40 Redis interview questions you can't miss (including answers and mind maps)
This article shares 40 Redis interview questions with you, including answer analysis and Redis knowledge point mind maps. It has certain reference value. Friends in need can refer to it. I hope it will be helpful to everyone.

Redis Interview Questions
#1. What is Redis?
Redis is Completely open source and free, complying with the BSD protocol, it is a high-performance key-value database.
Redis and other key-value caching products have the following three characteristics:
(1) Redis supports data persistence and can save the data in the memory to the disk when restarting Can be loaded again for use.
(2) Redis not only supports simple key-value type data, but also provides storage of data structures such as list, set, zset, and hash.
(3) Redis supports data backup, that is, data backup in master-slave mode.
[Related recommendations: Redis video tutorial]
Redis advantages
(1) Extremely high performance – Redis can read 110,000 times/ s, the writing speed is 81000 times/s.
(2) Rich data types – Redis supports Strings, Lists, Hashes, Sets and Ordered Sets data type operations for binary cases.
(3) Atomic - All operations of Redis are atomic, which means that they will either be executed successfully or not executed at all if they fail. Individual operations are atomic. Multiple operations also support transactions, that is, atomicity, wrapped by the MULTI and EXEC instructions.
(4) Rich features – Redis also supports publish/subscribe, notifications, key expiration and other features.
How is Redis different from other key-value stores?
(1) Redis has more complex data structures and provides atomic operations on them. This is an evolutionary path different from other databases. Redis's data types are based on basic data structures and are transparent to programmers, without the need for additional abstractions.
(2) Redis runs in memory but can be persisted to disk, so memory needs to be weighed when performing high-speed reading and writing of different data sets, because the amount of data cannot be larger than the hardware memory. Another advantage of in-memory databases is that compared to the same complex data structures on disk, operating in memory is very simple, so Redis can do a lot of things with strong internal complexity. Also, in terms of disk format they are compact append-generated since they do not require random access.
2. Redis data type?
Answer: Redis supports five data types: string (string), hash (hash), list (list), set (set) and zsetsorted set: ordered set).
The most commonly used ones in our actual projects are string and hash. If you are an advanced Redis user, you also need to add the following data structures: HyperLogLog, Geo, and Pub/Sub.
If you say that you have played with Redis Module, such as BloomFilter, RedisSearch, and Redis-ML, the interviewer's eyes will start to shine.
3. What are the benefits of using Redis?
(1) It is fast because the data is stored in the memory, similar to HashMap. The advantage of HashMap is that the time complexity of search and operation is both O1)
(2) Support Rich data types, supporting string, list, set, Zset, hash, etc.
(3) Support transactions, operations are atomic. The so-called atomicity means that all changes to the data are either executed or not executed at all.
(4) Rich features: can be used for caching, messages, set expiration time by key, and will be automatically deleted after expiration
4. What are the advantages of Redis compared to Memcached?
(1) All values in Memcached are simple strings, and redis, as its replacement, supports richer data types
(2) Redis is faster than Memcached Very quickly
(3) Redis can persist its data
5. What are the differences between Memcache and Redis?
(1) Storage method Memecache stores all data in the memory. It will hang up after a power outage. The data cannot exceed the memory size. Redis is partially stored on the hard disk, which ensures data persistence.
(2) Data support type Memcache has relatively simple support for data types. Redis has complex data types.
(3) The underlying models used are different. The underlying implementation methods and application protocols for communication with clients are different. Redis directly builds its own VM mechanism, because if the general system calls system functions, it will waste a certain amount of time to move and request.
6. Is Redis single-process and single-threaded?
Answer: Redis is a single process and single thread. Redis uses queue technology to turn concurrent access into serial access, eliminating the overhead of traditional database serial control.
7. What is the maximum capacity that a string type value can store?
Answer: 512M

8. What is the persistence mechanism of Redis? What are the advantages and disadvantages of each?
Redis provides two persistence mechanisms, RDB and AOF mechanisms:
1. RDBRedis DataBase) persistence method:
refers to the method of using data set snapshots Semi-persistent mode) records all key-value pairs of the redis database and writes the data to a temporary file at a certain point in time. After persistence is completed, this temporary file is used to replace the last persisted file to achieve data recovery.
Advantages:
(1) There is only one file dump.rdb, which is convenient for persistence.
(2) Disaster tolerance is good, a file can be saved to a safe disk.
