1. Master-slave replication overview
#65 Brother: With RDB and AOF, you are no longer afraid of data loss due to downtime, but the Redis instance How to achieve high availability when the machine is down?
Since one machine is down and unable to provide services, what about multiple machines? Can it be solved? Redis provides a master-slave mode, which copies a redundant copy of data to other Redis servers through master-slave replication.
The former is called the master node (master), and the latter is called the slave node (slave); data replication is one-way, and can only be from the master node to the slave node.
By default, each Redis server is a master node; and a master node can have multiple slave nodes (or no slave nodes), but a slave node can only have one master node.
65 Brother: How to ensure the consistency of data between master and slave?
In order to ensure the consistency of the replica data, the master-slave architecture adopts a read-write separation method.
- Read operation: both the master and slave libraries can execute;
- Write operation: the master library executes it first, and then synchronizes the write operation to the slave library;
#65 Brother: Why do we need to separate reading and writing?
We can assume that both the master and slave libraries can execute write instructions. If the same data is modified multiple times, and each modification is sent to a different master-slave instance, the copy data of the instance will be inconsistent. .
If in order to ensure data consistency, Redis needs to lock and coordinate the modification of multiple instances, Redis will naturally not do this!
65 Brother: Does master-slave replication have other functions?
Fault recovery: When the master node goes down, other nodes can still provide services;
Load balancing: The Master node provides write services, and the Slave node Provide read services and share pressure;
High availability cornerstone: It is the basis for the implementation of sentinel and cluster, and the cornerstone of high availability.
2. Set up master-slave replication
The activation of master-slave replication is completely initiated from the slave node and does not require us Do everything on the master node.
65 Brother: How to build a master-slave replication architecture?
The relationship between the master database and the slave database can be formed through the replicaof (slaveof was used before Redis 5.0) command.
There are 3 ways to enable master-slave replication on the slave node:
-
Configuration file
Add
to the configuration file of the slave server replicaof <masterip> <masterport></masterport></masterip> -
Start command
redis-server Add
--replicaof <masterip> < ;masterport></masterip> -
Client command
After starting multiple Redis instances, execute the command directly through the client:
replicaof <masterip> < ;masterport></masterip>, the Redis instance becomes a slave node.
For example, assuming there are instance 1 (172.16.88.1), instance 2 (172.16.88.2) and instance 3 (172.16.88.3), execute the following on instance 2 and instance 3 respectively. command, instance 2 and instance 3 become the slave libraries of instance 1, and instance 1 becomes the master.
replicaof 172.16.88.1 6379
3. Master-slave replication principle
Once the master-slave library mode adopts read-write separation, all data writing operations will only be performed on the master library, without the need to coordinate three Example.
After the master database has the latest data, it will be synchronized to the slave database, so that the data in the master and slave databases are consistent.
65 Brother: How is the master-slave database synchronization completed? Is the master database data transmitted to the slave database at once, or is it synchronized in batches? How to synchronize during normal operation? If the network between the master and slave libraries is disconnected, will the data remain consistent after reconnection?
65 Brother, why do you have so many questions? Synchronization is divided into three situations:
The first full copy of the master-slave library;
Synchronization during normal operation of the master and slave;
The network between the master and slave libraries is disconnected and reconnected for synchronization.
The first full copy of the master-slave database
65 Brother: I’m so dizzy, let’s synchronize the master-slave database for the first time Let’s talk about it.
The first replication process of the master-slave library can be roughly divided into three stages: the connection establishment stage (i.e., the preparation stage), the stage of synchronizing data from the master library to the slave library, and sending new write commands during synchronization. From the library stage;
, go directly to the picture, and you will have a global perspective as a whole, which will be introduced in detail later.
Establishing a connection
The main function of this stage is to establish a connection between the master and slave nodes. Be prepared for full data synchronization. The slave library will establish a connection with the master library. The slave library will execute replicaof and send the pync command and tell the master library that synchronization is about to take place. After the master library confirms the reply, synchronization between the master and slave libraries will begin.
65 Brother: How does the slave library know the main library information and establish a connection?
After configuring the IP and port of the master node in the replicaof configuration item in the configuration file of the slave node, the slave node will know which master node it wants to connect to.
The slave node maintains two fields, masterhost and masterport, which are used to store the IP and port information of the master node.
The slave library executes replicaof and sends the psync command, indicating that data synchronization is to be performed. After receiving the command, the master library starts replication according to the parameters. The command contains two parameters: runID of the main library and copy progress offset.
- runID: Each Redis instance will automatically generate a unique identification ID when it is started. For the first master-slave replication, the main database runID is not yet known, so the parameter is set to "?" .
- offset: The first copy is set to -1, indicating the first copy, and recording the copy progress offset.
FULLRESYNC to respond to the command with two parameters: the main library runID and the current copy progress offset of the main library, and return it to the slave library . After receiving the response from the library, these two parameters will be recorded.
