Notes Introduction, installation and deployment of Redis

Recommended (free): redis
##Article Directory
- 1. What is Redis
- 2. What can Redis do
- 3. Redis download, installation and deployment
- 4. Some little knowledge of Redis
1. What is Redis
Redis: REmote DIctionary Server (remote dictionary server)
Redis is completely Open source and free, written in C language, a high-performance (key/value) distributed memory database that complies with the BSD protocol. It is also a NoSQL database that runs based on memory and supports persistence, is one of the most popular NoSql databases, also known as data structure server. At the same time, Redis is also a simple, efficient, distributed, memory-based caching tool. After the server is constructed, Key-Value caching services are provided through network connections (similar to databases).
Redis has the following advantages:
- 1. Extremely high performance
The reading speed of Redis is 110,000 times/s. The writing speed is 80,000 times/second. - 2. Rich data types
The types supported by Redis include String, Hash, List, Set and Ordered Set database types. - 3. Atomicity
All Redis operations are atomic and wrapped through MULTI and EXEC instructions. - 4. Rich reading and writing
Redis supports publish/subscribe, notification, key expiration and other features. - 5. High-speed reading and writing
Redis uses its own separator. The amount of code is very short and no lock (MySQL) is used, so the efficiency is very high.
Redis also has the following disadvantages:
- 1. Persistence
Redis stores data directly in memory. If you want to save the data to the disk, the first method is to use① scheduled snapshot (snapshot): write the entire database to the disk every once in a while, and write all the data each time, but the cost Very high; the second method is②Append based on statement (aof): Only the changed data is tracked, but the appended log may be too large, and all operations must be re-executed, resulting in slow recovery. - 2. Memory consumption
, the memory occupied is too high.
2. What can Redis do
In enterprise development, Redis can be used as a database, cache, and hot data (frequently queried but not modified or deleted) data), message middleware and most other functions.Examples of common scenarios for Redis are as follows:
Caching Nowadays, caching is a requirement of almost all medium and large websites. The most effective way to use cache properly is to not only improve the access speed of the website, but also greatly reduce the pressure on the database. Redis provides key expiration function and flexible key elimination strategy.
Ranking list Such as Taobao's monthly sales list, product new listings by time, etc. The ordered set data structure provided by Redis can implement various complex ranking applications.
Counter Such as the number of views of products on e-commerce websites, the number of video plays on video websites, etc. In order to ensure the real-time performance of the data, 1 must be given for each browsing. When the concurrency is high, it will undoubtedly be a challenge and pressure to request database operations every time. The incr command provided by Redis implements counter functions and memory operations with very good performance and is very suitable for these counting scenarios.
Distributed session In cluster mode, when there are not many applications, it is generally sufficient to use the session replication function that comes with the container. In the application In increasingly complex systems, session services centered on in-memory databases such as Redis are generally built. Sessions are no longer managed by containers, but by session services and in-memory databases.
Distributed lock The technical challenge brought by distributed technology is concurrent access to the same resource, such as global ID, inventory reduction, flash sale, etc. Scenarios with low concurrency can be implemented using database pessimistic locks and optimistic locks. However, in scenarios with high concurrency, it is not ideal to use database locks to control concurrent access to resources, which greatly affects the performance of the database. . You can use the setnx function of Redis to write distributed locks. If the setting returns 1, it means the lock acquisition is successful. Otherwise, the lock acquisition fails. There are more details to consider in actual applications.
Social Network Likes, dislikes, following/being followed, mutual friends, etc. are the basic functions of social networking sites. The number of visits to social networking sites usually comes from It is relatively large, and traditional relational database types are not suitable for storing this type of data. The hash, set and other data structures provided by Redis can easily implement these functions.
Latest list Redis list structure, LPUSH can insert a content ID as a keyword at the head of the list, LTRIM can be used to limit the number of lists, so The list is always N IDs. There is no need to query the latest list, just go to the corresponding content page based on the ID.
