redis learns master-slave replication Master/slave

What is
Jargon: This is what we call master-slave replication. After the host data is updated, it is configured according to the configuration. and strategy, automatically synchronized to the master/slaver mechanism of the standby machine. The Master is mainly for writing, and the Slave is mainly for reading.
What can be done
Reading and writing separation
Disaster recovery
Recommended (free):redis
##How to play
• Configure slave (library) but not master (library) • Slave library configuration command: slaveof master library IP master library port
• Every time you disconnect from the master, you need to reconnect, unless you configure it in redis.conf File (specific location: redis.conf search
# REPLICATION
#)
• info replication
• Modify configuration file details operation
• Copy multiple redis.conf files, press 'redis[ port].conf'Rename
• Turn on daemonize yes
• pid file name
• Specify port
• Log file name
(painting, etc.) copy; copy; repeat (experiment); (especially the answer to the defense)
replication English [ˌreplɪ'keɪʃ(ə)n] American [ˌreplɪ'keɪʃ(ə)n] n.
3 common tricks
One master and two slaves (one host, two slaves)
Init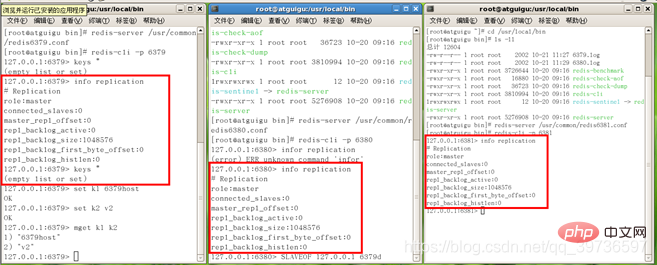
Set the slave through slaveof 127.0.0.1 6379d
At this time, one master and two slaves are set up
Set k4 v4 in the master, and get in the two slaves k4 can be displayed.
1. If I set k1 and k2 before slave, can the slave machine check their values?
Yes, the slave machine can only play from beginning to end after receiving it. Play all of them on the host
2. At this time, set k6 v6 is set on the host. And set k6 v66 is also set on the two slaves. What will happen at this time? First come first served, the latter overrides. Can the slave and the host execute the same command?
The master writes as the master, and the slave reads as the master.
At this time, the slave cannot write and an exception is reported.
3. The host is dead? What are the chances? From the machine? Stay put?
Still slave, stay put. If you can’t take over, the leader is back, everything will be the same as before
4. Is the slave machine dead? Recover from inability to function?
passing on the fire
Core idea: decentralization
The previous Slave can be the Master of the next slave, and the Slave can also receive connections and connections from other slaves. Synchronous request, then the slave becomes the next master in the chain, which can effectively reduce the writing pressure of the master (slave of slaves is still a slave)
Midway change direction: the previous data will be cleared and the latest copy will be re-established
slaveof new main library IP new main library port
Anti-customer-based
SLAVEOF no one
Stop the current database from synchronizing with other databases and turn it into the primary database
Copying Principle
After the slave is successfully started and connected to the master, it will send a sync command
The master receives the command to start the background save process, and at the same time collects all received is used to modify the data set command. After the background process is executed, the master will transfer the entire data file to the slave to complete a complete synchronization
Full copy: After the slave service receives the database file data, it will save it and loaded into memory.
Incremental replication: Master continues to pass all new collected modification commands to slave in order to complete synchronization
However, as long as the master is reconnected, a full synchronization (full replication) will be automatically executed
Sentinel mode(sentinel)
A group of sentinels can monitor multiple masters at the same time (patrol sentinel)What is it
An automatic version that is mainly anti-customer. It can monitor whether the host fails in the background. If it fails, it will automatically switch from the slave database to the main database based on the number of votes.How to play (usage steps)
### 1. Adjust the structure, 6379 brings 6380 and 6381
2. Create a new sentinel.conf file, the name must not be wrong
3. Configure the sentinel, fill in the content
1.sentinel monitor The name of the monitored database (Choose your own name) 127.0.0.1 6379 1
ˆ ˆ 2. The last number 1 above means that after the host hangs up, the salve will vote to see who will take over as the host. The person who gets the number of votes will become the host (PS. It is different from the description on the official website. , there are official documents below)
4. Start Sentinel
1. redis-sentinel /sentinel.conf (the above directories are configured according to their actual conditions, and the directories may be different)
5. Normal master-slave demonstration
6. The original master is down
7. Vote for a new one
8. Restart the master and slave and continue working, check info replication
Question: If the previously hung master is restarted, Will there be a conflict between the two masters?