FULLRESYNC response indicates the full replication used for the first replication, that is, the master database will copy all current data to the slave database.
The master database synchronizes data to the slave database
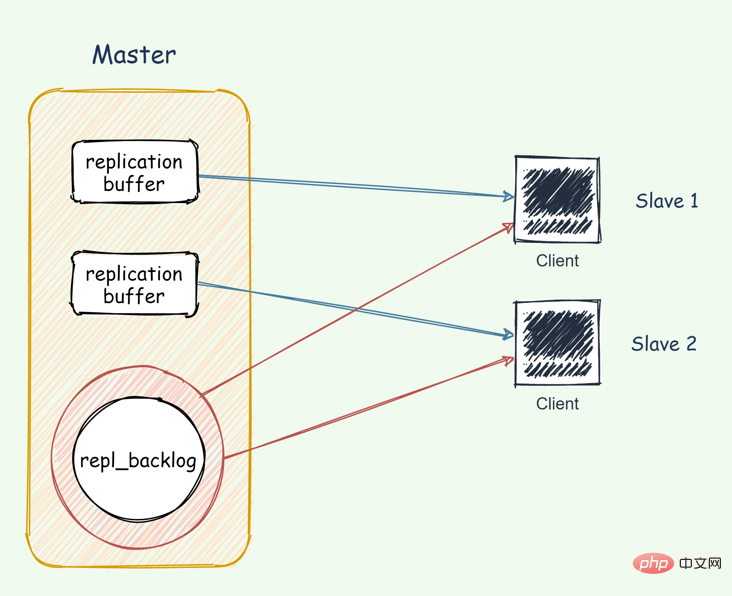
Second phasemaster executes thebgsave command to generate the RDB file and The file is sent to the slave library, and the main library opens a replication buffer for each slave to record all write commands received since the RDB file was generated.
Send a new write command to the slave library
The third phaseAfter the slave node loads the RDB, the master node will replicate the data in the buffer Sent to the slave node, Slave receives and executes, and the slave node synchronizes to the same state as the master node. 65 Brother: When the master database is synchronizing data to the slave database, can the request be accepted normally? The main database will not be blocked. As a man who only wants to be fast, Redis will be blocked at every turn. The write operation after generating the RDB file is not recorded in the RDB file just now. In order to ensure the consistency of the master-slave database data, the master database will use a replication buffer in the memory to record the RDB file generation. all subsequent write operations. 65 Brother: Why do we need to clear the current database after receiving the RDB file from the database? Because the slave library may save other data before starting to synchronize with the master library through thereplcaof command, to prevent the influence between the master and slave data.
Redis 和客户端通信也好,和从库通信也好,Redis 都分配一个内存 buffer 进行数据交互,客户端就是一个 client,从库也是一个 client,我们每个 client 连上 Redis 后,Redis 都会分配一个专有 client buffer,所有数据交互都是通过这个 buffer 进行的。
Master 先把数据写到这个 buffer 中,然后再通过网络发送出去,这样就完成了数据交互。
不管是主从在增量同步还是全量同步时,master 会为其分配一个 buffer ,只不过这个 buffer 专门用来传播写命令到从库,保证主从数据一致,我们通常把它叫做 replication buffer。
replication buffer 太小会引发的问题:
replication buffer 由 client-output-buffer-limit slave 设置,当这个值太小会导致主从复制连接断开。
1)当 master-slave 复制连接断开,master 会释放连接相关的数据。replication buffer 中的数据也就丢失了,此时主从之间重新开始复制过程。
2)还有个更严重的问题,主从复制连接断开,导致主从上出现重新执行 bgsave 和 rdb 重传操作无限循环。
当主节点数据量较大,或者主从节点之间网络延迟较大时,可能导致该缓冲区的大小超过了限制,此时主节点会断开与从节点之间的连接;
这种情况可能引起全量复制 -> replication buffer 溢出导致连接中断 -> 重连 -> 全量复制 -> replication buffer 缓冲区溢出导致连接中断……的循环。
具体详情:[top redis headaches for devops – replication buffer]
因而推荐把 replication buffer 的 hard/soft limit 设置成 512M。
config set client-output-buffer-limit "slave 536870912 536870912 0"
65 哥:主从库复制为何不使用 AOF 呢?相比 RDB 来说,丢失的数据更少。
这个问题问的好,原因如下:
RDB 文件是二进制文件,网络传输 RDB 和写入磁盘的 IO 效率都要比 AOF 高。
从库进行数据恢复的时候,RDB 的恢复效率也要高于 AOF。
增量复制
65 哥:主从库间的网络断了咋办?断开后要重新全量复制么?