Message system
Message queue is a necessary middleware for large websites, such as ActiveMQ, RabbitMQ, Kafka and other popular message queue middleware. It is mainly used for business decoupling, Traffic peak shaving and asynchronous processing of services with low real-time performance. Redis provides publish/subscribe and blocking queue functions, which can implement a simple message queue system. However, this cannot be compared with professional message middleware.
3. Redis download, installation and deployment
Redis English official website.
Redis Chinese website.
Since 99% of enterprises doing Redis development are using and installing the Linux version, this article only introduces the installation and operation under Linux. Friends can use Baidu for installation under Windows. Go to the official website above and click Download to download the .gz installation package and place it in the /opt directory under Linux (I installed version 6.0.5 of Redis here).
- The decompression command is:
tar -zxvf redis-6.0.5.tar.gz
The above command only decompresses Redis. If you want to install Redis, you need a gcc environment in your Linux system. If not, you can use
yum install gcc-cto install it, and then usegcc -vto check the version.
If the Linux environment already has a gcc environment, directly use the following command to install:
- The installation command is:
make install
After installation, the default is that it cannot start automatically like Tomcat. You can modify the daemonize attribute in the redis.conf file to yes.
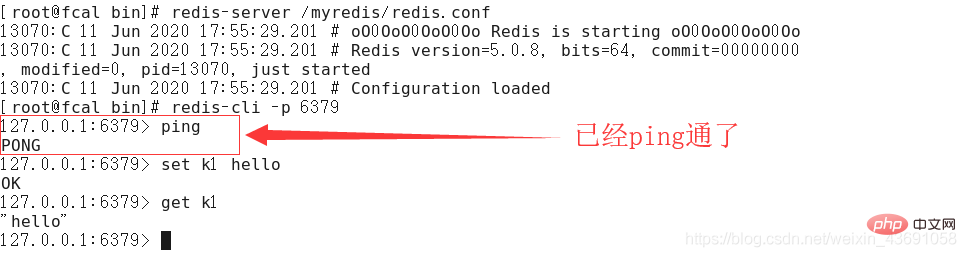
- Start the redis service:
redis-server /myredis/redis.conf(This is the redis configuration file after modifying the properties)
View Whether the background Redis service is started:
ps -ef|grep redis
Start the Redis service:
-
redis-cli -p 6379
Close normally and the data will be saved
Use in the redis command lineshutdownCommand shutdown.
Abnormal shutdown may easily lead to data loss
Power outage, manually kill the redis process, etc.
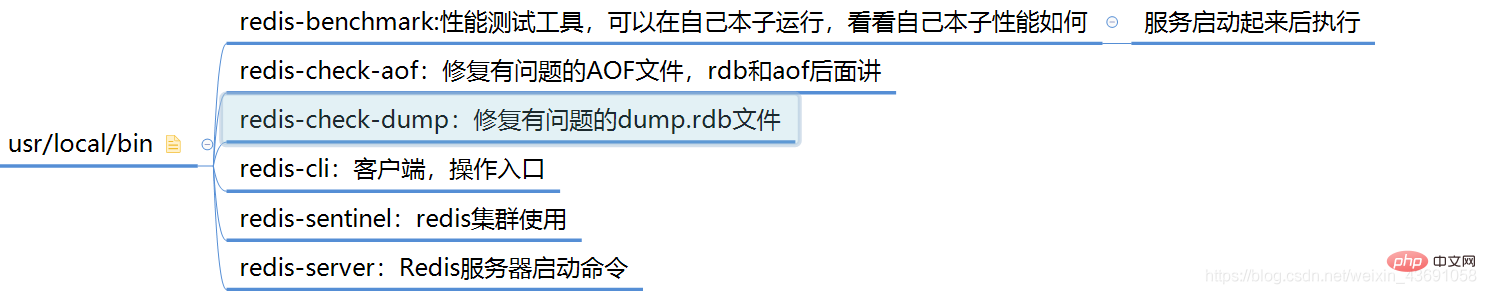
Several other redis commands
4. Some little knowledge of Redis
Redis is a single process and uses a single process model to handle client requests. Responses to events such as reading and writing are accomplished by wrapping the epoll function. The actual processing speed of Redis depends entirely on the execution efficiency of the main process.
epoll is an improved version of epoll made by the Linux kernel to handle large batches of file descriptors. It is an enhanced version of the multiplexed IO interface select/poll under Linux. It can significantly improve the performance of programs in a large number of System CPU utilization when there are only a few active concurrent connections.
