Java implementation of singly linked list (Linked List) related

Free learning recommendation: java basic tutorial
##Article directory
- 1. Introduction to singly linked list
- 2. Implementation of singly linked list
- 1. Creation (addition) of singly linked list
- 1.1 Add at the end
- 1.2 Add by ranking
2. Modification of singly linked list nodes- 3. Deletion of singly linked list nodes
- 4. Complete implementation of singly linked list
3. Single linked surface test questions
1. Introduction to singly linked list
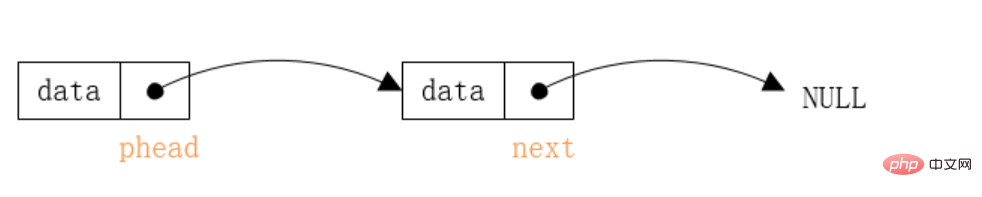
Singly linked list is anordered list that stores information in the form of node, but the node does not Must be continuous , each node includes data field and next field.
- data domain
- : used to store data.
- : Points to the next node.
 The linked list is divided into
The linked list is divided into
and the linked list without the head node.
-
 Singly linked list (without leading node)
Singly linked list (without leading node) -

Requirements: Use1. Creation (addition) of a singly linked listsingle linked list with header to implement – Water Margin hero ranking management.
1) Complete the addition, deletion, modification and check of the hero2) When adding a hero in the first method,is directly added to the end of the linked list
.3) In the second method, when adding a hero, insert the herointo the specified position according to the ranking
(if the ranking already exists, the addition will fail and a prompt will be given)
1.1 Adding the tail
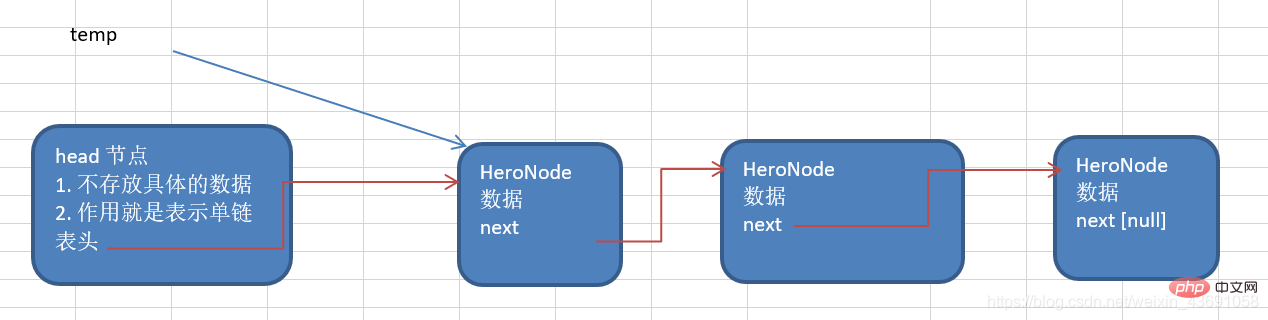
The idea of adding the tail
①
First create a head node, which is used to represent the head of a singly linked list. ② Then every time a node is added, it is added directly to the end of the linked list. Tail addition means: regardless of the numbering sequence, find the last node of the current linked list, and point the next of the last node to the new node.
