What is the time complexity of bubble sort, quick sort and heap sort?
The time complexity of bubble sorting: the best case is "O(n)", the worst case is "O(n2)". The time complexity of quick sort: the best case is "O(nlogn)", the worst case is "O(n2)". The time complexity of heap sort is "O(nlogn)".

The operating environment of this tutorial: Windows 7 system, Dell G3 computer.
Bubble Sort
Time complexity
Best case: the array itself is sequential , the outer loop traversal is completed once O(n)
Worst case scenario: the array itself is in reverse order, and the inner and outer loop traverses O(n2)
Space complexity
Create a space exchange sequenceO(1)
StabilityStable, because the if judgment is not established, the order will not be exchanged, and the same elements will not be exchanged
Bubble sorting is the simplest of all sorting algorithms. However, from a running time perspective, bubble sort is the worst one, with its complexity being O(n2).
Bubble sort compares any two adjacent items and swaps them if the first is greater than the second. The elements are moved up into the correct order as if bubbles were rising to the surface, hence the name bubble sort.
When exchanging, we use an intermediate value to store the value of a certain exchange item. Other sorting methods will also use this method, so we declare a method to place this exchange code for reuse. Using ES6 (ECMAScript 2015) ** enhanced object properties - destructuring assignment syntax of object arrays, ** this function can be written as follows:
[array[index1], array[index2]] = [array[index2], array[index1]];
Specific implementation:
function bubbleSort(arr) {
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {//外循环(行{2})会从数组的第一位迭代 至最后一位,它控制了在数组中经过多少轮排序
for (let j = 0; j < arr.length - i; j++) {//内循环将从第一位迭代至length - i位,因为后i位已经是排好序的,不用重新迭代
if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1]) {//如果前一位大于后一位
[arr[j], arr[j + 1]] = [arr[j + 1], arr[j]];//交换位置
}
}
}
return arr;
}Quick sort
Time complexity
Best case scenario: Each base value divides the entire array equally, O(nlogn)
Worst case scenario: Each base value is the maximum/minimum value in the array, O(n2)
Space complexity
Quick sort It is recursive and requires the use of a stack to save the call information of each level of recursion, so the space complexity is consistent with the depth of the recursion tree
Best case scenario: Each base value just divides the entire array equally, the depth of the recursion treeO(logn)
Worst case: every base value is the maximum/minimum value in the array, the depth of the recursion treeO(n)
Stability
Quick sort is unstable because the same keywords may be exchanged.
Quick sort is recursive,
Special case: left>right, exit directly.
Steps:
(1) First, select the middle item from the array as the pivotbase, usually the first value .
(2) Create two pointers, the left one points to the first item of the array, and the right one points to the last item of the array. Move the right pointer until we find an element that is smaller than the pivot , then, move the left pointer until we find an element that is larger than the pivot, then swap them , repeat this process until the left pointer meets the right pointer. This process will cause values smaller than the pivot to be sorted before the pivot, and values larger than the pivot to be sorted after the pivot. This step is called Dividing operation.