(3) To maximize performance, fork the child process to complete the write operation and let the main process continue to process the command, so IO is maximized. Use a separate sub-process for persistence, and the main process will not perform any IO operations, ensuring the high performance of redis)
(4) When the data set is large, the startup efficiency is higher than AOF.
Disadvantages:
Low data security. RDB is persisted at intervals. If redis fails between persistence, data loss will occur. Therefore, this method is more suitable when the data requirements are not strict.
2. AOFAppend-only file) persistence method:
means that all command line records are completely in the format of the redis command request protocol. Persistent storage) is saved as an aof file.
Advantages:
(1) Data security, aof persistence can be configured with the appendfsync attribute, with always, each command operation is recorded to the aof file.
(2) Write files through append mode. Even if the server goes down in the middle, you can use the redis-check-aof tool to solve the data consistency problem.
(3) Rewrite mode of AOF mechanism. Before the AOF file is rewritten (commands will be merged and rewritten when the file is too large), you can delete some of the commands (such as flushall by mistake))
Disadvantages:
( 1) AOF files are larger than RDB files and the recovery speed is slow.
(2) When the data set is large, the startup efficiency is lower than rdb.
9. Redis common performance problems and solutions:
(1) Master is best not to write memory snapshots. If Master writes memory snapshots, the save command schedules the rdbSave function. , will block the work of the main thread. When the snapshot is relatively large, the impact on performance will be very large, and the service will be suspended intermittently
(2) If the data is important, a Slave will enable AOF backup data, policy settings Synchronize one
per second (3) For the speed of master-slave replication and the stability of the connection, it is best for the Master and Slave to be on the same LAN
(4) Try to avoid being under great pressure Add slave
to the master library (5) Do not use a graph structure for master-slave replication. It is more stable to use a one-way linked list structure, that is: Master <- Slave1<- Slave2 <- Slave3... like this The structure facilitates solving the single point of failure problem and realizing the replacement of the Master by the Slave. If the Master hangs up, you can immediately enable Slave1 as the Master, leaving everything else unchanged.
10. What is the deletion strategy for redis expired keys?
(1) Scheduled deletion: While setting the expiration time of the key, create a timer (timer). Let the timer immediately perform the deletion of the key when the expiration time of the key comes.
(2) Lazy deletion: Let the key expire, but every time you get the key from the key space, check whether the obtained key has expired. If it has expired, delete the key; if it has not expired, just delete it. Return this key.
(3) Periodic deletion: Every once in a while, the program checks the database and deletes the expired keys. It's up to the algorithm to decide how many expired keys to delete and how many databases to check.
11. Redis recycling strategy (elimination strategy)?
volatile-lru: From the data set with expiration time set (server.db[i].expires ) to select the least recently used data for elimination
volatile-ttl: select the data that will expire from the data set (server.db[i].expires) with an expiration time set for elimination
volatile-random: Randomly select data for elimination from the data set (server.db[i].expires) with an expiration time set
allkeys-lru: From the data set (server.db[i].dict) Select the least recently used data for elimination
allkeys-random: Select any data from the data set (server.db[i].dict) for elimination
no-enviction (eviction): Forbidden Evicting data
Pay attention to the 6 mechanisms here. Volatile and allkeys specify whether to evict data from the data set with an expiration time or from all data sets. The following lru, ttl and random are three different elimination strategy, plus a no-enviction strategy of never recycling.
Use policy rules:
(1) If the data shows a power law distribution, that is, some data have high access frequency and some data have low access frequency, use allkeys-lru
(2) If the data is equally distributed, that is, all data access frequencies are the same, use allkeys-random
12. Why does edis need to put all data into memory?
Answer: In order to achieve the fastest reading and writing speed, Redis reads all the data into the memory and writes the data to the disk asynchronously. So redis has the characteristics of fast speed and data persistence. If the data is not placed in memory, disk I/O speed will seriously affect the performance of redis. Today, when memory is getting cheaper and cheaper, redis will become more and more popular. If the maximum memory used is set, new values cannot be inserted after the number of existing data records reaches the memory limit.
13. Do you understand the synchronization mechanism of Redis?
Answer: Redis can use master-slave synchronization and slave-slave synchronization. During the first synchronization, the primary node performs a bgsave and records subsequent modification operations to the memory buffer. After completion, the entire rdb file will be synchronized to the replica node. After the replica node accepts the data, it will load the rdb image into the memory. After the loading is completed, the master node is notified to synchronize the operation records modified during the period to the replica node for replay, and the synchronization process is completed.