 Code implementation
Code implementation // 添加方式1:尾添加
public void add(HeroNode heroNode) {
// 因为head头不能动,因此需要一个辅助变量(指针)temp
HeroNode temp = head;
while (true) {
// 如果遍历到链表的最后
if (temp.next == null) {
break;
}
// temp指针后移
temp = temp.next;
}
// 当退出循环时,temp指向链表的最后
temp.next = heroNode;
}
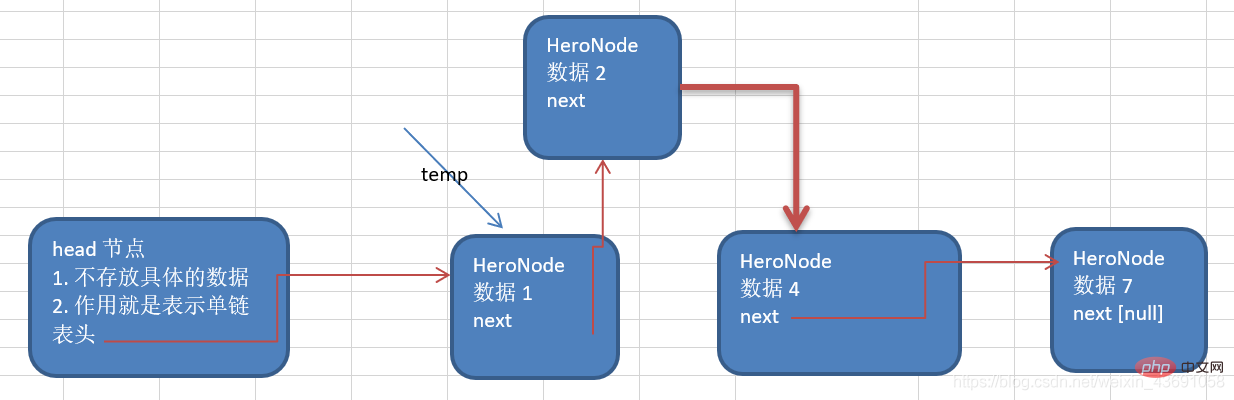
Ideas of adding by ranking
①First find the location of the newly added node through the auxiliary variable (temp pointer). ②New node.next=temp.next; ③temp.next=New node;
// 添加方式2:根据排名添加
public void addByOrder(HeroNode heroNode) {
HeroNode temp = head;// 借助辅助指针
boolean flag = false;// 添加的编号是否存在
while (true) {
if (temp.next == null) {// 遍历到结尾
break;
}
if (temp.next.no > heroNode.no) {// 位置找到,就在temp的后面插入
break;
} else if (temp.next.no == heroNode.no) {// 该编号已存在
flag = true;
break;
}
temp = temp.next;// 后移,遍历当前链表
}
if (flag) {
// 不能添加
System.out.printf("准备插入的英雄的编号%d已经存在,不能加入\n", heroNode.no);
} else {
// 插入到temp的后面
heroNode.next = temp.next;
temp.next = heroNode;
}
}
Modification ideas
①Find the node first through traversal. ②temp.name =newHeroNode.name;
, temp.nickname=newHeroNode.nickname;
// 修改节点信息,根据节点的no属性修改其他信息
public void update(HeroNode newHeroNode) {
// 空链表无法修改节点信息
if (head.next == null) {
System.out.println("链表为空~");
return;
}
// 根据no排名找到需要修改的节点
HeroNode temp = head.next;
boolean flag = false;// flag表示是否找到需要修改的节点
while (true) {
if (temp == null) {
// 遍历到结尾
break;
}
if (temp.no == newHeroNode.no) {
// 找到
flag = true;
break;
}
temp = temp.next;// 后移
}
if (flag) {
temp.name = newHeroNode.name;
temp.nickname = newHeroNode.nickname;
} else {
System.out.printf("没有找到编号为%d的节点,不能修改\n", newHeroNode.no);
}
}
Deletion ideas
①
Find the node that needs to be deleted the previous node. ②temp.next=temp.next.next ③The deleted node will not have other references pointing to it and will be recycled by the garbage collection mechanism. 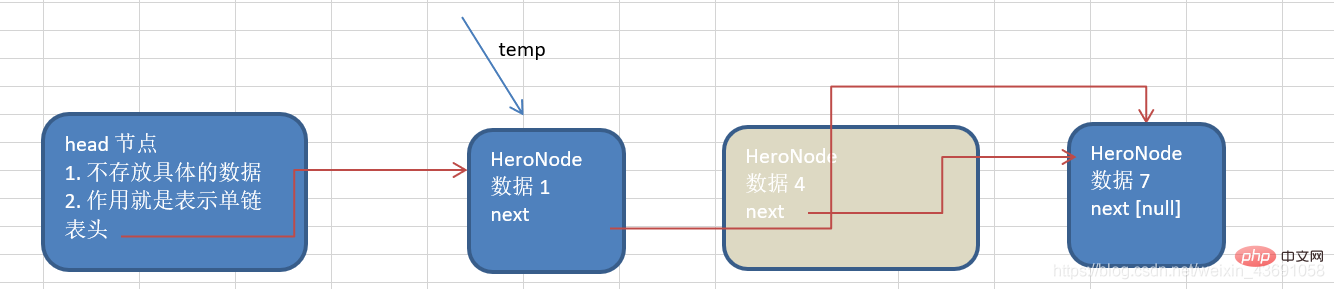 Code implementation
Code implementation public void delete(int no) {
HeroNode temp = head;
boolean flag = false;// 是否找到待删除节点
while (true) {
if (temp.next == null) {
// 遍历到结尾
break;
}
if (temp.next.no == no) {
// 找到了待删除节点的前一个节点
flag = true;
break;
}
temp = temp.next;// 后移
}
if (flag) {
// 可以删除
temp.next = temp.next.next;
} else {
System.out.printf("要删除的%d节点不存在\n", no);
}
}
package com.gql.linkedlist;/**
* 单链表
*
* @guoqianliang
*
*/public class SingleLinkedListDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建节点
HeroNode hero1 = new HeroNode(1, "宋江", "及时雨");
HeroNode hero2 = new HeroNode(2, "卢俊义", "玉麒麟");
HeroNode hero3 = new HeroNode(3, "吴用", "智多星");
HeroNode hero4 = new HeroNode(4, "林冲", "豹子头");
// 创建单向链表
SingleLinkedList singleLinkedList = new SingleLinkedList();
// 加入
singleLinkedList.addByOrder(hero1);
singleLinkedList.addByOrder(hero4);
singleLinkedList.addByOrder(hero3);
singleLinkedList.addByOrder(hero2);
singleLinkedList.list();
// 测试修改节点
HeroNode newHeroNode = new HeroNode(2, "小卢", "玉麒麟~");
singleLinkedList.update(newHeroNode);
