Introducing the process model of swoole

When we first met the server article, we said that swoole is event-driven. In the process of using swoole, we also realized that using swoole is very simple. We only need to register the corresponding callback to process our business logic.
However, before continuing to learn swoole, we need to take another look at swoole's operating process and process model.
Recommendation (free): swoole
We have briefly introduced server and task in the first two articles, and we will talk about server later. The creation and execution of the script are all executed under the CLI unless otherwise specified, so I won’t go into details.
Now, we create a simple server to analyze. The file is named server-process.php
$serv = new swoole_server('127.0.0.1', 9501);
$serv->set([
'worker_num' => 2,
'task_worker_num' => 1,
]);
$serv->on('Connect', function ($serv, $fd) {
});
$serv->on('Receive', function ($serv, $fd, $fromId, $data) {
});
$serv->on('Close', function ($serv, $fd) {
});
$serv->on('Task', function ($serv, $taskId, $fromId, $data) {
});
$serv->on('Finish', function ($serv, $taskId, $data) {
});
$serv->start();Note that here we have selected two worker processes and one task process. Is that right? Does it mean that creating this server starts 3 processes? Let's take a look
Open a new terminal, let's use the ps command to see the results
$ ps aux | grep server-process root 21843 xxx... php server-process.php root 21844 xxx... php server-process.php root 21846 xxx... php server-process.php root 21847 xxx... php server-process.php root 21848 xxx... php server-process.php root 21854 xxx... grep --color=auto server-process
For the convenience of reading, some unimportant data in the ps results have been slightly processed.
Excluding the last result (the last one is the ps command we ran), we found that there were as many as 5 similar processes running. According to our understanding, shouldn't there be 3? Why are there two more Which one?
Remember the implementation of multi-process we talked about in the article Process/Thread? When we talk about the implementation of multi-process, the Master-Worker mode is generally designed. The common default multi-process mode of nginx is exactly the same. Of course, the default multi-process model of swoole is also the multi-process model.
Compared with the Master-Worker model, swoole's process model can be described as Master-Manager-Worker. That is, an additional layer of Manager process is added on the basis of Master-Worker. This also answers the question we raised at the beginning: why there are 5 processes instead of 3 processes. (1 Master process, 1 Manager process, 2 Worker processes, 1 Task process)
As the saying goes, "existence is reasonable", let's take a look at the reasons why the three processes of Master\Manager\Worker exist.
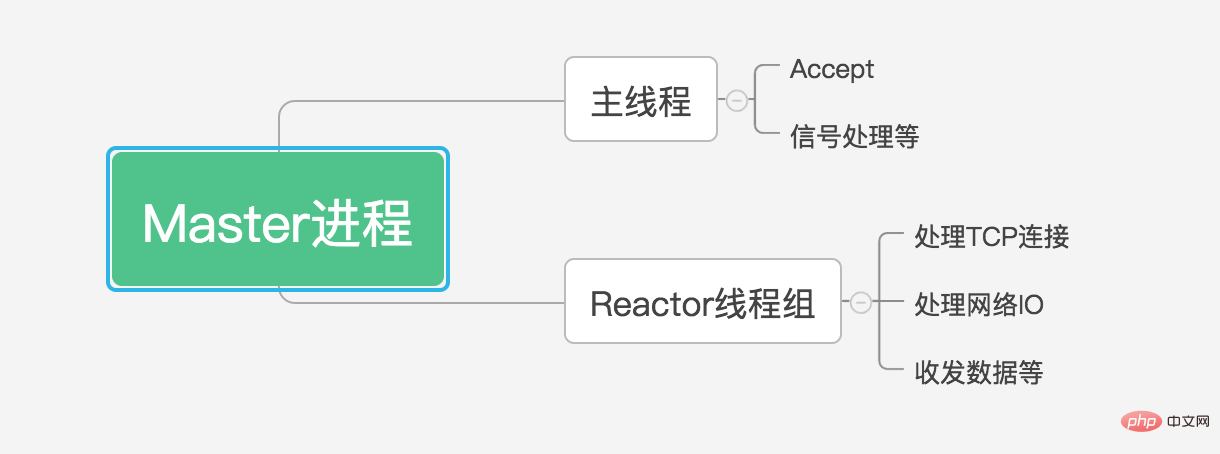
The Master process is a multi-threaded program. Note: According to our previous understanding, multiple threads run in the context of a single process. In fact, each thread in a single process has its own context, but since they coexist in the same process, they also share it. This process, including its code, data, etc.
