 Web Front-end
Web Front-end
 JS Tutorial
JS Tutorial
 Talk about the problem of implementing AST abstract syntax tree in JS
Talk about the problem of implementing AST abstract syntax tree in JS
Talk about the problem of implementing AST abstract syntax tree in JS

Free learning recommendation: javascript learning tutorial
AST abstract syntax tree problem in the front end
- Four arithmetic operations
- Regular expression
- Lexical analysis
- Syntax analysis
- Complete code
Four Arithmetic Operations
First of all, it is clear that the code this time is based on LL syntax analysis. It implements the function of the four arithmetic mixed operations. Let’s look at the definition first:
TokenNumber: · 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 combination
Operator: - * / One of
WhiteSpace:<sp></sp>
LineTerminator:
<lf></lf> <cr></cr>
Look at the production: 
##Regular Expression
We first implement the matching principle of regular expressions:<script>
var regexp = /([0-9\.]+)|([ \t]+)|([\r\n]+)|(\*)|(\/)|(\+)|(\-)/g
var dictionary = ["Number", "Whitespace", "LineTerminator", "*", "/", "+", "-"];
function tokenize(source) {
var result = null;
while(true) {
result = regexp.exec(source);
if(!result) break;
for(var i = 1; i <= dictionary.length; i ++) {
if(result[i])
console.log(dictionary[i - 1]);
}
console.log(result);
}
}
tokenize("1024 + 10 * 25");</script> It is worth mentioning that The exec method is used here. The exec() method is used to retrieve regular expression matches in a string.
It is worth mentioning that The exec method is used here. The exec() method is used to retrieve regular expression matches in a string.
Let's take a look at its syntax:
RegExpObject.exec(string)
Lexical analysis
We optimize the above code in this part. First of all, what was just mentioned:
When RegExpObject is a global regular expression, the behavior of exec() is slightly more complicated. It starts retrieving the string string at the character specified by the RegExpObject's lastIndex property. When exec() finds text that matches an expression, it sets the RegExpObject's lastIndex property to the position next to the last character of the matching text after the match. Then we have to consider the situation where there is no matching character and make a judgment:
<script>
var regexp = /([0-9\.]+)|([ \t]+)|([\r\n]+)|(\*)|(\/)|(\+)|(\-)/g
var dictionary = ["Number", "Whitespace", "LineTerminator", "*", "/", "+", "-"];
function* tokenize(source) {
var result = null;
var lastIndex = 0;
while(true) {
lastIndex = regexp.lastIndex;
result = regexp.exec(source);
if(!result) break;
if(regexp.lastIndex - lastIndex > result[0].length)
break;
let token = {
type: null,
value: null
}
for(var i = 1; i <= dictionary.length; i ++) {
if(result[i])
token.type = dictionary[i - 1];
}
token.value = result[0];
yield token }
yield {
type: 'EOF'
}
}
for (let token of tokenize("1024 + 10 * 25")) {
console.log(token)
}</script>regexp.lastIndex - lastIndex and The length of result[0] is compared to determine whether any string does not match. Change the entire function into the form of a generator function. Let’s look at the results of the operation: 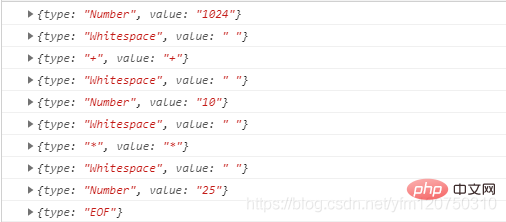
Syntax analysis
First write the chunks Production, let's take a look at the overall code structure:<script>
var regexp = /([0-9\.]+)|([ \t]+)|([\r\n]+)|(\*)|(\/)|(\+)|(\-)/g
var dictionary = ["Number", "Whitespace", "LineTerminator", "*", "/", "+", "-"];
function* tokenize(source) {
var result = null;
var lastIndex = 0;
while(true) {
lastIndex = regexp.lastIndex;
result = regexp.exec(source);
if(!result) break;
if(regexp.lastIndex - lastIndex > result[0].length)
break;
let token = {
type: null,
value: null
}
for(var i = 1; i <= dictionary.length; i ++) {
if(result[i])