System.out.println("修改后的链表情况:");
singleLinkedList.list();
// 删除一个节点
singleLinkedList.delete(1);
singleLinkedList.delete(2);
singleLinkedList.delete(3);
singleLinkedList.delete(4);
System.out.println("删除后的链表情况:");
singleLinkedList.list();
}}//定义SingleLinkedList,管理英雄class SingleLinkedList {
// 初始化头结点,不存放具体数据
private HeroNode head = new HeroNode(0, "", "");
// 添加方式1:尾添加
// 思路:
// 1.找到当前链表的最后节点
// 2.将这个最后的节点的next指向新的节点
public void add(HeroNode heroNode) {
// 因为head头不能动,因此需要一个辅助变量(指针)temp
HeroNode temp = head;
while (true) {
// 如果遍历到链表的最后
if (temp.next == null) {
break;
}
// temp指针后移
temp = temp.next;
}
// 当退出循环时,temp指向链表的最后
temp.next = heroNode;
}
// 添加方式2:根据排名添加
public void addByOrder(HeroNode heroNode) {
HeroNode temp = head;// 借助辅助指针
boolean flag = false;// 添加的编号是否存在
while (true) {
if (temp.next == null) {// 遍历到结尾
break;
}
if (temp.next.no > heroNode.no) {// 位置找到,就在temp的后面插入
break;
} else if (temp.next.no == heroNode.no) {// 该编号已存在
flag = true;
break;
}
temp = temp.next;// 后移,遍历当前链表
}
if (flag) {
// 不能添加
System.out.printf("准备插入的英雄的编号%d已经存在,不能加入\n", heroNode.no);
} else {
// 插入到temp的后面
heroNode.next = temp.next;
temp.next = heroNode;
}
}
// 修改节点信息,根据节点的no属性修改其他信息
public void update(HeroNode newHeroNode) {
// 空链表无法修改节点信息
if (head.next == null) {
System.out.println("链表为空~");
return;
}
// 根据no排名找到需要修改的节点
HeroNode temp = head.next;
boolean flag = false;// flag表示是否找到需要修改的节点
while (true) {
if (temp == null) {
// 遍历到结尾
break;
}
if (temp.no == newHeroNode.no) {
// 找到
flag = true;
break;
}
temp = temp.next;// 后移
}
if (flag) {
temp.name = newHeroNode.name;
temp.nickname = newHeroNode.nickname;
} else {
System.out.printf("没有找到编号为%d的节点,不能修改\n", newHeroNode.no);
}
}
// 删除节点
// 思路:
// 1.找到需要删除节点的前一个节点
// 2.temp.next=temp.next.next
// 3.被删除的节点将会被垃圾回收机制回收
public void delete(int no) {
HeroNode temp = head;
boolean flag = false;// 是否找到待删除节点
while (true) {
if (temp.next == null) {
// 遍历到结尾
break;
}
if (temp.next.no == no) {
// 找到了待删除节点的前一个节点
flag = true;
break;
}
temp = temp.next;// 后移
}
if (flag) {
// 可以删除
temp.next = temp.next.next;
} else {
System.out.printf("要删除的%d节点不存在\n", no);
}
}
// 显示链表[遍历]
public void list() {
// 空链表直接返回
if (head.next == null) {
System.out.println("链表为空");
return;
}
// 仍然使用辅助变量(指针),进行循环
HeroNode temp = head.next;
while (true) {
if (temp == null) {
break;
}
System.out.println(temp);
// 将temp后移
temp = temp.next;
}
}}//定义HeroNode,每一个HeroNode就是一个节点class HeroNode {
public int no;// 排名
public String name;
public String nickname;// 昵称
public HeroNode next;// 指向下一个节点
// 构造器
public HeroNode() {
super();
}
public HeroNode(int no, String name, String nickname) {
super();
this.no = no;
this.name = name;
this.nickname = nickname;
}
// 重写toString
@Override
public String toString() {
return "HeroNode [no=" + no + ", name=" + name + ", nickname=" + nickname + "]";
}}

The answers to the above four interview questions are In the following code
package com.gql.LinkedList;import java.util.Stack;/**
* 模拟单链表
*
* @author Hudie
