MyISAM的读写锁调度是写优先,这也是MyISAM不适合做写为主表的引擎,因为写锁以后,其它线程不能做任何操作,大量的更新使查询很难得到锁,从而造成永远阻塞。
InnoDB
开销、加锁时间和锁粒度介于表锁和行锁之间,会出现死锁,并发处理能力一般(此锁不做多介绍)
insert、update、delete //上写锁
Let's thoroughly understand the locking mechanism of MySQL together

Locks are a very important part in MySQL. Locks have a decisive impact on MySQL's data access concurrency. There is a lot of knowledge involved in locks, so to finish it and digest it into your stomach, you need to calm down and savor it over and over again several times. This article is a general overview of locks. For some related in-depth details, you still need to find relevant books to continue to consolidate.
##Related free learning recommendations: mysql video tutorial
Understanding of locks
1.1 Explanation of locks
计算机协调多个进程或线程并发访问某一资源的机制。
1.2 Importance of locks
在数据库中,除传统计算资源(CPU、RAM、I\O等)的争抢,数据也是一种供多用户共享的资源。 如何保证数据并发访问的一致性,有效性,是所有数据库必须要解决的问题。 锁冲突也是影响数据库并发访问性能的一个重要因素,因此锁对数据库尤其重要。
1.3 Disadvantages of locks
加锁是消耗资源的,锁的各种操作,包括获得锁、检测锁是否已解除、释放锁等 ,都会增加系统的开销。
1.4 Simple example
现如今网购已经特别普遍了,比如淘宝双十一活动,当天的人流量是千万及亿级别的,但商家的库存是有限的。 系统为了保证商家的商品库存不发生超卖现象,会对商品的库存进行锁控制。当有用户正在下单某款商品最后一件时, 系统会立马对该件商品进行锁定,防止其他用户也重复下单,直到支付动作完成才会释放(支付成功则立即减库存售罄,支付失败则立即释放)。
Types of locks
2.1 Table lock
Type
读锁(read lock),也叫共享锁(shared lock) 针对同一份数据,多个读操作可以同时进行而不会互相影响(select)
写锁(write lock),也叫排他锁(exclusive lock) 当前操作没完成之前,会阻塞其它读和写操作(update、insert、delete)
Storage engine default lock
MyISAM
Features
1. 对整张表加锁 2. 开销小 3. 加锁快 4. 无死锁 5. 锁粒度大,发生锁冲突概率大,并发性低
1. 读锁会阻塞写操作,不会阻塞读操作
2. 写锁会阻塞读和写操作
Copy after login
Suggestions1. 读锁会阻塞写操作,不会阻塞读操作 2. 写锁会阻塞读和写操作
MyISAM的读写锁调度是写优先,这也是MyISAM不适合做写为主表的引擎,因为写锁以后,其它线程不能做任何操作,大量的更新使查询很难得到锁,从而造成永远阻塞。
Copy after login
MyISAM的读写锁调度是写优先,这也是MyISAM不适合做写为主表的引擎,因为写锁以后,其它线程不能做任何操作,大量的更新使查询很难得到锁,从而造成永远阻塞。
2.2 Row lock
Types
读锁(read lock),也叫共享锁(shared lock) 允许一个事务去读一行,阻止其他事务获得相同数据集的排他锁
写锁(write lock),也叫排他锁(exclusive lock) 允许获得排他锁的事务更新数据,阻止其他事务取得相同数据集的共享锁和排他锁
意向共享锁(IS) 一个事务给一个数据行加共享锁时,必须先获得表的IS锁
意向排它锁(IX) 一个事务给一个数据行加排他锁时,必须先获得该表的IX锁
InnoDB
Copy after login
FeaturesInnoDB
1. 对一行数据加锁
2. 开销大
3. 加锁慢
4. 会出现死锁
5. 锁粒度小,发生锁冲突概率最低,并发性高
Copy after login
Problems caused by transaction concurrency1. 对一行数据加锁 2. 开销大 3. 加锁慢 4. 会出现死锁 5. 锁粒度小,发生锁冲突概率最低,并发性高
1. 更新丢失
解决:让事务变成串行操作,而不是并发的操作,即对每个事务开始---对读取记录加排他锁
2. 脏读
解决:隔离级别为Read uncommitted
3. 不可重读
解决:使用Next-Key Lock算法来避免
4. 幻读
解决:间隙锁(Gap Lock)
Copy after login
2.3 Page lock1. 更新丢失 解决:让事务变成串行操作,而不是并发的操作,即对每个事务开始---对读取记录加排他锁 2. 脏读 解决:隔离级别为Read uncommitted 3. 不可重读 解决:使用Next-Key Lock算法来避免 4. 幻读 解决:间隙锁(Gap Lock)
开销、加锁时间和锁粒度介于表锁和行锁之间,会出现死锁,并发处理能力一般(此锁不做多介绍)
Copy after login
开销、加锁时间和锁粒度介于表锁和行锁之间,会出现死锁,并发处理能力一般(此锁不做多介绍)
How to lock?