14. What are the benefits of Pipeline? Why use pipeline?
Answer: The time of multiple IO round-trips can be reduced to one, provided there is no causal correlation between instructions executed by the pipeline. When using redis-benchmark for stress testing, it can be found that an important factor affecting the QPS peak value of redis is the number of pipeline batch instructions.
15. Have you ever used Redis cluster? What is the principle of clustering?
(1) Redis Sentinal focuses on high availability. When the master goes down, it will automatically promote the slave to the master and continue to provide services.
(2) Redis Cluster focuses on scalability. When a single redis memory is insufficient, Cluster is used for shard storage.
16. Under what circumstances will the Redis cluster solution cause the entire cluster to be unavailable?
Answer: In a cluster with three nodes A, B, and C, without a replication model, if node B fails, the entire cluster will think that the range of 5501-11000 is missing. slot is not available.
17. What are the Java clients supported by Redis? Which one is officially recommended?
Answer: Redisson, Jedis, lettuce, etc., the official recommendation is to use Redisson.
18. What are the advantages and disadvantages of Jedis and Redisson?
Answer: Jedis is the client of the Java implementation of Redis, and its API provides relatively comprehensive support for Redis commands; Redisson implements distributed and scalable Java data structures, compared with Jedis , the function is relatively simple, does not support string operations, and does not support Redis features such as sorting, transactions, pipelines, and partitions.
The purpose of Redisson is to promote the separation of users' concerns from Redis, so that users can focus more on processing business logic.
19. How to set password and verify password in Redis?
Set password: config set requirepass 123456
Authorization password: auth 123456
20. Talk about the concept of Redis hash slot?
Answer: The Redis cluster does not use consistent hashing, but introduces the concept of hash slots. The Redis cluster has 16384 hash slots. Each key is checked modulo 16384 after passing CRC16 verification. To decide which slot to place, each node in the cluster is responsible for a portion of the hash slot.

#21. What is the master-slave replication model of Redis cluster?
Answer: In order to make the cluster still available when some nodes fail or most nodes cannot communicate, the cluster uses a master-slave replication model, and each node will have N-1 replicas. .
22. Will write operations be lost in the Redis cluster? Why?
Answer: Redis does not guarantee strong consistency of data, which means that in practice, the cluster may lose write operations under certain conditions.
23. How are Redis clusters replicated?
Answer: Asynchronous replication
24. What is the maximum number of nodes in a Redis cluster?
Answer: 16384.
25. How to choose a database for Redis cluster?
Answer: The Redis cluster cannot currently select a database, and the default is database 0.
26. How to test the connectivity of Redis?
Answer: Use the ping command.
27. How to understand Redis transactions?
Answer:
(1) A transaction is a separate isolation operation: all commands in the transaction will be serialized and executed in order. During the execution of the transaction, it will not be interrupted by command requests sent by other clients.
(2) A transaction is an atomic operation: either all commands in the transaction are executed, or none of them are executed.
28. What are the commands related to Redis transactions?
Answer: MULTI, EXEC, DISCARD, WATCH
29. How to set the expiration time and permanent validity of Redis key respectively?
Answer: EXPIRE and PERSIST commands.
30. How does Redis optimize memory?
Answer: Use hash tables (hashes) as much as possible. Hash tables (meaning that the number stored in the hash table is small) use very small memory, so you should try your best to convert your data model into Abstracted into a hash table. For example, if there is a user object in your web system, do not set a separate key for the user's name, surname, email, and password. Instead, store all the user's information in a hash table.
31. How does the Redis recycling process work?
Answer: A client ran a new command and added new data. Redi checks the memory usage. If it is greater than the maxmemory limit, it will be recycled according to the set policy. A new command is executed, etc. So we are constantly crossing the boundary of the memory limit by constantly reaching the boundary and then constantly recycling back below the boundary. If the result of a command results in a large amount of memory being used (such as saving the intersection of a large set to a new key), it won't take long for the memory limit to be exceeded by this memory usage.
32. What are some ways to reduce the memory usage of Redis?
Answer: If you are using a 32-bit Redis instance, you can make good use of collection type data such as Hash, list, sorted set, set, etc., because usually many small Key-Values can be used More compact way to store together.
33. What happens when Redis runs out of memory?
Answer: If the set upper limit is reached, the Redis write command will return an error message (but the read command can still return normally.) Or you can use Redis as a cache to use the configuration elimination mechanism. When Redis Old content will be flushed when the memory limit is reached.
