
./redis-server /usr/local/redis-4.0.6/redis.conf [root@iZwz991stxdwj560bfmadtZ src]# ./redis-server /usr/local/redis-4.0.6/redis.conf 18713:C 13 Dec 13:07:41.109 # oO0OoO0OoO0Oo Redis is starting oO0OoO0OoO0Oo18713:C 13 Dec 13:07:41.109 # Redis version=4.0.6, bits=64, commit=00000000, modified=0, pid=18713, just started18713:C 13 Dec 13:07:41.109 # Configuration loaded
Step 3: Close the redis process
First use ps - aux | grep redis to view the redis process
[root@iZwz991stxdwj560bfmadtZ src]# ps -aux | grep redis root 18714 0.0 0.1 141752 2008 ? Ssl 13:07 0:00 ./redis-server 127.0.0.1:6379root 18719 0.0 0.0 112644 968 pts/0 R+ 13:09 0:00 grep --color=auto redis
Use the kill command to kill the process
[root@iZwz991stxdwj560bfmadtZ src]# kill 18714
3. Set redis to start automatically after booting
1. Create a new redis directory in the /etc directory
mkdir redis [root@iZwz991stxdwj560bfmadtZ etc]# mkdir redis
2. Copy the /usr/local/redis-4.0.6/redis.conf file to the /etc/redis directory and name it 6379.conf
[root@iZwz991stxdwj560bfmadtZ redis]# cp /usr/local/redis-4.0.6/redis.conf /etc/redis/6379.conf
3 , Copy the redis startup script and put it in the /etc/init.d directory
[root@iZwz991stxdwj560bfmadtZ init.d]# cp /usr/local/redis-4.0.6/utils/redis_init_script /etc/init.d/redisd
4. Set redis to start automatically after booting
First switch to the /etc/init.d directory
Then execute the self-start command
[root@iZwz991stxdwj560bfmadtZ init.d]# chkconfig redisd on service redisd does not support chkconfig
The result is that redisd does not support chkconfig
Solution:
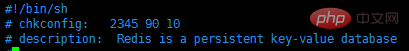
Use vim to edit the redisd file, in the first line Add the following two lines of comments, save and exit
# chkconfig: 2345 90 10# description: Redis is a persistent key-value database
The comment means that the redis service must be started or shut down in run levels 2, 3, 4, and 5. The startup priority is 90 and the shutdown priority is Yes 10
Execute the boot auto-start command again, success
[root@iZwz991stxdwj560bfmadtZ init.d]# chkconfig redisd on
Now you can start and shut down redis directly as a service
Startup:
service redisd start [root@izwz991stxdwj560bfmadtz ~]# service redisd startStarting Redis server...2288:C 13 Dec 13:51:38.087 # oO0OoO0OoO0Oo Redis is starting oO0OoO0OoO0Oo2288:C 13 Dec 13:51:38.087 # Redis version=4.0.6, bits=64, commit=00000000, modified=0, pid=2288, just started2288:C 13 Dec 13:51:38.087 # Configuration loaded
Shutdown:
Method 1: service redisd stop
[root@izwz991stxdwj560bfmadtz ~]# service redisd stop Stopping ... Redis stopped
Method 2: redis-cli SHUTDOWN
3. References
1. http://blog.csdn.net/zc474235918/article/details/50974483
2. http://blog.csdn.net/gxw19874/article/details/51992125
If the following problems occur:
[root@iZwz991stxdwj560bfmadtZ ~]# service redisd start/var/run/redis_6379.pid exists, process is already running or crashed
Reference materials: http://blog.csdn.net/luozhonghua2014/article/details/54649295
Related recommendations: redis database tutorial
The above is the detailed content of How to install redis database under centos system. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 How to optimize CentOS HDFS configuration
Apr 14, 2025 pm 07:15 PM
How to optimize CentOS HDFS configuration
Apr 14, 2025 pm 07:15 PM
Improve HDFS performance on CentOS: A comprehensive optimization guide to optimize HDFS (Hadoop distributed file system) on CentOS requires comprehensive consideration of hardware, system configuration and network settings. This article provides a series of optimization strategies to help you improve HDFS performance. 1. Hardware upgrade and selection resource expansion: Increase the CPU, memory and storage capacity of the server as much as possible. High-performance hardware: adopts high-performance network cards and switches to improve network throughput. 2. System configuration fine-tuning kernel parameter adjustment: Modify /etc/sysctl.conf file to optimize kernel parameters such as TCP connection number, file handle number and memory management. For example, adjust TCP connection status and buffer size
 Centos configuration IP address
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:06 PM
Centos configuration IP address
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:06 PM