(3) Then exchange the pivot element and the element at the position where the pointer stops (which is equivalent to returning the element to its original position . The element to the left of this element is smaller than the element
Small, the ones on the right are bigger than him, and this position is his final position)(4) Then, the algorithm divides the small array (a subarray composed of values smaller than the pivot element, and a subarray composed of values smaller than the pivot element) subarray composed of Yuanda values) repeat the previous two steps (recursive method
),The recursive exit is left/right=i
left>i-1 / i+1>right
Homing diagram: 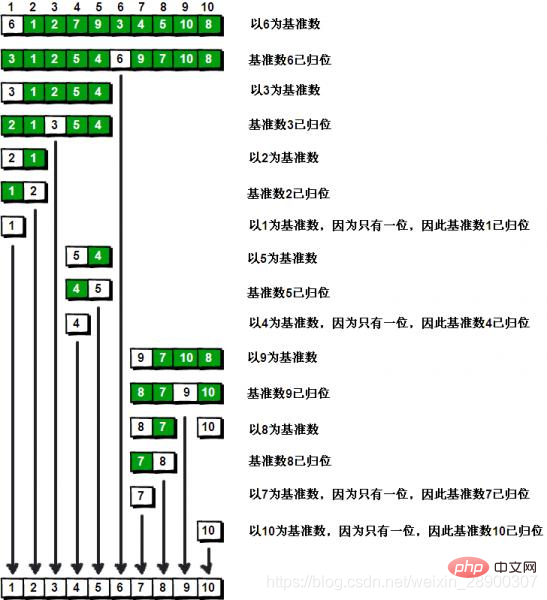
function quicksort(arr, left, right) {
if (left > right) {
return;
}
var i = left,
j = right,
base = arr[left]; //基准总是取序列开头的元素
// var [base, i, j] = [arr[left], left, right]; //以left指针元素为base
while (i != j) {
//i=j,两个指针相遇时,一次排序完成,跳出循环
// 因为每次大循环里面的操作都会改变i和j的值,所以每次循环/操作前都要判断是否满足i<j
while (i < j && arr[j] >= base) {
//寻找小于base的右指针元素a,跳出循环,否则左移一位
j--;
}
while (i < j && arr[i] <= base) {
//寻找大于base的左指针元素b,跳出循环,否则右移一位
i++;
}
if (i < j) {
[arr[i], arr[j]] = [arr[j], arr[i]]; //交换a和b
}
}
[arr[left], arr[j]] = [arr[j], arr[left]]; //交换相遇位置元素和base,base归位
// let k = i;
quicksort(arr, left, i - 1); //对base左边的元素递归排序
quicksort(arr, i + 1, right); //对base右边的元素递归排序
return arr;
}Heap sort
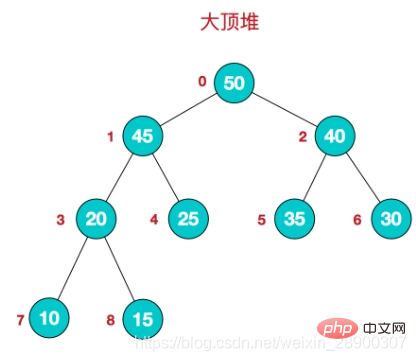
Heap concept###- 堆是一个完全二叉树。
- 完全二叉树: 二叉树除开最后一层,其他层结点数都达到最大,最后一层的所有结点都集中在左边(左边结点排列满的情况下,右边才能缺失结点)。
- 大顶堆:根结点为最大值,每个结点的值大于或等于其孩子结点的值。
- 小顶堆:根结点为最小值,每个结点的值小于或等于其孩子结点的值。
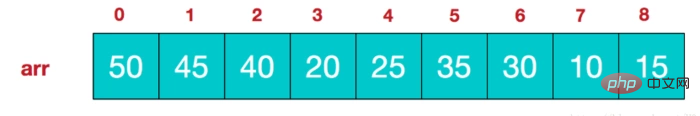
- 堆的存储: 堆由数组来实现,相当于对二叉树做层序遍历。如下图:


时间复杂度
总时间为建堆时间+n次调整堆 —— O(n)+O(nlogn)=O(nlogn)建堆时间:从最后一个非叶子节点遍历到根节点,复杂度为O(n)n次调整堆:每一次调整堆最长的路径是从树的根节点到叶子结点,也就是树的高度logn,所以每一次调整时间复杂度是O(logn),一共是O(nlogn)
空间复杂度
堆排序只需要在交换元素的时候申请一个空间暂存元素,其他操作都是在原数组操作,空间复杂度为O(1)
稳定性
