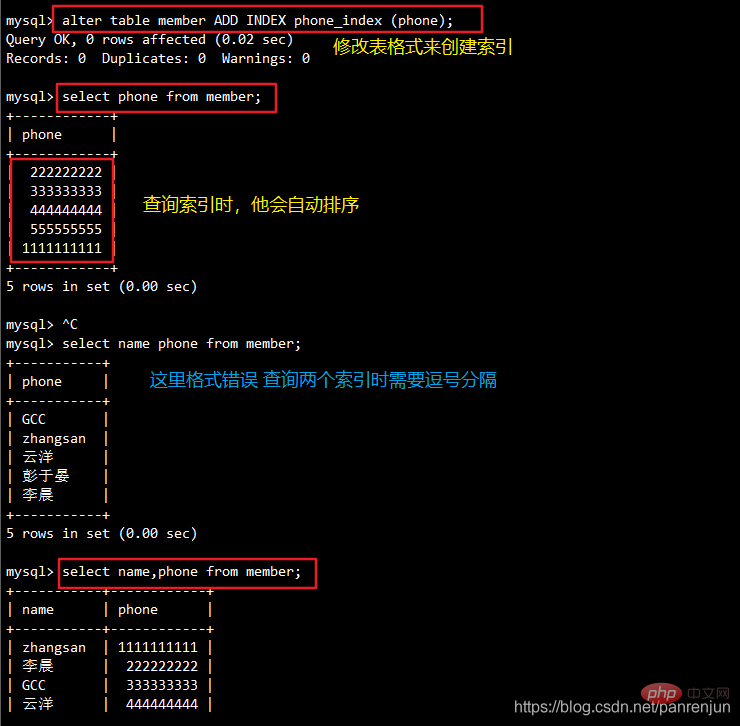
ALTER TABLE 表名 ADD INDEX 索引名 (列名);例:alter table member ADD INDEX phone_index (phone);select phone from member;
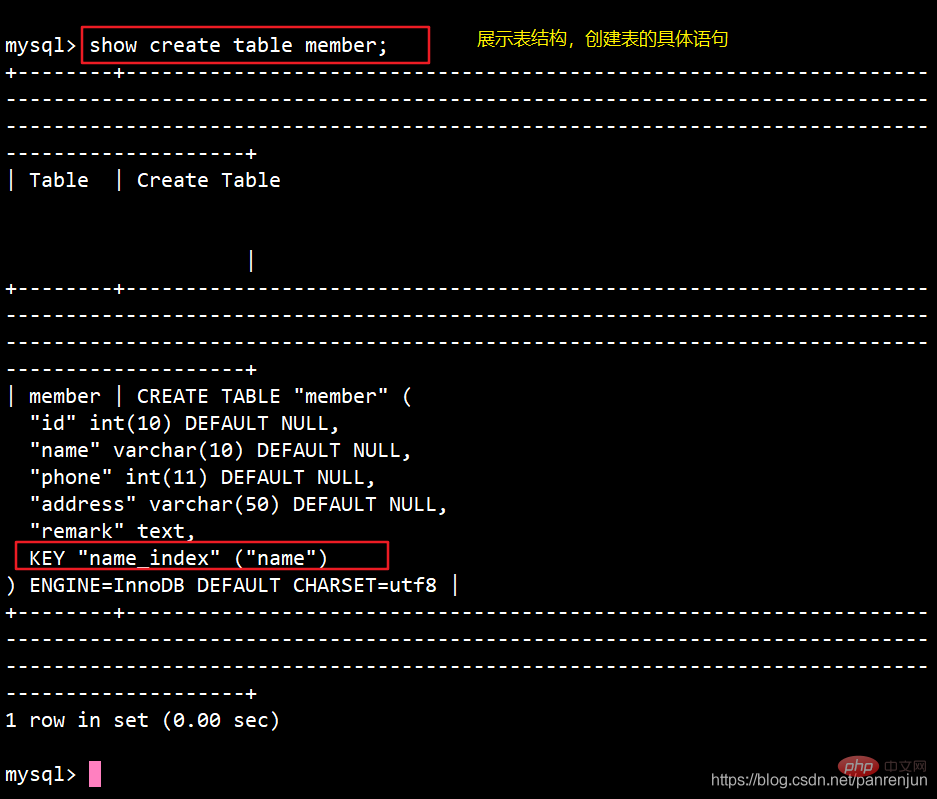
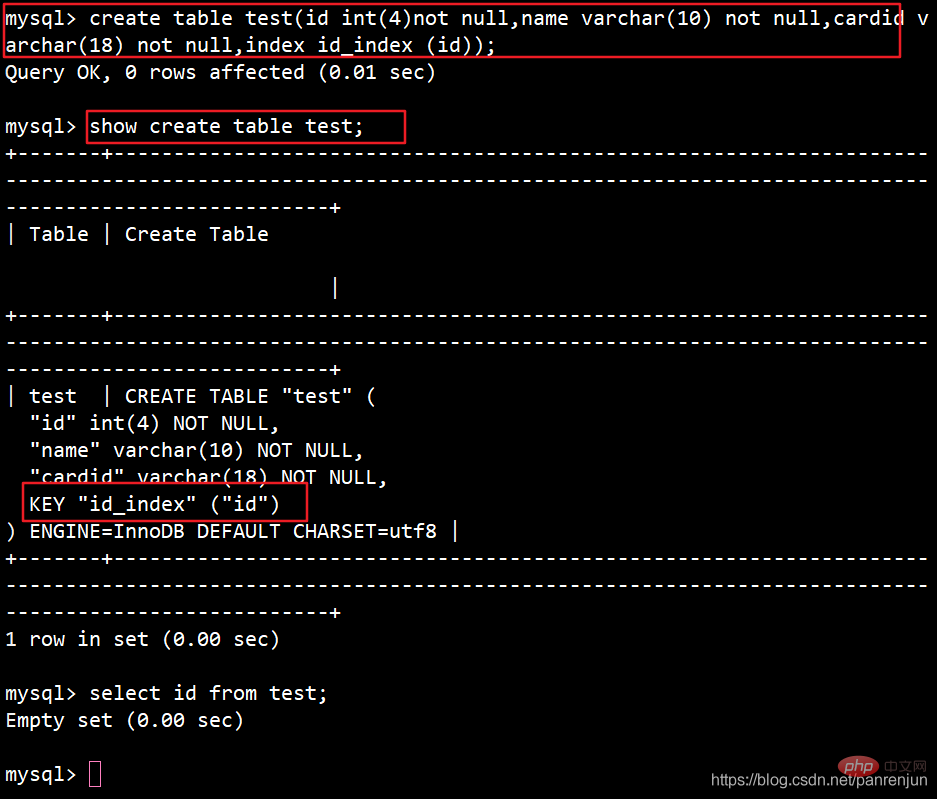
CREATE TABLE 表名 ( 字段1 数据类型,字段2 数据类型[,...],INDEX 索引名 (列名));例:create table test(id int(4) not null,name varchar(10) not null,cardid varchar(18) not null,index id_index (id));show create table test;
CREATE UNIQUE INDEX 索引名 ON 表名(列名);
ALTER TABLE 表名 ADD UNIQUE 索引名 (列名);例:alter table member add unique name_index (cardid);
 Database
Database
 Mysql Tutorial
Mysql Tutorial
 In-depth understanding of MySQL index principles and implementation, and rapid database retrieval
In-depth understanding of MySQL index principles and implementation, and rapid database retrieval
In-depth understanding of MySQL index principles and implementation, and rapid database retrieval

Free learning recommendation: mysql video tutorial
##1. The concept of index
1. The index is a sorted list, in which the index value and the physical address of the row containing the data containing the value are stored (similar to C language The linked list points to the memory address of the data record through a pointer). 2. After using the index, you do not need to scan the entire table to locate the data of a certain row. Instead, you first find the physical address corresponding to the row of data through the index table and then access the corresponding data, thus speeding up the query speed of the database. . 3.The index is like the table of contents of a book. You can quickly find the required content based on the page numbers in the table of contents.
4. Index is a method of sorting the values of one or several columns in a table. 5. The purpose of establishing an index is to speed up the search or sorting of records in the table.2. The role of index
