19 Things Angular Developers Must Learn
This article will introduce you to 19 things you need to learn to become an excellent Angular developer. It has certain reference value. Friends in need can refer to it. I hope it will be helpful to everyone.

A to-do app is basically equivalent to the "Hello world" of front-end development. While the CRUD aspects of creating applications are covered, it usually only scratches the surface of what a framework or library can do.
Angular may seem like it's always changing and updating - but in reality, some things still stay the same. The following is an overview of the core concepts you need to learn about Angular so that you can properly utilize the JavaScript framework. [Related tutorial recommendations: "angular tutorial"]
Speaking of Angular, we need to learn a lot of things. Many people are trapped in the circle of beginners just because they don’t know where to go. What keywords to search or should search for. This guide we'll talk about below (and a quick summary of Angular itself) is something I actually wish I had had when I first started using Angular 2.
1. Modular Angular Architecture
Theoretically, you can put all the Angular code on one page and put it into one large function, but This is not recommended, is not an efficient way to structure your code, and defeats the purpose of Angular's existence.
Angular uses the concept of modules as an important part of the framework architecture, which refers to a collection of code that has only one reason for existence. Your Angular app is basically made up of modules - some standalone and some shared.
There are many ways to structure modules in your application. A deeper understanding of different architectures can also help determine how to scale the application as it grows. It can also help isolate code and prevent code generation. coupling.
Search keywords:
Angular architecture pattern
Extensible Angular application architecture
2. One-way data flow and immutability
As early as Angular 1, two-way binding captured many front-end developers The heart of the people. This was actually one of Angular's original selling points. However, over time, when the application starts to become more complex, it starts to create problems in terms of performance.
It turns out that two-way binding is not required everywhere.
Two-way binding is still possible in Angular 2, but only if the developer explicitly requests it – this forces the person behind the code to think about data direction and data flow, and it also allows Applications can handle data more flexibly by determining how it flows.
Search keywords:
Angular data flow best practices
Unique in Angular Directional flow
Advantages of one-way binding
3. Attribute and structural instructions
directives are extensions of HTML through custom elements. Attribute directives allow you to change an element's properties, and structural directives change the layout by adding or removing elements from the DOM.
For example, ngSwitch and ngIf are structural directives because it evaluates parameters and determines whether certain parts of the DOM should be present.
Attribute directives are custom behaviors attached to elements, components, or other directives.
Learning how to use these two directives can extend the functionality of your application and reduce the amount of duplicate code in your project. Attributed directives can also help focus certain behaviors for use in different parts of the application.
Search keywords:
Angular attribute directive
Angular structural directive
Angular structural directive pattern
4. Component life cycle hook
Each Software has its own life cycle, which determines how certain content is created, rendered, and deleted. Angular's component life cycle is like this: create → render → render children → check when data-bound properties change → destroy → remove from DOM
We can do this within this cycle Seize the key moment and target him at a specific moment or event. This allows us to create appropriate responses and configure behavior based on the different stages of the component's existence.
For example, you might need to load some data before rendering the page, which you can do with ngOnInit(), or you might need to disconnect from the database, which can be done with ngOnDestroy().
Search keywords:
Angular life cycle hook
Component life cycle
5.Http and Observable Object Service
This is not a feature unique to Angular, but comes from ES7. Angular just happens to implement this as part of the framework's support functionality, and happens to understand this, and it also translates well to React, Vue, and any JavaScript-related library or framework.
Observable object services are patterns that allow you to efficiently handle data - allowing you to parse, modify, and maintain data in an event-based system. You can't completely escape HTTP and Observables because everything is data.
Search keywords:
JavaScript Observable Object Pattern
Angular HTTP and Observable Object
ES7 Observable Function
6.Smart/Dumb Component Architecture
When writing Angular applications, we tend to put everything into components. However, this is not a best practice. The concept of Smart/Dumb components in Angular needs more discussion, especially in beginner circles.
Whether a component is Smart/Dumb determines the role it plays in the overall planning of the application. Dumb components are generally stateless and their behavior is easy to predict and understand. Therefore, make your components as dumb as possible. Smart components are more difficult to master because they involve input and output. To properly leverage the power of Angular, study the Smart/Dumb component architecture, which will provide you with patterns and ways of thinking about how to deal with code and its interrelationships.
Search keywords:
Smart/Dumb Angular component
Stateless Dumb component
Demo Component
Smart Component in Angular
7. Application Structure and Best Practices
The CLI can only take you so far when it comes to structure and best practices. Building an Angular application (or any application in general) is like building a house. The community has been optimizing the setup process for years to achieve the most efficient and effective applications.
Angular is no exception.
Most complaints about Angular from those trying to learn Angular tend to be due to a lack of structural knowledge; the syntax is approachable and clear. However, structural knowledge of the application requires an understanding of the context, requirements, and how they fit together at both a conceptual and practical level. Understanding Angular's different potential application structures and their best practices will give you a new perspective on how to build applications.
