HTML is called Hypertext Markup Language and is a markup language. It includes a series of tags. These tags can unify the document format on the network and connect scattered Internet resources into a logical whole. HTML text is descriptive text composed of HTML commands. HTML commands can describe text, graphics, animations, sounds, tables, links, etc.
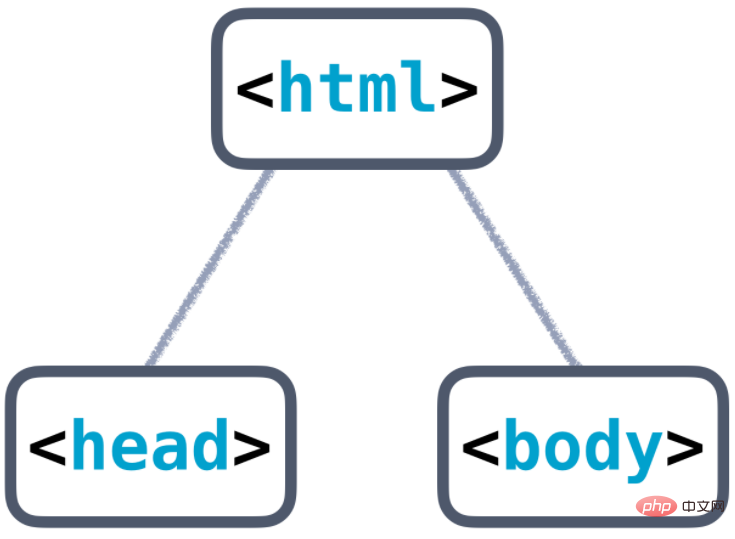
A complete HTML document must contain 3 parts: document declaration, document header and document body. It is they that constitute the skeleton structure of HTML. The document declaration and document header have been introduced respectively before. This article will introduce in detail the basic elements that constitute the HTML skeleton structure. The
HTML
element represents the root (root) of the HTML document. All other elements are descendants of this element. The and tags define the start and end points of the document, and between them are the head and body of the document. The head of the document is defined by the
tag, while the body is defined by the tag

[xmlns]
xmlns attribute is used for assignment The document's XML namespace. The default value is "http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml", which is required in XHTML and optional in HTML
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
Copy after login
HEAD
## The # tag is used to define the head of the document, which is a container for all head elements. ; is mostly invisible and describes some basic attributes and information of the document (title and icon can be presented). The sub-elements under the element mainly include six elements:
,
, <base>, <link>, <style> and <script><p></p> <title> defines the title of the document and is the only required element in the head section<p></p>If the <head> tag is omitted in the document, most browsers will automatically create a <head> element <p></p>More information about the document header can be found here<p></p>BODY<p></p><body> represents the main content of the HTML document. In any HTML document, only There is a <body> element<p></p>[Default style]<p><div class="code" style="position:relative; padding:0px; margin:0px;"><pre class='brush:php;toolbar:false;'>chrome/firefox/safari/IE8+
margin:8px;
IE7-
margin:15px 10px;</pre><div class="contentsignin">Copy after login</div></div></p>Structure<p></p>In the sublime editor, enter !, and then hold down the Tab key to generate a The basic HTML structure is as follows<p><div class="code" style="position:relative; padding:0px; margin:0px;"><pre class='brush:php;toolbar:false;'><!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body></body>
</html></pre><div class="contentsignin">Copy after login</div></div></p>In practice, the header structure of a document often needs to carry some common functions, so the HTML structure is more complex and the structure is as follows<p><div class="code" style="position:relative; padding:0px; margin:0px;"><pre class='brush:php;toolbar:false;'><!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8"/>
<title>Document</title>
<meta name="keywords" content=""/>
<meta name="description" content=""/>
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width"/>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="5/style.css"/>
<link rel="shortcut icon" href="ico.ico"/>
</head>
<body></body>
</html></pre><div class="contentsignin">Copy after login</div></div>Related recommendations:<p>html tutorial<a href="https://www.php.cn/div-tutorial.html" target="_blank"></a><br></p><p>The above is the detailed content of HTML basic structure analysis. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="wzconShengming_sp">
<div class="bzsmdiv_sp">Statement of this Website</div>
<div>The content of this article is voluntarily contributed by netizens, and the copyright belongs to the original author. This site does not assume corresponding legal responsibility. If you find any content suspected of plagiarism or infringement, please contact admin@php.cn</div>
</div>
</div>
<ins class="adsbygoogle"
style="display:block"