1. After setting up a suitable index, the database can greatly speed up the query by using various rapid positioning technologies. This is to create an index. The main reason. 2. When the table is very large or the query involves multiple tables, using indexes can increase the query speed by thousands or tens of thousands of times.
3. It can reduce the I/O cost of the database, and the index can also reduce the sorting cost of the database.
4. By creating a unique index, the uniqueness of each row of data in the data table can be guaranteed.
5. Can speed up the connection between tables.
6. When using grouping and sorting, the time of grouping and sorting can be greatly reduced.
3. Side Effects of Index
1. Indexes require additional disk space.- For the MyISAM engine, the index file and the data file are separated, and the index file is used to save the address of the data record.
- The table data file of the InnoDB engine itself is an index file.
4. Principles of creating indexes
Indexes can increase the speed of database queries, but they are not suitable for creating indexes in all circumstances. Because the index itself consumes system resources, if there is an index, the database will first perform an index query and then locate the specific data row. If the index is used improperly, it will increase the burden on the database. 1. The primary key and foreign key of the table must have indexes. Because the primary key is unique and the foreign key is associated with the primary key of the main table, it can be quickly located during querying. 2. Tables with more than 300 rows of records should have indexes. If there is no index, each query needs to traverse the table, which will seriously affect the performance of the database.
