Execution of a SQL statement

Recommended (free): SQL
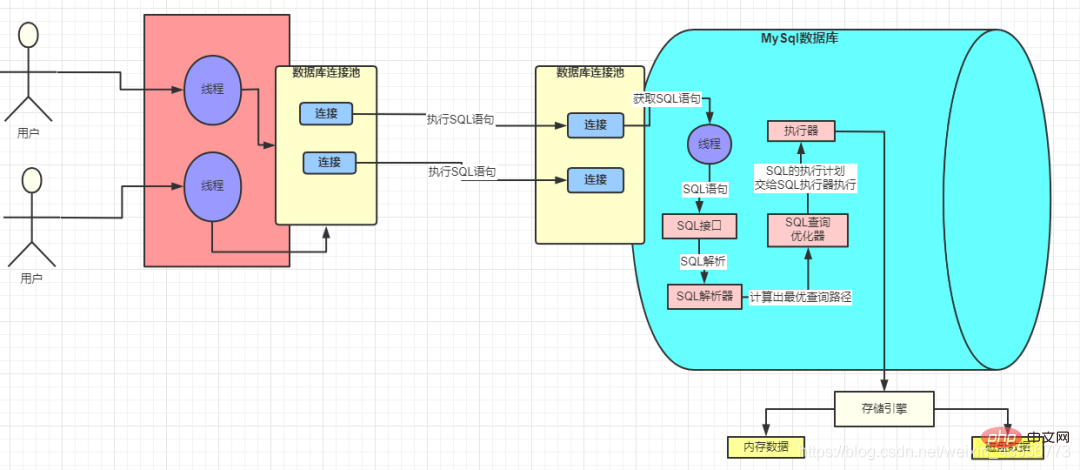
Zero, database driver
- The MySQL driver helps us connect to the database at the bottom level. Only after the connection is established can subsequent interactions be possible.
1. Database connection pool
- Database connection pools include Druid, C3P0, and DBCP
- Using connection pools saves a lot of money The overhead of constantly creating and destroying threads is the famous "pooling" idea. Whether it is a thread pool or an HTTP connection pool, you can see its presence
2. SQL interface
- The thread that processes the request in MySQL obtains the SQL statement after obtaining the request and hands it to the SQL interface for processing.
3. Query parser
- #Parses the SQL statement passed by the SQL interface and translates it into a language that MySQL can understand.
4. MySQL Query Optimizer
- MySQL will choose to use the corresponding index based on the minimum cost principle #Cost = IO cost CPU cost
- IO cost: That is, the cost of loading data from disk to memory. By default, the IO cost of reading a data page is 1, MySQL reads data in the form of pages. That is, when a certain data is used, it will not only read this data, but also read the data adjacent to this data into the memory. This is a famous program. The principle of locality, so MySQL will read a whole page each time, and the cost of one page is 1. Therefore, the cost of IO is mainly related to the size of the page
- CPU cost: After reading the data into the memory, it is also necessary to detect whether the data meets the conditions and the cost of sorting and other CPU operations. Obviously it is related to Depending on the number of rows, by default, the cost of detecting records is 0.2. MySQL optimizer will calculate the "IO cost CPU" index with the smallest cost to execute
5. Storage engine
- The query optimizer will call the storage engine interface to execute SQL, which means that the actual
- execution of SQL is completed in the storage engine. Data is stored in memory or disk
- Every time SQL is executed, its data will be loaded into memory. This memory is a very important component in InnoDB. :
- Buffer Pool
The executor finally goes according to a series of execution plans Call the storage engine interface to complete the execution of SQL
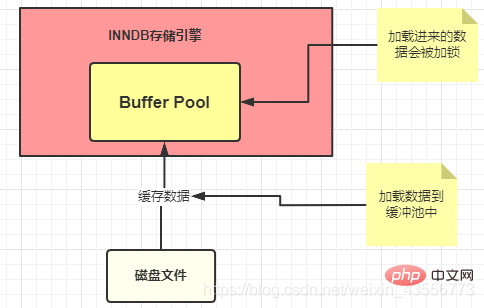
Buffer Pool ( Buffer Pool) is a very important memory structure in the InnoDB storage engine. It plays the role of a cache.