data-ad-format="autorelaxed"
data-ad-client="ca-pub-5902227090019525"
data-ad-slot="2507867629"></ins>
<script>
(adsbygoogle = window.adsbygoogle || []).push({});
</script>
<div class="AI_ToolDetails_main4sR">
<ins class="adsbygoogle"
style="display:block"
data-ad-client="ca-pub-5902227090019525"
data-ad-slot="3653428331"
data-ad-format="auto"
data-full-width-responsive="true"></ins>
<script>
(adsbygoogle = window.adsbygoogle || []).push({});
</script>
<!-- <div class="phpgenera_Details_mainR4">
<div class="phpmain1_4R_readrank">
<div class="phpmain1_4R_readrank_top">
<img onerror="this.onerror=''; this.src='/static/imghw/default1.png'"
onerror="this.onerror=''; this.src='/static/imghw/default1.png'"
src="/static/imghw/hotarticle2.png" alt="" />
<h2>Hot Article</h2>
</div>
<div class="phpgenera_Details_mainR4_bottom">
<div class="phpgenera_Details_mainR4_bottoms">
<a href="https://www.php.cn/faq/1796780570.html" title="R.E.P.O. Energy Crystals Explained and What They Do (Yellow Crystal)" class="phpgenera_Details_mainR4_bottom_title">R.E.P.O. Energy Crystals Explained and What They Do (Yellow Crystal)</a>
<div class="phpgenera_Details_mainR4_bottoms_info">
<span>2 weeks ago</span>
<span>By 尊渡假赌尊渡假赌尊渡假赌</span>
</div>
</div>
<div class="phpgenera_Details_mainR4_bottoms">
<a href="https://www.php.cn/faq/1796773439.html" title="Repo: How To Revive Teammates" class="phpgenera_Details_mainR4_bottom_title">Repo: How To Revive Teammates</a>
<div class="phpgenera_Details_mainR4_bottoms_info">
<span>4 weeks ago</span>
<span>By 尊渡假赌尊渡假赌尊渡假赌</span>
</div>
</div>
<div class="phpgenera_Details_mainR4_bottoms">
<a href="https://www.php.cn/faq/1796774171.html" title="Hello Kitty Island Adventure: How To Get Giant Seeds" class="phpgenera_Details_mainR4_bottom_title">Hello Kitty Island Adventure: How To Get Giant Seeds</a>
<div class="phpgenera_Details_mainR4_bottoms_info">
<span>3 weeks ago</span>
<span>By 尊渡假赌尊渡假赌尊渡假赌</span>
</div>
</div>
<div class="phpgenera_Details_mainR4_bottoms">
<a href="https://www.php.cn/faq/1796775427.html" title="How Long Does It Take To Beat Split Fiction?" class="phpgenera_Details_mainR4_bottom_title">How Long Does It Take To Beat Split Fiction?</a>
<div class="phpgenera_Details_mainR4_bottoms_info">
<span>3 weeks ago</span>
<span>By DDD</span>
</div>
</div>
<div class="phpgenera_Details_mainR4_bottoms">
<a href="https://www.php.cn/faq/1796775336.html" title="R.E.P.O. Save File Location: Where Is It & How to Protect It?" class="phpgenera_Details_mainR4_bottom_title">R.E.P.O. Save File Location: Where Is It & How to Protect It?</a>
<div class="phpgenera_Details_mainR4_bottoms_info">
<span>3 weeks ago</span>
<span>By DDD</span>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="phpgenera_Details_mainR3_more">
<a href="https://www.php.cn/article.html">Show More</a>
</div>
</div>
</div> -->
<div class="phpgenera_Details_mainR3">
<div class="phpmain1_4R_readrank">
<div class="phpmain1_4R_readrank_top">
<img onerror="this.onerror=''; this.src='/static/imghw/default1.png'"
onerror="this.onerror=''; this.src='/static/imghw/default1.png'"
src="/static/imghw/hottools2.png" alt="" />
<h2>Hot AI Tools</h2>
</div>
<div class="phpgenera_Details_mainR3_bottom">
<div class="phpmain_tab2_mids_top">
<a href="https://www.php.cn/ai/undresserai-undress" title="Undresser.AI Undress" class="phpmain_tab2_mids_top_img">
<img onerror="this.onerror=''; this.src='/static/imghw/default1.png'"
onerror="this.onerror=''; this.src='/static/imghw/default1.png'"
class="lazy" data-src="https://img.php.cn/upload/ai_manual/001/246/273/173411540686492.jpg?x-oss-process=image/resize,m_fill,h_50,w_50" src="/static/imghw/default1.png" alt="Undresser.AI Undress" />
</a>
<div class="phpmain_tab2_mids_info">
<a href="https://www.php.cn/ai/undresserai-undress" title="Undresser.AI Undress" class="phpmain_tab2_mids_title">
<h3>Undresser.AI Undress</h3>
</a>
<p>AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="phpmain_tab2_mids_top">
<a href="https://www.php.cn/ai/ai-clothes-remover" title="AI Clothes Remover" class="phpmain_tab2_mids_top_img">