Search keywords:
Single repository Angular apps
- ##Angular library, Angular package
- Angular
- Angular Micro Application
- Monolithic Repository
8. Template binding syntax
Binding is the crystallization of the JavaScript framework, which is one of the reasons for its existence in the first place. Template binding bridges the gap between static HTML and JavaScript, with Angular's template binding syntax acting as a facilitator between these two technologies.
Search keywords:
- Angular property binding
- Angular event binding
- Angular two-way binding, Angular interpolation
- Angular passing constant
9. Features Modules and Routing
The power of feature modules is underestimated in Angular. It's actually an excellent way to organize and respond to business needs. In the long run, it limits liability and helps prevent code pollution.
Search keywords:
- ##Angular feature module
- Shared feature structure in Angular
- Feature module provider
- Lazy loading routing and feature modules
Forms are an inevitable part of any front-end development.
Authentication also appears with the form.
In Angular, there are many ways to construct smart, data-driven forms. The most popular form iteration is the reactive form. However, there are other options, namely template-driven forms and custom validators.
Understanding how validators work with CSS will help speed up your workflow and transform your application into a validation error-ready space.
Search keywords:
- Angular formal verification
- Template driven verification
- Responsive form validation
Synchronous and Async Validators in Angular
Built-in Validators
Angular Custom Validators
Cross-field cross-validation
11. Content projection
Angular has a feature called Content projection is something that efficiently passes data from parent components to child components. While this may sound complicated, it's actually the act of putting views within views to produce a master view.
We usually understand content projection in a superficial sense - when we nest subviews within a parent view. However, to expand our understanding, we also need to understand how data is passed between different views. This is where understanding content projection comes in handy.
Understanding content projection can help you determine your application's data flow and where variability occurs.
Search keywords:
- ##Angular content projection
- Angular parent-child view relationship
- Angular view data relationship
12.onPush change detection
By default, Angular Use the default change detection strategy. This means the component will always be checked. While there's nothing wrong with using default values, it can be an inefficient way of detecting changes.
Search keywords:
- Angular onPush change detection
13. Path protection, preloading, delay Loading
If you have some type of login, you will need path protection. You can protect certain views from unauthorized views, which is an essential requirement in many applications. Path protection acts as an interface between routers and request routes. It is the decision maker who decides whether a route is allowed to be accessed. There's a lot to explore in the world of path protection - namely path decisions based on things like token expiration, user authentication, and path security.
Search keywords:
- Angular path protection
- Angular authentication mode
- Angular Preloading and Lazy Loading Modules
- Angular Safe Path Mode
Making data formatting incredibly easy with Angular Pipes. While many preconfigured and out-of-the-box pipelines cover a lot of things like dates, currencies, percentages, and character case, it doesn't cover everything you need.
This is where custom pipes come in handy. You can easily create your own filters and convert the data format to your liking. It's really easy, so go check it out!
Angular custom pipeline
viewChild and contentChild are how components communicate with each other. The whole point of Angular is that you have multiple components that are compiled together like a puzzle, but if those components are isolated from each other then the puzzle doesn't really do much good.
This is where viewChild and contentChild come in. Learning to use these two decorators gives you access to related components. This makes the task of data sharing easier and allows the transmission of data and events triggered by related components.
##Angular decorator
- Viewchild and contentchild in Angular
- Angular component data sharing
- 16. Dynamic components and ng-template
Components are the building blocks of Angular. However, not all components are fixed and some of them need to be created dynamically rather than pre-compiled.
Dynamic components allow applications to create certain components dynamically. Static components assume that things don't change. It can be predicted from expected inputs and outputs.
Search keywords:
Dynamic components in Angular
- Dynamic components and ng- templating
17.@Host @Hostingbinding and exportAs
@Host, @Hostingbinding and exportAs are Angular directive decorators that extend the attached parameters. They also enable you to create clean templates that can be exported for use within your application.
If the above sounds confusing, then you should first look up Angular directives and their purpose of existence. @Host, @Hostingbinding and exportAs are attributes of the directive that help implement it.
Search keywords:
Angular directive mode
Angular’s @Host, @Hostingbinding and exportAs
18. Using RxJs for state management
The state of the application ultimately determines the data displayed to the user. If your state is a messy mess of spaghetti, chances are your entire data structure will become brittle to any changes.
When you start to understand how state works in Angular, you will understand how and why data behaves.
While Angular has its own state management system, RxJs is an excellent way to centralize state and its related data. Data may be lost in the parent-child relationship chain. RxJs decouples things by creating a centralized store.