3.1 Table lock
Implicit locking (default, automatic locking and automatic release)
select //上读锁
Copy after loginrrree
Explicit locking (manual )select //上读锁
insert、update、delete //上写锁
Copy after loginCopy after login
Unlock (manual)insert、update、delete //上写锁
lock table tableName read;//读锁
lock table tableName write;//写锁
Copy after login
lock table tableName read;//读锁 lock table tableName write;//写锁
| session02 | |
|---|---|
| select * from teacher;//Can be read normally | |
| update teacher set name = 3 where id =2;//Blocked | |
| session02 | |
|---|---|
| select * from teacher;//is blocked | |
| update teacher set name = 4 where id =2;//Blocked | |
| ##select * from teacher;//Read successfully |
|
| update teacher set name = 4 where id =2;//Update operation successful |
Implicit locking (default, automatic locking and automatic release)
unlock tables;//所有锁表
select //不会上锁
insert、update、delete //上写锁
Copy after loginCopy after login
insert、update、delete //上写锁
|
##select * from teacher where id = 2 lock in share mode;//Read lock |
|
| update teacher set name = 3 where id =2;//Update operation possible | |
| commit; | |
| ##begin; | |
|---|---|
| select * from teacher where id = 2 for update;//write lock |
|
|
update teacher set name = 3 where id = 2;//Can update operation |
update teacher set name = 5 where id =2;//Blocked |
| rollback; | |