<img onerror="this.onerror=''; this.src='/static/imghw/default1.png'"
onerror="this.onerror=''; this.src='/static/imghw/default1.png'"
class="lazy" data-src="https://img.php.cn/upload/ai_manual/001/246/273/173411552797167.jpg?x-oss-process=image/resize,m_fill,h_50,w_50" src="/static/imghw/default1.png" alt="AI Clothes Remover" />
</a>
<div class="phpmain_tab2_mids_info">
<a href="https://www.php.cn/ai/ai-clothes-remover" title="AI Clothes Remover" class="phpmain_tab2_mids_title">
<h3>AI Clothes Remover</h3>
</a>
<p>Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="phpmain_tab2_mids_top">
<a href="https://www.php.cn/ai/undress-ai-tool" title="Undress AI Tool" class="phpmain_tab2_mids_top_img">
<img onerror="this.onerror=''; this.src='/static/imghw/default1.png'"
onerror="this.onerror=''; this.src='/static/imghw/default1.png'"
class="lazy" data-src="https://img.php.cn/upload/ai_manual/001/246/273/173410641626608.jpg?x-oss-process=image/resize,m_fill,h_50,w_50" src="/static/imghw/default1.png" alt="Undress AI Tool" />
</a>
<div class="phpmain_tab2_mids_info">
<a href="https://www.php.cn/ai/undress-ai-tool" title="Undress AI Tool" class="phpmain_tab2_mids_title">
<h3>Undress AI Tool</h3>
</a>
<p>Undress images for free</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="phpmain_tab2_mids_top">
<a href="https://www.php.cn/ai/clothoffio" title="Clothoff.io" class="phpmain_tab2_mids_top_img">
<img onerror="this.onerror=''; this.src='/static/imghw/default1.png'"
onerror="this.onerror=''; this.src='/static/imghw/default1.png'"
class="lazy" data-src="https://img.php.cn/upload/ai_manual/001/246/273/173411529149311.jpg?x-oss-process=image/resize,m_fill,h_50,w_50" src="/static/imghw/default1.png" alt="Clothoff.io" />
</a>
<div class="phpmain_tab2_mids_info">
<a href="https://www.php.cn/ai/clothoffio" title="Clothoff.io" class="phpmain_tab2_mids_title">
<h3>Clothoff.io</h3>
</a>
<p>AI clothes remover</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="phpmain_tab2_mids_top">
<a href="https://www.php.cn/ai/ai-hentai-generator" title="AI Hentai Generator" class="phpmain_tab2_mids_top_img">
<img onerror="this.onerror=''; this.src='/static/imghw/default1.png'"
onerror="this.onerror=''; this.src='/static/imghw/default1.png'"
class="lazy" data-src="https://img.php.cn/upload/ai_manual/001/246/273/173405034393877.jpg?x-oss-process=image/resize,m_fill,h_50,w_50" src="/static/imghw/default1.png" alt="AI Hentai Generator" />
</a>
<div class="phpmain_tab2_mids_info">
<a href="https://www.php.cn/ai/ai-hentai-generator" title="AI Hentai Generator" class="phpmain_tab2_mids_title">
<h3>AI Hentai Generator</h3>
</a>
<p>Generate AI Hentai for free.</p>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="phpgenera_Details_mainR3_more">
<a href="https://www.php.cn/ai">Show More</a>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<script src="https://sw.php.cn/hezuo/cac1399ab368127f9b113b14eb3316d0.js" type="text/javascript"></script>
<div class="phpgenera_Details_mainR4">
<div class="phpmain1_4R_readrank">
<div class="phpmain1_4R_readrank_top">
<img onerror="this.onerror=''; this.src='/static/imghw/default1.png'"
onerror="this.onerror=''; this.src='/static/imghw/default1.png'"
src="/static/imghw/hotarticle2.png" alt="" />
<h2>Hot Article</h2>
</div>
<div class="phpgenera_Details_mainR4_bottom">
<div class="phpgenera_Details_mainR4_bottoms">
<a href="https://www.php.cn/faq/1796780570.html" title="R.E.P.O. Energy Crystals Explained and What They Do (Yellow Crystal)" class="phpgenera_Details_mainR4_bottom_title">R.E.P.O. Energy Crystals Explained and What They Do (Yellow Crystal)</a>
<div class="phpgenera_Details_mainR4_bottoms_info">
<span>2 weeks ago</span>
<span>By 尊渡假赌尊渡假赌尊渡假赌</span>
</div>
</div>
<div class="phpgenera_Details_mainR4_bottoms">
<a href="https://www.php.cn/faq/1796773439.html" title="Repo: How To Revive Teammates" class="phpgenera_Details_mainR4_bottom_title">Repo: How To Revive Teammates</a>
<div class="phpgenera_Details_mainR4_bottoms_info">
<span>4 weeks ago</span>
<span>By 尊渡假赌尊渡假赌尊渡假赌</span>
</div>