3. Tables that are frequently connected to other tables should create indexes on the connection fields.
4. Fields with poor uniqueness are not suitable for indexing.
5. Fields that are updated too frequently are not suitable for creating indexes.
6. Fields that often appear in where clauses, especially fields in large tables, should be indexed.
7. Indexes should be built on highly selective fields.
8. Indexes should be built on small fields. Do not build indexes on large text fields or even very long fields.
5. Classification and creation of indexes
在做之前先用这张表做示范 create table member (id int(10),name varchar(10),Cardid varchar(10),phone int(11),address varchar(50),remark text);
(1) Ordinary index
Ordinary index: the most basic Index type, no restrictions such as uniqueness. 1. Create an index directlyCREATE INDEX 索引名 ON 表名 (列名[(length)]);
#(列名(length)):length是可选项,下同。如果忽略 length 的值,则使用整个列的值作为索引。如果指定使用列前的 length 个字符来创建索引,这样有利于减小索引文件的大小。
#索引名建议以“_index”结尾。
Copy after login
CREATE INDEX 索引名 ON 表名 (列名[(length)]); #(列名(length)):length是可选项,下同。如果忽略 length 的值,则使用整个列的值作为索引。如果指定使用列前的 length 个字符来创建索引,这样有利于减小索引文件的大小。 #索引名建议以“_index”结尾。
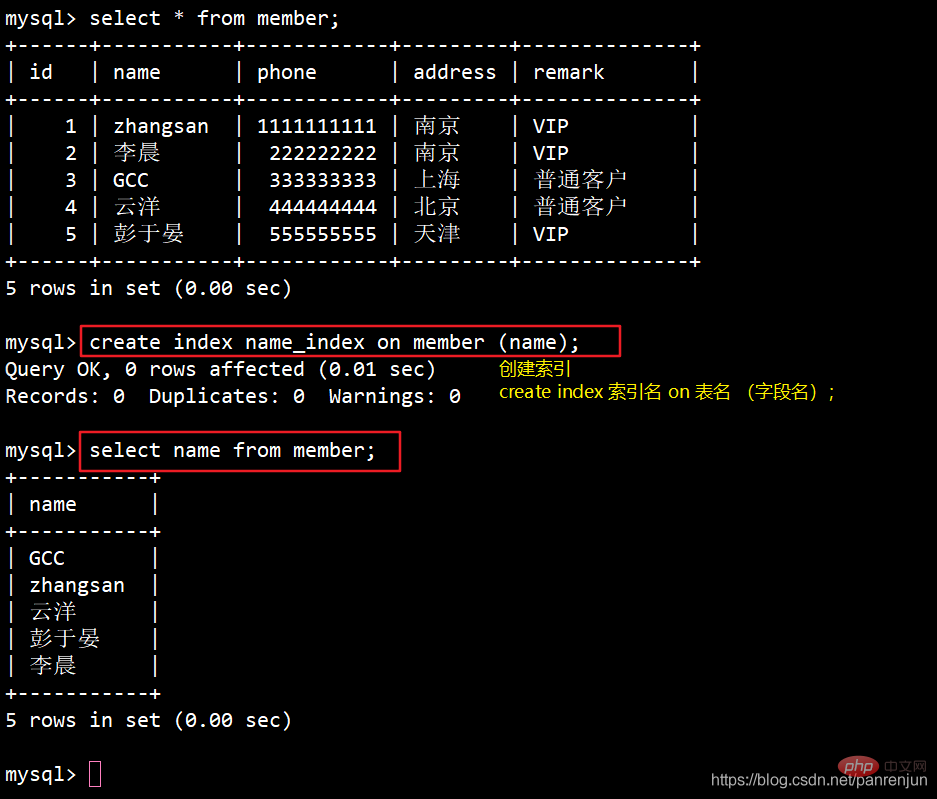
ALTER TABLE 表名 ADD INDEX 索引名 (列名);例:alter table member ADD INDEX phone_index (phone);select phone from member;
Copy after login
ALTER TABLE 表名 ADD INDEX 索引名 (列名);例:alter table member ADD INDEX phone_index (phone);select phone from member;
CREATE TABLE 表名 ( 字段1 数据类型,字段2 数据类型[,...],INDEX 索引名 (列名));例:create table test(id int(4) not null,name varchar(10) not null,cardid varchar(18) not null,index id_index (id));show create table test;
Copy after login
CREATE TABLE 表名 ( 字段1 数据类型,字段2 数据类型[,...],INDEX 索引名 (列名));例:create table test(id int(4) not null,name varchar(10) not null,cardid varchar(18) not null,index id_index (id));show create table test;