Search keywords:
- ##Angular RxJs ##Flux / Redux principle
- Angular State Management Principles
"Dependency Injection" Usually is a huge concept, so if you're not very familiar with it, this is one you really need to look up. There are several ways to efficiently create dependency injection in Angular, primarily through constructors. This is a way to make your application more efficient by importing only what you need, rather than loading everything.
Like "dependency injection", "area" is also a concept unique to Angular. It is a way for an application to detect asynchronous tasks from beginning to end. This is important because these asynchronous tasks can change the internal state of the application and therefore the view. "Zones" facilitate the change detection process.
- Angular area
- Dependency injection
Angular is a big topic. While building Angular applications may aid the learning process, sometimes you just don't know what you don't know. When you first start, it's hard to understand something you don't know. I hope this short guide can give you some inspiration beyond your usual Angular tutorials and give you a more comprehensive understanding of Angular.
For more programming-related knowledge, please visit:Introduction to Programming
The above is the detailed content of 19 Things Angular Developers Must Learn. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1659
1659
 14
14
 1416
1416
 52
52
 1310
1310
 25
25
 1259
1259
 29
29
 1233
1233
 24
24
 Let's talk about metadata and decorators in Angular
Feb 28, 2022 am 11:10 AM
Let's talk about metadata and decorators in Angular
Feb 28, 2022 am 11:10 AM
This article continues the learning of Angular, takes you to understand the metadata and decorators in Angular, and briefly understands their usage. I hope it will be helpful to everyone!
 How to install Angular on Ubuntu 24.04
Mar 23, 2024 pm 12:20 PM
How to install Angular on Ubuntu 24.04
Mar 23, 2024 pm 12:20 PM
Angular.js is a freely accessible JavaScript platform for creating dynamic applications. It allows you to express various aspects of your application quickly and clearly by extending the syntax of HTML as a template language. Angular.js provides a range of tools to help you write, update and test your code. Additionally, it provides many features such as routing and form management. This guide will discuss how to install Angular on Ubuntu24. First, you need to install Node.js. Node.js is a JavaScript running environment based on the ChromeV8 engine that allows you to run JavaScript code on the server side. To be in Ub
 An article exploring server-side rendering (SSR) in Angular
Dec 27, 2022 pm 07:24 PM
An article exploring server-side rendering (SSR) in Angular
Dec 27, 2022 pm 07:24 PM
Do you know Angular Universal? It can help the website provide better SEO support!
 Detailed explanation of angular learning state manager NgRx
May 25, 2022 am 11:01 AM
Detailed explanation of angular learning state manager NgRx
May 25, 2022 am 11:01 AM
This article will give you an in-depth understanding of Angular's state manager NgRx and introduce how to use NgRx. I hope it will be helpful to you!
 Angular + NG-ZORRO quickly develop a backend system
Apr 21, 2022 am 10:45 AM
Angular + NG-ZORRO quickly develop a backend system
Apr 21, 2022 am 10:45 AM
This article will share with you an Angular practical experience and learn how to quickly develop a backend system using angualr combined with ng-zorro. I hope it will be helpful to everyone!
 A brief analysis of how to use monaco-editor in angular
Oct 17, 2022 pm 08:04 PM
A brief analysis of how to use monaco-editor in angular
Oct 17, 2022 pm 08:04 PM
How to use monaco-editor in angular? The following article records the use of monaco-editor in angular that was used in a recent business. I hope it will be helpful to everyone!
 How to use PHP and Angular for front-end development
May 11, 2023 pm 04:04 PM
How to use PHP and Angular for front-end development
May 11, 2023 pm 04:04 PM
With the rapid development of the Internet, front-end development technology is also constantly improving and iterating. PHP and Angular are two technologies widely used in front-end development. PHP is a server-side scripting language that can handle tasks such as processing forms, generating dynamic pages, and managing access permissions. Angular is a JavaScript framework that can be used to develop single-page applications and build componentized web applications. This article will introduce how to use PHP and Angular for front-end development, and how to combine them
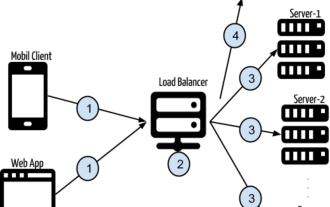 Token-based authentication with Angular and Node
Sep 01, 2023 pm 02:01 PM
Token-based authentication with Angular and Node
Sep 01, 2023 pm 02:01 PM
Authentication is one of the most important parts of any web application. This tutorial discusses token-based authentication systems and how they differ from traditional login systems. By the end of this tutorial, you will see a fully working demo written in Angular and Node.js. Traditional Authentication Systems Before moving on to token-based authentication systems, let’s take a look at traditional authentication systems. The user provides their username and password in the login form and clicks Login. After making the request, authenticate the user on the backend by querying the database. If the request is valid, a session is created using the user information obtained from the database, and the session information is returned in the response header so that the session ID is stored in the browser. Provides access to applications subject to