为什么上了写锁,别的事务还可以读操作? 因为InnoDB有MVCC机制(多版本并发控制),可以使用快照读,而不会被阻塞。 Copy after login 行锁的实现算法 4.1 Record Lock锁 单个行记录上的锁 Record Lock总是会去锁住索引记录,如果InnoDB存储引擎表建立的时候没有设置任何一个索引,这时InnoDB存储引擎会使用隐式的主键来进行锁定 Copy after login 4.2 Gap Lock锁 当我们用范围条件而不是相等条件检索数据,并请求共享或排他锁时,InnoDB会给符合条件的已有数据记录的索引加锁,对于键值在条件范围内但并不存在的记录。 优点:解决了事务并发的幻读问题 不足:因为query执行过程中通过范围查找的话,他会锁定争个范围内所有的索引键值,即使这个键值并不存在。 间隙锁有一个致命的弱点,就是当锁定一个范围键值之后,即使某些不存在的键值也会被无辜的锁定,而造成锁定的时候无法插入锁定键值范围内任何数据。在某些场景下这可能会对性能造成很大的危害。 Copy after login 4.3 Next-key Lock锁 同时锁住数据+间隙锁 在Repeatable Read隔离级别下,Next-key Lock 算法是默认的行记录锁定算法。 Copy after login 4.4 行锁的注意点 1. 只有通过索引条件检索数据时,InnoDB才会使用行级锁,否则会使用表级锁(索引失效,行锁变表锁) 2. 即使是访问不同行的记录,如果使用的是相同的索引键,会发生锁冲突 3. 如果数据表建有多个索引时,可以通过不同的索引锁定不同的行 Copy after login 如何排查锁? 5.1 表锁 查看表锁情况show open tables; Copy after login
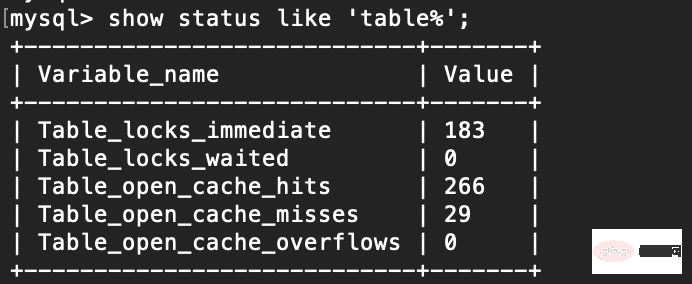
表锁分析show status like 'table%'; Copy after login
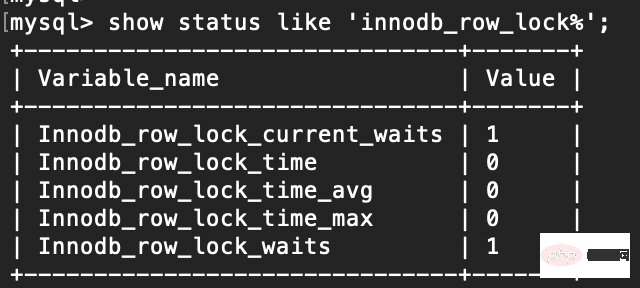
1. table_locks_waited 出现表级锁定争用而发生等待的次数(不能立即获取锁的次数,每等待一次值加1),此值高说明存在着较严重的表级锁争用情况 2. table_locks_immediate 产生表级锁定次数,不是可以立即获取锁的查询次数,每立即获取锁加1 Copy after login 5.2 行锁 行锁分析 show status like 'innodb_row_lock%'; Copy after login
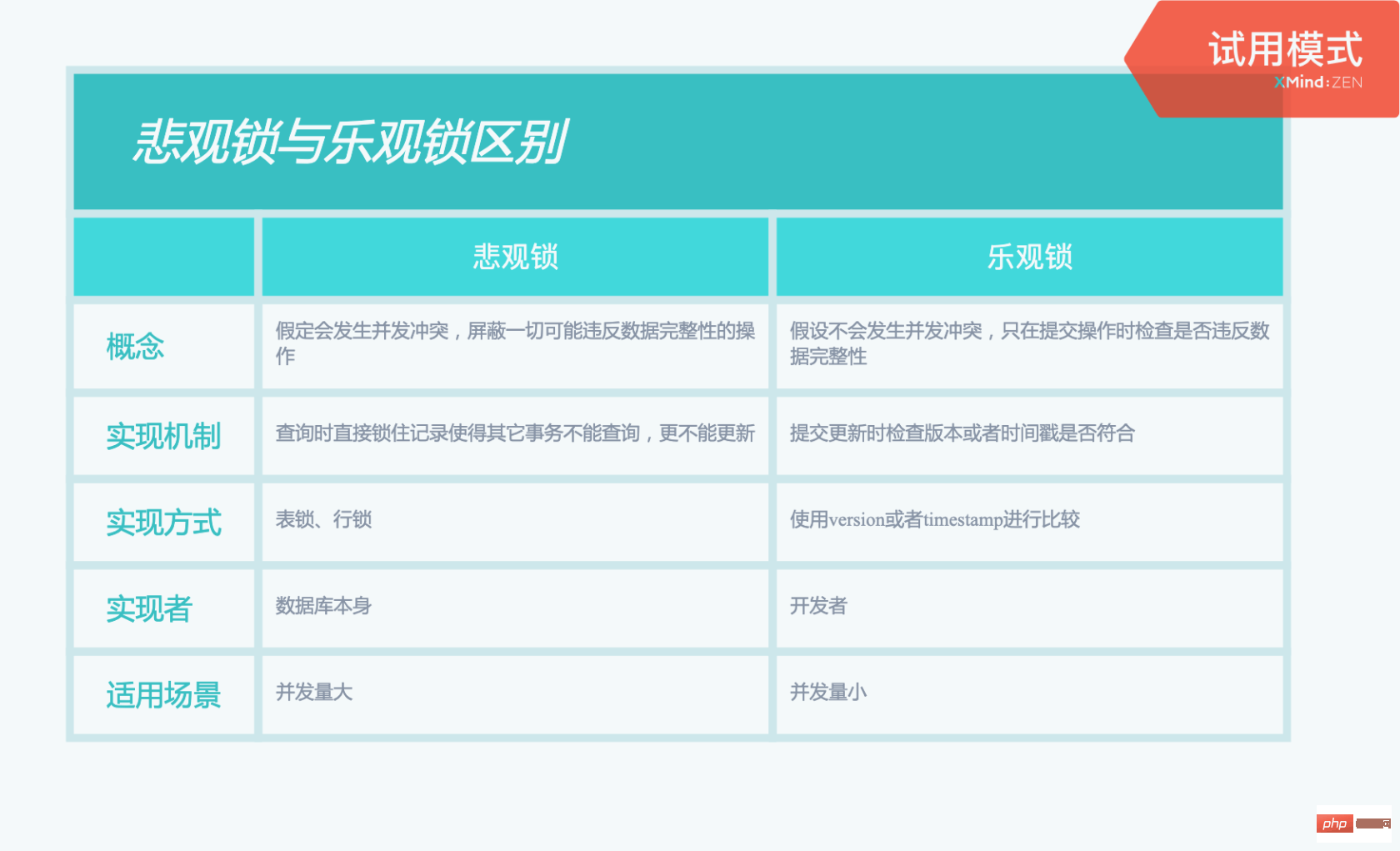
1. innodb_row_lock_current_waits //当前正在等待锁定的数量 2. innodb_row_lock_time //从系统启动到现在锁定总时间长度 3. innodb_row_lock_time_avg //每次等待所花平均时间 4. innodb_row_lock_time_max //从系统启动到现在等待最长的一次所花时间 5. innodb_row_lock_waits //系统启动后到现在总共等待的次数 Copy after login information_schema库1. innodb_lock_waits表 2. innodb_locks表 3. innodb_trx表 Copy after login 优化建议1. 尽可能让所有数据检索都通过索引来完成,避免无索引行锁升级为表锁 2. 合理设计索引,尽量缩小锁的范围 3. 尽可能较少检索条件,避免间隙锁 4. 尽量控制事务大小,减少锁定资源量和时间长度 5. 尽可能低级别事务隔离 Copy after login 死锁 6.1 解释 指两个或者多个事务在同一资源上相互占用,并请求锁定对方占用的资源,从而导致恶性循环的现象 Copy after login 6.2 产生的条件 1. 互斥条件:一个资源每次只能被一个进程使用 2. 请求与保持条件:一个进程因请求资源而阻塞时,对已获得的资源保持不放 3. 不剥夺条件:进程已获得的资源,在没有使用完之前,不能强行剥夺 4. 