在 Redis 2.8 之前,如果主从库在命令传播时出现了网络闪断,那么,从库就会和主库重新进行一次全量复制,开销非常大。
从 Redis 2.8 开始,网络断了之后,主从库会采用增量复制的方式继续同步。
增量复制:用于网络中断等情况后的复制,只将中断期间主节点执行的写命令发送给从节点,与全量复制相比更加高效。
repl_backlog_buffer
断开重连增量复制的实现奥秘就是 repl_backlog_buffer 缓冲区,不管在什么时候 master 都会将写指令操作记录在 repl_backlog_buffer 中,因为内存有限, repl_backlog_buffer 是一个定长的环形数组,如果数组内容满了,就会从头开始覆盖前面的内容。
master 使用 master_repl_offset记录自己写到的位置偏移量,slave 则使用 slave_repl_offset记录已经读取到的偏移量。
master 收到写操作,偏移量则会增加。从库持续执行同步的写指令后,在 repl_backlog_buffer 的已复制的偏移量 slave_repl_offset 也在不断增加。
正常情况下,这两个偏移量基本相等。在网络断连阶段,主库可能会收到新的写操作命令,所以 master_repl_offset会大于 slave_repl_offset。
当主从断开重连后,slave 会先发送 psync 命令给 master,同时将自己的 runID,slave_repl_offset发送给 master。
master 只需要把 master_repl_offset与 slave_repl_offset之间的命令同步给从库即可。
增量复制执行流程如下图:
65 哥:repl_backlog_buffer 太小的话从库还没读取到就被 Master 的新写操作覆盖了咋办?
我们要想办法避免这个情况,一旦被覆盖就会执行全量复制。我们可以调整 repl_backlog_size 这个参数用于控制缓冲区大小。计算公式:
repl_backlog_buffer = second * write_size_per_second
second:从服务器断开重连主服务器所需的平均时间;
write_size_per_second:master 平均每秒产生的命令数据量大小(写命令和数据大小总和);
例如,如果主服务器平均每秒产生 1 MB 的写数据,而从服务器断线之后平均要 5 秒才能重新连接上主服务器,那么复制积压缓冲区的大小就不能低于 5 MB。
为了安全起见,可以将复制积压缓冲区的大小设为2 * second * write_size_per_second,这样可以保证绝大部分断线情况都能用部分重同步来处理。
基于长连接的命令传播
65 哥:完成全量同步后,正常运行过程如何同步呢?
当主从库完成了全量复制,它们之间就会一直维护一个网络连接,主库会通过这个连接将后续陆续收到的命令操作再同步给从库,这个过程也称为基于长连接的命令传播,使用长连接的目的就是避免频繁建立连接导致的开销。
在命令传播阶段,除了发送写命令,主从节点还维持着心跳机制:PING 和 REPLCONF ACK。
主->从:PING
每隔指定的时间,主节点会向从节点发送 PING 命令,这个 PING 命令的作用,主要是为了让从节点进行超时判断。
从->主:REPLCONF ACK
在命令传播阶段,从服务器默认会以每秒一次的频率,向主服务器发送命令:
REPLCONF ACK <replication_offset></replication_offset>
其中 replication_offset 是从服务器当前的复制偏移量。发送 REPLCONF ACK 命令对于主从服务器有三个作用:
检测主从服务器的网络连接状态。
辅助实现 min-slaves 选项。
检测命令丢失, 从节点发送了自身的 slave_replication_offset,主节点会用自己的 master_replication_offset 对比,如果从节点数据缺失,主节点会从
repl_backlog_buffer缓冲区中找到并推送缺失的数据。注意,offset 和 repl_backlog_buffer 缓冲区,不仅可以用于部分复制,也可以用于处理命令丢失等情形;区别在于前者是在断线重连后进行的,而后者是在主从节点没有断线的情况下进行的。
如何确定执行全量同步还是部分同步?