token.type = dictionary[i - 1];
}
token.value = result[0];
yield token }
yield {
type: 'EOF'
}
}
let source = [];
for(let token of tokenize("10 * 25")) {
if (token.type !== "Whitespace" && token.type !== "LineTerminator")
source.push(token);
}
function Expression(tokens) {
}
function AdditiveExpression(source){
}
function MultiplicativeExpresson(source) {
console.log(source);
}
MultiplicativeExpresson("10 * 25")</script>MultiplicativeExpresson, which is divided into four situations:
function MultiplicativeExpresson(source) {
//如果是数字则进行封装
if(source[0].type === "Number") {
let node = {
type: "MultiplicativeExpresson",
children:[source[0]]
}
source[0] = node;
return MultiplicativeExpresson(source)
}
//如果是乘号或者除号,则将三项出栈,进行重组
if(source[0].type === "MultiplicativeExpresson" && source[1] && source[1].type === "*") {
let node = {
type: "MultiplicativeExpresson",
operator: "*",
children: []
}
node.children.push(source.shift());
node.children.push(source.shift());
node.children.push(source.shift());
source.unshift(node);
return MultiplicativeExpresson(source)
}
if(source[0].type === "MultiplicativeExpresson" && source[1] && source[1].type === "/") {
let node = {
type: "MultiplicativeExpresson",
operator: "*",
children: []
}
node.children.push(source.shift());
node.children.push(source.shift());
node.children.push(source.shift());
source.unshift(node);
return MultiplicativeExpresson(source)
}
//递归结束的条件
if(source[0].type === "MultiplicativeExpresson")
return source[0];
return MultiplicativeExpresson(source);
}"10 * 25 / 2", call console.log(MultiplicativeExpresson(source))The final running result:  Let’s see next
Let’s see next
AdditiveExpression is essentially the same as MultiplicativeExpresson. The differences have been marked in the code:
function AdditiveExpression(source){
if(source[0].type === "MultiplicativeExpresson") {
let node = {
type: "AdditiveExpression",
children:[source[0]]
}
source[0] = node;
return AdditiveExpression(source)
}
//如果是乘号或者除号,则将三项出栈,进行重组
if(source[0].type === "AdditiveExpression" && source[1] && source[1].type === "+") {
let node = {
type: "AdditiveExpression",
operator: "+",
children: []
}
node.children.push(source.shift());
node.children.push(source.shift());
//考虑到第三个数可能时Number 需要在这里再次调用一下 MultiplicativeExpresson 做处理
MultiplicativeExpresson(source);
node.children.push(source.shift());
source.unshift(node);
return AdditiveExpression(source)
}
if(source[0].type === "AdditiveExpression" && source[1] && source[1].type === "-") {
let node = {
type: "AdditiveExpression",
operator: "-",
children: []
}
node.children.push(source.shift());
node.children.push(source.shift());
MultiplicativeExpresson(source);
node.children.push(source.shift());
source.unshift(node);
return AdditiveExpression(source)
}
//递归结束的条件
if(source[0].type === "AdditiveExpression")
return source[0];
//第一次进循环 调用
MultiplicativeExpresson(source);
return AdditiveExpression(source);
}我们看一下当source为"10 * 25 / 2"时调用console.log(AdditiveExpression(source))最后运行的结果: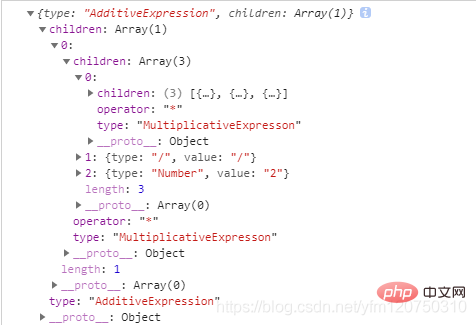
那么Expression的代码逻辑就很好表达了:
function Expression(tokens) {
if(source[0].type === "AdditiveExpression" && source[1] && source[1].type === "EOF") {
let node = {
type: "Expression",
children: [source.shift(), source.shift()]
}
source.unshift(node);
return node;
}
AdditiveExpression(source);
return Expression(source);
}看下运行后的结果:
以上就是所有的js解析抽象语法树的代码。
完整代码
<script>
var regexp = /([0-9\.]+)|([ \t]+)|([\r\n]+)|(\*)|(\/)|(\+)|(\-)/g
var dictionary = ["Number", "Whitespace", "LineTerminator", "*", "/", "+", "-"];
function* tokenize(source) {
var result = null;
var lastIndex = 0;
while(true) {
lastIndex = regexp.lastIndex;
result = regexp.exec(source);
if(!result) break;
if(regexp.lastIndex - lastIndex > result[0].length)
break;
let token = {
type: null,
value: null
}