</div>
<div class="phpgenera_Details_mainR4_bottoms">
<a href="https://www.php.cn/faq/1796774171.html" title="Hello Kitty Island Adventure: How To Get Giant Seeds" class="phpgenera_Details_mainR4_bottom_title">Hello Kitty Island Adventure: How To Get Giant Seeds</a>
<div class="phpgenera_Details_mainR4_bottoms_info">
<span>3 weeks ago</span>
<span>By 尊渡假赌尊渡假赌尊渡假赌</span>
</div>
</div>
<div class="phpgenera_Details_mainR4_bottoms">
<a href="https://www.php.cn/faq/1796775427.html" title="How Long Does It Take To Beat Split Fiction?" class="phpgenera_Details_mainR4_bottom_title">How Long Does It Take To Beat Split Fiction?</a>
<div class="phpgenera_Details_mainR4_bottoms_info">
<span>3 weeks ago</span>
<span>By DDD</span>
</div>
</div>
<div class="phpgenera_Details_mainR4_bottoms">
<a href="https://www.php.cn/faq/1796775336.html" title="R.E.P.O. Save File Location: Where Is It & How to Protect It?" class="phpgenera_Details_mainR4_bottom_title">R.E.P.O. Save File Location: Where Is It & How to Protect It?</a>
<div class="phpgenera_Details_mainR4_bottoms_info">
<span>3 weeks ago</span>
<span>By DDD</span>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="phpgenera_Details_mainR3_more">
<a href="https://www.php.cn/article.html">Show More</a>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="phpgenera_Details_mainR3">
<div class="phpmain1_4R_readrank">
<div class="phpmain1_4R_readrank_top">
<img onerror="this.onerror=''; this.src='/static/imghw/default1.png'"
onerror="this.onerror=''; this.src='/static/imghw/default1.png'"
src="/static/imghw/hottools2.png" alt="" />
<h2>Hot Tools</h2>
</div>
<div class="phpgenera_Details_mainR3_bottom">
<div class="phpmain_tab2_mids_top">
<a href="https://www.php.cn/toolset/development-tools/92" title="Notepad++7.3.1" class="phpmain_tab2_mids_top_img">
<img onerror="this.onerror=''; this.src='/static/imghw/default1.png'"
onerror="this.onerror=''; this.src='/static/imghw/default1.png'"
class="lazy" data-src="https://img.php.cn/upload/manual/000/000/001/58ab96f0f39f7357.jpg?x-oss-process=image/resize,m_fill,h_50,w_72" src="/static/imghw/default1.png" alt="Notepad++7.3.1" />
</a>
<div class="phpmain_tab2_mids_info">
<a href="https://www.php.cn/toolset/development-tools/92" title="Notepad++7.3.1" class="phpmain_tab2_mids_title">
<h3>Notepad++7.3.1</h3>
</a>
<p>Easy-to-use and free code editor</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="phpmain_tab2_mids_top">
<a href="https://www.php.cn/toolset/development-tools/93" title="SublimeText3 Chinese version" class="phpmain_tab2_mids_top_img">
<img onerror="this.onerror=''; this.src='/static/imghw/default1.png'"
onerror="this.onerror=''; this.src='/static/imghw/default1.png'"
class="lazy" data-src="https://img.php.cn/upload/manual/000/000/001/58ab97a3baad9677.jpg?x-oss-process=image/resize,m_fill,h_50,w_72" src="/static/imghw/default1.png" alt="SublimeText3 Chinese version" />
</a>
<div class="phpmain_tab2_mids_info">
<a href="https://www.php.cn/toolset/development-tools/93" title="SublimeText3 Chinese version" class="phpmain_tab2_mids_title">
<h3>SublimeText3 Chinese version</h3>
</a>
<p>Chinese version, very easy to use</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="phpmain_tab2_mids_top">
<a href="https://www.php.cn/toolset/development-tools/121" title="Zend Studio 13.0.1" class="phpmain_tab2_mids_top_img">
<img onerror="this.onerror=''; this.src='/static/imghw/default1.png'"
onerror="this.onerror=''; this.src='/static/imghw/default1.png'"
class="lazy" data-src="https://img.php.cn/upload/manual/000/000/001/58ab97ecd1ab2670.jpg?x-oss-process=image/resize,m_fill,h_50,w_72" src="/static/imghw/default1.png" alt="Zend Studio 13.0.1" />
</a>
<div class="phpmain_tab2_mids_info">
<a href="https://www.php.cn/toolset/development-tools/121" title="Zend Studio 13.0.1" class="phpmain_tab2_mids_title">
<h3>Zend Studio 13.0.1</h3>
</a>
<p>Powerful PHP integrated development environment</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="phpmain_tab2_mids_top">
<a href="https://www.php.cn/toolset/development-tools/469" title="Dreamweaver CS6" class="phpmain_tab2_mids_top_img">