与普通索引类似,但区别是唯一索引列的每个值都唯一。
唯一索引允许有空值(注意和主键不同)。如果是用组合索引创建,则列值的组合必须唯一。添加唯一键将自动创建唯一索引。
Copy after login
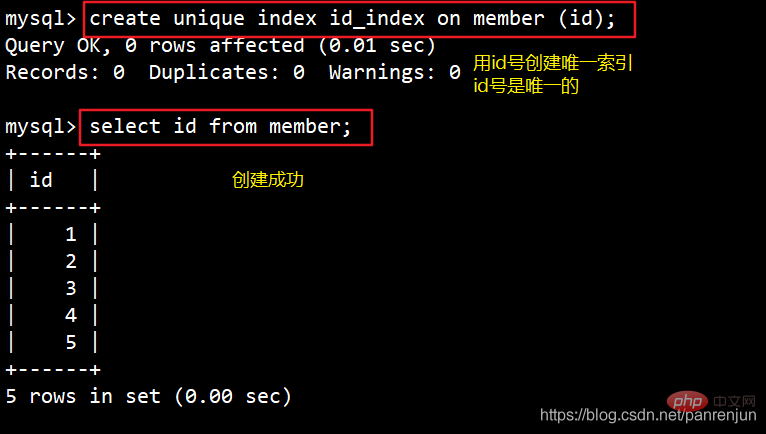
1. Create a unique index directly与普通索引类似,但区别是唯一索引列的每个值都唯一。 唯一索引允许有空值(注意和主键不同)。如果是用组合索引创建,则列值的组合必须唯一。添加唯一键将自动创建唯一索引。
CREATE UNIQUE INDEX 索引名 ON 表名(列名);
Copy after login
CREATE UNIQUE INDEX 索引名 ON 表名(列名);
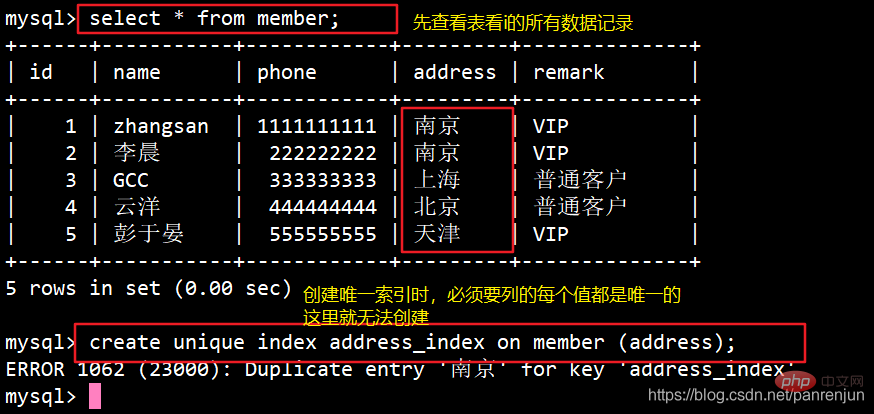
ALTER TABLE 表名 ADD UNIQUE 索引名 (列名);例:alter table member add unique name_index (cardid);
Copy after login
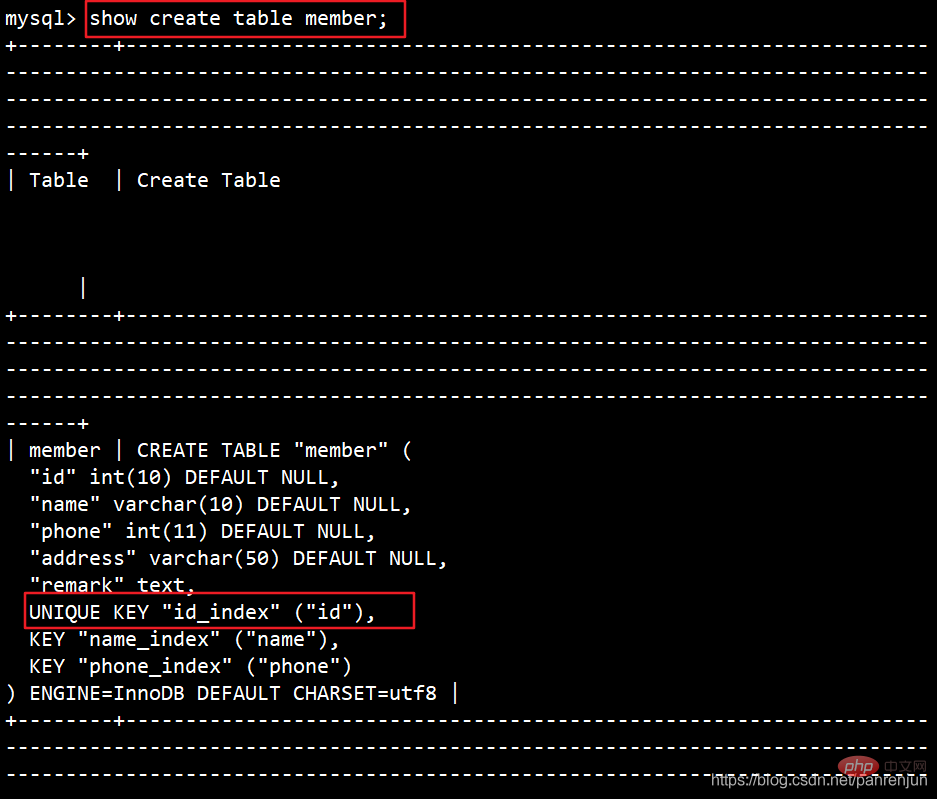
In order to facilitate the experiment, I first deleted the previous indexALTER TABLE 表名 ADD UNIQUE 索引名 (列名);例:alter table member add unique name_index (cardid);
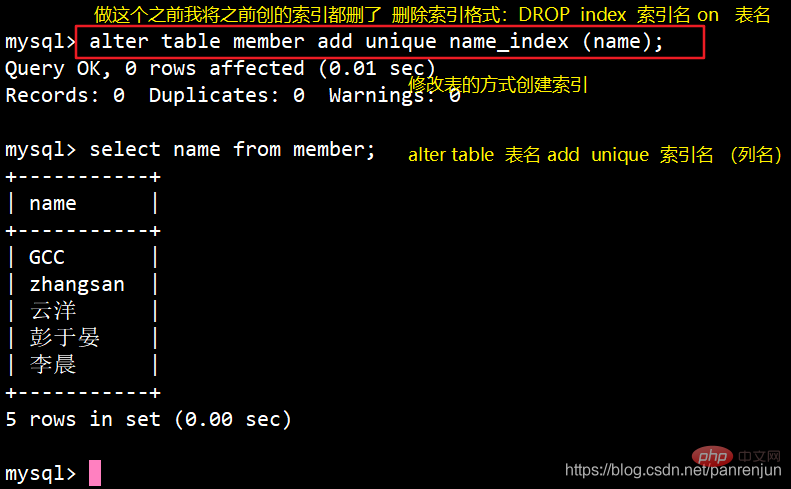
3、创建表的时候指定
CREATE TABLE 表名 (字段1 数据类型,字段2 数据类型[,...],UNIQUE 索引名 (列名));
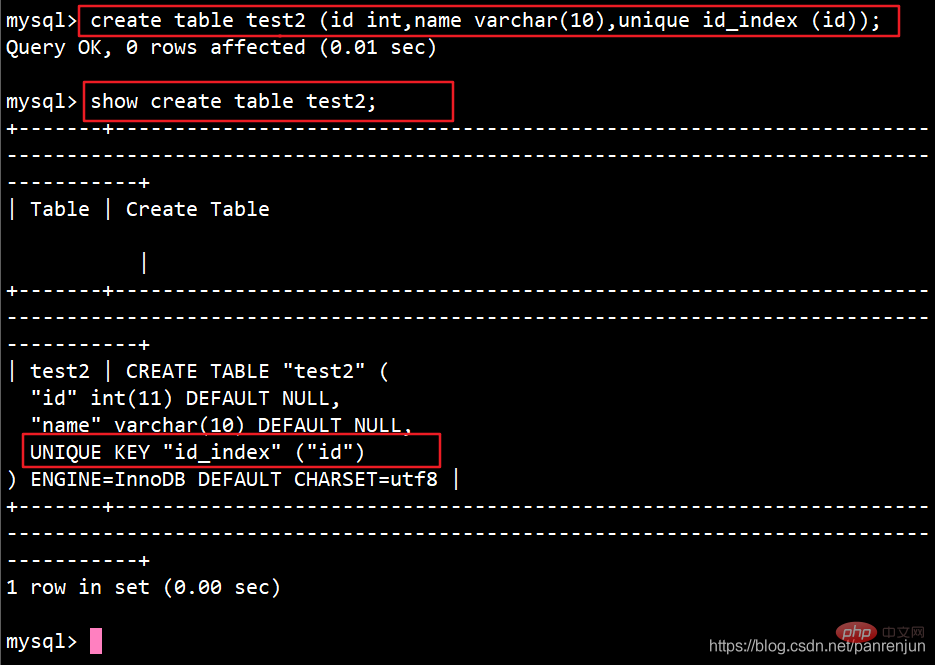
(三)、主键索引
是一种特殊的唯一索引,必须指定为“PRIMARY KEY”。 一个表只能有一个主键,不允许有空值。 添加主键将自动创建主键索引。
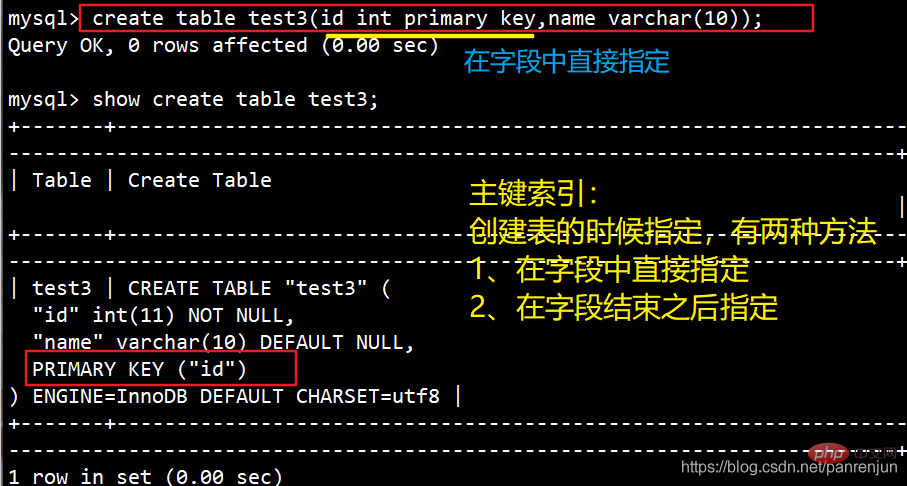
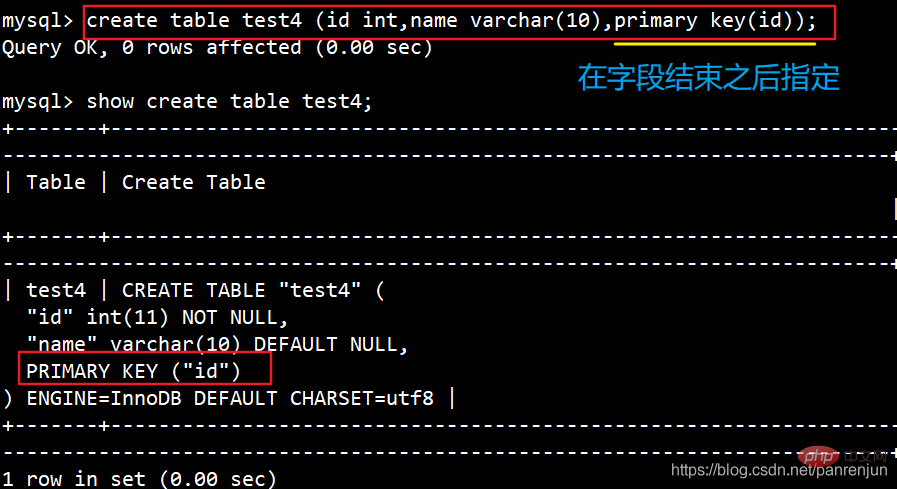
ALTER TABLE 表名 ADD PRIMARY KEY (列名);
(四)、组合索引(单列索引与多列索引)
组合索引:可以是单列上创建的索引,也可以是在多列上创建的索引。需要满足最左原则,因为 select语句的 where 条件是依次从左往右执行的,所以在使用 select 语句查询时 where 条件使用的字段顺序必须和组合索引中的排序一致,否则索引将不会生效。
CREATE TABLE 表名 (列名1 数据类型,列名2 数据类型,列名3 数据类型,INDEX 索引名(列名1,列名2,列名3));select * from 表名 where 列名1='...' AND 列名2='...' AND 列名3='...';
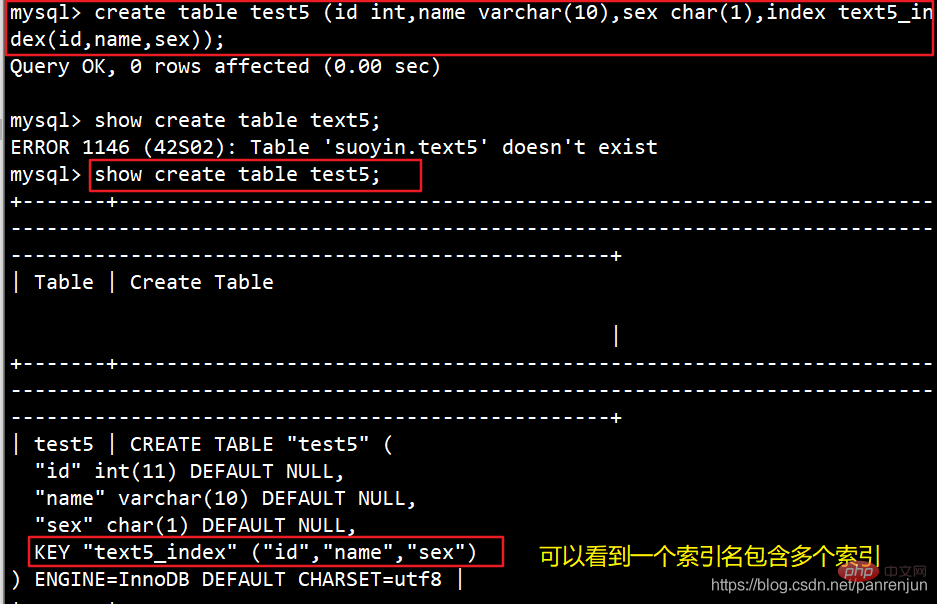
(五)、全文索引
适合在进行模糊查询的时候使用,可用于在一篇文章中检索文本信息。 在 MySQL5.6 版本以前FULLTEXT 索引仅可用于 MyISAM 引擎,在 5.6 版本之后 innodb 引擎也支持 FULLTEXT 索引。全文索引可以在 CHAR、VARCHAR 或者 TEXT 类型的列上创建。每个表只允许有一个全文索引。
CREATE FULLTEXT INDEX 索引名 ON 表名 (列名);例:select * from member;create fulltext index name_index on member (name);
