A brief discussion on the basic usage of built-in modules in Nodejs
本篇文章带大家一起了解一下Nodejs内置模块的基本用法。有一定的参考价值,有需要的朋友可以参考一下,希望对大家有所帮助。

相关推荐:《nodejs 教程》
内置模块的基本使用
// 01. 导包
const fs = require("fs");
// 02. 调用unlink删除方法
// 第一个参数:要删除的文件的路径
// 第二个参数:回调函数
fs.unlink("01-内置模块fs的使用/tmp/hello.txt", (err) => {
if (err) throw err;
console.log("已成功删除 /tmp/hello");
});fs模块的读文件
fs.readFile(path[, options], callback)
第一个参数:文件的路径
第二个参数:可选参数,读取文件的编码格式
第三个参数:回调函数
fs.readFile("01-内置模块fs的使用/etc/passwd.txt", "utf-8", (err, data) => {
// err是一个错误对象,如果没有错就返回一个null
// data是读的文件内容
// console.log(err); // null
console.log(data); // 这是一个寂寞的天,下着有些伤心的雨!
});Npdemon全局模块
作用:终端下自动执行代码
安装
npm i nodemon -gnodemon文件名即可自动监视文件的修改,自动重新运行
vscode快捷键
ctrl+d 选择相同的下一个
ctrl+左右 按单词跳转光标
ctrl+enter 光标另起一行
同步异步
- 同步
console.log("哈哈");
for (var i = 0; i
哈哈
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
呵呵- 异步
console.log("哈哈");
setTimeout(() => {
console.log("啦啦啦");
}, 1000);
console.log("呵呵"); ->
哈哈
呵呵
啦啦啦- 刚才我们学习的fs模块读/写操作就是一个异步操作
console.log("哈哈");
const fs = require("fs");
fs.readFile("01-内置模块fs的使用/etc/望庐山瀑布.txt", "utf-8", (err, data) => {
if (err === null) {
console.log(data);
} else {
console.log(err);
}
});
console.log("呵呵"); ->
哈哈
呵呵
望庐山瀑布
唐·李白
日照香炉生紫烟,
遥看瀑布挂前川。
飞流直下三千尺,
疑是银河落九天。- 其实读文件也有同步操作
console.log("哈哈");
const fs = require("fs");
let data = fs.readFileSync("01-内置模块fs的使用/etc/passwd.txt", "utf-8");
console.log(data);
console.log("呵呵"); ->
哈哈
这是一个寂寞的天,下着有些伤心的雨!
呵呵同步异步面试题
// 看代码,说出运行结果
var t = true;
while (t) {
window.setTimeout(function () {
t = false;
}, 1000);
}
alert("end"); -> 死循环和路径相关的两个变量
- __dirname: 获现的是当前这个文件所在的整个文件夹的绝对路径
- __filename: 拿到的是当前这个文件的绝对路径
console.log(__dirname); // d:\前端\NodeJs\nodejs code\02-内置模块path的使用 console.log(__filename); // d:\前端\NodeJs\nodejs code\02-内置模块path的使用\03-和路径相关的两个变量.js
使用拼接的绝对路径来读取文件
const fs = require("fs");
const fullPath = __dirname + "\\etc\\1.txt";
fs.readFile(fullPath, "utf-8", (err, data) => {
if (err === null) {
console.log(data);
} else {
console.log(err);
}
});path.join([…paths])
path.join() 方法会将所有给定的 path 片段连接到一起(使用平台特定的分隔符作为定界符),然后规范化生成的路径。
长度为零的 path 片段会被忽略。 如果连接后的路径字符串为长度为零的字符串,则返回 '.',表示当前工作目录。
// 01. 导入模块
const path = require("path");
// 02. 使用方法
// join方法是把路径片段,连接成一个新的路径.
const fullPath = path.join(__dirname, "etc", "1.txt");
console.log(fullPath);使用path模块拼接而成的绝对路径来读取文件
// 1. 导入模块
const fs = require("fs");
const path = require("path");
// 2. 调用方法
// 2.1 使用path.joiin来拼接一个绝对路径(要读取文件的绝对路径)
const fullPath = path.join(__dirname, "etc", "1.txt");
// 2.2 读文件
fs.readFile(fullPath, "utf-8", (err, data) => {
if (err === null) {
console.log(data);
} else {
console.log(err);
}
});使用内置模块http来创建一个服务器
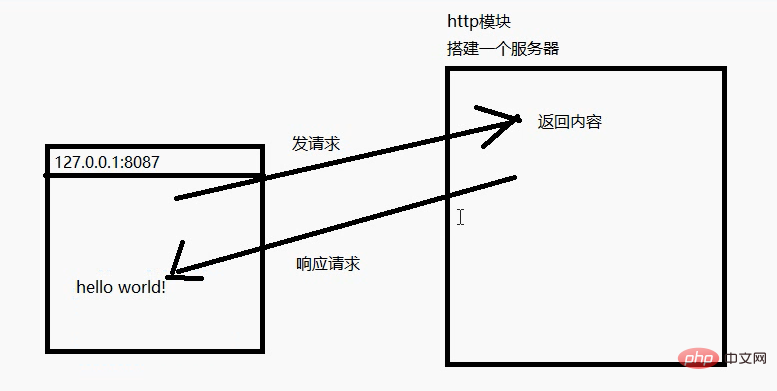
// 1. 导入http模块
const http = require("http");
// 2. 创建一个服务器
// 这个方法有一个返回值,返回值就代表这个服务器
const server = http.createServer((require, response) => {
// 3. 设置返回给用户看的内容
response.end("hello world!");
});
// 4. 开启服务器
server.listen(8087, () => {
console.log("服务器开启了:8087");
});request.setHeader(name, value)
为请求头对象设置单个请求头的值。 如果此请求头已存在于待发送的请求头中,则其值将被替换。 这里可以使用字符串数组来发送具有相同名称的多个请求头。 非字符串值将被原样保存。 因此 request.getHeader() 可能会返回非字符串值。 但是非字符串值将转换为字符串以进行网络传输。
request.setHeader('Content-Type', 'application/json');或:
request.setHeader('Cookie', ['type=ninja', 'language=javascript']);如果想要返回去的中文不乱码,那就要设置响应头.
