 Backend Development
Backend Development
 Python Tutorial
Python Tutorial
 Python geographic data processing analysis uses GR for vectors
Python geographic data processing analysis uses GR for vectors
Python geographic data processing analysis uses GR for vectors

Free learning recommendations: python video tutorial
1. Overlay analysis
Overlay analysis operation: 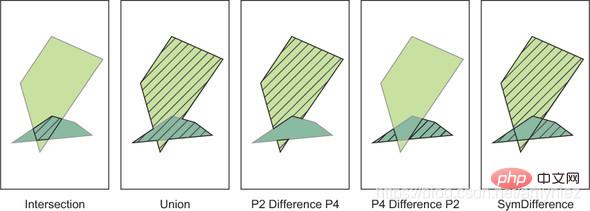
Plot color: 'r' red, 'g' green, 'b' Blue, 'c' cyan, 'y' yellow, 'm' magenta, 'k' black, 'w' white.
Simple map of New Orleans city boundaries, water bodies and wetlands: ## sync
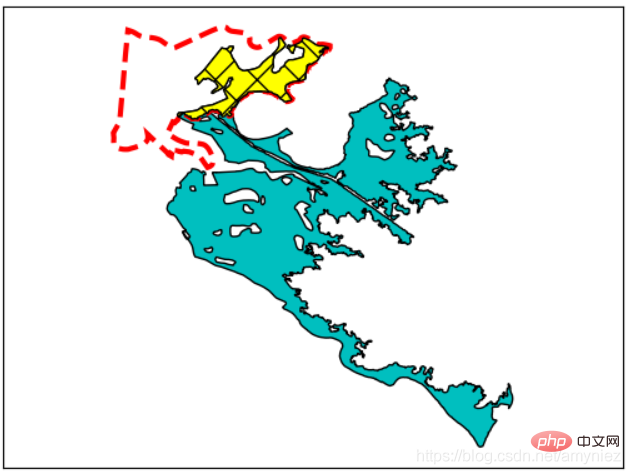
synopsis 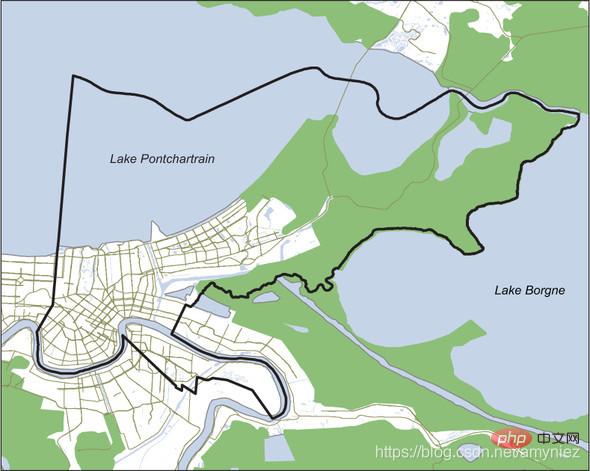 1. Analysis of urban swamp areas in New Orleans:
1. Analysis of urban swamp areas in New Orleans: import osfrom osgeo import ogrfrom ospybook.vectorplotter import VectorPlotter
data_dir = r'E:\Google chrome\Download\gis with python\osgeopy data'# 得到新奥尔良附近的一个特定的沼泽特征vp = VectorPlotter(True)water_ds = ogr.Open(os.path.join(data_dir, 'US', 'wtrbdyp010.shp'))water_lyr = water_ds.GetLayer(0)water_lyr.SetAttributeFilter('WaterbdyID = 1011327')marsh_feat = water_lyr.GetNextFeature()marsh_geom = marsh_feat.geometry().Clone()vp.plot(marsh_geom, 'c')# 获得新奥尔良边城市边界nola_ds = ogr.Open(os.path.join(data_dir, 'Louisiana', 'NOLA.shp'))nola_lyr = nola_ds.GetLayer(0)nola_feat = nola_lyr.GetNextFeature()nola_geom = nola_feat.geometry().Clone()vp.plot(nola_geom, fill=False, ec='red', ls='dashed', lw=3)# 相交沼泽和边界多边形得到沼泽的部分# 位于新奥尔良城市边界内intersection = marsh_geom.Intersection(nola_geom)vp.plot(intersection, 'yellow', hatch='x')vp.draw()
 2. Calculate the wetland area of the city: Filtering out unnecessary features can significantly reduce processing time.
2. Calculate the wetland area of the city: Filtering out unnecessary features can significantly reduce processing time.
3. Intersection of two layers:
# 获得城市内的湿地多边形# 将多边形的面积进行累加# 除以城市面积water_lyr.SetAttributeFilter("Feature != 'Lake'") # 限定对象water_lyr.SetSpatialFilter(nola_geom)wetlands_area = 0# 累加多边形面积for feat in water_lyr:
intersect = feat.geometry().Intersection(nola_geom)
wetlands_area += intersect.GetArea()pcnt = wetlands_area / nola_geom.GetArea()print('{:.1%} of New Orleans is wetland'.format(pcnt))28.7% of New Orleans is wetland
OGR includes two proximity analysis tools: measuring distances between geometric features and creating buffers.