- 修改表的方式创建
ALTER TABLE 表名 ADD FULLTEXT 索引名 (列名);
- 创建表的时候指定索引
CREATE TABLE 表名 (字段1 数据类型[,...],FULLTEXT 索引名 (列名));
#数据类型可以为 CHAR、VARCHAR 或者 TEXT
- 使用全文索引查询
SELECT * FROM 表名 WHERE MATCH(列名) AGAINST('查询内容');例:select * from member where match(remark) against('this is vip');
六、查看索引
show index from 表名;show index from 表名\G; 竖向显示表索引信息 show keys from 表名;show keys from 表名\G;
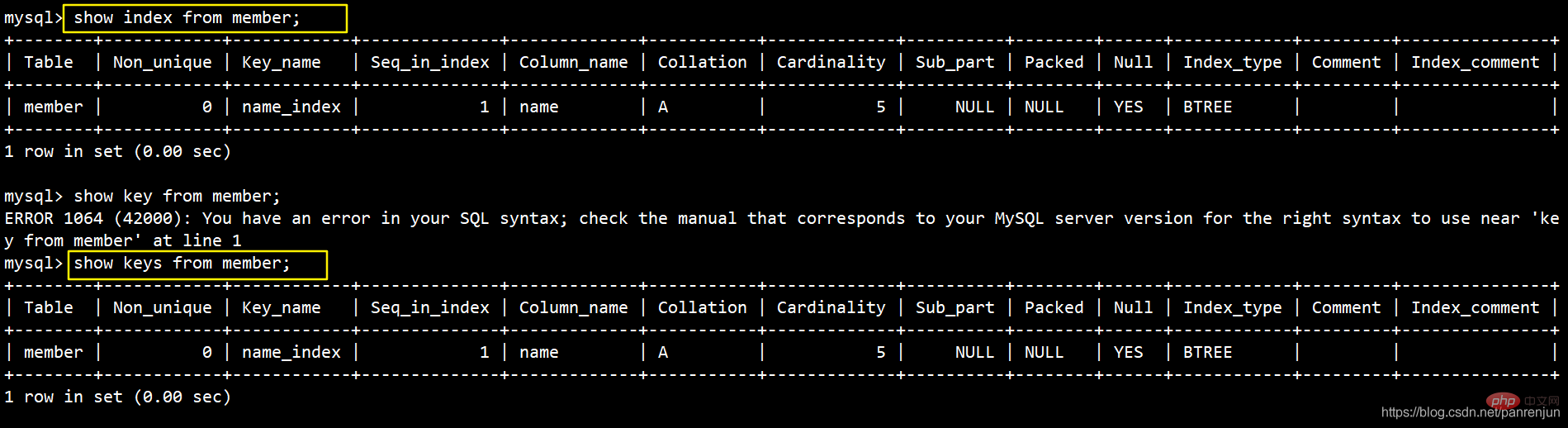
| Table | 表的名称 |
|---|---|
| Non_unique | 如果索引不能包括重复词,则为 0;如果可以,则为 1。 |
| Key_name | 索引的名称。 |
| Seq_in_index | 索引中的列序号,从 1 开始。 |
| Column_name | 列名称。 |
| Collation | 列以什么方式存储在索引中。在 MySQL 中,有值‘A’(升序)或 NULL(无分类) |
| Cardinality | 索引中唯一值数目的估计值。 |
| Sub_part | 如果列只是被部分地编入索引,则为被编入索引的字符的数目。如果整列被编入索引,则为 NULL。 |
| Packed | 指示关键字如何被压缩。如果没有被压缩,则为 NULL |
| Null | 如果列含有 NULL,则含有 YES。如果没有,则该列含有 NO |
| Index_type | 用过的索引方法(BTREE, FULLTEXT, HASH, RTREE) |
| Comment | 备注 |
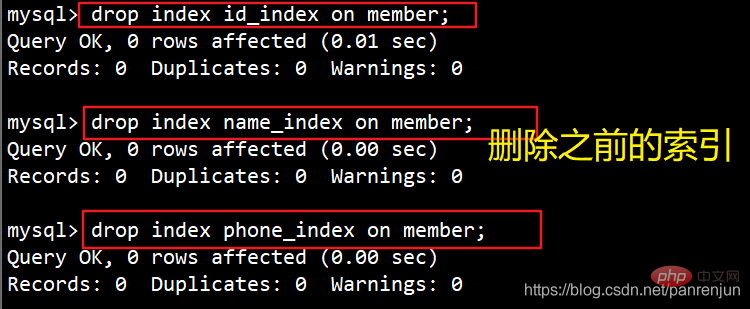
七、删除索引
1、直接删除索引 DROP INDEX 索引名 ON 表名;2、修改表方式删除索引 ALTER TABLE 表名 DROP INDEX 索引名;3、删除主键索引 ALTER TABLE 表名 DROP PRIMARY KEY;
八、实例
案例:为某商场做一个会员卡的系统。这个系统有一个会员表,有下列字段:会员编号 INT 会员姓名 VARCHAR(10)会员身份证号码 VARCHAR(18)会员电话 INT(11)会员住址 VARCHAR (50)会员备注信息 TEXT create table member (id int(10),name varchar(10),cardid varchar(18),phone int(11),address varchar(50),remark text);alter table member add primary key (id);create index name_index on member (name); create unique index cardid_index on member (cardid);alter table member add fulltext remark_index (remark);会员编号,作为主键,使用 PRIMARY KEY 会员姓名,如果要建索引的话,那么就是普通的 INDEX 会员身份证号码,如果要建索引的话,那么可以选择 UNIQUE (唯一的,不允许重复)会员备注信息,如果需要建索引的话,可以选择 FULLTEXT,全文搜索。 不过 FULLTEXT 用于搜索很长一篇文章的时候,效果最好。用在比较短的文本,如果就一两行字的,普通的 INDEX 也可以。
更多相关免费学习推荐:mysql教程(视频)