在 Redis 2.8 及以后,从节点可以发送 psync 命令请求同步数据,此时根据主从节点当前状态的不同,同步方式可能是全量复制或部分复制。本文以 Redis 2.8 及之后的版本为例。
关键就是 psync的执行:
-
从节点根据当前状态,发送
psync命令给 master:- 如果从节点从未执行过
replicaof,则从节点发送psync ? -1,向主节点发送全量复制请求; - 如果从节点之前执行过
replicaof则发送psync <runid> <offset></offset></runid>, runID 是上次复制保存的主节点 runID,offset 是上次复制截至时从节点保存的复制偏移量。
- 如果从节点从未执行过
-
主节点根据接受到的
psync命令和当前服务器状态,决定执行全量复制还是部分复制:- runID 与从节点发送的 runID 相同,且从节点发送的
slave_repl_offset之后的数据在repl_backlog_buffer缓冲区中都存在,则回复CONTINUE,表示将进行部分复制,从节点等待主节点发送其缺少的数据即可; - runID 与从节点发送的 runID 不同,或者从节点发送的 slave_repl_offset 之后的数据已不在主节点的
repl_backlog_buffer缓冲区中 (在队列中被挤出了),则回复从节点FULLRESYNC <runid> <offset></offset></runid>,表示要进行全量复制,其中 runID 表示主节点当前的 runID,offset 表示主节点当前的 offset,从节点保存这两个值,以备使用。
- runID 与从节点发送的 runID 相同,且从节点发送的
一个从库如果和主库断连时间过长,造成它在主库 repl_backlog_buffer 的 slave_repl_offset 位置上的数据已经被覆盖掉了,此时从库和主库间将进行全量复制。
总结下
每个从库会记录自己的 slave_repl_offset,每个从库的复制进度也不一定相同。
在和主库重连进行恢复时,从库会通过 psync 命令把自己记录的 slave_repl_offset 发给主库,主库会根据从库各自的复制进度,来决定这个从库可以进行增量复制,还是全量复制。
replication buffer and repl_backlog
replication buffer corresponds to each slave, through
config set client-output-buffer-limit slaveset up.repl_backlog_bufferis a ring buffer, there will only be one in the entire master process, and it is common to all slaves. The size of repl_backlog is set by the repl-backlog-size parameter. The default size is 1M. The size can be calculated based on the sum of the commands generated per second, (master executes rdb bgsave) (master sends rdb to slave) (slave load rdb file) time Estimate the size of the backlog buffer, repl-backlog-size value is not less than the product of these two.
In general, replication buffer is the buffer used by the client on the master library to connect to the slave library when the master-slave library performs full replication, and repl_backlog_buffer is a dedicated buffer on the main library used to continuously save write operations in order to support incremental replication from the slave library.
repl_backlog_buffer is a dedicated buffer. After the Redis server is started, it begins to receive write operation commands. This is shared by all slave libraries. The master library and the slave library will each record their own replication progress. Therefore, when different slave libraries are recovering, they will send their own replication progress (slave_repl_offset) to the master library, and the master library can communicate with it. Independent synchronization.
As shown in the figure:
4. Master-slave application problem
4.1 The problem of read-write separation
Data expiration problem
65 Brother: In the scenario of master-slave replication, will the slave node delete expired data? ?
This is a good question. For the sake of data consistency between the master and slave nodes, the slave nodes will not actively delete data. We know that Redis has two deletion strategies:
Lazy deletion: When the client queries the corresponding data, Redis determines whether the data has expired and deletes it if it expires.
Regular deletion: Redis deletes expired data through scheduled tasks.
65 Brother: Will the client read expired data by reading data from the slave node?
Starting from Redis 3.2, when reading data from the node, first determine whether the data has expired. If it expires, it will not be returned to the client and the data will be deleted.
4.2 Single-machine memory size limit
If the Redis single-machine memory reaches 10GB, the synchronization time of a slave node will be at the level of several minutes; if there are more slave nodes, recovery will The speed will be slower. If the read load of the system is very high and the slave node cannot provide services during this period, it will put a lot of pressure on the system.
If the amount of data is too large, it takes too long for the master node to fork to save the RDB file during the full replication phase. The slave node cannot receive data for a long time and triggers a timeout. The data synchronization of the master and slave nodes may also fall into full volume. Copy->Timeout causes replication interruption->Reconnect->Full copy->Timeout causes replication interruption... cycle.
In addition, in addition to the absolute amount of the master node's single-machine memory, the proportion of the host memory it occupies should not be too large: it is best to only use 50% - 65% of the memory, leaving 30% - 45% The memory is used to execute the bgsave command and create copy buffers, etc.
Summary
The role of master-slave replication: AOF and RDB binary files ensure rapid recovery of data from downtime and prevent data loss as much as possible . However, services were still unable to be provided after a downtime, so a master-slave architecture and read-write separation evolved.
Master-slave replication principle: connection establishment phase, data synchronization phase, command propagation phase; the data synchronization phase is divided into full replication and partial replication; in the command propagation phase, there are The PING and REPLCONF ACK commands perform heartbeat detection on each other.
Although master-slave replication solves or alleviates problems such as data redundancy, failure recovery, and read load balancing, its flaws are still obvious: Failure recovery cannot be automated; write operations Unable to load balance; the storage capacity is limited by a single machine; the solution to these problems requires the help of Sentinel and cluster , which I will introduce in a later article. Welcome to pay attention.
65 Brother: Brother Ma, your pictures are really beautiful and the content is good. I have learned a lot from your articles. I want to collect, like, read and share them. Let more outstanding developers see common progress!
For more programming related knowledge, please visit: Programming Video! !



























![[Web front-end] Node.js quick start](https://img.php.cn/upload/course/000/000/067/662b5d34ba7c0227.png)