Let’s come back and continue talking about the Master process. The Master process is our main process and is responsible for the power of life and death. If it dies, everything underneath will have to be finished. Master process, including main thread, multiple Reactor threads, etc.
Each thread has its own purpose. For example, the main thread is used for Accept, signal processing and other operations, while the Reactor thread is the thread that handles tcp connections, handles network IO, and sends and receives data.
Two points to note:
- The accept operation of the main thread, the socket server often uses accept to block, there is a picture when introducing socket programming in the previous section, you can take a look
- Signal processing, a signal is equivalent to a message. For example, the Ctrl C we often operate actually sends a SIGINT signal to the main thread of the Master process, which means you can terminate. There are many kinds of signals, and there will be more later. There is an introduction
Usually, after the main thread handles the new connection, it will allocate the connection to a fixed Reactor thread, and this Reactor thread will always be responsible for monitoring this socket (socket will be faced later in the above) Updated to socket, which is a file used for cross-network communication with another process. The file can be read and written). In other words, when the socket is readable, the data will be read and the request will be processed. Assigned to the worker process, this also explains the meaning of the third parameter $fromId of the callback onReceive in the worker process when we first introduced it in swoole; when the socket is writable, the data will be sent to the tcp client.
Use a picture to sort it out clearly
Then why can’t swoole have a Master-Worker process structure like Nginx? What does the Manager process do?
I was about to say this.
We know that in the Master-Worker model, there is only one Master, and the Worker is copied from the parent process Master process, and there can be multiple Worker processes.
Note: In Linux, the parent process can create a new child process by calling the fork function. The child process is a copy of the parent process, almost but not exactly the same. The biggest difference between the two is that they both have their own Independent process ID, namely PID.
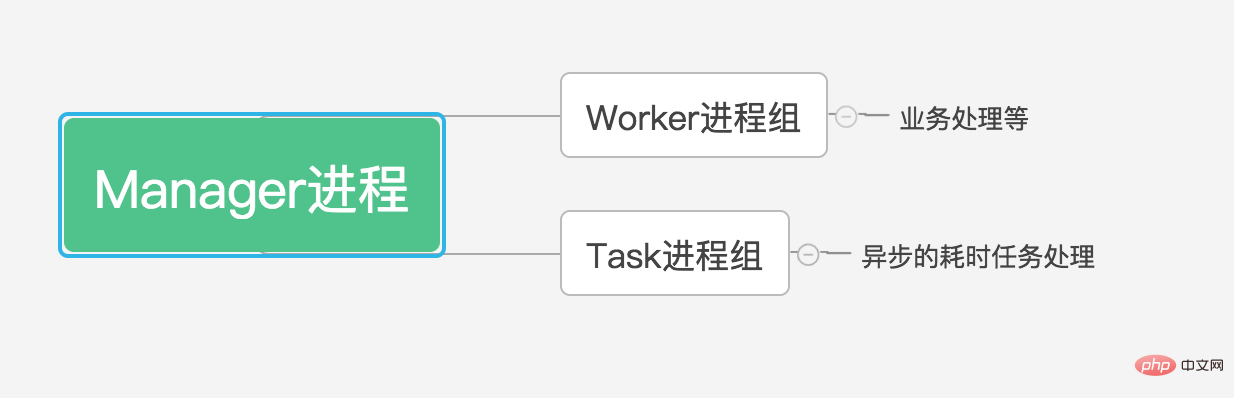
For a multi-threaded Master process, if you want to have multiple Worker processes, you must fork the operation, but the fork operation is unsafe. Therefore, in swoole, there is a full-time Manager process, and the Manager process is dedicated Responsible for the fork operation and management of worker/task processes. In other words, the "nanny" Manager process has full authority to manage the creation, recycling and other operations of the worker process.