34. How many keys can a Redis instance store at most? List, Set, Sorted Set How many elements can they store at most?
Answer: In theory, Redis can handle up to 232 keys, and in actual tests, each instance stored at least 250 million keys. We are testing some larger values. Any list, set, and sorted set can hold 232 elements. In other words, the storage limit of Redis is the amount of memory available in the system.
35. There are 20 million data in MySQL, but only 20 million data are stored in redis. How to ensure that the data in redis are hot data?
Answer: When the size of the Redis memory data set increases to a certain size, the data elimination strategy will be implemented.
Related knowledge: Redis provides 6 data elimination strategies:
volatile-lru: Select the least recently used data set (server.db[i].expires) with an expiration time set Data elimination
volatile-ttl: Select the data that will expire from the data set (server.db[i].expires) that has set expiration time.
volatile-random: From the data set that has set expiration time Select any data from the data set (server.db[i].expires) with expiration time to eliminate
allkeys-lru: Select the least recently used data from the data set (server.db[i].dict) Data elimination
allkeys-random: Randomly select data elimination from the data set (server.db[i].dict)
no-enviction (eviction): prohibit eviction of data
36. What is the most suitable scenario for Redis?
1. Session Cache
One of the most commonly used scenarios for using Redis is session cache. The advantage of caching sessions with Redis over other stores such as Memcached is that Redis provides persistence. When maintaining a cache that does not strictly require consistency, most people would be unhappy if all the user's shopping cart information was lost. Now, would they still be? Fortunately, as Redis has improved over the years, it's easy to figure out how to properly use Redis to cache session documents. Even the well-known commercial platform Magento provides a plug-in for Redis.
2. Full Page Cache (FPC)
In addition to basic session tokens, Redis also provides a very simple FPC platform. Back to the consistency issue, even if the Redis instance is restarted, users will not see a drop in page loading speed because of disk persistence. This is a great improvement, similar to PHP local FPC. Taking Magento as an example again, Magento provides a plugin to use Redis as a full page cache backend. In addition, for WordPress users, Pantheon has a very good plug-in wp-redis, which can help you load the pages you have browsed as quickly as possible.
3. Queue
One of the great advantages of Redis in the field of memory storage engines is that it provides list and set operations, which allows Redis to be used as a good message queue platform. The operations used by Redis as a queue are similar to the push/pop operations of local programming languages (such as Python) on lists. If you quickly search "Redis queues" in Google, you will immediately find a large number of open source projects. The purpose of these projects is to use Redis to create very good back-end tools to meet various queue needs. For example, Celery has a backend that uses Redis as a broker. You can view it from here.
4, Ranking/Counter
Redis implements the operation of incrementing or decrementing numbers in memory very well. Sets and Sorted Sets also make it very simple for us to perform these operations. Redis just provides these two data structures. So, to get the top 10 users from the sorted set – let’s call them “user_scores”, we just do it like this: Of course, this assumes you’re doing it based on your user’s scores Increasing sorting. If you want to return the user and the user's score, you need to execute it like this: ZRANGE user_scores 0 10 WITHSCORES Agora Games is a good example, implemented in Ruby, and its rankings use Redis to store data, you can here See.
5. Publish/Subscribe
Last (but certainly not least) is the publish/subscribe function of Redis. There are indeed many use cases for publish/subscribe. I've seen people use it in social network connections, as triggers for publish/subscribe based scripts, and even to build chat systems using Redis' publish/subscribe functionality!

37. If there are 100 million keys in Redis, 100,000 of them start with a fixed, known prefix. If they are Find them all?
Answer: Use the keys command to scan out the key list of the specified mode.
The other party then asked: If this redis is providing services to online businesses, what are the problems with using the keys command?
At this time you have to answer one of the key features of redis: redis's single-threading. The keys instruction will cause the thread to block for a period of time, and the online service will pause. The service cannot be restored until the instruction is executed. At this time, you can use the scan command. The scan command can extract the key list of the specified mode without blocking, but there will be a certain probability of duplication. Just do it once on the client, but the overall time spent will be longer than using it directly. keys command length.
38. If there are a large number of keys that need to be set to expire at the same time, what should you generally pay attention to?
Answer: If the expiration time of a large number of keys is set too concentratedly, redis may experience a brief lag at the time of expiration. Generally, a random value needs to be added to the time to make the expiration time spread out.