Redis has 16 databases by default. The subscripts start from zero. The initial default is to use the zero database. You can use the
SELECT <dbid></dbid>command to connect. specified database.
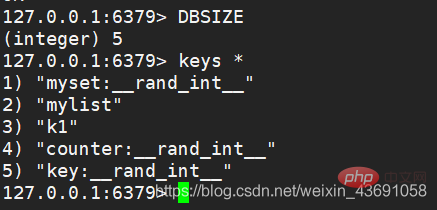
dbsizecommand can view the number of keys in the current database,keys *View all keys.
flushdb: Clear the current library (use with caution)##Flushall
: Clear all libraries (use with caution)- Unified password management, 16 libraries have the same password, either all are OK or none can be connected.
- Redis indexes all start from zero
- The default port of Redis is 6379
More related free learning recommendations: redis introductory tutorial
The above is the detailed content of Notes Introduction, installation and deployment of Redis. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
Redis cluster mode deploys Redis instances to multiple servers through sharding, improving scalability and availability. The construction steps are as follows: Create odd Redis instances with different ports; Create 3 sentinel instances, monitor Redis instances and failover; configure sentinel configuration files, add monitoring Redis instance information and failover settings; configure Redis instance configuration files, enable cluster mode and specify the cluster information file path; create nodes.conf file, containing information of each Redis instance; start the cluster, execute the create command to create a cluster and specify the number of replicas; log in to the cluster to execute the CLUSTER INFO command to verify the cluster status; make
 How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear Redis data: Use the FLUSHALL command to clear all key values. Use the FLUSHDB command to clear the key value of the currently selected database. Use SELECT to switch databases, and then use FLUSHDB to clear multiple databases. Use the DEL command to delete a specific key. Use the redis-cli tool to clear the data.
 How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
Using the Redis directive requires the following steps: Open the Redis client. Enter the command (verb key value). Provides the required parameters (varies from instruction to instruction). Press Enter to execute the command. Redis returns a response indicating the result of the operation (usually OK or -ERR).
 How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
To read a queue from Redis, you need to get the queue name, read the elements using the LPOP command, and process the empty queue. The specific steps are as follows: Get the queue name: name it with the prefix of "queue:" such as "queue:my-queue". Use the LPOP command: Eject the element from the head of the queue and return its value, such as LPOP queue:my-queue. Processing empty queues: If the queue is empty, LPOP returns nil, and you can check whether the queue exists before reading the element.
 How to use redis lock
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
How to use redis lock
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
Using Redis to lock operations requires obtaining the lock through the SETNX command, and then using the EXPIRE command to set the expiration time. The specific steps are: (1) Use the SETNX command to try to set a key-value pair; (2) Use the EXPIRE command to set the expiration time for the lock; (3) Use the DEL command to delete the lock when the lock is no longer needed.
 How to read the source code of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
How to read the source code of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
The best way to understand Redis source code is to go step by step: get familiar with the basics of Redis. Select a specific module or function as the starting point. Start with the entry point of the module or function and view the code line by line. View the code through the function call chain. Be familiar with the underlying data structures used by Redis. Identify the algorithm used by Redis.
 How to solve data loss with redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:24 PM
How to solve data loss with redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:24 PM
Redis data loss causes include memory failures, power outages, human errors, and hardware failures. The solutions are: 1. Store data to disk with RDB or AOF persistence; 2. Copy to multiple servers for high availability; 3. HA with Redis Sentinel or Redis Cluster; 4. Create snapshots to back up data; 5. Implement best practices such as persistence, replication, snapshots, monitoring, and security measures.
 How to use the redis command line
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
How to use the redis command line
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
Use the Redis command line tool (redis-cli) to manage and operate Redis through the following steps: Connect to the server, specify the address and port. Send commands to the server using the command name and parameters. Use the HELP command to view help information for a specific command. Use the QUIT command to exit the command line tool.