Steps to configure IP address in CentOS: View the current network configuration: ip addr Edit the network configuration file: sudo vi /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0 Change IP address: Edit IPADDR= Line changes the subnet mask and gateway (optional): Edit NETMASK= and GATEWAY= Lines Restart the network service: sudo systemctl restart network verification IP address: ip addr
 CentOS HDFS performance tuning tips
Apr 14, 2025 pm 06:00 PM
CentOS HDFS performance tuning tips
Apr 14, 2025 pm 06:00 PM
CentOS Platform Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) Performance Optimization Guide Optimizing HDFS Performance is a multi-faceted issue, and multiple parameters need to be adjusted for specific situations. The following are some key optimization strategies: 1. Memory management adjusts the NameNode and DataNode memory configuration: reasonably configure the HADOOP_NAMENODE_OPTS and HADOOP_DATANODE_OPTS environment variables according to the actual memory size of the server to optimize memory utilization. Enable large page memory: For high memory consumption applications (such as HDFS), enabling large page memory can reduce memory page allocation and management overhead and improve efficiency. 2. Disk I/O optimization uses high-speed storage
 Difference between centos and ubuntu
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:09 PM
Difference between centos and ubuntu
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:09 PM
The key differences between CentOS and Ubuntu are: origin (CentOS originates from Red Hat, for enterprises; Ubuntu originates from Debian, for individuals), package management (CentOS uses yum, focusing on stability; Ubuntu uses apt, for high update frequency), support cycle (CentOS provides 10 years of support, Ubuntu provides 5 years of LTS support), community support (CentOS focuses on stability, Ubuntu provides a wide range of tutorials and documents), uses (CentOS is biased towards servers, Ubuntu is suitable for servers and desktops), other differences include installation simplicity (CentOS is thin)
 Centos shutdown command line
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:12 PM
Centos shutdown command line
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:12 PM
The CentOS shutdown command is shutdown, and the syntax is shutdown [Options] Time [Information]. Options include: -h Stop the system immediately; -P Turn off the power after shutdown; -r restart; -t Waiting time. Times can be specified as immediate (now), minutes ( minutes), or a specific time (hh:mm). Added information can be displayed in system messages.
 How is the GPU support for PyTorch on CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 06:48 PM
How is the GPU support for PyTorch on CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 06:48 PM
Enable PyTorch GPU acceleration on CentOS system requires the installation of CUDA, cuDNN and GPU versions of PyTorch. The following steps will guide you through the process: CUDA and cuDNN installation determine CUDA version compatibility: Use the nvidia-smi command to view the CUDA version supported by your NVIDIA graphics card. For example, your MX450 graphics card may support CUDA11.1 or higher. Download and install CUDAToolkit: Visit the official website of NVIDIACUDAToolkit and download and install the corresponding version according to the highest CUDA version supported by your graphics card. Install cuDNN library:
 What files do you need to modify in HDFS configuration CentOS?
Apr 14, 2025 pm 07:27 PM
What files do you need to modify in HDFS configuration CentOS?
Apr 14, 2025 pm 07:27 PM
When configuring Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) on CentOS, the following key configuration files need to be modified: core-site.xml: fs.defaultFS: Specifies the default file system address of HDFS, such as hdfs://localhost:9000. hadoop.tmp.dir: Specifies the storage directory for Hadoop temporary files. hadoop.proxyuser.root.hosts and hadoop.proxyuser.ro
 Redis: Classifying Its Database Approach
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:06 AM
Redis: Classifying Its Database Approach
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:06 AM
Redis's database methods include in-memory databases and key-value storage. 1) Redis stores data in memory, and reads and writes fast. 2) It uses key-value pairs to store data, supports complex data structures such as lists, collections, hash tables and ordered collections, suitable for caches and NoSQL databases.