* @Email:guoqianliang@foxmail.com
* @date 2020年7月16日下午6:47:42
*/public class SingleLinkedListDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建节点
HeroNode hero1 = new HeroNode(1, "宋江", "及时雨");
HeroNode hero2 = new HeroNode(2, "卢俊义", "玉麒麟");
HeroNode hero3 = new HeroNode(3, "吴用", "智多星");
HeroNode hero4 = new HeroNode(4, "林冲", "豹子头");
// 创建单向链表
SingleLinkedList singleLinkedList = new SingleLinkedList();
// 加入
singleLinkedList.addByOrder(hero1);
singleLinkedList.addByOrder(hero4);
singleLinkedList.addByOrder(hero3);
singleLinkedList.addByOrder(hero2);
singleLinkedList.list();
// 测试修改节点
HeroNode newHeroNode = new HeroNode(2, "小卢", "玉麒麟~");
singleLinkedList.update(newHeroNode);
System.out.println("修改后的链表情况:");
singleLinkedList.list();
// 删除一个节点
singleLinkedList.delete(4);
System.out.println("删除后的链表情况:");
singleLinkedList.list();
//练习4:反向打印单链表
System.out.println("反向打印单链表:");
reversePrint(singleLinkedList.getHead());
//练习3:反转单链表
reversalList(singleLinkedList.getHead());
System.out.println("反转过后的单链表为:");
singleLinkedList.list();
// 练习1:获取单链表节点个数
System.out.println("单链表的有效个数为:");
System.out.println(getLength(singleLinkedList.getHead()));
int index = 2;
//练习2:获取单链表倒数第index给节点
System.out.println("倒数第"+ index +"个节点为:");
System.out.println(getLastKNode(singleLinkedList.getHead(),index));
}
/**
* @Description: 获取单链表节点个数 思路: while循环 + 遍历指针
*/
public static int getLength(HeroNode head) {
if (head.next == null) {
return 0;
}
int length = 0;
// 辅助指针
HeroNode p = head.next;
while (p != null) {
length++;
p = p.next;
}
return length;
}
/**
* @Description:
* 查找单链表中倒数第index个节点 index:表示倒数第index给节点
* 思路:
* 1.首先获取链表的长度length,可直接调用getLength
* 2.然后从链表第一个开始遍历,遍历(length-index)个
* 3.找不到返回null
*/
public static HeroNode getLastKNode(HeroNode head, int index) {
if (head.next == null) {
return null;
}
int length = getLength(head);
if (index <= 0 || index > length) {
return null;
}
HeroNode p = head.next;
for(int i = 0;i < length-index;i++){
p = p.next;
}
return p;
}
/**
* @Description:
* 反转单链表[带头节点]
* 思路:
* 1.先定义一个节点reversalHead = new HeroNode(0,"","");
* 2.遍历原来的链表,每遍历一个节点,就将其取出,并放在新的链表reversalHead的最前端
* 3.原来的链表的head.next = reversalHead;
*/
public static void reversalList(HeroNode head){
//链表为空或只有一个节点,无需反转,直接返回
if(head.next == null || head.next.next == null){
return;
}
//辅助指针p
HeroNode p = head.next;
HeroNode next = null;//指向辅助指针p的下一个位置
HeroNode reversalHead = new HeroNode(0,"","");
//遍历原来的链表,每遍历一个节点,就将其取出,并放在新的链表reversalHead的最前端
while(p != null){
next = p.next;
p.next = reversalHead.next;
reversalHead.next = p;
p = next;
}
head.next = reversalHead.next;
}
/**
* @Description:
* 反向打印单链表[带头节点]
* 思路1:单链表反转后打印(不建议,因为破坏了单链表的结构)
* 思路2:使用栈结构,利用栈先进后出的特点
*/
public static void reversePrint(HeroNode head){
if(head.next == null){
return;
}
Stack stack = new Stack();
HeroNode p = head.next;
while(p != null){
stack.push(p);
p = p.next;
}
//将栈中的节点进行打印
while(stack.size() > 0){
System.out.println(stack.pop());
}
}}// 定义SingleLinkedList,管理英雄,即链表的增删改查class SingleLinkedList {