堆排序是不稳定的,因为可能会交换相同的子结点。
步骤一:建堆
- 以升序遍历为例子,需要先将将初始二叉树转换成大顶堆,要求满足:
树中任一非叶子结点大于其左右孩子。 - 实质上是调整数组元素的位置,不断比较,做交换操作。
- 找到第一个非叶子结点——
Math.floor(arr.length / 2 - 1),从后往前依次遍历 - 对每一个结点,检查结点和子结点的大小关系,调整成大根堆
// 建立大顶堆
function buildHeap(arr) {
//从最后一个非叶子节点开始,向前遍历,
for (let i = Math.floor(arr.length / 2 - 1); i >= 0; i--) {
headAdjust(arr, i, arr.length); //对每一个节点都调整堆,使其满足大顶堆规则
}
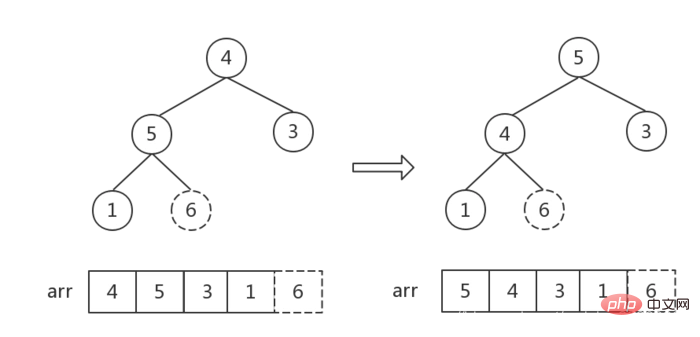
}步骤二:调整指定结点形成大根堆
- 建立
childMax指针指向child最大值节点,初始值为2 * cur + 1,指向左节点 - 当左节点存在时(左节点索引小于数组
length),进入循环,递归调整所有节点位置,直到没有左节点为止(cur指向一个叶结点为止),跳出循环,遍历结束 - 每次循环,先判断右节点存在时,右节点是否大于左节点,是则改变childMax的指向
- 然后判断cur根节点是否大于childMax,
- 大于的话,说明满足大顶堆规律,不需要再调整,跳出循环,结束遍历
- 小于的话,说明不满足大顶堆规律,交换根节点和子结点,
- 因为交换了节点位置,子结点可能会不满足大顶堆顺序,所以还要判断子结点然后,改变
cur和childMax指向子结点,继续循环判断。
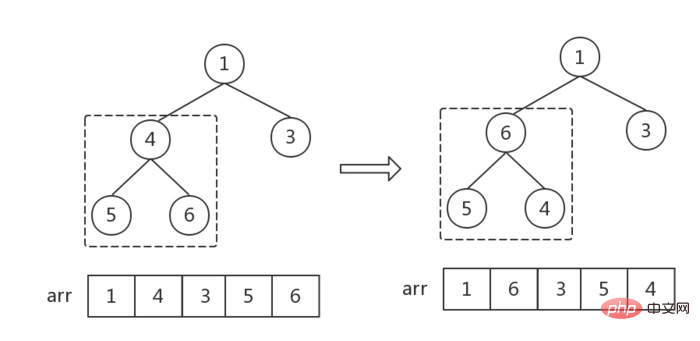
//从输入节点处调整堆
function headAdjust(arr, cur, len) {
let intialCur = arr[cur]; //存放最初始的
let childMax = 2 * cur + 1; //指向子树中较大的位置,初始值为左子树的索引
//子树存在(索引没超过数组长度)而且子树值大于根时,此时不符合大顶堆结构,进入循环,调整堆的结构
while (childMax < len) {
//判断左右子树大小,如果右子树更大,而且右子树存在,childMax指针指向右子树
if (arr[childMax] < arr[childMax + 1] && childMax + 1 < len) childMax++;
//子树值小于根节点,不需要调整,退出循环
if (arr[childMax] < arr[cur]) break;
//子树值大于根节点,需要调整,先交换根节点和子节点
swap(arr, childMax, cur);
cur = childMax; //根节点指针指向子节点,检查子节点是否满足大顶堆规则
childMax = 2 * cur + 1; //子节点指针指向新的子节点
}
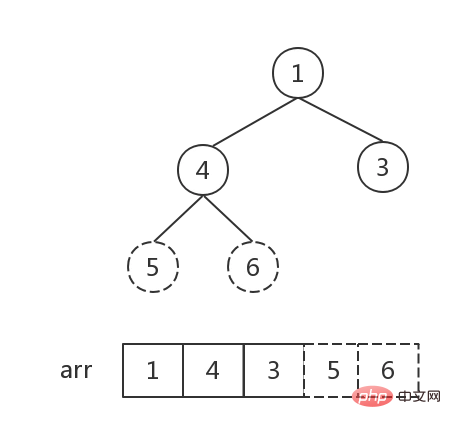
}步骤三:利用堆进行排序
- 从后往前遍历大顶堆(数组),交换堆顶元素
a[0]和当前元素a[i]的位置,将最大值依次放入数组末尾。 - 每交换一次,就要重新调整一下堆,从根节点开始,调整
根节点~i-1个节点(数组长度为i),重新生成大顶堆

// 堆排序
function heapSort(arr) {
if (arr.length <= 1) return arr;
//构建大顶堆
buildHeap(arr);
//从后往前遍历,
for (let i = arr.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
swap(arr, i, 0); //交换最后位置和第一个位置(堆顶最大值)的位置
headAdjust(arr, 0, i); //调整根节点~i-1个节点,重新生成大顶堆
}
return arr;
}完整代码:
// 交换数组元素
function swap(a, i, j) {
[a[i], a[j]] = [a[j], a[i]];
}
//从输入节点处调整堆
function headAdjust(arr, cur, len) {