- Buffer Pool means that when we query for the first time, we will store the query results in the Buffer Pool, so that later When there is another request, it will first be queried from the buffer pool. If there is no search, it will be searched on the disk, and then placed in the Buffer Pool.
- The data used in the Buffer Pool will be locked.
-

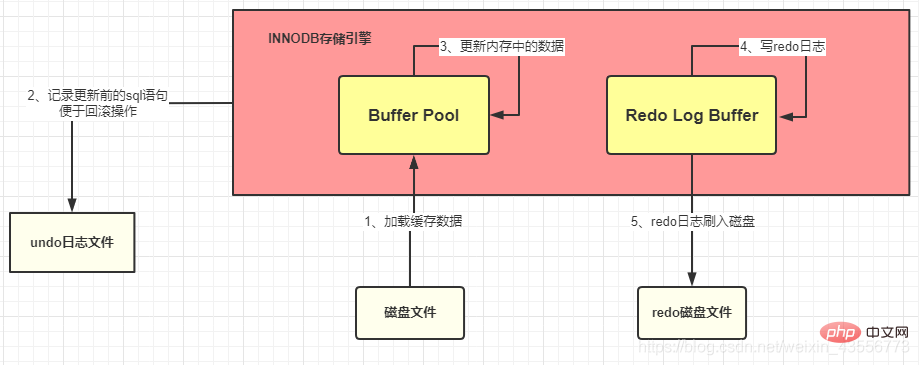
1. Undo log file
: before the recorded data is modified Appearance
Function: Use undo log files to complete transaction rollback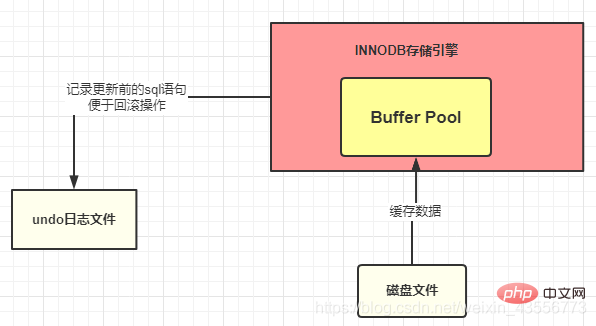
: Record the appearance of the modified data
redo records the value after the data modification, regardless of whether the transaction is submitted or not.- MySQL In order to improve efficiency, these operations are It is first placed in memory to complete. The updated data will be recorded in the redo log buffer, and then persisted to disk at a certain opportunity.
-

Record the entire operation process
bin log records the entire operation record (this is very important for master-slave replication)
Property
redo Log
bin Log
File size
The size of the redo log is fixed (it can also be set in the configuration, generally the default is enough)
bin log can be set for each # through the configuration parameter
max_bin log_size ##bin logThe size of the file (but it is generally not recommended to modify it).
Implementation method
redo log
is implemented by the InnoDB engine layer (that is to say, Innodb storage causes excessive Yes)
bin log
is implemented by the MySQL layer, and all engines can use bin loglog
to record Method
redo log records in a loop writing method. When writing to the end, it will return to the beginning to write logs in a loop. bin log is recorded by appending. When the file size is larger than the given value, subsequent logs will be recorded to new files
Usage scenarios
redo log
Suitable for crash recovery (crash-safe) (this is actually very similar to the persistence feature of Redis)
bin log
Suitable for master From replication and data recovery
The above is the detailed content of Execution of a SQL statement. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 What is the difference between HQL and SQL in Hibernate framework?
Apr 17, 2024 pm 02:57 PM
What is the difference between HQL and SQL in Hibernate framework?
Apr 17, 2024 pm 02:57 PM
HQL and SQL are compared in the Hibernate framework: HQL (1. Object-oriented syntax, 2. Database-independent queries, 3. Type safety), while SQL directly operates the database (1. Database-independent standards, 2. Complex executable queries and data manipulation).
 Usage of division operation in Oracle SQL
Mar 10, 2024 pm 03:06 PM
Usage of division operation in Oracle SQL
Mar 10, 2024 pm 03:06 PM
"Usage of Division Operation in OracleSQL" In OracleSQL, division operation is one of the common mathematical operations. During data query and processing, division operations can help us calculate the ratio between fields or derive the logical relationship between specific values. This article will introduce the usage of division operation in OracleSQL and provide specific code examples. 1. Two ways of division operations in OracleSQL In OracleSQL, division operations can be performed in two different ways.