The above is the detailed content of In-depth understanding of MySQL index principles and implementation, and rapid database retrieval. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1389
1389
 52
52
 How to open phpmyadmin
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:51 PM
How to open phpmyadmin
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:51 PM
You can open phpMyAdmin through the following steps: 1. Log in to the website control panel; 2. Find and click the phpMyAdmin icon; 3. Enter MySQL credentials; 4. Click "Login".
 MySQL: An Introduction to the World's Most Popular Database
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:18 AM
MySQL: An Introduction to the World's Most Popular Database
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:18 AM
MySQL is an open source relational database management system, mainly used to store and retrieve data quickly and reliably. Its working principle includes client requests, query resolution, execution of queries and return results. Examples of usage include creating tables, inserting and querying data, and advanced features such as JOIN operations. Common errors involve SQL syntax, data types, and permissions, and optimization suggestions include the use of indexes, optimized queries, and partitioning of tables.
 How to use single threaded redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:12 PM
How to use single threaded redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:12 PM
Redis uses a single threaded architecture to provide high performance, simplicity, and consistency. It utilizes I/O multiplexing, event loops, non-blocking I/O, and shared memory to improve concurrency, but with limitations of concurrency limitations, single point of failure, and unsuitable for write-intensive workloads.
 MySQL's Place: Databases and Programming
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:18 AM
MySQL's Place: Databases and Programming
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:18 AM
MySQL's position in databases and programming is very important. It is an open source relational database management system that is widely used in various application scenarios. 1) MySQL provides efficient data storage, organization and retrieval functions, supporting Web, mobile and enterprise-level systems. 2) It uses a client-server architecture, supports multiple storage engines and index optimization. 3) Basic usages include creating tables and inserting data, and advanced usages involve multi-table JOINs and complex queries. 4) Frequently asked questions such as SQL syntax errors and performance issues can be debugged through the EXPLAIN command and slow query log. 5) Performance optimization methods include rational use of indexes, optimized query and use of caches. Best practices include using transactions and PreparedStatemen
 Why Use MySQL? Benefits and Advantages
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:17 AM
Why Use MySQL? Benefits and Advantages
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:17 AM
MySQL is chosen for its performance, reliability, ease of use, and community support. 1.MySQL provides efficient data storage and retrieval functions, supporting multiple data types and advanced query operations. 2. Adopt client-server architecture and multiple storage engines to support transaction and query optimization. 3. Easy to use, supports a variety of operating systems and programming languages. 4. Have strong community support and provide rich resources and solutions.