<img onerror="this.onerror=''; this.src='/static/imghw/default1.png'"
onerror="this.onerror=''; this.src='/static/imghw/default1.png'"
class="lazy" data-src="https://img.php.cn/upload/manual/000/000/001/58d0e0fc74683535.jpg?x-oss-process=image/resize,m_fill,h_50,w_72" src="/static/imghw/default1.png" alt="Dreamweaver CS6" />
</a>
<div class="phpmain_tab2_mids_info">
<a href="https://www.php.cn/toolset/development-tools/469" title="Dreamweaver CS6" class="phpmain_tab2_mids_title">
<h3>Dreamweaver CS6</h3>
</a>
<p>Visual web development tools</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="phpmain_tab2_mids_top">
<a href="https://www.php.cn/toolset/development-tools/500" title="SublimeText3 Mac version" class="phpmain_tab2_mids_top_img">
<img onerror="this.onerror=''; this.src='/static/imghw/default1.png'"
onerror="this.onerror=''; this.src='/static/imghw/default1.png'"
class="lazy" data-src="https://img.php.cn/upload/manual/000/000/001/58d34035e2757995.png?x-oss-process=image/resize,m_fill,h_50,w_72" src="/static/imghw/default1.png" alt="SublimeText3 Mac version" />
</a>
<div class="phpmain_tab2_mids_info">
<a href="https://www.php.cn/toolset/development-tools/500" title="SublimeText3 Mac version" class="phpmain_tab2_mids_title">
<h3>SublimeText3 Mac version</h3>
</a>
<p>God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)</p>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="phpgenera_Details_mainR3_more">
<a href="https://www.php.cn/ai">Show More</a>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="phpgenera_Details_mainR4">
<div class="phpmain1_4R_readrank">
<div class="phpmain1_4R_readrank_top">
<img onerror="this.onerror=''; this.src='/static/imghw/default1.png'"
onerror="this.onerror=''; this.src='/static/imghw/default1.png'"
src="/static/imghw/hotarticle2.png" alt="" />
<h2>Hot Topics</h2>
</div>
<div class="phpgenera_Details_mainR4_bottom">
<div class="phpgenera_Details_mainR4_bottoms">
<a href="https://www.php.cn/faq/gmailyxdlrkzn" title="Where is the login entrance for gmail email?" class="phpgenera_Details_mainR4_bottom_title">Where is the login entrance for gmail email?</a>
<div class="phpgenera_Details_mainR4_bottoms_info">
<div class="phpgenera_Details_mainR4_bottoms_infos">
<img src="/static/imghw/eyess.png" alt="" />
<span>7316</span>
</div>
<div class="phpgenera_Details_mainR4_bottoms_infos">
<img src="/static/imghw/tiezi.png" alt="" />
<span>9</span>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="phpgenera_Details_mainR4_bottoms">
<a href="https://www.php.cn/faq/java-tutorial" title="Java Tutorial" class="phpgenera_Details_mainR4_bottom_title">Java Tutorial</a>
<div class="phpgenera_Details_mainR4_bottoms_info">
<div class="phpgenera_Details_mainR4_bottoms_infos">
<img src="/static/imghw/eyess.png" alt="" />
<span>1625</span>
</div>
<div class="phpgenera_Details_mainR4_bottoms_infos">
<img src="/static/imghw/tiezi.png" alt="" />
<span>14</span>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="phpgenera_Details_mainR4_bottoms">
<a href="https://www.php.cn/faq/cakephp-tutor" title="CakePHP Tutorial" class="phpgenera_Details_mainR4_bottom_title">CakePHP Tutorial</a>
<div class="phpgenera_Details_mainR4_bottoms_info">
<div class="phpgenera_Details_mainR4_bottoms_infos">
<img src="/static/imghw/eyess.png" alt="" />
<span>1349</span>
</div>
<div class="phpgenera_Details_mainR4_bottoms_infos">
<img src="/static/imghw/tiezi.png" alt="" />
<span>46</span>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="phpgenera_Details_mainR4_bottoms">
<a href="https://www.php.cn/faq/laravel-tutori" title="Laravel Tutorial" class="phpgenera_Details_mainR4_bottom_title">Laravel Tutorial</a>
<div class="phpgenera_Details_mainR4_bottoms_info">
<div class="phpgenera_Details_mainR4_bottoms_infos">
<img src="/static/imghw/eyess.png" alt="" />
<span>1261</span>
</div>
<div class="phpgenera_Details_mainR4_bottoms_infos">
<img src="/static/imghw/tiezi.png" alt="" />
<span>25</span>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="phpgenera_Details_mainR4_bottoms">