 Comparison and differences of SQL syntax between Oracle and DB2
Mar 11, 2024 pm 12:09 PM
Comparison and differences of SQL syntax between Oracle and DB2
Mar 11, 2024 pm 12:09 PM
Oracle and DB2 are two commonly used relational database management systems, each of which has its own unique SQL syntax and characteristics. This article will compare and differ between the SQL syntax of Oracle and DB2, and provide specific code examples. Database connection In Oracle, use the following statement to connect to the database: CONNECTusername/password@database. In DB2, the statement to connect to the database is as follows: CONNECTTOdataba
 What does the identity attribute in SQL mean?
Feb 19, 2024 am 11:24 AM
What does the identity attribute in SQL mean?
Feb 19, 2024 am 11:24 AM
What is Identity in SQL? Specific code examples are needed. In SQL, Identity is a special data type used to generate auto-incrementing numbers. It is often used to uniquely identify each row of data in a table. The Identity column is often used in conjunction with the primary key column to ensure that each record has a unique identifier. This article will detail how to use Identity and some practical code examples. The basic way to use Identity is to use Identit when creating a table.
 Detailed explanation of the Set tag function in MyBatis dynamic SQL tags
Feb 26, 2024 pm 07:48 PM
Detailed explanation of the Set tag function in MyBatis dynamic SQL tags
Feb 26, 2024 pm 07:48 PM
Interpretation of MyBatis dynamic SQL tags: Detailed explanation of Set tag usage MyBatis is an excellent persistence layer framework. It provides a wealth of dynamic SQL tags and can flexibly construct database operation statements. Among them, the Set tag is used to generate the SET clause in the UPDATE statement, which is very commonly used in update operations. This article will explain in detail the usage of the Set tag in MyBatis and demonstrate its functionality through specific code examples. What is Set tag Set tag is used in MyBati
 How does Java use the MySQL driver interceptor to implement SQL time-consuming calculations?
May 27, 2023 pm 01:10 PM
How does Java use the MySQL driver interceptor to implement SQL time-consuming calculations?
May 27, 2023 pm 01:10 PM
Background: One of the company's needs is that the company's existing link tracking log component must support MySQL's SQL execution time printing. The common method to implement link tracking is to implement the interceptor interface or filter interface provided by a third-party framework or tool. MySQL is no exception. In fact, it just implements the interceptor interface driven by MySQL. There are different versions of MySQL channels, and the interceptor interfaces of different versions are different, so you need to implement the response interceptor according to the different versions of MySQL drivers you use. Next, we will introduce MySQL channels 5 and 6 respectively. 8 version implementation. MySQL5 is implemented here using MySQL channel 5.1.18 version as an example to implement Statem
 How to solve the 5120 error in SQL
Mar 06, 2024 pm 04:33 PM
How to solve the 5120 error in SQL
Mar 06, 2024 pm 04:33 PM
Solution: 1. Check whether the logged-in user has sufficient permissions to access or operate the database, and ensure that the user has the correct permissions; 2. Check whether the account of the SQL Server service has permission to access the specified file or folder, and ensure that the account Have sufficient permissions to read and write the file or folder; 3. Check whether the specified database file has been opened or locked by other processes, try to close or release the file, and rerun the query; 4. Try as administrator Run Management Studio as etc.
 How to use SQL statements for data aggregation and statistics in MySQL?
Dec 17, 2023 am 08:41 AM
How to use SQL statements for data aggregation and statistics in MySQL?
Dec 17, 2023 am 08:41 AM
How to use SQL statements for data aggregation and statistics in MySQL? Data aggregation and statistics are very important steps when performing data analysis and statistics. As a powerful relational database management system, MySQL provides a wealth of aggregation and statistical functions, which can easily perform data aggregation and statistical operations. This article will introduce the method of using SQL statements to perform data aggregation and statistics in MySQL, and provide specific code examples. 1. Use the COUNT function for counting. The COUNT function is the most commonly used