1. Determine how many cities in the United States are within 10 miles of a volcano.A problematic way to determine the number of cities near a volcano:
# 将湖泊数据排除# 在内存中创建一个临时图层# 将图层相交,将结果储存在临时图层中water_lyr.SetAttributeFilter("Feature != 'Lake'")water_lyr.SetSpatialFilter(nola_geom)wetlands_area = 0for feat in water_lyr:
intersect = feat.geometry().Intersection(nola_geom) # 求交
wetlands_area += intersect.GetArea()pcnt = wetlands_area / nola_geom.GetArea()print('{:.1%} of New Orleans is wetland'.format(pcnt))water_lyr.SetSpatialFilter(None)water_lyr.SetAttributeFilter("Feature != 'Lake'")memory_driver = ogr.GetDriverByName('Memory')temp_ds = memory_driver.CreateDataSource('temp')temp_lyr = temp_ds.CreateLayer('temp')nola_lyr.Intersection(water_lyr, temp_lyr)sql = 'SELECT SUM(OGR_GEOM_AREA) AS area FROM temp'lyr = temp_ds.ExecuteSQL(sql)pcnt = lyr.GetFeature(0).GetField('area') / nola_geom.GetArea()print('{:.1%} of New Orleans is wetland'.format(pcnt))28.7% of New Orleans is wetland
2. A better way to determine the number of cities near a volcano:
from osgeo import ogr
shp_ds = ogr.Open(r'E:\Google chrome\Download\gis with python\osgeopy data\US')volcano_lyr = shp_ds.GetLayer('us_volcanos_albers')cities_lyr = shp_ds.GetLayer('cities_albers')# 在内存中创建一个临时层来存储缓冲区memory_driver = ogr.GetDriverByName('memory')memory_ds = memory_driver.CreateDataSource('temp')buff_lyr = memory_ds.CreateLayer('buffer')buff_feat = ogr.Feature(buff_lyr.GetLayerDefn())# 缓缓冲每一个火山点,将结果添加到缓冲图层中for volcano_feat in volcano_lyr:
buff_geom = volcano_feat.geometry().Buffer(16000)
tmp = buff_feat.SetGeometry(buff_geom)
tmp = buff_lyr.CreateFeature(buff_feat)# 将城市图层与火山缓冲区图层相交result_lyr = memory_ds.CreateLayer('result')buff_lyr.Intersection(cities_lyr, result_lyr)print('Cities: {}'.format(result_lyr.GetFeatureCount()))Cities: 83
In the first example, whenever a city is within the volcano buffer, it will be copied to the output result. Note that a city located within multiple 16,000-meter buffer zones will be included more than once. # synchronization
##from osgeo import ogr
shp_ds = ogr.Open(r'E:\Google chrome\Download\gis with python\osgeopy data\US')volcano_lyr = shp_ds.GetLayer('us_volcanos_albers')cities_lyr = shp_ds.GetLayer('cities_albers')# 将缓冲区添加到一个复合多边形,而不是一个临时图层multipoly = ogr.Geometry(ogr.wkbMultiPolygon)for volcano_feat in volcano_lyr:
buff_geom = volcano_feat.geometry().Buffer(16000)
multipoly.AddGeometry(buff_geom)# 将所有的缓冲区联合在一起得到一个可以使用的多边形作为空间过滤器cities_lyr.SetSpatialFilter(multipoly.UnionCascaded())print('Cities: {}'.format(cities_lyr.GetFeatureCount()))Cities: 78
import osfrom osgeo import ogrfrom ospybook.vectorplotter import VectorPlotter
data_dir = r'E:\Google chrome\Download\gis with python\osgeopy data'shp_ds = ogr.Open(os.path.join(data_dir, 'US'))volcano_lyr = shp_ds.GetLayer('us_volcanos_albers')cities_lyr = shp_ds.GetLayer('cities_albers')# 西雅图到雷尼尔山的距离volcano_lyr.SetAttributeFilter("NAME = 'Rainier'")feat = volcano_lyr.GetNextFeature()rainier = feat.geometry().Clone()cities_lyr.SetSpatialFilter(None)cities_lyr.SetAttributeFilter("NAME = 'Seattle'")feat = cities_lyr.GetNextFeature()seattle = feat.geometry().Clone()meters = round(rainier.Distance(seattle))miles = meters / 1600print('{} meters ({} miles)'.format(meters, miles))92656 meters (57.91 miles)
Taking the elevation Z value into account, the true distance is 5. # 2Dpt1_2d = ogr.Geometry(ogr.wkbPoint)pt1_2d.AddPoint(15, 15)pt2_2d = ogr.Geometry(ogr.wkbPoint)pt2_2d.AddPoint(15, 19)print(pt1_2d.Distance(pt2_2d))
4.0
# 2.5Dpt1_25d = ogr.Geometry(ogr.wkbPoint25D)pt1_25d.AddPoint(15, 15, 0)pt2_25d = ogr.Geometry(ogr.wkbPoint25D)pt2_25d.AddPoint(15, 19, 3)print(pt1_25d.Distance(pt2_25d))
4.0
# 用2D计算面积ring = ogr.Geometry(ogr.wkbLinearRing)ring.AddPoint(10, 10)ring.AddPoint(10, 20)ring.AddPoint(20, 20)ring.AddPoint(20, 10)poly_2d = ogr.Geometry(ogr.wkbPolygon)poly_2d.AddGeometry(ring)poly_2d.CloseRings()print(poly_2d.GetArea())
Related free learning recommendations:
python tutorial
(Video)The above is the detailed content of Python geographic data processing analysis uses GR for vectors. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1385
1385
 52
52
 PHP and Python: Code Examples and Comparison
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:07 AM
PHP and Python: Code Examples and Comparison
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:07 AM
PHP and Python have their own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice depends on project needs and personal preferences. 1.PHP is suitable for rapid development and maintenance of large-scale web applications. 2. Python dominates the field of data science and machine learning.