循环等待条件:多个进程之间形成的一种互相循环等待的资源的关系 Copy after login 6.1 解决 1. 查看死锁:show engine innodb status \G 2. 自动检测机制,超时自动回滚代价较小的事务(innodb_lock_wait_timeout 默认50s) 3. 人为解决,kill阻塞进程(show processlist) 4. wait for graph 等待图(主动检测) Copy after login 6.1 如何避免 1. 加锁顺序一致,尽可能一次性锁定所需的数据行 2. 尽量基于primary(主键)或unique key更新数据 3. 单次操作数据量不宜过多,涉及表尽量少 4. 减少表上索引,减少锁定资源 5. 尽量使用较低的隔离级别 6. 尽量使用相同条件访问数据,这样可以避免间隙锁对并发的插入影响 7. 精心设计索引,尽量使用索引访问数据 8. 借助相关工具:pt-deadlock-logger Copy after login 乐观锁与悲观锁
7.1 悲观锁 解释假定会发生并发冲突,屏蔽一切可能违反数据完整性的操作 Copy after login 实现机制表锁、行锁等 Copy after login 实现层面数据库本身 Copy after login 适用场景并发量大 Copy after login 7.2 乐观锁 解释假设不会发生并发冲突,只在提交操作时检查是否违反数据完整性 Copy after login 实现机制提交更新时检查版本号或者时间戳是否符合 Copy after login 实现层面业务代码 Copy after login 适用场景并发量小 Copy after login
|
The above is the detailed content of Let's thoroughly understand the locking mechanism of MySQL together. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1382
1382
 52
52
 MySQL: Simple Concepts for Easy Learning
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:29 AM
MySQL: Simple Concepts for Easy Learning
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:29 AM
MySQL is an open source relational database management system. 1) Create database and tables: Use the CREATEDATABASE and CREATETABLE commands. 2) Basic operations: INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE and SELECT. 3) Advanced operations: JOIN, subquery and transaction processing. 4) Debugging skills: Check syntax, data type and permissions. 5) Optimization suggestions: Use indexes, avoid SELECT* and use transactions.