let intialCur = arr[cur]; //存放最初始的
let childMax = 2 * cur + 1; //指向子树中较大的位置,初始值为左子树的索引
//子树存在(索引没超过数组长度)而且子树值大于根时,此时不符合大顶堆结构,进入循环,调整堆的结构
while (childMax < len) {
//判断左右子树大小,如果右子树更大,而且右子树存在,childMax指针指向右子树
if (arr[childMax] < arr[childMax + 1] && childMax + 1 < len) childMax++;
//子树值小于根节点,不需要调整,退出循环
if (arr[childMax] < arr[cur]) break;
//子树值大于根节点,需要调整,先交换根节点和子节点
swap(arr, childMax, cur);
cur = childMax; //根节点指针指向子节点,检查子节点是否满足大顶堆规则
childMax = 2 * cur + 1; //子节点指针指向新的子节点
}
}
// 建立大顶堆
function buildHeap(arr) {
//从最后一个非叶子节点开始,向前遍历,
for (let i = Math.floor(arr.length / 2 - 1); i >= 0; i--) {
headAdjust(arr, i, arr.length); //对每一个节点都调整堆,使其满足大顶堆规则
}
}
// 堆排序
function heapSort(arr) {
if (arr.length <= 1) return arr;
//构建大顶堆
buildHeap(arr);
//从后往前遍历,
for (let i = arr.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
swap(arr, i, 0); //交换最后位置和第一个位置(堆顶最大值)的位置
headAdjust(arr, 0, i); //调整根节点~i-1个节点,重新生成大顶堆
}
return arr;
}更多编程相关知识,请访问:编程视频!!
The above is the detailed content of What is the time complexity of bubble sort, quick sort and heap sort?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1393
1393
 52
52
 1207
1207
 24
24
 Java data structures and algorithms: in-depth explanation
May 08, 2024 pm 10:12 PM
Java data structures and algorithms: in-depth explanation
May 08, 2024 pm 10:12 PM
Data structures and algorithms are the basis of Java development. This article deeply explores the key data structures (such as arrays, linked lists, trees, etc.) and algorithms (such as sorting, search, graph algorithms, etc.) in Java. These structures are illustrated through practical examples, including using arrays to store scores, linked lists to manage shopping lists, stacks to implement recursion, queues to synchronize threads, and trees and hash tables for fast search and authentication. Understanding these concepts allows you to write efficient and maintainable Java code.