for(var i = 1; i <= dictionary.length; i ++) {
if(result[i])
token.type = dictionary[i - 1];
}
token.value = result[0];
yield token }
yield {
type: 'EOF'
}
}
let source = [];
for(let token of tokenize("10 * 25 / 2")) {
if (token.type !== "Whitespace" && token.type !== "LineTerminator")
source.push(token);
}
function Expression(tokens) {
if(source[0].type === "AdditiveExpression" && source[1] && source[1].type === "EOF") {
let node = {
type: "Expression",
children: [source.shift(), source.shift()]
}
source.unshift(node);
return node;
}
AdditiveExpression(source);
return Expression(source);
}
function AdditiveExpression(source){
if(source[0].type === "MultiplicativeExpresson") {
let node = {
type: "AdditiveExpression",
children:[source[0]]
}
source[0] = node;
return AdditiveExpression(source)
}
//如果是乘号或者除号,则将三项出栈,进行重组
if(source[0].type === "AdditiveExpression" && source[1] && source[1].type === "+") {
let node = {
type: "AdditiveExpression",
operator: "+",
children: []
}
node.children.push(source.shift());
node.children.push(source.shift());
//考虑到第三个数可能时Number 需要在这里再次调用一下 MultiplicativeExpresson 做处理
MultiplicativeExpresson(source);
node.children.push(source.shift());
source.unshift(node);
return AdditiveExpression(source)
}
if(source[0].type === "AdditiveExpression" && source[1] && source[1].type === "-") {
let node = {
type: "AdditiveExpression",
operator: "-",
children: []
}
node.children.push(source.shift());
node.children.push(source.shift());
MultiplicativeExpresson(source);
node.children.push(source.shift());
source.unshift(node);
return AdditiveExpression(source)
}
//递归结束的条件
if(source[0].type === "AdditiveExpression")
return source[0];
//第一次进循环 调用
MultiplicativeExpresson(source);
return AdditiveExpression(source);
}
function MultiplicativeExpresson(source) {
if(source[0].type === "Number") {
let node = {
type: "MultiplicativeExpresson",
children:[source[0]]
}
source[0] = node;
return MultiplicativeExpresson(source)
}
//如果是乘号或者除号,则将三项出栈,进行重组
if(source[0].type === "MultiplicativeExpresson" && source[1] && source[1].type === "*") {
let node = {
type: "MultiplicativeExpresson",
operator: "*",
children: []
}
node.children.push(source.shift());
node.children.push(source.shift());
node.children.push(source.shift());
source.unshift(node);
return MultiplicativeExpresson(source)
}
if(source[0].type === "MultiplicativeExpresson" && source[1] && source[1].type === "/") {
let node = {
type: "MultiplicativeExpresson",
operator: "*",
children: []
}
node.children.push(source.shift());
node.children.push(source.shift());
node.children.push(source.shift());
source.unshift(node);
return MultiplicativeExpresson(source)
}
//递归结束的条件
if(source[0].type === "MultiplicativeExpresson")
return source[0];
return MultiplicativeExpresson(source);
}
console.log(Expression(source))</script>相关免费学习推荐:javascript(视频)
The above is the detailed content of Talk about the problem of implementing AST abstract syntax tree in JS. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1376
1376
 52
52
 How to implement an online speech recognition system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 pm 02:54 PM
How to implement an online speech recognition system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 pm 02:54 PM
How to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online speech recognition system Introduction: With the continuous development of technology, speech recognition technology has become an important part of the field of artificial intelligence. The online speech recognition system based on WebSocket and JavaScript has the characteristics of low latency, real-time and cross-platform, and has become a widely used solution. This article will introduce how to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online speech recognition system.