// 初始化头结点,不存放具体数据
private HeroNode head = new HeroNode(0, "", "");
// 添加方式1:尾添加
// 思路:
// 1.找到当前链表的最后节点
// 2.将这个最后的节点的next指向新的节点
public void add(HeroNode heroNode) {
// 因为head头不能动,因此需要一个辅助变量(指针)temp
HeroNode temp = head;
while (true) {
// 如果遍历到链表的最后
if (temp.next == null) {
break;
}
// temp指针后移
temp = temp.next;
}
// 当退出循环时,temp指向链表的最后
temp.next = heroNode;
}
public HeroNode getHead() {
return head;
}
// 添加方式2:根据排名添加
public void addByOrder(HeroNode heroNode) {
HeroNode temp = head;// 借助辅助指针
boolean flag = false;// 添加的编号是否存在
while (true) {
if (temp.next == null) {// 遍历到结尾
break;
}
if (temp.next.no > heroNode.no) {// 位置找到,就在temp的后面插入
break;
} else if (temp.next.no == heroNode.no) {// 该编号已存在
flag = true;
break;
}
temp = temp.next;// 后移,遍历当前链表
}
if (flag) {
// 不能添加
System.out.printf("准备插入的英雄的编号%d已经存在,不能加入\n", heroNode.no);
} else {
// 插入到temp的后面
heroNode.next = temp.next;
temp.next = heroNode;
}
}
// 修改节点信息,根据节点的no属性修改其他信息
public void update(HeroNode newHeroNode) {
// 空链表无法修改节点信息
if (head.next == null) {
System.out.println("链表为空~");
return;
}
// 根据no排名找到需要修改的节点
HeroNode temp = head.next;
boolean flag = false;// flag表示是否找到需要修改的节点
while (true) {
if (temp == null) {
// 遍历到结尾
break;
}
if (temp.no == newHeroNode.no) {
// 找到
flag = true;
break;
}
temp = temp.next;// 后移
}
if (flag) {
temp.name = newHeroNode.name;
temp.nickname = newHeroNode.nickname;
} else {
System.out.printf("没有找到编号为%d的节点,不能修改\n", newHeroNode.no);
}
}
// 删除节点
// 思路:
// 1.找到需要删除节点的前一个节点
// 2.temp.next=temp.next.next
// 3.被删除的节点将会被垃圾回收机制回收
public void delete(int no) {
HeroNode temp = head;
boolean flag = false;// 是否找到待删除节点
while (true) {
if (temp.next == null) {
// 遍历到结尾
break;
}
if (temp.next.no == no) {
// 找到了待删除节点的前一个节点
flag = true;
break;
}
temp = temp.next;// 后移
}
if (flag) {
// 可以删除
temp.next = temp.next.next;
} else {
System.out.printf("要删除的%d节点不存在\n", no);
}
}
// 显示链表[遍历]
public void list() {
// 空链表直接返回
if (head.next == null) {
System.out.println("链表为空");
return;
}
// 仍然使用辅助变量(指针),进行循环
HeroNode temp = head.next;
while (true) {
if (temp == null) {
break;
}
System.out.println(temp);
// 将temp后移
temp = temp.next;
}
}}// 定义HeroNode,每一个HeroNode就是一个节点class HeroNode {
public int no;// 排名
public String name;
public String nickname;// 昵称
public HeroNode next;// 指向下一个节点
// 构造器
public HeroNode() {
super();
}
public HeroNode(int no, String name, String nickname) {
super();
this.no = no;
this.name = name;
this.nickname = nickname;
}
// 重写toString
@Override
public String toString() {
return "HeroNode [no=" + no + ", name=" + name + ", nickname=" + nickname + "]";
}} Related learning recommendations:
The above is the detailed content of Java implementation of singly linked list (Linked List) related. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Perfect Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check Perfect number in Java?, examples with code implementation.
 Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Weka in Java. Here we discuss the Introduction, how to use weka java, the type of platform, and advantages with examples.
 Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Smith Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check smith number in Java? example with code implementation.
 Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
In this article, we have kept the most asked Java Spring Interview Questions with their detailed answers. So that you can crack the interview.
 Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8 introduces the Stream API, providing a powerful and expressive way to process data collections. However, a common question when using Stream is: How to break or return from a forEach operation? Traditional loops allow for early interruption or return, but Stream's forEach method does not directly support this method. This article will explain the reasons and explore alternative methods for implementing premature termination in Stream processing systems. Further reading: Java Stream API improvements Understand Stream forEach The forEach method is a terminal operation that performs one operation on each element in the Stream. Its design intention is
 TimeStamp to Date in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
TimeStamp to Date in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to TimeStamp to Date in Java. Here we also discuss the introduction and how to convert timestamp to date in java along with examples.
 Java Program to Find the Volume of Capsule
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Java Program to Find the Volume of Capsule
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Capsules are three-dimensional geometric figures, composed of a cylinder and a hemisphere at both ends. The volume of the capsule can be calculated by adding the volume of the cylinder and the volume of the hemisphere at both ends. This tutorial will discuss how to calculate the volume of a given capsule in Java using different methods. Capsule volume formula The formula for capsule volume is as follows: Capsule volume = Cylindrical volume Volume Two hemisphere volume in, r: The radius of the hemisphere. h: The height of the cylinder (excluding the hemisphere). Example 1 enter Radius = 5 units Height = 10 units Output Volume = 1570.8 cubic units explain Calculate volume using formula: Volume = π × r2 × h (4
 How to Run Your First Spring Boot Application in Spring Tool Suite?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:11 PM
How to Run Your First Spring Boot Application in Spring Tool Suite?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:11 PM
Spring Boot simplifies the creation of robust, scalable, and production-ready Java applications, revolutionizing Java development. Its "convention over configuration" approach, inherent to the Spring ecosystem, minimizes manual setup, allo




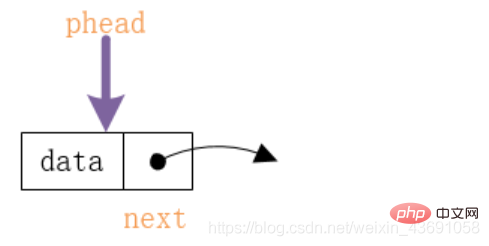 Singly linked list (without leading node)
Singly linked list (without leading node)