 Transform code with C++ function pointers: improve efficiency and reusability
Apr 29, 2024 pm 06:45 PM
Transform code with C++ function pointers: improve efficiency and reusability
Apr 29, 2024 pm 06:45 PM
Function pointer technology can improve code efficiency and reusability, specifically as follows: Improved efficiency: Using function pointers can reduce repeated code and optimize the calling process. Improve reusability: Function pointers allow the use of general functions to process different data, improving program reusability.
 How to implement bubble sort algorithm in C#
Sep 19, 2023 am 11:10 AM
How to implement bubble sort algorithm in C#
Sep 19, 2023 am 11:10 AM
How to implement the bubble sort algorithm in C# Bubble sort is a simple but effective sorting algorithm that arranges an array by comparing adjacent elements multiple times and exchanging positions. In this article, we will introduce how to implement the bubble sort algorithm using C# language and provide specific code examples. First, let us understand the basic principles of bubble sort. The algorithm starts from the first element of the array and compares it with the next element. If the current element is larger than the next element, swap their positions; if the current element is smaller than the next element, keep it
 Java quick sorting tips and precautions
Feb 25, 2024 pm 10:24 PM
Java quick sorting tips and precautions
Feb 25, 2024 pm 10:24 PM
Master the key skills and precautions of Java quick sort. Quick sort (QuickSort) is a commonly used sorting algorithm. Its core idea is to divide the sequence to be sorted into two independent parts by selecting a benchmark element, and all the elements in one part are equal. is less than the base element, and all elements of the other part are greater than the base element, then the two parts are recursively sorted, and finally an ordered sequence is obtained. Although quick sort has a time complexity of O(nlogn) in the average case, it degenerates to O(nlogn) in the worst case
 Guide to writing a custom sorting algorithm for PHP arrays
Apr 27, 2024 pm 06:12 PM
Guide to writing a custom sorting algorithm for PHP arrays
Apr 27, 2024 pm 06:12 PM
How to write a custom PHP array sorting algorithm? Bubble sort: Sorts an array by comparing and exchanging adjacent elements. Selection sort: Select the smallest or largest element each time and swap it with the current position. Insertion sort: Insert elements one by one into the sorted part.
 How to implement quick sort using Python
Dec 18, 2023 pm 03:37 PM
How to implement quick sort using Python
Dec 18, 2023 pm 03:37 PM
How to implement quick sorting in Python: 1. Define a function called quick_sort and use the recursive method to implement quick sorting; 2. Check the length of the array. If the length is less than or equal to 1, return the array directly. Otherwise, select the array. The first element is used as the pivot element (pivot), and then the array is divided into two sub-arrays smaller than the pivot element and larger than the pivot element; 3. Connect the two sub-arrays and the pivot element to form a sorted array. .
 Complexity analysis of various PHP array sorting algorithms
Apr 27, 2024 am 09:03 AM
Complexity analysis of various PHP array sorting algorithms
Apr 27, 2024 am 09:03 AM
PHP array sorting algorithm complexity: Bubble sort: O(n^2) Quick sort: O(nlogn) (average) Merge sort: O(nlogn)
 Analyze time complexity and space complexity in Go language
Mar 27, 2024 am 09:24 AM
Analyze time complexity and space complexity in Go language
Mar 27, 2024 am 09:24 AM
Go is an increasingly popular programming language that is designed to be easy to write, easy to read, and easy to maintain, while also supporting advanced programming concepts. Time complexity and space complexity are important concepts in algorithm and data structure analysis. They measure the execution efficiency and memory size of a program. In this article, we will focus on analyzing the time complexity and space complexity in the Go language. Time Complexity Time complexity refers to the relationship between the execution time of an algorithm and the size of the problem. Time is usually expressed in Big O notation