39. Have you ever used Redis as an asynchronous queue? How did you use it?
Answer: Generally, the list structure is used as the queue, rpush produces messages, and lpop consumes messages. When there is no message from lpop, sleep for a while and try again. What if the other party asks if sleep can be used? There is also a command called blpop in list. When there is no message, it will block until the message arrives. What if the other party asks if it can be produced once and consumed multiple times? Using the pub/sub topic subscriber model, a 1:N message queue can be implemented.
If the other party asks what are the disadvantages of pub/sub?
When the consumer goes offline, the produced messages will be lost, so you must use a professional message queue such as RabbitMQ.
If the other party asks how redis implements a delay queue?
I guess now you want to beat the interviewer to death. If you have a baseball bat in your hand, why do you ask such detailed questions? But you were very restrained, and then answered calmly: Use sortedset, use the timestamp as the score, the message content as the key, call zadd to produce the message, and the consumer uses the zrangebyscore instruction to obtain the data polling N seconds ago for processing. At this point, the interviewer has secretly given you a thumbs up. But what he didn’t know was that you were raising your middle finger behind the chair at this moment.
40. Have you ever used Redis distributed lock? What is it?
First use setnx to grab the lock. After grabbing it, use expire to add an expiration time to the lock to prevent the lock from forgetting to release.
At this time, the other party will tell you that your answer is good, and then ask what will happen if the process crashes unexpectedly or needs to be restarted for maintenance before executing expire after setnx? At this time you have to give surprising feedback: Oh, yes, this lock will never be released. Then you need to scratch your head, pretend to think for a moment, as if the next result is your own initiative, and then answer: I remember that the set command has very complicated parameters. This should be able to set setnx and expire at the same time. Combined into one instruction to use! At this time, the other party will smile and start to say silently in his heart: Press, this guy is not bad.
About the knowledge points summarized into a mind map
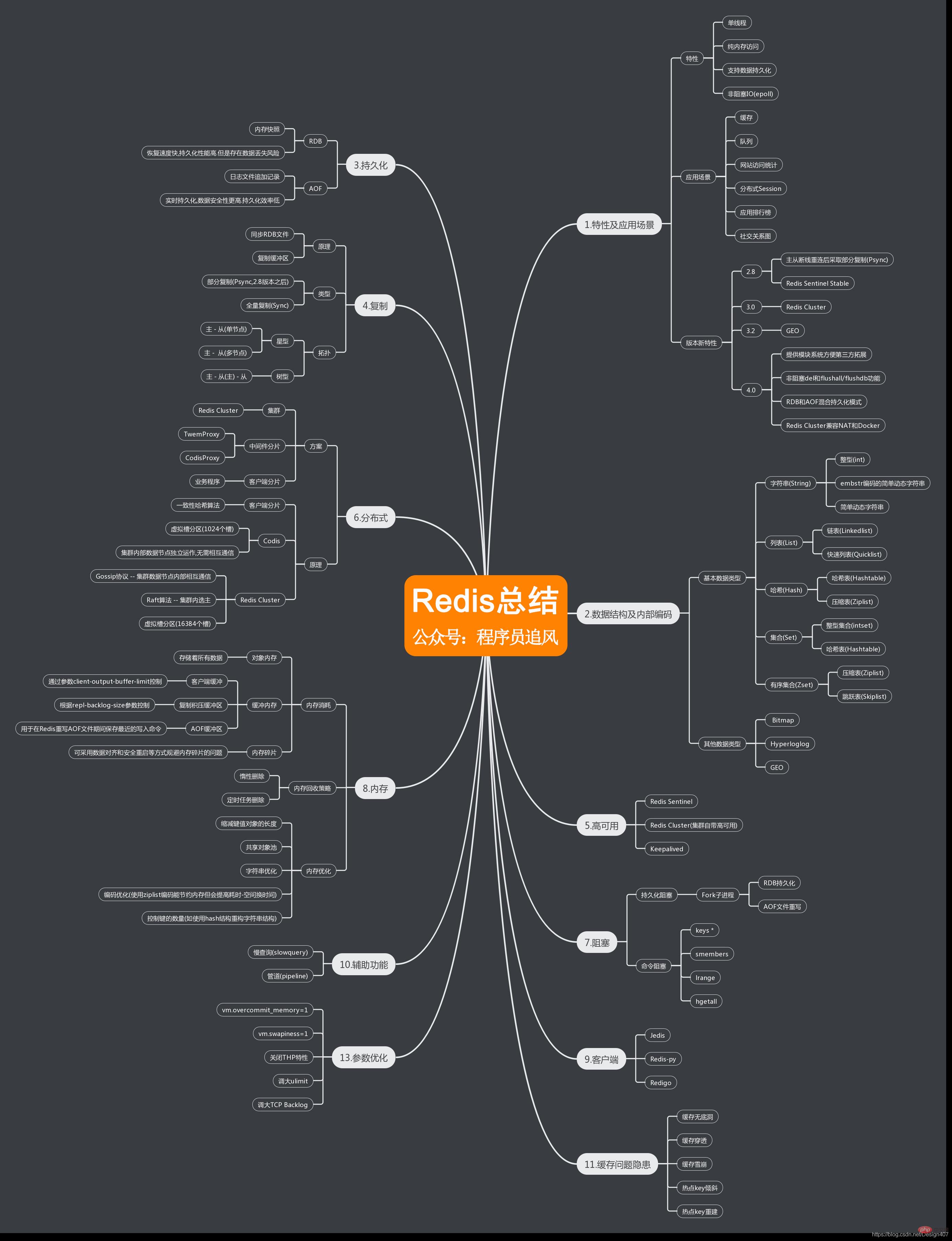
For more programming-related knowledge, please visit: Introduction to Programming! !