通常,worker进程被误杀或者由于程序的原因会异常退出,Manager进程为了保证服务的稳定性,会重新拉起新的worker进程,意思就是Worker进程你发生意外“死”了,没关系,我自身不“死”,就可以fork千千万万个你。
当然,Master进程和Manager进程我们是不怎么关心的,从前面两篇文章我们了解到,真正实现业务逻辑,是在worker/task进程内完成的。
再来一张图梳理下Manager进程和Worker/Task进程的关系。
再回到我们开篇抛出的的5个进程的问题,ps的结果简直一模一样,有没有办法能区分这5个进程哪个是哪个呢?
有同学要说啦,既然各个进程之间存在父子关系,那我们就可以通过linux的pstree命令查看结果。
$ pstree | grep server-process | | \-+= 02548 manks php server-process.php | | \-+- 02549 manks php server-process.php | | |--- 02550 manks php server-process.php | | |--- 02551 manks php server-process.php | | \--- 02552 manks php server-process.php | \--- 02572 manks grep server-process
注:centos下命令可修改为 pstree -ap | grep server-process
从结果中我们可以看出,进程id等于02548的进程就是Master进程,因为从结构上看就它是“父”嘛,02549是Manager进程,Worker进程和Task进程就是02550、02551和02552了(每个人的电脑上显示的进程id可能不同,但顺序是一致的,依照此模型分析即可)。
我们看到pstree命令也只能得到大致结果,而且在事先不知道的情况下,根本无法区分Worker进程和Task进程。
在swoole中,我们可以在各个进程启动和关闭的回调中去解决上面这个问题。各个进程的启动和关闭?那岂不是又要记住主进程、Manager进程、Worker进程,二三得六,6个回调函数?
是的,不过这6个是最简单也是最好记的,你实际需要了解的可能还要更多。
Master进程:
启动:onStart
关闭:onShutdown
Manager进程:
启动:onManagerStart
关闭:onManagerStop
Worker进程:
启动:onWorkerStart
关闭:onWorkerStop提醒:task_worker也会触发onWorkerStart回调。
是不是很好记?那我们就在server-process.php中通过上面这几种回调来实现对各个进程名的修改。
$serv->on("start", function ($serv){
swoole_set_process_name('server-process: master');
});
// 以下回调发生在Manager进程
$serv->on('ManagerStart', function ($serv){
swoole_set_process_name('server-process: manager');
});
$serv->on('WorkerStart', function ($serv, $workerId){
if($workerId >= $serv->setting['worker_num']) {
swoole_set_process_name("server-process: task");
} else {
swoole_set_process_name("server-process: worker");
}
});注意:因mac下不支持swoole_set_process_name函数,即不能修改进程名,我们换台centos运行下看看结果(实际上你的服务器也不可能是mac)
# ps aux | grep server-process root 27546 xxx... server-process: master root 27547 xxx... server-process: manager root 27549 xxx... server-process: task worker root 27550 xxx... server-process: worker root 27551 xxx... server-process: worker root 27570 xxx... grep --color=auto simple
运行结果谁是谁一目了然,简直了!
有同学傻眼了,说在workerStart回调中写的看不明白,worker进程和task进程怎么区分的?
我来解释一下:在onWorkerStart回调中,$workerId表示的是一个值,这个值的范围是0~worker_num,worker_num是我们的对worker进程的配置,其中0~worker_num表示worker进程的标识,包括0但不包括worker_num;worker_num~worker_num+task_worker_num是task进程的标识,包括worker_num不包括worker_num+task_worker_num。
按照高中学的区间的知识可能更好理解,以我们案例的配置,workerId的值的范围就是[0,2],[0,2)表示worker进程,[2,3)就表示task_worker进程。
swoole的进程模型很重要,本篇掌握不好,后面的理解可能就会有些问题。
补充:
我们在onWorkerStart的回调中,用了serv−>setting去获取配置的server信息,在swoole中预留了一些swooleserver的属性,我们可以在回调函数中访问。比如说我们可以用serv−>setting去获取配置的server信息,在swoole中预留了一些swooleserver的属性,我们可以在回调函数中访问。比如说我们可以用serv->connections属性获取当前server的所有的连接,再比如我们可以通过$serv->master_pid属性获取当前server的主进程id等等。
The above is the detailed content of Introducing the process model of swoole. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1385
1385
 52
52
 How to use swoole coroutine in laravel
Apr 09, 2024 pm 06:48 PM
How to use swoole coroutine in laravel
Apr 09, 2024 pm 06:48 PM
Using Swoole coroutines in Laravel can process a large number of requests concurrently. The advantages include: Concurrent processing: allows multiple requests to be processed at the same time. High performance: Based on the Linux epoll event mechanism, it processes requests efficiently. Low resource consumption: requires fewer server resources. Easy to integrate: Seamless integration with Laravel framework, simple to use.