 Python vs. JavaScript: Community, Libraries, and Resources
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:16 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: Community, Libraries, and Resources
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:16 AM
Python and JavaScript have their own advantages and disadvantages in terms of community, libraries and resources. 1) The Python community is friendly and suitable for beginners, but the front-end development resources are not as rich as JavaScript. 2) Python is powerful in data science and machine learning libraries, while JavaScript is better in front-end development libraries and frameworks. 3) Both have rich learning resources, but Python is suitable for starting with official documents, while JavaScript is better with MDNWebDocs. The choice should be based on project needs and personal interests.
 Detailed explanation of docker principle
Apr 14, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
Detailed explanation of docker principle
Apr 14, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
Docker uses Linux kernel features to provide an efficient and isolated application running environment. Its working principle is as follows: 1. The mirror is used as a read-only template, which contains everything you need to run the application; 2. The Union File System (UnionFS) stacks multiple file systems, only storing the differences, saving space and speeding up; 3. The daemon manages the mirrors and containers, and the client uses them for interaction; 4. Namespaces and cgroups implement container isolation and resource limitations; 5. Multiple network modes support container interconnection. Only by understanding these core concepts can you better utilize Docker.
 How to run programs in terminal vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 06:42 PM
How to run programs in terminal vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 06:42 PM
In VS Code, you can run the program in the terminal through the following steps: Prepare the code and open the integrated terminal to ensure that the code directory is consistent with the terminal working directory. Select the run command according to the programming language (such as Python's python your_file_name.py) to check whether it runs successfully and resolve errors. Use the debugger to improve debugging efficiency.
 Python: Automation, Scripting, and Task Management
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:14 AM
Python: Automation, Scripting, and Task Management
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:14 AM
Python excels in automation, scripting, and task management. 1) Automation: File backup is realized through standard libraries such as os and shutil. 2) Script writing: Use the psutil library to monitor system resources. 3) Task management: Use the schedule library to schedule tasks. Python's ease of use and rich library support makes it the preferred tool in these areas.
 Is the vscode extension malicious?
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:57 PM
Is the vscode extension malicious?
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:57 PM
VS Code extensions pose malicious risks, such as hiding malicious code, exploiting vulnerabilities, and masturbating as legitimate extensions. Methods to identify malicious extensions include: checking publishers, reading comments, checking code, and installing with caution. Security measures also include: security awareness, good habits, regular updates and antivirus software.
 How to install nginx in centos
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:06 PM
How to install nginx in centos
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:06 PM
CentOS Installing Nginx requires following the following steps: Installing dependencies such as development tools, pcre-devel, and openssl-devel. Download the Nginx source code package, unzip it and compile and install it, and specify the installation path as /usr/local/nginx. Create Nginx users and user groups and set permissions. Modify the configuration file nginx.conf, and configure the listening port and domain name/IP address. Start the Nginx service. Common errors need to be paid attention to, such as dependency issues, port conflicts, and configuration file errors. Performance optimization needs to be adjusted according to the specific situation, such as turning on cache and adjusting the number of worker processes.
 What is vscode What is vscode for?
Apr 15, 2025 pm 06:45 PM
What is vscode What is vscode for?
Apr 15, 2025 pm 06:45 PM
VS Code is the full name Visual Studio Code, which is a free and open source cross-platform code editor and development environment developed by Microsoft. It supports a wide range of programming languages and provides syntax highlighting, code automatic completion, code snippets and smart prompts to improve development efficiency. Through a rich extension ecosystem, users can add extensions to specific needs and languages, such as debuggers, code formatting tools, and Git integrations. VS Code also includes an intuitive debugger that helps quickly find and resolve bugs in your code.



