Learn the history of Linux commands
This article will bring you information about the history command in Linux

- Preface
- 1. Linux operations on command history
-
- 1 , Use history to view the history record
- 2, Use Ctrl r to directly search the execution record
- 3, Repeat the previous command
- 4, Execute the command with the corresponding serial number
- 5. Modify the total number of lines in the history record
- 6. Clear the history record
Preface
Have you ever executed a long command when developing on Linux, and then you need to re-enter it after a while if you want to execute the command?
Everyone must know that in Linux, you can use the ↑ up arrow to find the previously executed command, but if this command takes a long time to execute, it will be very long. Hard to find.
If you are using the xsheel client, it will not be found even if the client is closed.
So how to solve this problem!

##1. Linux operations on command history
When you execute the history command, the 1000 previously executed commands will be displayed.
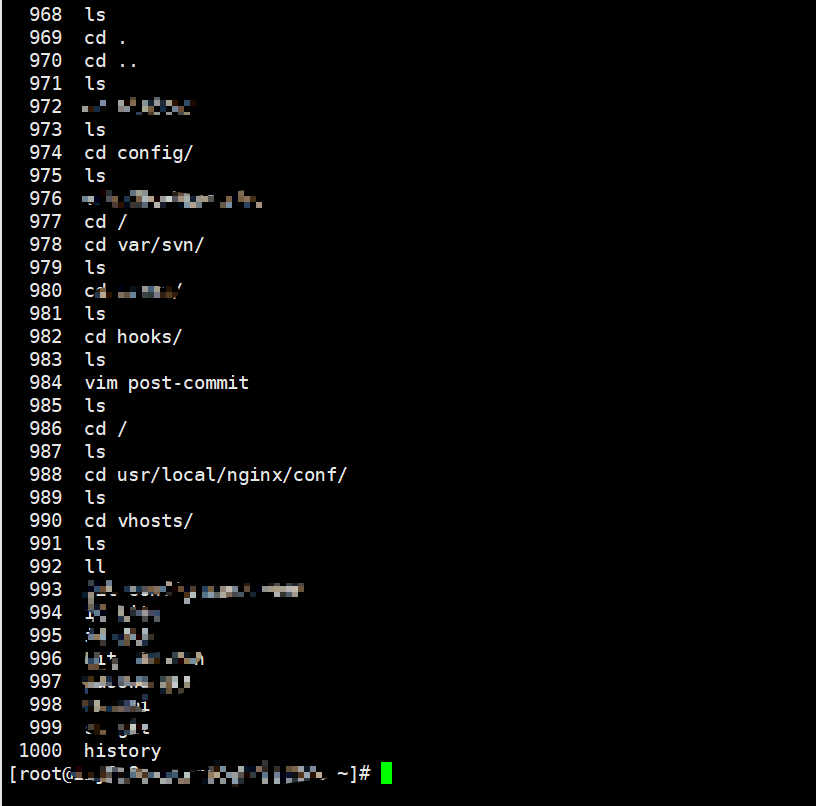
But if you don’t log out or shut down, you can save more than 1000 commands. This 1000 is a default value.
Of course, this value can also be modified. If you want to modify it, you can execute the following command.