 How to connect to the database of apache
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
How to connect to the database of apache
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
Apache connects to a database requires the following steps: Install the database driver. Configure the web.xml file to create a connection pool. Create a JDBC data source and specify the connection settings. Use the JDBC API to access the database from Java code, including getting connections, creating statements, binding parameters, executing queries or updates, and processing results.
 How to view sql database error
Apr 10, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
How to view sql database error
Apr 10, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
The methods for viewing SQL database errors are: 1. View error messages directly; 2. Use SHOW ERRORS and SHOW WARNINGS commands; 3. Access the error log; 4. Use error codes to find the cause of the error; 5. Check the database connection and query syntax; 6. Use debugging tools.
 Monitor Redis Droplet with Redis Exporter Service
Apr 10, 2025 pm 01:36 PM
Monitor Redis Droplet with Redis Exporter Service
Apr 10, 2025 pm 01:36 PM
Effective monitoring of Redis databases is critical to maintaining optimal performance, identifying potential bottlenecks, and ensuring overall system reliability. Redis Exporter Service is a powerful utility designed to monitor Redis databases using Prometheus. This tutorial will guide you through the complete setup and configuration of Redis Exporter Service, ensuring you seamlessly build monitoring solutions. By studying this tutorial, you will achieve fully operational monitoring settings