 WebSocket and JavaScript: key technologies for implementing real-time monitoring systems
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:30 PM
WebSocket and JavaScript: key technologies for implementing real-time monitoring systems
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:30 PM
WebSocket and JavaScript: Key technologies for realizing real-time monitoring systems Introduction: With the rapid development of Internet technology, real-time monitoring systems have been widely used in various fields. One of the key technologies to achieve real-time monitoring is the combination of WebSocket and JavaScript. This article will introduce the application of WebSocket and JavaScript in real-time monitoring systems, give code examples, and explain their implementation principles in detail. 1. WebSocket technology
 How to implement an online reservation system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 am 09:39 AM
How to implement an online reservation system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 am 09:39 AM
How to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online reservation system. In today's digital era, more and more businesses and services need to provide online reservation functions. It is crucial to implement an efficient and real-time online reservation system. This article will introduce how to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online reservation system, and provide specific code examples. 1. What is WebSocket? WebSocket is a full-duplex method on a single TCP connection.
 How to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 12:09 PM
How to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 12:09 PM
Introduction to how to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system: With the popularity of the Internet and the advancement of technology, more and more restaurants have begun to provide online ordering services. In order to implement a real-time online ordering system, we can use JavaScript and WebSocket technology. WebSocket is a full-duplex communication protocol based on the TCP protocol, which can realize real-time two-way communication between the client and the server. In the real-time online ordering system, when the user selects dishes and places an order
 JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecasting system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecasting system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecast system Introduction: Today, the accuracy of weather forecasts is of great significance to daily life and decision-making. As technology develops, we can provide more accurate and reliable weather forecasts by obtaining weather data in real time. In this article, we will learn how to use JavaScript and WebSocket technology to build an efficient real-time weather forecast system. This article will demonstrate the implementation process through specific code examples. We
 Simple JavaScript Tutorial: How to Get HTTP Status Code
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
Simple JavaScript Tutorial: How to Get HTTP Status Code
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
JavaScript tutorial: How to get HTTP status code, specific code examples are required. Preface: In web development, data interaction with the server is often involved. When communicating with the server, we often need to obtain the returned HTTP status code to determine whether the operation is successful, and perform corresponding processing based on different status codes. This article will teach you how to use JavaScript to obtain HTTP status codes and provide some practical code examples. Using XMLHttpRequest
 How to use insertBefore in javascript
Nov 24, 2023 am 11:56 AM
How to use insertBefore in javascript
Nov 24, 2023 am 11:56 AM
Usage: In JavaScript, the insertBefore() method is used to insert a new node in the DOM tree. This method requires two parameters: the new node to be inserted and the reference node (that is, the node where the new node will be inserted).
 How to get HTTP status code in JavaScript the easy way
Jan 05, 2024 pm 01:37 PM
How to get HTTP status code in JavaScript the easy way
Jan 05, 2024 pm 01:37 PM
Introduction to the method of obtaining HTTP status code in JavaScript: In front-end development, we often need to deal with the interaction with the back-end interface, and HTTP status code is a very important part of it. Understanding and obtaining HTTP status codes helps us better handle the data returned by the interface. This article will introduce how to use JavaScript to obtain HTTP status codes and provide specific code examples. 1. What is HTTP status code? HTTP status code means that when the browser initiates a request to the server, the service