<a href="https://www.php.cn/faq/php-tutorial" title="PHP Tutorial" class="phpgenera_Details_mainR4_bottom_title">PHP Tutorial</a>
<div class="phpgenera_Details_mainR4_bottoms_info">
<div class="phpgenera_Details_mainR4_bottoms_infos">
<img src="/static/imghw/eyess.png" alt="" />
<span>1208</span>
</div>
<div class="phpgenera_Details_mainR4_bottoms_infos">
<img src="/static/imghw/tiezi.png" alt="" />
<span>29</span>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="phpgenera_Details_mainR3_more">
<a href="https://www.php.cn/faq/zt">Show More</a>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="Article_Details_main2">
<div class="phpgenera_Details_mainL4">
<div class="phpmain1_2_top">
<a href="javascript:void(0);" class="phpmain1_2_top_title">Related knowledge<img
src="/static/imghw/index2_title2.png" alt="" /></a>
</div>
<div class="phpgenera_Details_mainL4_info">
<div class="phphistorical_Version2_mids">
<a href="https://www.php.cn/faq/1796600245.html" title="Table Border in HTML" class="phphistorical_Version2_mids_img">
<img onerror="this.onerror=''; this.src='/static/imghw/default1.png'"
src="/static/imghw/default1.png" class="lazy" data-src="https://img.php.cn/upload/article/202409/04/2024090416492486715.jpg?x-oss-process=image/resize,m_fill,h_207,w_330" alt="Table Border in HTML" />
</a>
<a href="https://www.php.cn/faq/1796600245.html" title="Table Border in HTML" class="phphistorical_Version2_mids_title">Table Border in HTML</a>
<span class="Articlelist_txts_time">Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:49 PM</span>
<p class="Articlelist_txts_p">Guide to Table Border in HTML. Here we discuss multiple ways for defining table-border with examples of the Table Border in HTML.</p>
</div>
<div class="phphistorical_Version2_mids">
<a href="https://www.php.cn/faq/1796600244.html" title="Nested Table in HTML" class="phphistorical_Version2_mids_img">
<img onerror="this.onerror=''; this.src='/static/imghw/default1.png'"
src="/static/imghw/default1.png" class="lazy" data-src="https://img.php.cn/upload/article/202409/04/2024090416491283996.jpg?x-oss-process=image/resize,m_fill,h_207,w_330" alt="Nested Table in HTML" />
</a>
<a href="https://www.php.cn/faq/1796600244.html" title="Nested Table in HTML" class="phphistorical_Version2_mids_title">Nested Table in HTML</a>
<span class="Articlelist_txts_time">Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:49 PM</span>
<p class="Articlelist_txts_p">This is a guide to Nested Table in HTML. Here we discuss how to create a table within the table along with the respective examples.</p>
</div>
<div class="phphistorical_Version2_mids">
<a href="https://www.php.cn/faq/1796600238.html" title="HTML margin-left" class="phphistorical_Version2_mids_img">
<img onerror="this.onerror=''; this.src='/static/imghw/default1.png'"
src="/static/imghw/default1.png" class="lazy" data-src="https://img.php.cn/upload/article/202409/04/2024090416482056439.jpg?x-oss-process=image/resize,m_fill,h_207,w_330" alt="HTML margin-left" />
</a>
<a href="https://www.php.cn/faq/1796600238.html" title="HTML margin-left" class="phphistorical_Version2_mids_title">HTML margin-left</a>
<span class="Articlelist_txts_time">Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:48 PM</span>
<p class="Articlelist_txts_p">Guide to HTML margin-left. Here we discuss a brief overview on HTML margin-left and its Examples along with its Code Implementation.</p>
</div>
<div class="phphistorical_Version2_mids">
<a href="https://www.php.cn/faq/1796600271.html" title="HTML Table Layout" class="phphistorical_Version2_mids_img">
<img onerror="this.onerror=''; this.src='/static/imghw/default1.png'"
src="/static/imghw/default1.png" class="lazy" data-src="https://img.php.cn/upload/article/202409/04/2024090416543391948.jpg?x-oss-process=image/resize,m_fill,h_207,w_330" alt="HTML Table Layout" />
</a>
<a href="https://www.php.cn/faq/1796600271.html" title="HTML Table Layout" class="phphistorical_Version2_mids_title">HTML Table Layout</a>