response.setHeader("Content-Type", "text/html;charset=utf-8");更多编程相关知识,请访问:编程视频!!
The above is the detailed content of A brief discussion on the basic usage of built-in modules in Nodejs. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 The difference between nodejs and vuejs
Apr 21, 2024 am 04:17 AM
The difference between nodejs and vuejs
Apr 21, 2024 am 04:17 AM
Node.js is a server-side JavaScript runtime, while Vue.js is a client-side JavaScript framework for creating interactive user interfaces. Node.js is used for server-side development, such as back-end service API development and data processing, while Vue.js is used for client-side development, such as single-page applications and responsive user interfaces.
 Is nodejs a backend framework?
Apr 21, 2024 am 05:09 AM
Is nodejs a backend framework?
Apr 21, 2024 am 05:09 AM
Node.js can be used as a backend framework as it offers features such as high performance, scalability, cross-platform support, rich ecosystem, and ease of development.
 How to connect nodejs to mysql database
Apr 21, 2024 am 06:13 AM
How to connect nodejs to mysql database
Apr 21, 2024 am 06:13 AM
To connect to a MySQL database, you need to follow these steps: Install the mysql2 driver. Use mysql2.createConnection() to create a connection object that contains the host address, port, username, password, and database name. Use connection.query() to perform queries. Finally use connection.end() to end the connection.
 What is the difference between npm and npm.cmd files in the nodejs installation directory?
Apr 21, 2024 am 05:18 AM
What is the difference between npm and npm.cmd files in the nodejs installation directory?
Apr 21, 2024 am 05:18 AM
There are two npm-related files in the Node.js installation directory: npm and npm.cmd. The differences are as follows: different extensions: npm is an executable file, and npm.cmd is a command window shortcut. Windows users: npm.cmd can be used from the command prompt, npm can only be run from the command line. Compatibility: npm.cmd is specific to Windows systems, npm is available cross-platform. Usage recommendations: Windows users use npm.cmd, other operating systems use npm.
 What are the global variables in nodejs
Apr 21, 2024 am 04:54 AM
What are the global variables in nodejs
Apr 21, 2024 am 04:54 AM
The following global variables exist in Node.js: Global object: global Core module: process, console, require Runtime environment variables: __dirname, __filename, __line, __column Constants: undefined, null, NaN, Infinity, -Infinity
 Is there a big difference between nodejs and java?
Apr 21, 2024 am 06:12 AM
Is there a big difference between nodejs and java?
Apr 21, 2024 am 06:12 AM
The main differences between Node.js and Java are design and features: Event-driven vs. thread-driven: Node.js is event-driven and Java is thread-driven. Single-threaded vs. multi-threaded: Node.js uses a single-threaded event loop, and Java uses a multi-threaded architecture. Runtime environment: Node.js runs on the V8 JavaScript engine, while Java runs on the JVM. Syntax: Node.js uses JavaScript syntax, while Java uses Java syntax. Purpose: Node.js is suitable for I/O-intensive tasks, while Java is suitable for large enterprise applications.
 Is nodejs a back-end development language?
Apr 21, 2024 am 05:09 AM
Is nodejs a back-end development language?
Apr 21, 2024 am 05:09 AM
Yes, Node.js is a backend development language. It is used for back-end development, including handling server-side business logic, managing database connections, and providing APIs.
 How to deploy nodejs project to server
Apr 21, 2024 am 04:40 AM
How to deploy nodejs project to server
Apr 21, 2024 am 04:40 AM
Server deployment steps for a Node.js project: Prepare the deployment environment: obtain server access, install Node.js, set up a Git repository. Build the application: Use npm run build to generate deployable code and dependencies. Upload code to the server: via Git or File Transfer Protocol. Install dependencies: SSH into the server and use npm install to install application dependencies. Start the application: Use a command such as node index.js to start the application, or use a process manager such as pm2. Configure a reverse proxy (optional): Use a reverse proxy such as Nginx or Apache to route traffic to your application