echo "HISTSIZE=2000" >> .bash_profile echo "HISFILETSIZE=2000" >> .bash_profilesource ~/.bash_profile (使其生效即可)
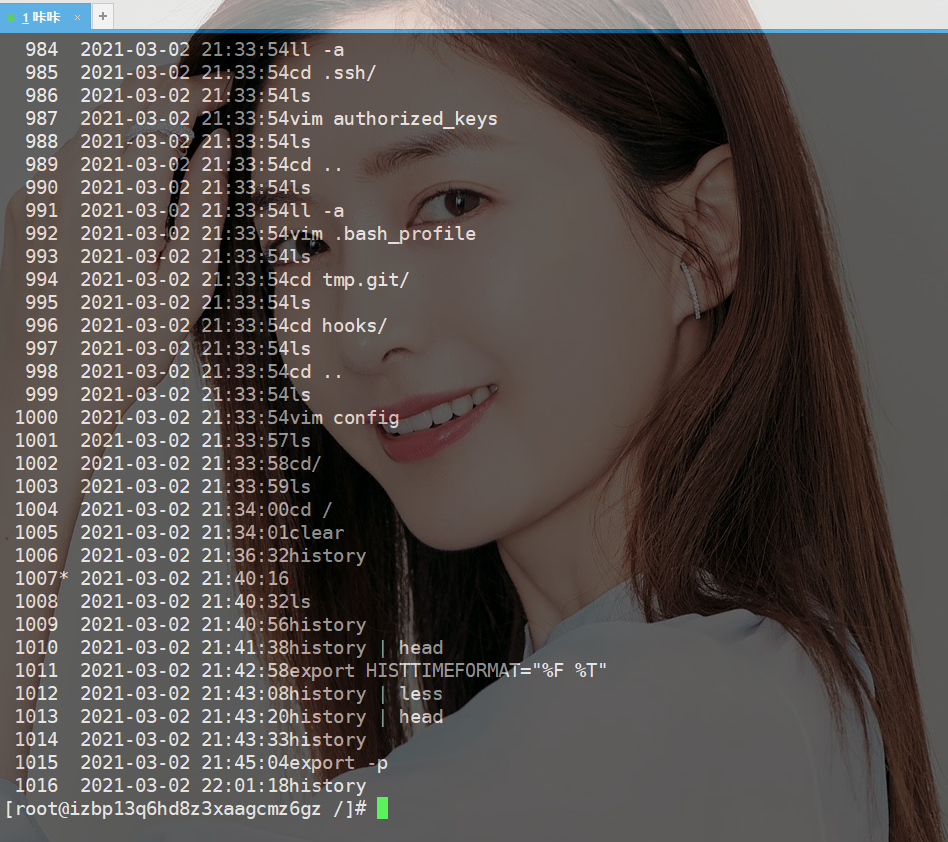
If you are the person in charge of the server and you need to see what command was executed at what point in time, you only need to execute the following command
export HISTTIMEFORMAT="%F %T"
Then you can see the time after executing the history command
usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -t
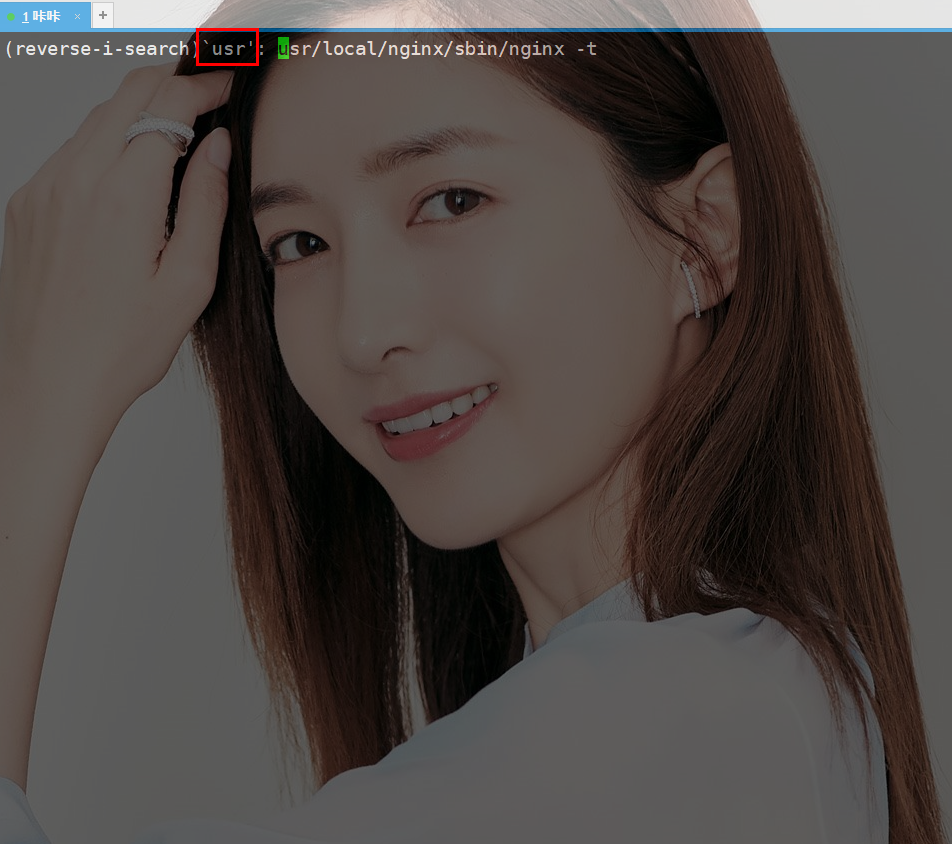
There are several ways to execute the previous command. The most commonly used one is probably↑This kind of thing.