The above is the detailed content of 40 Redis interview questions you can't miss (including answers and mind maps). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1382
1382
 52
52
 How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
Redis cluster mode deploys Redis instances to multiple servers through sharding, improving scalability and availability. The construction steps are as follows: Create odd Redis instances with different ports; Create 3 sentinel instances, monitor Redis instances and failover; configure sentinel configuration files, add monitoring Redis instance information and failover settings; configure Redis instance configuration files, enable cluster mode and specify the cluster information file path; create nodes.conf file, containing information of each Redis instance; start the cluster, execute the create command to create a cluster and specify the number of replicas; log in to the cluster to execute the CLUSTER INFO command to verify the cluster status; make
 How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear Redis data: Use the FLUSHALL command to clear all key values. Use the FLUSHDB command to clear the key value of the currently selected database. Use SELECT to switch databases, and then use FLUSHDB to clear multiple databases. Use the DEL command to delete a specific key. Use the redis-cli tool to clear the data.
 How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
Using the Redis directive requires the following steps: Open the Redis client. Enter the command (verb key value). Provides the required parameters (varies from instruction to instruction). Press Enter to execute the command. Redis returns a response indicating the result of the operation (usually OK or -ERR).
 How to use redis lock
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
How to use redis lock
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
Using Redis to lock operations requires obtaining the lock through the SETNX command, and then using the EXPIRE command to set the expiration time. The specific steps are: (1) Use the SETNX command to try to set a key-value pair; (2) Use the EXPIRE command to set the expiration time for the lock; (3) Use the DEL command to delete the lock when the lock is no longer needed.
 How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
To read a queue from Redis, you need to get the queue name, read the elements using the LPOP command, and process the empty queue. The specific steps are as follows: Get the queue name: name it with the prefix of "queue:" such as "queue:my-queue". Use the LPOP command: Eject the element from the head of the queue and return its value, such as LPOP queue:my-queue. Processing empty queues: If the queue is empty, LPOP returns nil, and you can check whether the queue exists before reading the element.
 How to use single threaded redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:12 PM
How to use single threaded redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:12 PM
Redis uses a single threaded architecture to provide high performance, simplicity, and consistency. It utilizes I/O multiplexing, event loops, non-blocking I/O, and shared memory to improve concurrency, but with limitations of concurrency limitations, single point of failure, and unsuitable for write-intensive workloads.
 How to implement the underlying redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:21 PM
How to implement the underlying redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:21 PM
Redis uses hash tables to store data and supports data structures such as strings, lists, hash tables, collections and ordered collections. Redis persists data through snapshots (RDB) and append write-only (AOF) mechanisms. Redis uses master-slave replication to improve data availability. Redis uses a single-threaded event loop to handle connections and commands to ensure data atomicity and consistency. Redis sets the expiration time for the key and uses the lazy delete mechanism to delete the expiration key.
 How to read the source code of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
How to read the source code of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
The best way to understand Redis source code is to go step by step: get familiar with the basics of Redis. Select a specific module or function as the starting point. Start with the entry point of the module or function and view the code line by line. View the code through the function call chain. Be familiar with the underlying data structures used by Redis. Identify the algorithm used by Redis.