 How to open phpmyadmin
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:51 PM
How to open phpmyadmin
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:51 PM
You can open phpMyAdmin through the following steps: 1. Log in to the website control panel; 2. Find and click the phpMyAdmin icon; 3. Enter MySQL credentials; 4. Click "Login".
 MySQL: An Introduction to the World's Most Popular Database
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:18 AM
MySQL: An Introduction to the World's Most Popular Database
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:18 AM
MySQL is an open source relational database management system, mainly used to store and retrieve data quickly and reliably. Its working principle includes client requests, query resolution, execution of queries and return results. Examples of usage include creating tables, inserting and querying data, and advanced features such as JOIN operations. Common errors involve SQL syntax, data types, and permissions, and optimization suggestions include the use of indexes, optimized queries, and partitioning of tables.
 Why Use MySQL? Benefits and Advantages
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:17 AM
Why Use MySQL? Benefits and Advantages
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:17 AM
MySQL is chosen for its performance, reliability, ease of use, and community support. 1.MySQL provides efficient data storage and retrieval functions, supporting multiple data types and advanced query operations. 2. Adopt client-server architecture and multiple storage engines to support transaction and query optimization. 3. Easy to use, supports a variety of operating systems and programming languages. 4. Have strong community support and provide rich resources and solutions.
 How to use single threaded redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:12 PM
How to use single threaded redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:12 PM
Redis uses a single threaded architecture to provide high performance, simplicity, and consistency. It utilizes I/O multiplexing, event loops, non-blocking I/O, and shared memory to improve concurrency, but with limitations of concurrency limitations, single point of failure, and unsuitable for write-intensive workloads.
 MySQL and SQL: Essential Skills for Developers
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:30 AM
MySQL and SQL: Essential Skills for Developers
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:30 AM
MySQL and SQL are essential skills for developers. 1.MySQL is an open source relational database management system, and SQL is the standard language used to manage and operate databases. 2.MySQL supports multiple storage engines through efficient data storage and retrieval functions, and SQL completes complex data operations through simple statements. 3. Examples of usage include basic queries and advanced queries, such as filtering and sorting by condition. 4. Common errors include syntax errors and performance issues, which can be optimized by checking SQL statements and using EXPLAIN commands. 5. Performance optimization techniques include using indexes, avoiding full table scanning, optimizing JOIN operations and improving code readability.
 MySQL's Place: Databases and Programming
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:18 AM
MySQL's Place: Databases and Programming
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:18 AM
MySQL's position in databases and programming is very important. It is an open source relational database management system that is widely used in various application scenarios. 1) MySQL provides efficient data storage, organization and retrieval functions, supporting Web, mobile and enterprise-level systems. 2) It uses a client-server architecture, supports multiple storage engines and index optimization. 3) Basic usages include creating tables and inserting data, and advanced usages involve multi-table JOINs and complex queries. 4) Frequently asked questions such as SQL syntax errors and performance issues can be debugged through the EXPLAIN command and slow query log. 5) Performance optimization methods include rational use of indexes, optimized query and use of caches. Best practices include using transactions and PreparedStatemen
 How to recover data after SQL deletes rows
Apr 09, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
How to recover data after SQL deletes rows
Apr 09, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
Recovering deleted rows directly from the database is usually impossible unless there is a backup or transaction rollback mechanism. Key point: Transaction rollback: Execute ROLLBACK before the transaction is committed to recover data. Backup: Regular backup of the database can be used to quickly restore data. Database snapshot: You can create a read-only copy of the database and restore the data after the data is deleted accidentally. Use DELETE statement with caution: Check the conditions carefully to avoid accidentally deleting data. Use the WHERE clause: explicitly specify the data to be deleted. Use the test environment: Test before performing a DELETE operation.