But what I told Daji today is that you can use !! to operate
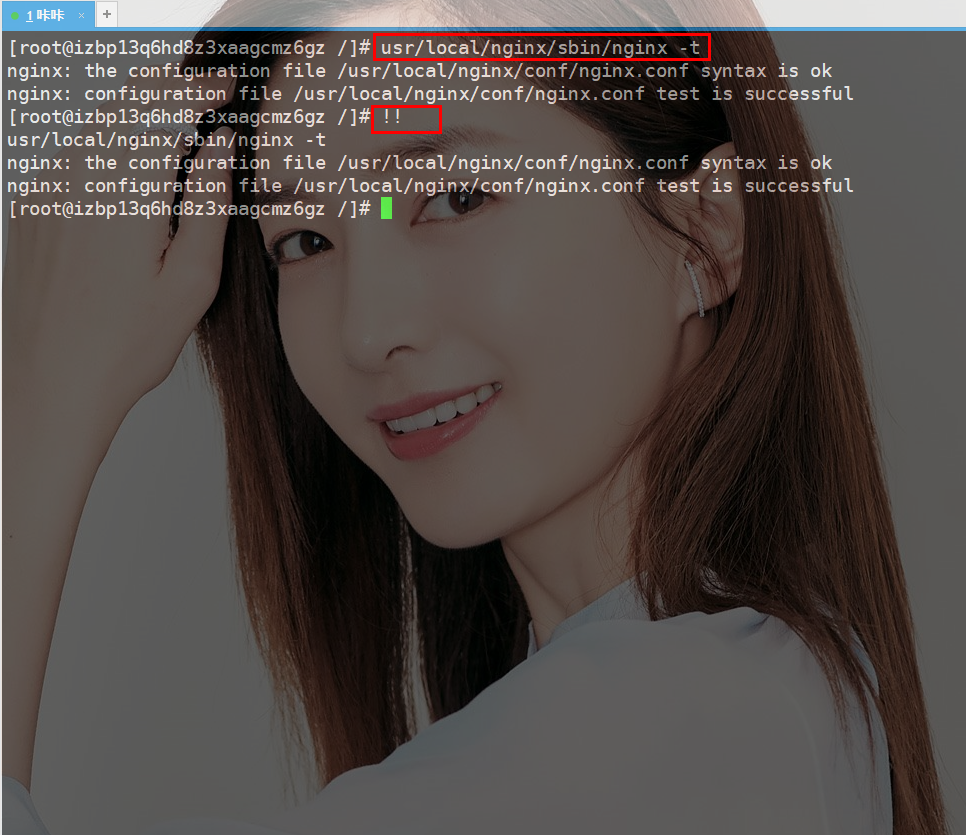
!-1 to execute
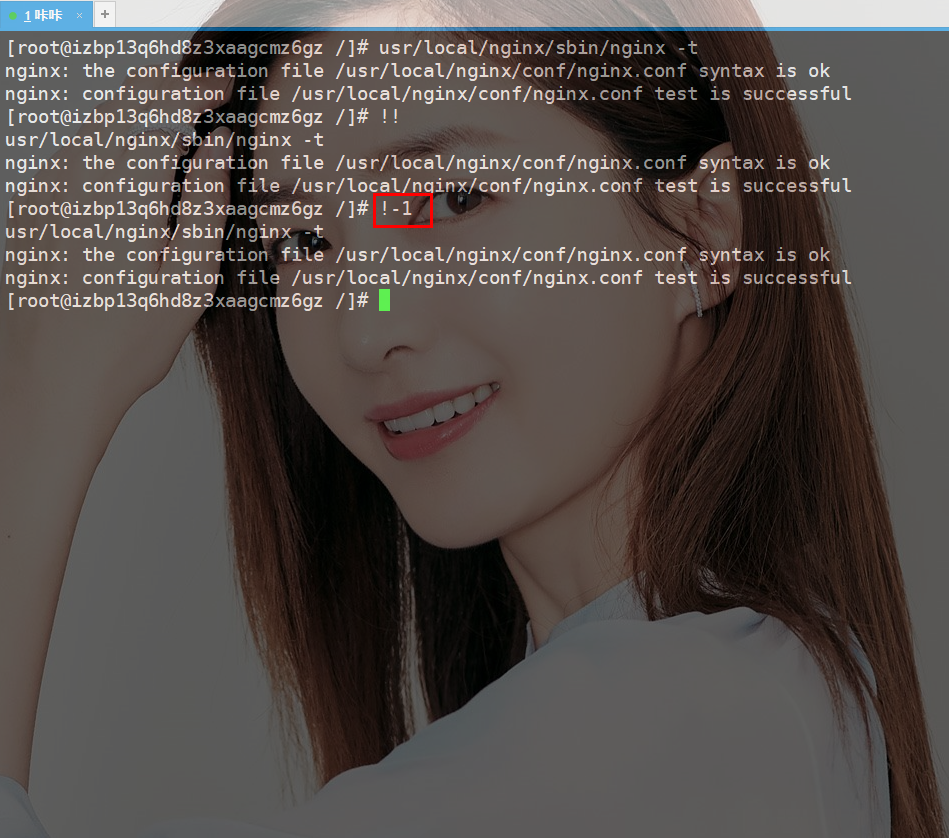
Where does this serial number come from? , which is the command history mentioned first in this article. The serial number of each command will appear after execution.