<span class="Articlelist_txts_time">Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:54 PM</span>
<p class="Articlelist_txts_p">Guide to HTML Table Layout. Here we discuss the Values of HTML Table Layout along with the examples and outputs n detail.</p>
</div>
<div class="phphistorical_Version2_mids">
<a href="https://www.php.cn/faq/1796600227.html" title="Moving Text in HTML" class="phphistorical_Version2_mids_img">
<img onerror="this.onerror=''; this.src='/static/imghw/default1.png'"
src="/static/imghw/default1.png" class="lazy" data-src="https://img.php.cn/upload/article/202409/04/2024090416455153019.jpg?x-oss-process=image/resize,m_fill,h_207,w_330" alt="Moving Text in HTML" />
</a>
<a href="https://www.php.cn/faq/1796600227.html" title="Moving Text in HTML" class="phphistorical_Version2_mids_title">Moving Text in HTML</a>
<span class="Articlelist_txts_time">Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:45 PM</span>
<p class="Articlelist_txts_p">Guide to Moving Text in HTML. Here we discuss an introduction, how marquee tag work with syntax and examples to implement.</p>
</div>
<div class="phphistorical_Version2_mids">
<a href="https://www.php.cn/faq/1796600210.html" title="HTML Ordered List" class="phphistorical_Version2_mids_img">
<img onerror="this.onerror=''; this.src='/static/imghw/default1.png'"
src="/static/imghw/default1.png" class="lazy" data-src="https://img.php.cn/upload/article/202409/04/2024090416432927533.jpg?x-oss-process=image/resize,m_fill,h_207,w_330" alt="HTML Ordered List" />
</a>
<a href="https://www.php.cn/faq/1796600210.html" title="HTML Ordered List" class="phphistorical_Version2_mids_title">HTML Ordered List</a>
<span class="Articlelist_txts_time">Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:43 PM</span>
<p class="Articlelist_txts_p">Guide to the HTML Ordered List. Here we also discuss introduction of HTML Ordered list and types along with their example respectively</p>
</div>
<div class="phphistorical_Version2_mids">
<a href="https://www.php.cn/faq/1796764479.html" title="How do you parse and process HTML/XML in PHP?" class="phphistorical_Version2_mids_img">
<img onerror="this.onerror=''; this.src='/static/imghw/default1.png'"
src="/static/imghw/default1.png" class="lazy" data-src="https://img.php.cn/upload/article/001/246/273/173890063284749.png?x-oss-process=image/resize,m_fill,h_207,w_330" alt="How do you parse and process HTML/XML in PHP?" />
</a>
<a href="https://www.php.cn/faq/1796764479.html" title="How do you parse and process HTML/XML in PHP?" class="phphistorical_Version2_mids_title">How do you parse and process HTML/XML in PHP?</a>
<span class="Articlelist_txts_time">Feb 07, 2025 am 11:57 AM</span>
<p class="Articlelist_txts_p">This tutorial demonstrates how to efficiently process XML documents using PHP. XML (eXtensible Markup Language) is a versatile text-based markup language designed for both human readability and machine parsing. It's commonly used for data storage an</p>
</div>
<div class="phphistorical_Version2_mids">
<a href="https://www.php.cn/faq/1796600246.html" title="HTML onclick Button" class="phphistorical_Version2_mids_img">
<img onerror="this.onerror=''; this.src='/static/imghw/default1.png'"
src="/static/imghw/default1.png" class="lazy" data-src="https://img.php.cn/upload/article/202409/04/2024090416493797970.jpg?x-oss-process=image/resize,m_fill,h_207,w_330" alt="HTML onclick Button" />
</a>
<a href="https://www.php.cn/faq/1796600246.html" title="HTML onclick Button" class="phphistorical_Version2_mids_title">HTML onclick Button</a>
<span class="Articlelist_txts_time">Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:49 PM</span>
<p class="Articlelist_txts_p">Guide to HTML onclick Button. Here we discuss their introduction, working, examples and onclick Event in various events respectively.</p>
</div>
</div>
<a href="https://www.php.cn/web-designer.html" class="phpgenera_Details_mainL4_botton">
<span>See all articles</span>
<img src="/static/imghw/down_right.png" alt="" />
</a>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</main>
<footer>
<div class="footer">