Answer: No, the original master becomes a slave
Disadvantages of replication
Replication delay
Because all write operations are It is operated on the Master first, and then synchronized to the slave, so there is a certain delay in synchronizing from the Master to the Slave machine. When the system is very busy, the delay problem will be more serious, and the increase in the number of Slave machines will also make this problem worse. serious.
More related free learning recommendations: redis tutorial
The above is the detailed content of redis learns master-slave replication Master/slave. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
Redis cluster mode deploys Redis instances to multiple servers through sharding, improving scalability and availability. The construction steps are as follows: Create odd Redis instances with different ports; Create 3 sentinel instances, monitor Redis instances and failover; configure sentinel configuration files, add monitoring Redis instance information and failover settings; configure Redis instance configuration files, enable cluster mode and specify the cluster information file path; create nodes.conf file, containing information of each Redis instance; start the cluster, execute the create command to create a cluster and specify the number of replicas; log in to the cluster to execute the CLUSTER INFO command to verify the cluster status; make
 How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
Using the Redis directive requires the following steps: Open the Redis client. Enter the command (verb key value). Provides the required parameters (varies from instruction to instruction). Press Enter to execute the command. Redis returns a response indicating the result of the operation (usually OK or -ERR).
 How to use single threaded redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:12 PM
How to use single threaded redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:12 PM
Redis uses a single threaded architecture to provide high performance, simplicity, and consistency. It utilizes I/O multiplexing, event loops, non-blocking I/O, and shared memory to improve concurrency, but with limitations of concurrency limitations, single point of failure, and unsuitable for write-intensive workloads.
 How to read the source code of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
How to read the source code of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
The best way to understand Redis source code is to go step by step: get familiar with the basics of Redis. Select a specific module or function as the starting point. Start with the entry point of the module or function and view the code line by line. View the code through the function call chain. Be familiar with the underlying data structures used by Redis. Identify the algorithm used by Redis.
 How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear Redis data: Use the FLUSHALL command to clear all key values. Use the FLUSHDB command to clear the key value of the currently selected database. Use SELECT to switch databases, and then use FLUSHDB to clear multiple databases. Use the DEL command to delete a specific key. Use the redis-cli tool to clear the data.
 How to view all keys in redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:15 PM
How to view all keys in redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:15 PM
To view all keys in Redis, there are three ways: use the KEYS command to return all keys that match the specified pattern; use the SCAN command to iterate over the keys and return a set of keys; use the INFO command to get the total number of keys.
 How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
To read a queue from Redis, you need to get the queue name, read the elements using the LPOP command, and process the empty queue. The specific steps are as follows: Get the queue name: name it with the prefix of "queue:" such as "queue:my-queue". Use the LPOP command: Eject the element from the head of the queue and return its value, such as LPOP queue:my-queue. Processing empty queues: If the queue is empty, LPOP returns nil, and you can check whether the queue exists before reading the element.
 How to start the server with redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:12 PM
How to start the server with redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:12 PM
The steps to start a Redis server include: Install Redis according to the operating system. Start the Redis service via redis-server (Linux/macOS) or redis-server.exe (Windows). Use the redis-cli ping (Linux/macOS) or redis-cli.exe ping (Windows) command to check the service status. Use a Redis client, such as redis-cli, Python, or Node.js, to access the server.