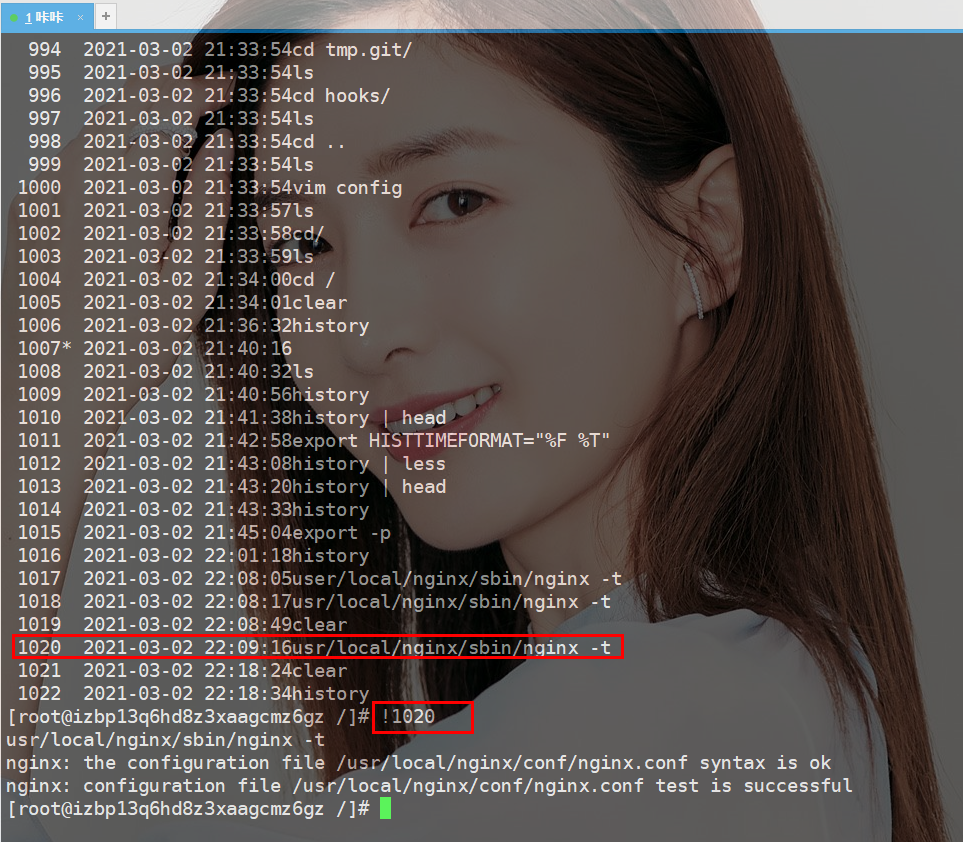
As shown below, I want to execute the 1020th command, then I can execute it like this !1020.
In fact, anyone with some programming knowledge should be able to understand this command. In the third section, we used !! to execute the previous command, which is actually The last record in history.