<div class="footertop">
<img src="/static/imghw/logo.png" alt="">
<p>Public welfare online PHP training,Help PHP learners grow quickly!</p>
</div>
<div class="footermid">
<a href="https://www.php.cn/about/us.html">About us</a>
<a href="https://www.php.cn/about/disclaimer.html">Disclaimer</a>
<a href="https://www.php.cn/update/article_0_1.html">Sitemap</a>
</div>
<div class="footerbottom">
<p>
© php.cn All rights reserved
</p>
</div>
</div>
</footer>
<input type="hidden" id="verifycode" value="/captcha.html">
<script>layui.use(['element', 'carousel'], function () {var element = layui.element;$ = layui.jquery;var carousel = layui.carousel;carousel.render({elem: '#test1', width: '100%', height: '330px', arrow: 'always'});$.getScript('/static/js/jquery.lazyload.min.js', function () {$("img").lazyload({placeholder: "/static/images/load.jpg", effect: "fadeIn", threshold: 200, skip_invisible: false});});});</script>
<script src="/static/js/common_new.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="/static/js/jquery.cookie.js?1743505818"></script>
<script src="https://vdse.bdstatic.com//search-video.v1.min.js"></script>
<link rel='stylesheet' id='_main-css' href='/static/css/viewer.min.css?2' type='text/css' media='all' />
<script type='text/javascript' src='/static/js/viewer.min.js?1'></script>
<script type='text/javascript' src='/static/js/jquery-viewer.min.js'></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="/static/js/global.min.js?5.5.53"></script>
<script>
var _paq = window._paq = window._paq || [];
/* tracker methods like "setCustomDimension" should be called before "trackPageView" */
_paq.push(['trackPageView']);
_paq.push(['enableLinkTracking']);
(function () {
var u = "https://tongji.php.cn/";
_paq.push(['setTrackerUrl', u + 'matomo.php']);
_paq.push(['setSiteId', '9']);
var d = document,
g = d.createElement('script'),
s = d.getElementsByTagName('script')[0];
g.async = true;
g.src = u + 'matomo.js';
s.parentNode.insertBefore(g, s);
})();
</script>
<script>
// top
layui.use(function () {
var util = layui.util;
util.fixbar({
on: {
mouseenter: function (type) {
layer.tips(type, this, {
tips: 4,
fixed: true,
});
},
mouseleave: function (type) {
layer.closeAll("tips");
},
},
});
});
document.addEventListener("DOMContentLoaded", (event) => {
// 定义一个函数来处理滚动链接的点击事件
function setupScrollLink(scrollLinkId, targetElementId) {
const scrollLink = document.getElementById(scrollLinkId);
const targetElement = document.getElementById(targetElementId);
if (scrollLink && targetElement) {
scrollLink.addEventListener("click", (e) => {
e.preventDefault(); // 阻止默认链接行为
targetElement.scrollIntoView({
behavior: "smooth"
}); // 平滑滚动到目标元素
});
} else {
console.warn(
`Either scroll link with ID '${scrollLinkId}' or target element with ID '${targetElementId}' not found.`
);
}
}
// 使用该函数设置多个滚动链接
setupScrollLink("Article_Details_main1L2s_1", "article_main_title1");
setupScrollLink("Article_Details_main1L2s_2", "article_main_title2");
setupScrollLink("Article_Details_main1L2s_3", "article_main_title3");
setupScrollLink("Article_Details_main1L2s_4", "article_main_title4");
setupScrollLink("Article_Details_main1L2s_5", "article_main_title5");
setupScrollLink("Article_Details_main1L2s_6", "article_main_title6");
// 可以继续添加更多的滚动链接设置
});
window.addEventListener("scroll", function () {
var fixedElement = document.getElementById("Article_Details_main1Lmain");
var scrollTop = window.scrollY || document.documentElement.scrollTop; // 兼容不同浏览器
var clientHeight = window.innerHeight || document.documentElement.clientHeight; // 视口高度
var scrollHeight = document.documentElement.scrollHeight; // 页面总高度
// 计算距离底部的距离
var distanceToBottom = scrollHeight - scrollTop - clientHeight;
// 当距离底部小于或等于300px时,取消固定定位
if (distanceToBottom <= 980) {
fixedElement.classList.remove("Article_Details_main1Lmain");
fixedElement.classList.add("Article_Details_main1Lmain_relative");
} else {
// 否则,保持固定定位
fixedElement.classList.remove("Article_Details_main1Lmain_relative");
fixedElement.classList.add("Article_Details_main1Lmain");
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>