 How to use Swoole to implement a high-performance HTTP reverse proxy server
Nov 07, 2023 am 08:18 AM
How to use Swoole to implement a high-performance HTTP reverse proxy server
Nov 07, 2023 am 08:18 AM
How to use Swoole to implement a high-performance HTTP reverse proxy server Swoole is a high-performance, asynchronous, and concurrent network communication framework based on the PHP language. It provides a series of network functions and can be used to implement HTTP servers, WebSocket servers, etc. In this article, we will introduce how to use Swoole to implement a high-performance HTTP reverse proxy server and provide specific code examples. Environment configuration First, we need to install the Swoole extension on the server
 Which one is better, swoole or workerman?
Apr 09, 2024 pm 07:00 PM
Which one is better, swoole or workerman?
Apr 09, 2024 pm 07:00 PM
Swoole and Workerman are both high-performance PHP server frameworks. Known for its asynchronous processing, excellent performance, and scalability, Swoole is suitable for projects that need to handle a large number of concurrent requests and high throughput. Workerman offers the flexibility of both asynchronous and synchronous modes, with an intuitive API that is better suited for ease of use and projects that handle lower concurrency volumes.
 How does swoole_process allow users to switch?
Apr 09, 2024 pm 06:21 PM
How does swoole_process allow users to switch?
Apr 09, 2024 pm 06:21 PM
Swoole Process allows users to switch. The specific steps are: create a process; set the process user; start the process.
 How to restart the service in swoole framework
Apr 09, 2024 pm 06:15 PM
How to restart the service in swoole framework
Apr 09, 2024 pm 06:15 PM
To restart the Swoole service, follow these steps: Check the service status and get the PID. Use "kill -15 PID" to stop the service. Restart the service using the same command that was used to start the service.
 Which one has better performance, swoole or java?
Apr 09, 2024 pm 07:03 PM
Which one has better performance, swoole or java?
Apr 09, 2024 pm 07:03 PM
Performance comparison: Throughput: Swoole has higher throughput thanks to its coroutine mechanism. Latency: Swoole's coroutine context switching has lower overhead and smaller latency. Memory consumption: Swoole's coroutines occupy less memory. Ease of use: Swoole provides an easier-to-use concurrent programming API.
 Swoole in action: How to use coroutines for concurrent task processing
Nov 07, 2023 pm 02:55 PM
Swoole in action: How to use coroutines for concurrent task processing
Nov 07, 2023 pm 02:55 PM
Swoole in action: How to use coroutines for concurrent task processing Introduction In daily development, we often encounter situations where we need to handle multiple tasks at the same time. The traditional processing method is to use multi-threads or multi-processes to achieve concurrent processing, but this method has certain problems in performance and resource consumption. As a scripting language, PHP usually cannot directly use multi-threading or multi-process methods to handle tasks. However, with the help of the Swoole coroutine library, we can use coroutines to achieve high-performance concurrent task processing. This article will introduce
 Swoole Advanced: How to Optimize Server CPU Utilization
Nov 07, 2023 pm 12:27 PM
Swoole Advanced: How to Optimize Server CPU Utilization
Nov 07, 2023 pm 12:27 PM
Swoole is a high-performance PHP network development framework. With its powerful asynchronous mechanism and event-driven features, it can quickly build high-concurrency and high-throughput server applications. However, as the business continues to expand and the amount of concurrency increases, the CPU utilization of the server may become a bottleneck, affecting the performance and stability of the server. Therefore, in this article, we will introduce how to optimize the CPU utilization of the server while improving the performance and stability of the Swoole server, and provide specific optimization code examples. one,