同样的道理这个命令使用的是!1020,这样对于这个命令的记忆就有了规律。
在第一节中对于这个总行数的修改也简单的说了一下,但是没有亲自操作,接下来操作一下。
这个命令中HISTSIZE是控制history命令显示的数量
而HISTFILETSIZE控制的是文件中存储的数量
1039 2021-03-02 22:29:37 echo "HISTSIZE=2000" >> .bash_profile 1040 2021-03-02 22:29:58 echo "HISTFILETSIZE=2000" >> .bash_profile 1041 2021-03-02 22:30:20 source ~/.bash_profile
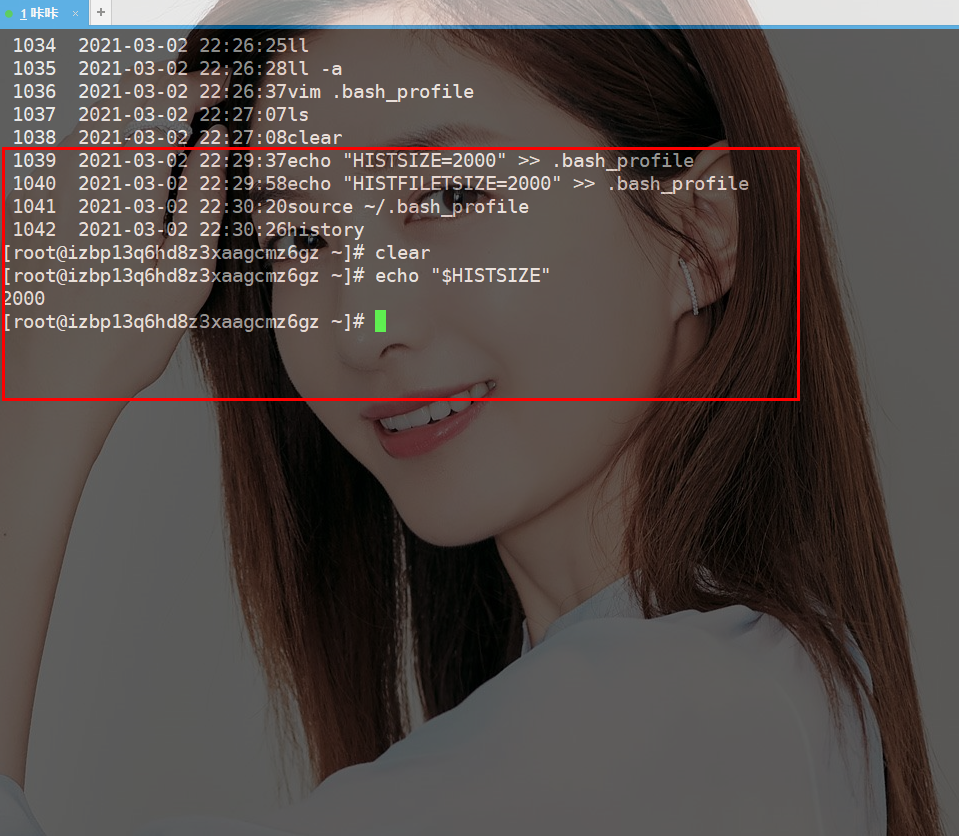
Since this command can modify the number of history displays, it can also modify the number of file storage history records.
Just imagine, what if you don’t want the server to record history!
Just change both values to 0.
Can you try it yourself?
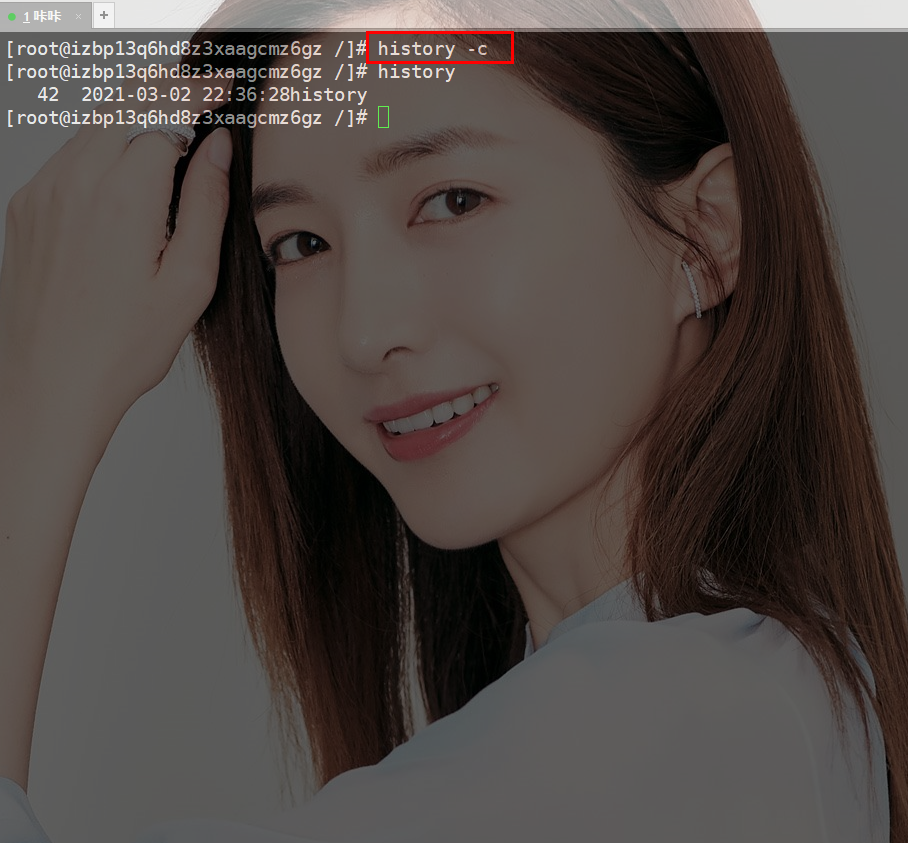
Clear the history record and execute the commandhistory -c
- View history using history
- Search history using ctrl r
- Repeat the previous command! ! or! -1
- Execute the corresponding serial number command to use! 1020
- HISTSIZE is the number displayed for executing history
- HISTFILETSIZEThe number of historical records saved
- To clear the history, use history -c
Persistence in learning, persistence in blogging, and persistence in sharing are the beliefs that Kaka has always adhered to since its beginning. I hope that Kaka’s articles on the huge Internet can bring you a little bit of help. I’m Kaka, see you next time.
The above is the detailed content of Learn the history of Linux commands. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1359
1359
 52
52
 How do I use regular expressions (regex) in Linux for pattern matching?
Mar 17, 2025 pm 05:25 PM
How do I use regular expressions (regex) in Linux for pattern matching?
Mar 17, 2025 pm 05:25 PM
The article explains how to use regular expressions (regex) in Linux for pattern matching, file searching, and text manipulation, detailing syntax, commands, and tools like grep, sed, and awk.
 How do I implement two-factor authentication (2FA) for SSH in Linux?
Mar 17, 2025 pm 05:31 PM
How do I implement two-factor authentication (2FA) for SSH in Linux?
Mar 17, 2025 pm 05:31 PM
The article provides a guide on setting up two-factor authentication (2FA) for SSH on Linux using Google Authenticator, detailing installation, configuration, and troubleshooting steps. It highlights the security benefits of 2FA, such as enhanced sec
 How do I monitor system performance in Linux using tools like top, htop, and vmstat?
Mar 17, 2025 pm 05:28 PM
How do I monitor system performance in Linux using tools like top, htop, and vmstat?
Mar 17, 2025 pm 05:28 PM
The article discusses using top, htop, and vmstat for monitoring Linux system performance, detailing their unique features and customization options for effective system management.
 How do I configure SELinux or AppArmor to enhance security in Linux?
Mar 12, 2025 pm 06:59 PM
How do I configure SELinux or AppArmor to enhance security in Linux?
Mar 12, 2025 pm 06:59 PM
This article compares SELinux and AppArmor, Linux kernel security modules providing mandatory access control. It details their configuration, highlighting the differences in approach (policy-based vs. profile-based) and potential performance impacts
 How do I back up and restore a Linux system?
Mar 12, 2025 pm 07:01 PM
How do I back up and restore a Linux system?
Mar 12, 2025 pm 07:01 PM
This article details Linux system backup and restoration methods. It compares full system image backups with incremental backups, discusses optimal backup strategies (regularity, multiple locations, versioning, testing, security, rotation), and da
 How do I use sudo to grant elevated privileges to users in Linux?
Mar 17, 2025 pm 05:32 PM
How do I use sudo to grant elevated privileges to users in Linux?
Mar 17, 2025 pm 05:32 PM
The article explains how to manage sudo privileges in Linux, including granting, revoking, and best practices for security. Key focus is on editing /etc/sudoers safely and limiting access.Character count: 159
 How do I set up a firewall in Linux using firewalld or iptables?
Mar 12, 2025 pm 06:58 PM
How do I set up a firewall in Linux using firewalld or iptables?
Mar 12, 2025 pm 06:58 PM
This article compares Linux firewall configuration using firewalld and iptables. Firewalld offers a user-friendly interface for managing zones and services, while iptables provides low-level control via command-line manipulation of the netfilter fra
 How do I manage software packages in Linux using package managers (apt, yum, dnf)?
Mar 17, 2025 pm 05:26 PM
How do I manage software packages in Linux using package managers (apt, yum, dnf)?
Mar 17, 2025 pm 05:26 PM
Article discusses managing software packages in Linux using apt, yum, and dnf, covering installation, updates, and removals. It compares their functionalities and suitability for different distributions.




